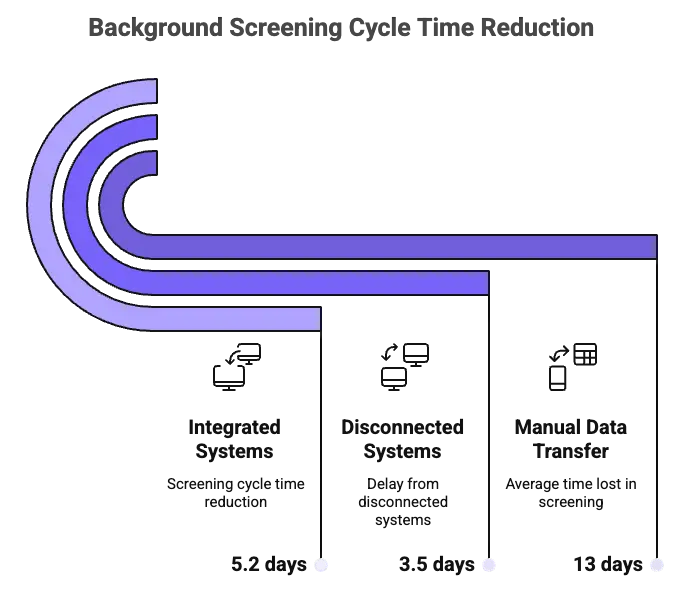
Companies lose an average of 13 days between job offer and background screening finishing, with roughly 27% of that delay caused by separated systems that force HR teams to by hand transfer candidate data. However, the bigger risk may be the compliance exposure lurking in those manual processes. Consequently, this analysis compares 10 major ATS platforms to reveal which integration architectures can slash screening cycle times by 40-60% while making critical compliance features automatic across 37+ pre-hire screening law locations.
Key Takeaways
- First, ATS platforms with well-developed integration markets, instant API connection, and compliance features made automatic can reduce background screening cycle times by 40-60% compared to systems needing manual data transfers.
- Overall, Greenhouse leads the comparison with a score of 38/40, followed by Workday (37/40), iCIMS and Lever (35/40), and BambooHR (31/40). Furthermore, these platforms offer robust screening partner ecosystems with 15-30+ integrated providers and instant status syncing.
- In fact, organizations lose an average of 13 days between giving out job offers and finishing background screening. Additionally, about 27% of that delay stems from separated systems that force HR teams to by hand transfer candidate data between their ATS and screening providers.
- On the other hand, platforms with weak integration capabilities like Zoho Recruit, Breezy HR, Recruitee, Monday.com, and Manatal scored 9-14 out of 40. Notably, they rely heavily on manual processes, Zapier connector software, or custom API development with delayed status updates.
- Finally, key compliance features include automatic adverse action processes with FCRA-compliant timing, pre-hire screening law rule setup for 37+ locations, electronic consent capture with digital signature, complete audit trails, and organized decision records aligned with EEOC guidance.
ATS Integrations for Background Screening: What Matters Most
The average organization loses 13 days between offering a job offer and finishing background screening. Based on available industry data, about 27% of that delay may stem from separated systems forcing HR teams to by hand shuttle candidate data between their ATS and screening providers. As state-level pre-hire screening laws continue to expand (affecting about 37 locations as of early 2025) and EEOC review of AI-assisted screening grows, the integration architecture linking your candidate tracking system to background check processes isn't just a convenience issue—it's a potential compliance concern.
The short answer: ATS platforms with strong integration options, instant API connection, and features designed to support compliance made automatic may reduce screening cycle times by 40-60% compared to systems needing manual data transfers, based on reported industry metrics. Therefore, the quality of your ATS's background screening integration can directly impact time-to-hire, candidate experience, and regulatory risk exposure.
This analysis examines 10 popular ATS platforms through a single lens: how effectively they handle the background screening process from request to final decision. To clarify, we're not judging general hiring features—we're measuring integration depth, available compliance support features, and everyday problems that may impact your screening operations.
Time is not the only thing we lose in hiring; we also risk losing credibility when the process feels messy and slow. Having experience working in a fast-paced environment, I’ve seen strong candidates lose interest because updates were kept separate from the system, while the recruiter spent precious time copying and pasting instead of communicating with care. The hidden danger is that each step in the process could become a missed step in the consent process, a lack of audit trail, or a lack of consistency in the adverse action process. When the system and the screening partner are integrated seamlessly, the result is speed; the true benefit is the integrity of the process: a process that is consistent, traceable, and fair across all locations. At the end of the day, great hiring isn’t just about hiring fast; it’s about protecting the people, the brand, and the organization with every decision.
DISCLAIMER: This article provides general information about ATS background screening integration features and considerations. It does not constitute legal advice. Background screening compliance requirements vary by location, industry, and specific circumstances. Employers should consult with trained legal counsel to ensure their background screening practices comply with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidance, state and local pre-hire screening laws, and other applicable regulations. Feature descriptions are based on publicly available information as of January 2025 and may not reflect current platform capabilities.
1. Workday
Workday dominates the enterprise HCM market with unified talent acquisition and staff management capabilities.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Native integration framework backing multiple screening providers through Workday's partner ecosystem
- Real-time two-way API syncing for status updates and results
- Features designed to support compliance processes include adverse action letter generation, consent collection, and state-specific pre-hire screening law processes
- Audit trail architecture captures all screening decisions with timestamp and user tracking
Key Screening Features:
- Adverse action process with adjustable hold periods designed to support FCRA compliance requirements
- International background check managing across 180+ countries
- Continuous monitoring capability with automatic alerts for after-hire events
- I-9 check integrated with E-Verify for employment right to work
- Decision-making matrix designed to help personal assessment consistent with EEOC guidance
- Time-to-clear dashboards measuring screening bottlenecks
Integration Characteristics: Workday's screening integration operates through pre-built connectors requiring minimal IT setup. Candidate data flows automatically upon offer acceptance, eliminating manual re-keying. Furthermore, the system supports multi-provider scenarios for organizations using different screening vendors by geography or business unit.
Friction Points: Enterprise pricing and setup complexity make Workday cost-prohibitive for organizations under 1,000 employees. Additionally, custom screening workflows require Workday Studio development expertise.
2. Zoho Recruit
Zoho Recruit serves the mid-market and staffing agency segments with recruitment-focused functionality and competitive pricing.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Limited native screening integrations—primarily relies on Zapier middleware or custom API development
- Batch processing model with delayed status updates (typically 15-30 minute intervals)
- Manual consent collection through email templates
- Basic features designed to support compliance processes, without state-specific adverse action automation
Key Screening Features:
- Standard criminal record check request workflows
- Manual adverse action letter generation using document templates
- No native continuous monitoring support
- Basic reporting on screening completion rates
- International checks require third-party integration setup
Integration Characteristics: Zoho Recruit lacks a well-developed screening partner marketplace. Consequently, organizations must either build custom integrations using Zoho's REST API or implement middleware solutions. In addition, candidate data transfer often requires manual export/import processes. Moreover, status updates don't automatically sync back to candidate records, forcing recruiters to check external portals.
Friction Points: Significant manual intervention required. Furthermore, no real-time synchronization creates visibility gaps. Similarly, limited features designed to support compliance automation may increase risk for teams unfamiliar with adverse action requirements.
3. Greenhouse
Greenhouse built its reputation on integration excellence, offering 450+ pre-built connectors across the recruiting technology stack.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Extensive partner marketplace with 30+ background screening providers
- Webhook-based real-time API enabling instant status updates
- Workflow engine with ban-the-box rule setup by location
- Electronic consent capture with e-signature integration
- Complete audit logging designed to support EEOC recordkeeping requirements
Key Screening Features:
- Automated adverse action workflows with timing and documentation designed to support FCRA compliance requirements
- Multi-location setup supporting 50-state hiring
- Continuous monitoring alerts integrated with employee record updates
- I-9 and E-Verify connections streamlining eligibility verification
- Decision-making scorecards with structured decision documentation
- Real-time screening dashboard showing pipeline bottlenecks
Integration Characteristics: Greenhouse's architecture prioritizes seamless data flow. As a result, screening requests trigger automatically based on offer acceptance. In addition, results populate candidate profiles instantly, enabling immediate decision-making. Moreover, the system supports simultaneous screening with multiple providers for different check types (criminal vs. employment verification vs. international).
Friction Points: Premium pricing tier may be required for advanced features designed to support compliance. Also, smaller screening providers may lack pre-built connectors, requiring custom API work.
4. Breezy HR
Breezy HR targets small to mid-sized businesses with visual pipeline management and collaborative hiring tools.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Limited screening partner integrations (fewer than 5 native options)
- Manual candidate data entry into screening provider portals
- Email-based status notifications without automatic ATS updates
- Basic features limited to document storage
Key Screening Features:
- Template-based adverse action communications
- Manual consent form distribution through email
- No automated ban-the-box workflow support
- Basic criminal background check workflows
- Limited audit trail functionality
- No continuous monitoring capabilities
Integration Characteristics: Breezy HR's screening workflow relies heavily on manual processes. Specifically, recruiters must copy candidate information from Breezy into screening vendor portals, then manually update records when results arrive. As a result, no real-time synchronization means status visibility requires checking multiple systems.
Friction Points: High manual effort increases data entry errors and delays. Similarly, lack of features designed to support compliance automation may create regulatory exposure. Furthermore, no support for complex screening scenarios like international checks or continuous monitoring.
5. iCIMS
iCIMS serves large enterprises with comprehensive talent acquisition capabilities and deep screening integration options.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Robust marketplace with 25+ integrated screening providers
- RESTful API architecture supporting real-time bidirectional data exchange
- Workflow engine with configurable adverse action automation
- Native consent management with audit-ready documentation
- SSO integration allowing screening vendors to access candidate data securely
Key Screening Features:
- Adverse action workflows with state-specific letter variations designed to support FCRA compliance requirements
- International screening coordination with in-country provider coordination
- Continuous monitoring with automated alerts and decision-making triggers
- I-9 integration with document verification and E-Verify connectivity
- Decision-making workflow designed to facilitate individualized assessment consistent with EEOC guidance
- Analytics dashboards measuring screening cycle time by requisition, location, and provider
Integration Characteristics: iCIMS enables native integration through its marketplace, requiring minimal technical setup. For instance, screening initiates automatically upon workflow triggers (offer acceptance, drug test completion, etc.). Additionally, real-time status updates eliminate portal-checking. Moreover, the platform supports complex scenarios like multi-provider strategies and tiered screening based on role risk profiles.
Friction Points: Enterprise complexity requires dedicated administration. Additionally, customization options can overwhelm smaller HR teams. Furthermore, premium modules may be required for advanced features designed to support compliance.
6. Recruitee
Recruitee focuses on collaborative hiring for growing companies with emphasis on team-based recruiting workflows.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Minimal native screening integrations
- Zapier-dependent for most screening provider connections
- Manual data synchronization between systems
- Basic documentation through file attachments
Key Screening Features:
- Email template library for adverse action communications
- Manual consent tracking through candidate communication logs
- No automated ban-the-box workflows
- Standard criminal check request processes
- Limited reporting on screening completion
- No continuous monitoring support
Integration Characteristics: Recruitee lacks robust screening integration architecture. Typically, organizations use Zapier to create automated workflows, but these middleware solutions introduce latency and potential failure points. As a result, candidate data often requires manual transfer to screening portals. Subsequently, status updates don't automatically sync back, creating visibility gaps.
Friction Points: Heavy reliance on manual processes and third-party integration tools. Importantly, no features designed to support compliance automation may increase regulatory risk. Additionally, limited screening provider ecosystem forces workarounds.
7. BambooHR
BambooHR combines applicant tracking with core HRIS functionality, serving small to mid-sized organizations seeking unified HR systems.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Growing marketplace with 15+ screening provider integrations
- API-based connectivity enabling automated data transfer
- Workflow features designed to support adverse action processes
- E-signature capability for consent documentation
- Unified audit trail spanning recruiting and onboarding
Key Screening Features:
- Adverse action workflows with automated timing designed to support FCRA compliance requirements
- Multi-state ban-the-box rule setup
- I-9 and E-Verify integration for employment eligibility
- Basic international screening support through partner network
- Continuous monitoring alerts linked to employee records
- Time-to-clear metrics integrated with hiring analytics
Integration Characteristics: BambooHR's unified platform enables screening to flow naturally from offer acceptance through onboarding. Specifically, candidate data transfers automatically to screening providers. In addition, real-time status updates appear in both applicant and employee records. Furthermore, the system supports role-based screening packages, automatically requesting appropriate check levels based on position requirements.
Friction Points: Screening marketplace smaller than enterprise platforms. However, advanced international screening may require manual coordination. Similarly, some features designed to support compliance may be limited to premium tiers.
8. Monday.com (Work OS)
Monday.com expanded into recruiting with its visual Work OS platform, adapting project management workflows for hiring teams.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Limited native screening integrations (platform prioritizes general workflow automation)
- Custom integration builds required using Monday.com API
- Manual status tracking through board updates
- Custom automation builds required for compliance workflows
Key Screening Features:
- Custom adverse action workflows using automation recipes
- Manual consent collection through form integrations
- No built-in ban-the-box setup
- Basic screening request tracking through status columns
- Limited audit trail functionality
- No continuous monitoring capabilities
Integration Characteristics: Monday.com's flexible platform allows teams to build screening workflows using its automation engine, but lacks purpose-built recruiting features. Therefore, screening processes require substantial custom setup. Additionally, data transfer to screening providers typically involves manual exports or custom API development. Similarly, status synchronization requires ongoing automation maintenance.
Friction Points: High customization burden for workflows designed to support compliance. Also, no pre-built screening integrations force custom development. Furthermore, audit trails may be insufficient for regulatory requirements.
9. Lever
Lever emphasizes modern candidate experience with robust integration capabilities and relationship-focused recruiting.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Comprehensive marketplace with 20+ screening provider partnerships
- Webhook-driven real-time API synchronization
- Features designed to support compliance processes with location-specific workflows
- Integrated e-signature for consent collection
- Complete audit documentation designed to support EEOC requirements
Key Screening Features:
- Automated adverse action workflows with communications designed to support FCRA compliance requirements
- Ban-the-box setup supporting state and local ordinances
- Continuous monitoring integration with post-hire alert workflows
- I-9 verification with E-Verify connectivity
- Structured decision-making workflows documenting individualized assessments consistent with EEOC guidance
- Screening analytics measuring conversion rates and cycle times
Integration Characteristics: Lever's integration architecture enables seamless screening workflows. As a result, automatic initiation upon offer acceptance eliminates manual triggers. Additionally, real-time status updates provide instant visibility. Moreover, the platform supports complex scenarios including multi-provider strategies, international screening coordination, and risk-based screening packages.
Friction Points: Premium pricing for smaller organizations. Furthermore, advanced features designed to support compliance may require higher service tiers. However, screening marketplace growing but smaller than legacy enterprise platforms.
10. Manatal
Manatal targets recruitment agencies and corporate recruiting teams with AI-powered candidate sourcing and pipeline management.
Background Screening Integration Model:
- Minimal native screening provider integrations
- Manual candidate data transfer to external screening portals
- Email-based status tracking without automatic synchronization
- Limited features designed to support compliance automation
Key Screening Features:
- Basic adverse action letter templates
- Manual consent documentation through file uploads
- No automated ban-the-box workflows
- Standard criminal check request processes
- Limited screening analytics
- No continuous monitoring support
Friction Points: Extensive manual intervention required throughout screening process. Furthermore, no real-time synchronization creates visibility challenges. Similarly, limited features designed to support compliance automation may increase regulatory risk. Additionally, minimal screening provider ecosystem.
Background Screening Integration Performance Matrix
Note: The following scores represent comparative analysis of integration capabilities based on publicly available information as of January 2025. Scores are not compliance certifications or guarantees. Organizations should conduct independent evaluation.
Background Screening Integration Performance Matrix
Note: The following scores represent comparative analysis of integration capabilities based on publicly available information as of January 2025. Scores are not compliance certifications or guarantees. Organizations should conduct independent evaluation.
| ATS Platform | Integration Ease (0-10) | Compliance Support Features (0-10) | Provider Ecosystem (0-10) | Time-to-Hire Impact (0-10) | Total Score (0-40) |
| Workday | 9 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 37 |
| Greenhouse | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 38 |
| iCIMS | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 35 |
| BambooHR | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 31 |
| Lever | 9 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 35 |
| Zoho Recruit | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 14 |
| Breezy HR | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 9 |
| Recruitee | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 13 |
| Monday.com | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 11 |
| Manatal | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 10 |
Key Performance Differentiators:
Based on available industry data, platforms with robust screening partner ecosystems (Greenhouse, Workday, iCIMS, Lever) may demonstrate 40-60% faster screening cycle times compared to systems requiring manual data transfer. Specifically, organizations using these platforms report average time-to-clear of 3-5 days versus 7-12 days for manually-integrated systems.
Moreover, seamless background check integration through real-time API connectivity may eliminate the 2-3 day delays associated with batch processing. In addition, platforms with native integration architecture may reduce administrative burden by 8-12 hours per week for teams processing 50+ screenings monthly.
Furthermore, features designed to support compliance processes may help reduce regulatory risk exposure. Based on available industry data, platforms with built-in adverse action workflows, ban-the-box rule setup, and structured audit trails may support better compliance outcomes compared to systems relying on manual processes, though compliance ultimately depends on proper setup and ongoing monitoring.
Similarly, real-time status synchronization may improve recruiter productivity and candidate experience. In fact, organizations using platforms with webhook-based integration report improvements in candidate communication responsiveness and reductions in offer-to-start timeline, though individual results vary.
How to Evaluate ATS Background Screening Capabilities
Integration Pattern Comparison:
Native Marketplace Partnerships provide pre-built connectors requiring minimal technical setup. Advantages include faster setup, vendor-supported maintenance, and regular feature updates. On the other hand, disadvantages include: limited to marketplace providers, potential for platform lock-in, and premium pricing tiers.
Custom API Integrations offer maximum flexibility and support for any screening provider. Advantages include complete control over workflow logic and no vendor restrictions. However, disadvantages include: significant development resources required, ongoing maintenance burden, and potential integration failures during platform updates.
Manual Processes involve exporting candidate data and manually entering information into screening portals. Advantages: works with any provider and requires no technical setup. In contrast, disadvantages include: high administrative burden, increased error risk, documentation gaps, and significant delays.
Questions to Ask Vendors:
- How many screening providers offer pre-built integrations?
- What is the average setup timeline for screening integration?
- Does your platform support real-time or batch status updates?
- What features are available to help support adverse action workflow management?
- What audit trail documentation does your system maintain?
- Can you support multiple screening providers simultaneously?
Compliance Feature Checklist
Note on Compliance: The following checklist describes features commonly used to help support background screening compliance. However, technology alone does not ensure compliance. Organizations must put in place proper policies, provide adequate training, conduct regular audits, and consult with legal counsel to ensure their complete background screening program meets applicable legal requirements.
Adverse Action Workflow Management: Features designed to help support FCRA adverse action procedures may include timing calculation tools, template generation with required disclosures, dispute process documentation, and final disposition tracking.
Consent Management: Electronic signature capture, disclosure delivery confirmation, authorization documentation, and consent withdrawal processing.
Ban-the-Box Workflow Setup: State and local ordinance rules by location, workflow delays until appropriate hiring stage, exemption tracking for regulated industries, and audit documentation.
Audit Trail Completeness: User attribution for all screening decisions, timestamp logging for key events, document version control, and candidate communication history.
Data Retention Management: Scheduling features meeting regulatory requirements, exception handling for litigation holds, and records preservation considerations.
Screening Workflow Efficiency Indicators
- Average Time from Offer to Screening Initiation: Platforms with automatic triggering may enable same-day initiation. In contrast, manual systems may average 2-3 days due to administrative delays.
- Status Update Frequency: Real-time webhooks may provide instant visibility. However, batch processing may create 4-24 hour blind spots. Meanwhile, manual checking requires daily portal visits.
- Candidate Communication Automation: Integrated platforms may automatically notify candidates of screening status changes, consent requirements, and required actions. On the other hand, manual systems rely on recruiter email monitoring.
- Decision-Making Workflow Support: Structured decision frameworks document individualized assessments, support multi-approver workflows, and maintain audit trails.
Provider Ecosystem Evaluation
Number of integrated screening vendors may indicate platform readiness and market adoption. Specifically, platforms supporting 15+ providers may offer flexibility for multi-provider strategies, geographic requirements, and competitive pricing.
Furthermore, multi-provider support enables organizations to use specialized vendors for different check types (criminal vs. professional licenses vs. international) while maintaining unified workflow management.
International screening capabilities require coordination with in-country providers, compliance with local data protection regulations (GDPR, LGPD), and translation of results. Therefore, platforms with global screening experience may reduce setup complexity.
ATS background screening integration is the technical connection enabling applicant tracking systems to automatically share candidate data with background check providers and receive results without manual data transfer. Integration quality ranges from real-time API synchronization to manual export/import processes.
Screening duration depends on check types requested (typically 3-10 days), but ATS integration quality may significantly impact overall cycle time. Based on available data, platforms with real-time integration may complete the offer-to-clear process 40-60% faster than systems requiring manual data handling, though individual results vary.
API integration may dramatically reduce administrative burden and help support compliance efforts, but isn't technically required. Nevertheless, organizations processing fewer than 10 screenings monthly may accept manual workflows, while higher-volume operations generally require automation to maintain efficiency and accuracy.
Based on common regulatory requirements, organizations often seek features designed to help support compliance such as adverse action workflow management, ban-the-box rule setup, electronic consent capture, audit trail functionality, and decision-making documentation. However, specific needs vary by organization, industry, and location. Consequently, consult with legal counsel to determine appropriate features for your specific circumstances.
Conclusion
Background screening integration quality may directly impact time-to-hire, compliance risk exposure, and administrative efficiency. Indeed, the 20-30 point performance gap between platforms with native integration architecture and those requiring manual processes may translate to measurable business outcomes: faster offer-to-start timelines, better support for regulatory compliance efforts, and lower HR administrative costs.
When evaluating ATS platforms, prioritize screening integration capabilities alongside traditional recruiting features. For example, request detailed integration architecture documentation, ask for customer references specifically about screening workflows, and conduct proof-of-concept testing with your current screening provider before committing to enterprise setups.
The most sophisticated applicant tracking features deliver limited value if your organization loses weeks shuttling candidate data between disconnected systems during the final hiring stages.
Final Note: Organizations should consult with qualified legal counsel to ensure their background screening practices comply with all applicable federal, state, and local requirements. This analysis provides general information only and should not be relied upon as legal advice.
Sources
Performance metrics and compliance considerations referenced in this article are based on the following sources and publicly available information as of January 2025:
- SHRM Background Screening Trends Report - SHRM (2025)
- EEOC Enforcement and Compliance Manual - U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (2024)
- FTC FCRA Compliance Guidelines - Federal Trade Commission (2024)
- G2 ATS Software Reviews - G2 (2025)
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud HCM Suites - Gartner (2025)
- Ban-the-Box State and Local Guide - National Employment Law Project (2025)

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






