I-9 form management systems have evolved from simple document storage solutions into comprehensive compliance platforms that address the complexities of remote workforce verification, audit preparedness, and evolving federal requirements. As organizations navigate heightened ICE enforcement activity and expanded remote work policies in 2026, sophisticated I-9 management technology has become essential infrastructure for mitigating compliance risk while maintaining operational efficiency across distributed teams.
Key Takeaways
- I-9 violations may result in penalties that have historically ranged from approximately $272 to $2,701 per form error, with known hire violations potentially reaching substantially higher amounts depending on circumstances.
- Manual I-9 processes expose organizations to substantive and technical compliance failures, with ICE audits frequently revealing substantial error rates in paper-based systems.
- Modern I-9 form management systems provide automated workflows, real-time validation, and centralized audit trails that significantly reduce administrative burden compared to manual processes.
- Remote verification procedures introduced during the pandemic remain authorized as of January 2026, requiring organizations to maintain hybrid I-9 processes with enhanced documentation requirements.
- E-Verify integration within I-9 management platforms creates seamless eligibility verification while helping ensure proper sequencing and timing compliance.
- Automated expiration tracking and reverification workflows help prevent employment authorization gaps that create liability exposure for continuing to employ workers without valid documentation.
- Cloud-based I-9 systems enable real-time collaboration between HR teams, hiring managers, and remote employees while maintaining required confidentiality and access controls.
- Organizations with 50 or more employees may face heightened scrutiny under enforcement patterns observed in recent years, making systematic I-9 compliance a critical risk management function.
Understanding the I-9 Form Management Challenge
The Regulatory Foundation of Employment Eligibility Verification
The Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986 established mandatory employment eligibility verification requirements for all U.S. employers. Every employer must complete Form I-9 for each employee hired after November 6, 1986, documenting the verification of identity and employment authorization. This federal mandate applies universally, regardless of company size, industry, or location.
Form I-9 consists of three sections that create a documented chain of verification:
- Section 1: Employee attestation of employment authorization status, completed on or before the first day of work
- Section 2: Employer examination of original documents establishing identity and employment authorization, completed within three business days of hire
- Section 3: Reverification when employment authorization expires or when employees are rehired within three years
Under standard requirements, employers must retain I-9 forms for three years after the date of hire or one year after employment termination, whichever is later, though longer retention may be required in cases involving pending litigation or government investigations. During this retention period, forms must remain accessible for inspection by authorized government officers from the Department of Homeland Security, Department of Labor, or Department of Justice.
The High Cost of I-9 Compliance Failures
U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement conducts thousands of I-9 audits annually, with violation penalties adjusted for inflation each year. Actual penalties vary based on violation type, employer history, and other factors ICE considers during enforcement actions. Technical violations carry substantial penalties when patterns demonstrate lack of good faith compliance efforts.
| Violation Type | Typical Penalty Range | Common Examples |
| Technical Violations | $272 - $2,701 per form | Missing signatures, incorrect dates, incomplete fields |
| Substantive Violations | $272 - $2,701 per form | Failure to verify, accepting unacceptable documents |
| Knowing Hire Violations | $676 - $27,018+ per unauthorized worker | Employing workers without valid authorization |
Beyond direct financial penalties, I-9 compliance failures create operational disruption and reputational damage. Organizations facing ICE audits typically invest substantial legal and administrative resources responding to Notices of Inspection. In cases involving pattern and practice violations, criminal prosecution of company officers is possible, though the majority of I-9 enforcement actions involve civil penalties rather than criminal charges.
Why Manual I-9 Processes Fail at Scale
Traditional paper-based I-9 processes introduce multiple failure points that compound as organizations grow. Hiring managers across different locations may receive inconsistent training on acceptable documents, proper examination procedures, and timing requirements.
Manual systems create these critical vulnerabilities:
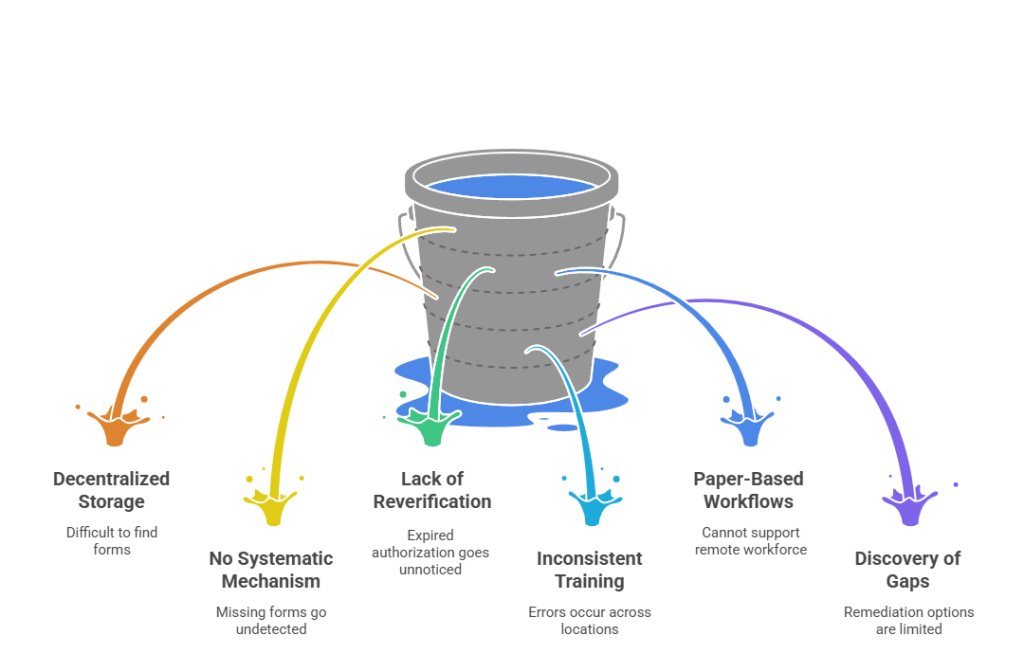
- Decentralized storage makes it difficult to track which forms exist and where they are located
- No systematic mechanism for identifying missing forms or incomplete sections
- Lack of reverification tracking leads to expired authorization going undetected
- Inconsistent training results in document examination errors across locations
- Paper-based workflows cannot accommodate remote workforce verification needs
- Discovery of gaps occurs only during audits when remediation options are limited
Remote and hybrid work models introduced additional complexity that manual systems cannot adequately address. Organizations discover compliance gaps only during internal audits or ICE inspections, when penalties may be imminent.
Core Components of Effective I-9 Form Management Systems
Intelligent Form Completion and Validation
Modern I-9 form management systems guide users through compliant form completion with real-time validation that helps prevent common errors before they occur. Smart forms automatically check for required fields, flag inconsistent information, and help guide proper document list selections.
Electronic signature capabilities streamline the execution process while maintaining legal validity. Employees can complete Section 1 remotely using secure authentication, with system-generated timestamps documenting compliance with timing requirements. The technology creates an auditable record showing exactly when each section was completed.
Document Examination Workflow Management
Systematic document examination workflows help employers meet the three-business-day deadline while properly reviewing acceptable documents. The system assigns document review tasks to authorized personnel, tracks when documents were presented, and records specific document details required for compliant Section 2 completion.
Digital document imaging capabilities allow employers to create and store copies of presented documents:
- Consistent documentation practices across all employees help protect against discrimination claims
- Automatic linking of images to corresponding forms creates complete verification packages
- Centralized storage demonstrates good faith compliance efforts during audits
- Authorized representative management tracks who examined documents for which employees
For organizations using authorized representatives for document examination, the system maintains current representative information and helps ensure representatives complete required attestations.
E-Verify Integration and Case Management
E-Verify participation is mandatory for federal contractors and employers in certain states, while remaining voluntary for most private employers. Organizations that participate in E-Verify must create cases for all new hires, following strict timing and procedural requirements.
Integrated platforms eliminate manual data entry by populating E-Verify cases directly from completed I-9 forms. The system helps enforce proper sequencing by preventing E-Verify case creation before I-9 Section 1 completion or after the three-day document examination window closes. When E-Verify returns Tentative Nonconfirmations, integrated systems manage the employee notification process and track response deadlines.
Advanced Compliance Features for Enterprise Organizations
Automated Expiration Tracking and Reverification
Employment authorization documents have varying expiration dates that require systematic tracking to help prevent gaps in work authorization. I-9 management systems monitor document expiration dates and trigger reverification workflows before authorization expires.
| Document Type | Typical Validity Period | Reverification Requirement |
| Permanent Resident Card | 10 years (conditional: 2 years) | Required upon expiration |
| Employment Authorization Document | Varies (typically 1-2 years) | Required upon expiration |
| Foreign Passport with I-94 | Varies by visa type | Required when authorization expires |
| U.S. Passport | 10 years (adult) / 5 years (minor) | Not required for citizens |
Automated notifications alert HR personnel and employees of approaching deadlines, providing sufficient time to complete reverification procedures. The reverification process in Section 3 requires specific procedures depending on the employee's authorization type. For organizations with large populations of employees on temporary work authorization, automated expiration tracking becomes essential infrastructure.
Centralized Audit Trail and Reporting
Comprehensive audit trails document every action taken on I-9 forms, creating defensible records that demonstrate good faith compliance efforts. The system logs when forms were accessed, what changes were made, who made changes, and the business justification for corrections or updates.
Real-time compliance reporting allows HR leaders to identify systematic issues before they become widespread problems:
- Dashboard views show form completion rates, pending actions, and common errors
- Department-level reporting enables targeted training and intervention
- Location-based analytics identify geographic compliance patterns
- Custom reports support internal audits and legal review
- Trend analysis reveals systematic problems requiring policy changes
This visibility enables proactive remediation rather than reactive crisis management. Organizations can generate reports showing all forms with specific characteristics, making it feasible to conduct regular internal audits even with thousands of employees.
Role-Based Access and Workflow Automation
Enterprise I-9 management requires carefully controlled access to sensitive information distributed across multiple stakeholders. Role-based permissions help ensure hiring managers can initiate I-9 processes for their new hires while HR administrators can monitor compliance and conduct audits.
Workflow automation routes forms to appropriate personnel based on organizational structure and employment type. When an employee completes Section 1, the system automatically notifies the designated document examiner. After Section 2 completion, the form routes to HR for final review. Integration with applicant tracking systems eliminates duplicate data entry and helps ensure I-9 processes initiate automatically when offers are accepted.
Addressing Remote Workforce Verification Challenges
Alternative Examination Procedures and Documentation Requirements
The Department of Homeland Security implemented temporary flexibility for remote document examination during the COVID-19 pandemic. As of January 2026, DHS has continued to authorize alternative remote examination procedures, though organizations should monitor official USCIS guidance as these temporary measures remain subject to modification or termination. Employees working exclusively in remote status can have their documents inspected via video call under current guidance.
Organizations utilizing alternative examination procedures must maintain detailed documentation:
- Video conferencing sessions with screen capture capabilities for document examination
- Structured documentation workflows ensuring all required steps are completed and recorded
- Tracking systems identifying which employees were verified using alternative procedures
- Transition management triggering required in-person examination when employees move to in-office work
The alternative procedure may require employers to conduct in-person document examination when employees transition to in-person work or if temporary flexibility provisions change. Systems track which employees were verified remotely and trigger required in-person examination workflows when applicable.
Authorized Representative Management for Distributed Teams
Organizations with employees in locations without on-site HR staff may designate authorized representatives to conduct document examination. Authorized representatives may include various individuals such as notaries or personnel at remote locations, subject to restrictions including that they cannot be the employee's relative or have certain financial interests in the hire. Organizations should consult current USCIS guidance when designating authorized representatives.
I-9 management platforms maintain authorized representative networks, including current contact information and location coverage. When new hires are located in areas requiring authorized representative services, the system automatically routes document examination tasks to appropriate representatives. The technology facilitates secure communication while maintaining confidentiality.
Technology Solutions for Hybrid Work Models
Hybrid work arrangements create ongoing verification challenges as employees transition between remote and in-office status. I-9 management systems must accommodate initial remote verification followed by in-person examination, or vice versa, while maintaining clear records of which procedures were followed.
Mobile-responsive platforms enable employees and employers to complete I-9 requirements on any device. Cloud-based systems help ensure real-time synchronization so all stakeholders access current information regardless of location or device. Digital signature technology paired with identity verification measures provides secure form execution without requiring physical presence.
Strategic Implementation of I-9 Management Systems
Assessing Organizational Needs and Current State
Successful I-9 management system implementation begins with comprehensive assessment of current processes and compliance status. Organizations should evaluate their current I-9 population, error rates, storage methods, and audit history to establish baseline compliance metrics.
Key assessment factors include:
- Number of locations and hiring volume per location
- Remote workforce percentage and geographic distribution
- E-Verify participation requirements at federal or state level
- International assignee populations requiring specialized handling
- Current error rates and most common compliance gaps
- Integration requirements with existing HR technology systems
Stakeholder input from HR, legal, IT, and business units helps ensure the selected system addresses actual operational needs. Systems that seamlessly exchange data with applicant tracking systems and payroll platforms deliver greater value than standalone solutions requiring duplicate data entry.
Change Management and Training for Adoption Success
Technology implementation succeeds only when users adopt new systems and follow established processes. Comprehensive training programs for HR staff, hiring managers, and employees help ensure all stakeholders understand their roles and can navigate system functionality.
Organizations should develop role-specific training content that focuses on the tasks each user group performs:
- Hiring managers: Document examination procedures and Section 2 completion
- HR administrators: System administration, reporting, and compliance monitoring
- Employees: Section 1 completion and document presentation procedures
- Authorized representatives: Remote examination protocols and documentation requirements
Ongoing support resources facilitate long-term adoption as new personnel join the organization. Regular refresher training keeps compliance knowledge current as regulations evolve.
Establishing Ongoing Compliance Monitoring and Auditing
I-9 management systems provide tools for ongoing compliance monitoring, but organizations must establish processes for regular review. Designated compliance personnel should conduct weekly reviews of pending actions, approaching deadlines, and flagged issues.
| Monitoring Activity | Recommended Frequency | Key Focus Areas |
| Pending Action Review | Weekly | Incomplete forms, missing signatures, approaching deadlines |
| Compliance Dashboard Review | Weekly | Error patterns, training needs, systematic issues |
| Internal Audit Sample | Quarterly | Random sample for substantive and technical compliance |
| Reverification Tracking | Monthly | Upcoming expirations, completed reverifications |
| System Access Review | Quarterly | Role assignments, terminated user access |
Internal audit schedules should include quarterly or semi-annual I-9 compliance reviews using system reporting capabilities. When internal audits identify issues, organizations should document remediation efforts within the I-9 management system itself. This creates a complete compliance record showing the organization's good faith efforts to correct issues.
I-9 Compliance Best Practices for 2026
Maintaining Separation Between I-9 and Other Employment Records
Immigration law requires organizations to store I-9 forms separately from other personnel records to help prevent unauthorized access and facilitate production during government inspections. While this physical separation was straightforward with paper forms, electronic systems must implement access controls that achieve the same protective effect.
I-9 management platforms should restrict access to employment eligibility information, preventing individuals who do not have legitimate business need from viewing I-9 data. This separation also helps protect against potential discrimination issues by limiting hiring manager access to citizenship status information or document types that might reveal national origin. Organizations must maintain similar separation for E-Verify information.
Avoiding Discrimination and Document Abuse
The Immigration and Nationality Act prohibits document abuse and discrimination based on citizenship status or national origin. Employers cannot specify which acceptable documents employees must present, reject reasonably genuine-appearing documents, or apply different verification standards.
Compliant I-9 systems incorporate these anti-discrimination protections:
- Equal document presentation: All List A, B, and C documents displayed without preferences or hierarchy
- Training reinforcement: Embedded guidance on anti-discrimination principles throughout workflows
- Flagging mechanisms: Suspected fraudulent documents escalated for legal review without preventing form completion
- Audit trail protection: Documentation shows consistent treatment across all employees
When organizations identify suspected fraudulent documents, they must follow specific procedures that avoid discrimination. Systems can facilitate appropriate escalation while avoiding the appearance of disparate treatment.
Preparing for ICE Audits and Government Inspections
ICE generally provides three business days' notice when issuing a Notice of Inspection for I-9 audits. Organizations using I-9 management systems are typically able to generate I-9 packages for current and terminated employees more quickly than with manual systems, which may help facilitate responses to government inspections.
The Notice of Inspection specifies which forms must be produced and the timeframe for production. System reporting capabilities allow organizations to quickly identify and produce requested records in organized formats. Organizations should conduct mock ICE audits periodically using the same procedures they would follow during actual inspections.
Emerging Technology and Future I-9 Verification Trends
Digital Identity Solutions and Biometric Verification
Emerging digital identity technologies may transform employment eligibility verification in coming years. Biometric verification, blockchain-based identity credentials, and mobile driver's licenses could eventually reduce reliance on physical document examination while enhancing security.
Several states have begun issuing mobile driver's licenses that allow digital presentation and verification of identity documents:
- Digital credentials may enable secure remote verification without physical document examination
- Blockchain technology could provide tamper-proof identity verification trails
- Biometric matching may help confirm document presenter matches credential holder
- Regulatory evolution required before widespread adoption for I-9 purposes
As these digital credentials gain acceptance for I-9 purposes, management systems will need to incorporate technology for secure digital document examination. Organizations implementing I-9 management systems in 2026 should consider platform flexibility to accommodate emerging verification technologies.
Artificial Intelligence for Compliance Risk Assessment
Advanced I-9 management platforms are beginning to incorporate artificial intelligence capabilities that analyze patterns across large form populations to identify potential compliance risks. These systems can flag anomalies such as unusual document combinations or systematic errors by specific document examiners.
Predictive analytics may help identify employees at elevated risk for authorization expiration based on document type and historical patterns. Organizations should evaluate these emerging capabilities carefully, ensuring AI-enhanced systems provide explainable recommendations rather than black-box decisions. Human oversight remains essential for compliance decisions that carry legal and ethical implications.
Potential Legislative Changes Affecting I-9 Requirements
Immigration reform proposals regularly surface in Congress, with potential impacts on employment eligibility verification requirements. Some proposals would expand E-Verify to all employers, while others would modify acceptable document lists or introduce new verification methods.
Organizations should monitor legislative developments and ensure their I-9 management systems can adapt to regulatory changes. Platform providers that maintain systems in accordance with current regulations and deploy updates automatically provide stronger protection against compliance gaps. The Department of Homeland Security periodically updates Form I-9 itself, introducing revised versions that employers must use after specified transition periods.
Conclusion
I-9 form management systems have evolved into essential compliance infrastructure for organizations navigating complex employment eligibility verification requirements in 2026. By helping transition traditionally manual, error-prone processes toward more automated workflows with built-in validation and audit capabilities, these platforms support organizations in working toward federal compliance objectives while reducing administrative burden and helping to mitigate potential violation risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an I-9 form management system and why do organizations need one?
An I-9 form management system is a technology platform that automates employment eligibility verification, providing electronic form completion, document examination workflows, and compliance reporting. Organizations benefit from these systems because manual I-9 processes frequently produce substantial error rates, exposing companies to significant penalties per form violation. Modern systems help reduce administrative burden while improving compliance accuracy through real-time validation and centralized record-keeping.
Are electronic I-9 forms legally acceptable and do they meet federal requirements?
Yes, electronic I-9 systems are fully compliant with federal requirements when they meet specific regulatory standards outlined in USCIS guidance. Electronic systems must ensure document integrity, include audit trails tracking all form access, implement access controls, enable electronic signatures with identity verification, and allow forms to be retrieved for government inspections. The Department of Homeland Security has explicitly approved electronic I-9 completion and storage.
How do I-9 management systems handle remote employees and document examinations?
I-9 management systems accommodate remote employees through alternative examination procedures currently authorized by the Department of Homeland Security. These systems typically include video conferencing integration for remote document examination, screen capture capabilities, structured workflows ensuring all steps are completed, and tracking mechanisms identifying which employees may require in-person examination when they transition to in-office work. Organizations may also designate authorized representatives at remote locations.
What is the difference between I-9 compliance and E-Verify?
I-9 compliance is the mandatory federal requirement for all U.S. employers to verify identity and employment authorization using Form I-9. E-Verify is an optional electronic system that most employers may voluntarily use to confirm employment eligibility by matching I-9 information against government databases. E-Verify is mandatory only for federal contractors and employers in certain states with participation requirements.
How long must employers retain I-9 forms and how do management systems handle retention?
Under standard requirements, employers must retain I-9 forms for three years after the date of hire or one year after employment termination, whichever is later, though longer retention may be required in cases involving pending litigation, government investigations, or other legal circumstances. I-9 management systems automatically calculate retention deadlines, help prevent premature deletion of forms, archive forms that have met retention requirements, and generate retention compliance reports.
What happens during an ICE I-9 audit and how do management systems support the process?
During an ICE I-9 audit, employers receive a Notice of Inspection requiring production of I-9 forms within three business days. I-9 management systems support audits by helping generate form sets more quickly, producing organized digital or printed packages with documentation, creating audit reports showing compliance status, and providing detailed audit trails demonstrating good faith compliance efforts. These capabilities may help facilitate government inspection responses.
Can I-9 management systems prevent all compliance violations?
I-9 management systems help reduce the likelihood of compliance violations by providing tools to avoid common technical errors and automate tracking of timing-sensitive requirements. However, systems cannot guarantee zero violations because compliance also depends on proper document examination by trained personnel, appropriate system usage following established procedures, and timely action on system-generated alerts. Organizations achieve best results by combining robust technology with comprehensive training, clear policies, and regular internal audits.
What are the most common I-9 errors that management systems help prevent?
The most common I-9 errors include missing signatures, incorrect or missing dates, unchecked boxes, accepting expired documents, failing to complete reverification when authorization expires, improper corrections, missing employer information, accepting unacceptable document combinations, and exceeding the three-business-day deadline. I-9 management systems help address these errors through required field validation, automated signature capture with timestamps, real-time checking of document expiration dates, and automated deadline alerts.
How do I-9 management systems integrate with existing HR technology?
Modern I-9 management systems integrate with applicant tracking systems to automatically initiate I-9 processes when offers are accepted, connect with human resource information systems to synchronize employee data, link to onboarding platforms to coordinate all new hire compliance activities, and interface with payroll systems. Integration methods include application programming interfaces for real-time data exchange, single sign-on for unified user experience, and automated file transfers for batch data updates.
What should organizations look for when selecting an I-9 form management system?
Organizations should evaluate systems based on compliance features including current form versions with automatic updates, comprehensive validation helping prevent common errors, E-Verify integration if applicable, and audit trail capabilities. Additional considerations include user experience factors such as intuitive interfaces, mobile accessibility, multilingual support, and integration capabilities with existing HR technology. Organizations should also assess vendor regulatory expertise, customer support quality, implementation services, and long-term platform stability.
Additional Resources
- Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification
https://www.uscis.gov/i-9 - Handbook for Employers: Guidance for Completing Form I-9 (M-274)
https://www.uscis.gov/i-9-central/form-i-9-resources/handbook-for-employers-m-274 - E-Verify Program Overview and Requirements
https://www.e-verify.gov/ - U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement Worksite Enforcement
https://www.ice.gov/factsheets/worksite - Department of Justice Civil Rights Division: Immigrant and Employee Rights Section
https://www.justice.gov/crt/immigrant-and-employee-rights-section

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






