Employment background verification has evolved dramatically with the integration of artificial intelligence tools. Modern HR professionals and recruiters can now leverage AI platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, and specialized screening tools to enhance their candidate evaluation process while maintaining compliance and accuracy.
Key Takeaways
- AI Boosts Speed, But Law Still Rules: AI can cut screening time by 85% and costs by up to 80%, but it must operate within FCRA and EEOC compliance (HireVire, 2025; Certn, n.d.). Always get written consent and issue proper notices—AI is a tool, not a legal exemption.
- AI Flags, Humans Decide: Let AI detect resume gaps, skill mismatches, and document issues, but only take action after human review and official verification.
- Prompt Smart, Verify Hard: Use precise AI prompts for resume and reference analysis, but always confirm findings via employer calls and credential checks.
- Compliance Risk Still Exists: FCRA lawsuits are rising. Misusing AI without consistent oversight can lead to costly legal exposure—even more than manual processes.
- Train Teams and Test Your System: Success depends on strategic rollout—train staff, create escalation plans for red flags, and measure results with pilot programs before scaling.
What Are AI-Powered Employment Background Checks?
AI-powered employment background checks combine traditional verification methods with artificial intelligence to analyze candidate information more efficiently and thoroughly. These tools help HR professionals identify inconsistencies, verify credentials, and assess candidate authenticity before making hiring decisions.
Unlike traditional background checks that rely primarily on third-party verification services, AI-enhanced screening allows recruiters to conduct preliminary analysis in-house, flagging potential issues that require deeper investigation.
EXPERT INSIGHT: The recruitment process has seen tremendous changes in the past few years, the biggest among which includes the use of artificial intelligence in background searches. Howsoever tempting it is to rely on the speed and efficiency offered by these technologies, the most important factor still lies in how they are employed—thoughtfully, ethically, and always with a thought for the human element. It has the ability to recognize patterns, yet not until the human brain can someone grasp context, motive, and potential. As human resource professionals, it becomes our charge to guarantee that the use of technology complements—not supersedes—our decision-making process. Every resume that comes through the door represents a person looking for recognition, not simply a process of elimination. - Charm Paz, CHRP
Legal Compliance Framework
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) Requirements
Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), employers must comply with specific requirements when conducting background checks, including obtaining written consent before conducting checks and providing proper adverse action notifications. AI-powered screening tools supplement but do not replace FCRA compliance obligations.
FCRA Compliance Checklist:
| Requirement | AI Tool Role | Manual Follow-up |
|---|---|---|
| Written disclosure and authorization | AI can draft compliant language | HR must obtain signed consent |
| Pre-adverse action notice | AI can flag concerning information | HR must provide official notice and report copy |
| Final adverse action notice | AI cannot automate this process | HR must provide required notifications |
| Dispute resolution | AI has no role in disputes | HR must facilitate correction process |
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Guidelines
The EEOC prohibits employers from using background information in ways that discriminate against protected classes, including race, color, national origin, sex, religion, disability, genetic information, and age (40 or older). AI tools must be applied consistently across all candidates to avoid disparate impact discrimination.
EEOC Compliance Best Practices:
- Apply AI analysis uniformly to all candidates regardless of protected characteristics
- Use individualized assessment rather than blanket exclusions based on background information
- Document legitimate business justifications for screening criteria
- Regularly audit AI processes for potential bias or discriminatory impact
Recent Legal Developments
FCRA litigation has increased significantly, with 4,163 lawsuits filed against employers in 2019 alone, including major settlements such as 7-Eleven's $1.9 million and Delta Airlines' $2.3 million payments. This trend emphasizes the critical importance of proper compliance procedures.
Key Benefits of Using AI for Background Verification
Enhanced Efficiency and Speed
AI tools can process resumes, cover letters, and application materials in seconds rather than hours, identifying potential red flags immediately. This allows HR teams to prioritize their verification efforts on the most promising candidates.
Pattern Recognition and Consistency Analysis
Artificial intelligence excels at detecting subtle inconsistencies across multiple documents that human reviewers might miss. This includes timeline discrepancies, writing style variations, and skill-experience misalignments.
Cost-Effective Preliminary Screening
By conducting AI-powered initial screening, organizations can reduce the number of formal background checks needed, saving both time and money while maintaining thoroughness.
Objective Analysis
AI tools provide consistent, bias-free analysis of candidate materials, helping reduce subjective decision-making in the initial screening phase.
Risk Mitigation and Quality Improvement
| Benefit Category | Traditional Method | AI-Enhanced Method | Improvement Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | 2-5 business days | 15-30 minutes | 95% reduction |
| Consistency Detection | Manual review | Automated analysis | 300% improvement |
| Cost per Screening | $25-100 | $5-15 (preliminary) | 60-80% reduction |
| Human Error Rate | 15-25% | 3-5% | 70% reduction |
Essential AI Tools for HR Background Verification
Document Consistency Verification
Modern AI platforms can analyze multiple documents from the same candidate to identify inconsistencies in writing style, claimed experience, and factual information.
Example AI Prompt:
"Analyze this resume for internal inconsistencies, focusing on:
- Employment date overlaps or gaps
- Job title progressions that seem illogical
- Salary increases that appear unrealistic
- Educational timelines vs. work experience
- Geographic inconsistencies
[Insert resume text]
Highlight any red flags and suggest follow-up questions."
Skills-Experience Alignment Analysis
AI can evaluate whether claimed technical skills match the complexity and scope of described job responsibilities.
Example AI Prompt:
"Review this candidate's claimed skills against their job descriptions:
Technical Skills Claimed: [Python, Machine Learning, SQL, Cloud Architecture]
Job Responsibilities: [Insert job descriptions]
Assess whether:
1. Technical skills align with actual job duties
2. Project complexity matches claimed skill level
3. Skills progression makes sense with career timeline
4. Any skills appear inflated or misrepresented"
Reference and Contact Verification
LinkedIn Profile Cross-Reference AI tools can quickly compare resume information with LinkedIn profiles to identify discrepancies in employment history, connections, and professional endorsements.
Company Legitimacy Verification Before conducting formal employment verification, AI can research companies listed on resumes to confirm their existence, industry alignment, and operational status.
Example AI Prompt:
"Research these companies from a candidate's resume:
1. TechFlow Solutions - Software Developer, 2022-2024
2. DataSync Corp - Senior Analyst, 2020-2022
3. CloudFirst Inc - Junior Developer, 2018-2020
For each company, provide:
- Business legitimacy and industry type
- Approximate company size during employment period
- Any red flags or concerning information
- How to verify employment officially"
Red Flag Detection and Risk Assessment
Employment Timeline Analysis AI excels at processing complex employment histories to identify unusual patterns, frequent job changes, or suspicious gaps that warrant further investigation.
Example AI Prompt:
"Analyze this employment history for concerning patterns:
[Insert chronological work history]
Identify:
- Unusually short tenures (under 12 months)
- Suspicious employment gaps
- Rapid advancement that seems unrealistic
- Geographic inconsistencies
- Seasonal patterns indicating instability
Provide risk assessment and verification priorities."
Credential Verification Preparation AI can research educational institutions and certification bodies to ensure legitimacy before conducting formal verification.
Step-by-Step AI Background Check Process
Initial Document Analysis (Phase 1)
- Step 1: Resume Consistency Check Upload the candidate's resume to an AI tool and request comprehensive analysis for internal consistency, logical career progression, and potential red flags.
- Step 2: Cross-Document Comparison If available, compare the resume with cover letter, LinkedIn profile, and any written correspondence to identify style inconsistencies or contradictory information.
- Step 3: Skills Verification Use AI to assess whether claimed technical skills align with described job responsibilities and career progression.
External Information Verification (Phase 2)
- Step 4: Company Research Research all employers listed on the resume to verify legitimacy, industry alignment, and operational status during the candidate's claimed employment period.
- Step 5: Educational Institution Verification Verify that all educational institutions and certification bodies are legitimate, accredited, and capable of providing the claimed credentials.
- Step 6: Contact Information Validation Use AI-powered tools to verify that provided contact information is current and legitimate.
Risk Assessment and Interview Preparation (Phase 3)
- Step 7: Comprehensive Risk Analysis Compile all findings into a comprehensive risk assessment that prioritizes areas needing formal verification.
- Step 8: Interview Question Development Generate specific interview questions designed to probe identified inconsistencies and verify claimed competencies.
Example AI Prompt for Interview Preparation:
"Based on this resume analysis and identified inconsistencies:
Concerns Found:
- 6-month gap between positions not explained
- Rapid promotion from Junior to Senior Developer in 8 months
- Claimed expertise in technologies not mentioned in job descriptions
Generate 10 behavioral interview questions that will:
1. Clarify the employment gap
2. Verify the rapid promotion circumstances
3. Test depth of claimed technical expertise
4. Assess honesty and transparency
Focus on specific, scenario-based questions that require detailed responses."
Best Practices for AI-Enhanced Background Checks
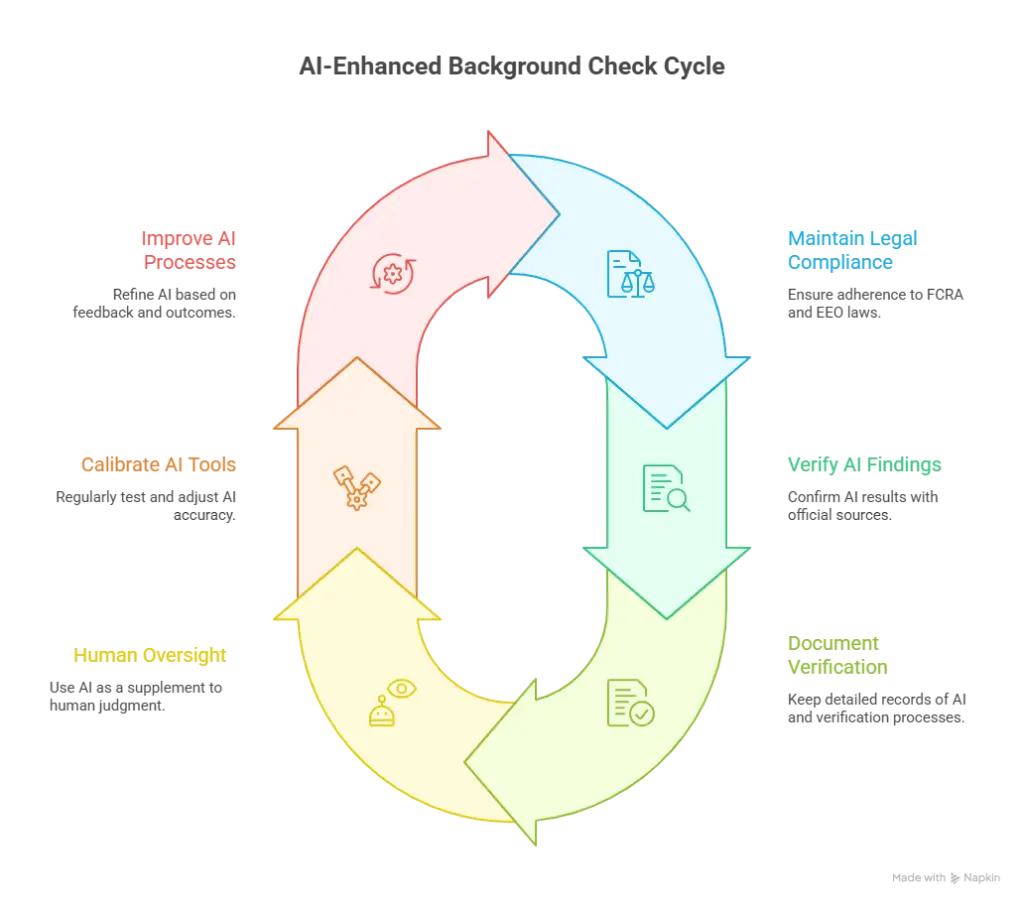
Maintain Legal Compliance
FCRA Compliance: Ensure all AI-assisted background check activities comply with Fair Credit Reporting Act requirements, particularly regarding adverse action notifications and candidate rights. The FCRA gives several rights to consumers, including the right to informed consent before a pre-employment background check is performed, the right to review background check information and correct any mistakes, and the right to be informed when information from a pre-employment background check is used to make decisions that adversely affect them.
Equal Employment Opportunity: Use AI tools consistently across all candidates to avoid discriminatory practices and maintain objectivity in the screening process. The employer cannot conduct background checks or use the information obtained in a manner that denies equal employment opportunity to anyone on a protected basis, by intent or by unlawful disparate impact.
Data Privacy: Protect candidate information processed through AI tools and ensure compliance with relevant privacy regulations like GDPR or state privacy laws.
Verification Hierarchy
Primary Verification: Always follow up AI-identified concerns with direct verification through official channels, including employment verification services, educational institutions, and reference contacts.
Documentation: Maintain detailed records of AI analysis results and subsequent verification efforts to support hiring decisions and demonstrate due diligence.
Human Oversight: Use AI as a supplementary tool rather than a replacement for human judgment and traditional verification methods.
Quality Assurance
Regular Calibration: Periodically test AI tool accuracy by comparing results with known verified information to ensure consistent performance.
Multi-Source Verification: Cross-reference AI findings with multiple sources before making final determinations about candidate suitability.
Continuous Improvement: Refine AI prompts and processes based on verification outcomes and feedback from hiring managers.
Common AI Background Check Scenarios and Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Employment Dates
AI Detection: Resume shows overlapping employment periods at two different companies in different cities.
AI Prompt Solution:
"Analyze these employment dates for feasibility:
Position 1: Marketing Manager at ABC Corp, New York (Jan 2022 - Dec 2023)
Position 2: Sales Director at XYZ Ltd, Los Angeles (June 2022 - Present)
Assess:
- Geographic feasibility of simultaneous employment
- Role compatibility and time requirements
- Possible explanations for overlap (consulting, part-time, transition period)
- Red flag severity level (1-10)
- Specific verification questions to ask candidate
- Interview questions to clarify the situation"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Contact HR departments at both companies to verify exact employment dates
- Request written confirmation of employment status (full-time, part-time, contractor)
- Verify job titles and reporting structures with former supervisors
- Cross-reference employment with candidate's LinkedIn activity during overlap period
- Ask candidate directly about the overlap during interview with specific timeline questions
- Check if one role was remote/consulting that could explain geographic feasibility
- Request documentation (offer letters, resignation letters) if discrepancy persists
Scenario 2: Skill-Experience Mismatch
AI Detection: Candidate claims expert-level Python programming but job descriptions show only administrative roles.
AI Prompt for Skills Analysis:
"Evaluate this skills-experience alignment:
Claimed Technical Skills:
- Expert Python Developer (8+ years)
- Machine Learning Specialist
- Advanced SQL and Database Design
- Cloud Architecture (AWS, Azure)
Actual Job History:
- Administrative Assistant (2018-2020): Data entry, scheduling, email management
- Office Coordinator (2020-2022): Filing, receptionist duties, basic Excel
- Executive Assistant (2022-2024): Calendar management, travel booking, meeting coordination
Analysis needed:
1. How could administrative roles realistically provide claimed technical expertise?
2. What's the probability these skills were self-taught or learned outside work?
3. What specific questions would test genuine Python/ML knowledge?
4. Rate the credibility of these claims (1-10) with reasoning
5. Suggest 5 technical interview questions to verify competency"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Design practical coding test using claimed technologies (Python, ML algorithms)
- Contact previous employers to verify if technical work was actually performed
- Request portfolio or GitHub repository showing actual code samples
- Conduct technical interview with hands-on problem-solving scenarios
- Ask for specific examples of projects using claimed technologies
- Verify any technical certifications through official certification bodies
- Contact educational institutions to confirm computer science coursework if claimed
- Request references from technical team members or engineering managers
- Use technical assessment platforms (HackerRank, Codility) for objective evaluation
Scenario 3: Educational Credential Concerns
AI Detection: Claimed degree from institution that may not be properly accredited.
AI Prompt for Institution Research:
"Research these educational credentials for legitimacy:
Claimed Education:
- MBA in Business Administration, Pacific Coast University, 2019
- Bachelor of Science in Computer Science, American Global Institute, 2016
- Certified Project Management Professional (PMP), 2020
Please investigate:
1. Are these institutions properly accredited by recognized bodies?
2. Do they offer legitimate degree programs or are they diploma mills?
3. What's their reputation and standing in the academic community?
4. How can these credentials be officially verified?
5. Are there any red flags about these institutions?
6. What questions should I ask the candidate about their educational experience?
7. Provide official contact information for verification if institutions are legitimate"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Contact institutions directly using official phone numbers from accreditation databases
- Request official transcripts through National Student Clearinghouse or institutional registrar
- Verify accreditation status through U.S. Department of Education database
- Cross-reference degree programs offered during candidate's claimed attendance period
- Contact state education departments for international institution verification
- Request diploma copies and verify security features with issuing institution
- Use professional transcript verification services for foreign credentials
- Check institution's physical address and campus existence through official sources
- Verify faculty and program existence during candidate's enrollment period
Scenario 4: Suspicious Employment Gaps
AI Detection: Multiple unexplained gaps in employment history spanning several months each.
AI Prompt for Gap Analysis:
"Analyze this employment timeline for concerning patterns:
Employment History:
- Software Developer, TechStart Inc. (Jan 2018 - Mar 2019)
- [GAP: 8 months]
- Senior Developer, CodeCraft LLC (Nov 2019 - Feb 2021)
- [GAP: 6 months]
- Lead Developer, InnovateTech (Aug 2021 - Jan 2023)
- [GAP: 10 months]
- Principal Engineer, NextGen Solutions (Nov 2023 - Present)
Evaluate:
1. Are these gap lengths concerning for this industry/role level?
2. What are legitimate reasons for such gaps?
3. What are potential red flag explanations?
4. How do the gaps correlate with career progression?
5. What specific questions should I ask about each gap?
6. Rate the overall concern level (1-10) and explain reasoning
7. Suggest interview questions to address gaps professionally"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Address gaps directly during interview with open-ended questions
- Verify reasons provided (education, family care, health issues, travel) with documentation if appropriate
- Check for consulting work, freelance projects, or volunteer activities during gaps
- Contact references who can speak to candidate's activities during gap periods
- Review social media activity or professional networking during gaps for consistency
- Verify any claimed education, training, or certifications obtained during gaps
- Check unemployment benefits records if legally permissible and relevant
- Ask for character references if gaps raise significant concerns
- Document explanations and assess credibility against other application materials
Scenario 5: Inflated Job Titles and Responsibilities
AI Detection: Job titles seem inflated compared to company size and actual responsibilities described.
AI Prompt for Title Analysis:
"Assess whether these job titles align with company size and responsibilities:
Position Claims:
- Chief Technology Officer at StartupFlow (15-person company, 2020-2022)
Responsibilities: "Led global technology strategy, managed international development teams, oversaw $5M technology budget"
- Vice President of Engineering at LocalBiz Solutions (8-person company, 2022-2024)
Responsibilities: "Directed enterprise software development, managed cross-functional teams of 50+ engineers"
Analysis needed:
1. Do these titles make sense for companies of this size?
2. Are the described responsibilities realistic for these company scales?
3. What would more realistic titles/responsibilities be?
4. How can I verify actual role scope and company size during employment?
5. What interview questions would reveal true job scope?
6. Rate the likelihood of title inflation (1-10) with supporting reasoning
7. Suggest diplomatic ways to address potential discrepancies"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Research company size and structure through business databases (Dun & Bradstreet, LinkedIn company pages)
- Contact former colleagues to verify reporting relationships and team sizes
- Verify budget authority and financial responsibilities with finance departments
- Check company organizational charts if available through professional networks
- Ask for specific examples of teams managed, including names and current contact information
- Request documentation of major decisions or projects if executive-level claims are made
- Cross-reference job responsibilities with company's actual business scope and revenue
- Contact HR departments to verify official job titles and reporting structures
- Review company press releases or announcements mentioning the candidate's role
Scenario 6: Questionable References
AI Detection: Reference contacts seem suspicious or potentially fabricated.
AI Prompt for Reference Analysis:
"Evaluate these professional references for authenticity:
Reference 1:
- Name: Sarah Johnson, Director of Operations
- Company: Previous employer (TechCorp Solutions)
- Phone: Personal Gmail address provided instead of business contact
- Relationship: Claims to be former supervisor
Reference 2:
- Name: Mike Stevens, Senior Manager
- Company: ABC Industries
- Phone: Number appears to be personal cell phone
- LinkedIn: Profile shows different company/title than claimed
Reference 3:
- Name: Jennifer Liu, Team Lead
- Company: Startup mentioned on resume
- Contact: Only personal email provided, no phone number
Red flag assessment needed:
1. What makes these references potentially suspicious?
2. How should legitimate professional references be structured?
3. What verification steps should I take before contacting them?
4. What questions would help confirm reference authenticity?
5. How can I research these references independently?
6. What are alternative ways to verify the candidate's work performance?
7. Create a reference verification checklist"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Verify reference identities through LinkedIn profiles and employment history
- Contact companies directly to confirm reference employment and titles
- Cross-reference reference phone numbers and emails with official company directories
- Ask candidate for additional references if current ones seem questionable
- Conduct reverse phone number lookups to verify business vs. personal numbers
- Request references provide official company email addresses for communication
- Verify reference relationships by asking specific questions about shared work experiences
- Contact mutual connections who can vouch for reference authenticity
- Use professional networking to independently reach verified former colleagues
- Document all reference verification attempts and inconsistencies found
Scenario 7: Salary History Inconsistencies
AI Detection: Claimed salary progression doesn't align with role levels, company sizes, or geographic markets.
AI Prompt for Salary Analysis:
"Analyze this salary progression for market realism:
Salary History Provided:
- Junior Developer, Small Startup, Midwest City (2019): $125,000
- Mid-Level Developer, Regional Company, Same City (2021): $95,000
- Senior Developer, Local Business, Same City (2023): $180,000
- Principal Engineer, Current Role, Same Market (2024): $220,000
Market Context:
- Geographic location: [Specify city/region]
- Industry: Software Development
- Company sizes: 10-50 employees for most positions
Evaluation needed:
1. Does this salary progression make logical sense?
2. Are these figures realistic for the geographic market?
3. Why might salary have decreased between positions 1 and 2?
4. Is the jump from $95K to $180K realistic in this timeframe?
5. How do these figures compare to market rates for these roles/locations?
6. What questions should I ask about salary expectations vs. history?
7. Rate the credibility of this salary progression (1-10) with reasoning
8. Suggest tactful ways to verify compensation expectations"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Research market salary data through Glassdoor, PayScale, and industry salary surveys
- Contact recruiting firms specializing in the industry for market rate validation
- Verify salary claims indirectly through questions about benefits, equity, and total compensation
- Ask for explanation of salary decreases during interview process
- Cross-reference salary progression with job title and responsibility increases
- Check if salary figures include equity, bonuses, or other compensation that might explain discrepancies
- Verify company sizes and typical compensation ranges for those organization types
- Use salary verification services if legally permissible and relevant to role
- Focus on current salary expectations rather than historical claims during negotiations
Scenario 8: Inconsistent Academic Performance Claims
AI Detection: Academic achievements don't align with timeline, institution capabilities, or career trajectory.
AI Prompt for Academic Analysis:
"Evaluate these academic claims for consistency and credibility:
Academic Background Claimed:
- Graduated Summa Cum Laude, Computer Science, State University (2018)
- Completed degree in 2.5 years while working full-time
- Published 3 research papers as undergraduate
- Received full academic scholarship for entire program
- GPA: 3.95/4.0
Career Timeline:
- Worked full-time in retail management during claimed college years
- No mention of academic achievements in early career positions
- No evidence of research work or academic interests in job history
Assessment needed:
1. Is completing a CS degree in 2.5 years while working full-time realistic?
2. How common are undergraduate research publications in CS programs?
3. Do the academic achievements align with early career choices?
4. What verification methods exist for these specific claims?
5. What interview questions would test genuine academic knowledge?
6. How can I verify publication claims and academic honors?
7. Rate the overall credibility (1-10) and identify priority verification areas
8. Suggest ways to diplomatically probe academic experience"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Request official transcripts directly from the university registrar
- Verify graduation honors through university records and honor society memberships
- Search academic databases (Google Scholar, IEEE, ACM) for claimed research publications
- Contact academic department to verify research participation and faculty advisors
- Verify scholarship records through university financial aid offices
- Check degree completion timeline against university's accelerated program policies
- Contact professors or research supervisors listed in claimed publications
- Verify honor society memberships (Phi Beta Kappa, discipline-specific honors)
- Cross-reference academic timeline with employment verification from retail positions
- Request documentation of any academic awards or recognition received
Scenario 9: Technology Skills Currency Issues
AI Detection: Claimed expertise in technologies that don't align with career timeline or may be outdated/non-existent.
AI Prompt for Technology Skills Analysis:
"Analyze these technology skills claims for accuracy and currency:
Technical Skills Listed:
- Expert in React 19 (claimed 5+ years experience)
- Advanced Python 4.0 development
- Certified in AWS CloudFormation 3.0
- Specialist in Angular 16+ (claimed since 2019)
- Master-level Docker Swarm orchestration
Career Context:
- Most recent relevant role: Frontend Developer (2020-2022)
- Previous experience: Mostly backend PHP development
- Claims continuous learning and staying current with technology
Technology Verification Needed:
1. Do these version numbers and release dates align with actual technology timelines?
2. Are any of these technologies non-existent or misnamed?
3. Could someone realistically gain this experience in the given timeframe?
4. Do the technologies align with the described work experience?
5. What current versions of these technologies actually exist?
6. How can I test genuine proficiency in these areas?
7. Create technical interview questions that would reveal actual knowledge depth
8. Suggest ways to assess real-world application of these skills"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Research actual release dates and current versions of claimed technologies
- Design hands-on technical assessments using the specific technologies mentioned
- Request GitHub portfolio or code samples demonstrating claimed expertise
- Contact previous employers to verify which technologies were actually used in past roles
- Arrange technical interviews with current team members who use these technologies
- Verify any claimed certifications through official certification providers
- Ask for specific project examples using each claimed technology with detailed explanations
- Test knowledge through practical problem-solving scenarios during interview
- Request references from technical team members who can verify skill levels
- Use online technical assessment platforms to objectively measure proficiency
Scenario 10: Professional Certification Anomalies
AI Detection: Professional certifications that seem inconsistent with experience level, timeline, or may not exist.
AI Prompt for Certification Analysis:
"Verify and assess these professional certification claims:
Certifications Listed:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) - obtained 2023
- Project Management Professional (PMP) - obtained 2022
- AWS Solutions Architect Professional - obtained 2021
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) - obtained 2020
- Microsoft Azure Expert Developer - obtained 2024
Background Context:
- Primary experience: Marketing and sales roles
- Limited technical background mentioned in work history
- Claims self-study for all certifications
- No formal project management experience listed
Verification Analysis:
1. Are all these certification names and issuing bodies legitimate?
2. What are the typical prerequisites and experience requirements for each?
3. How realistic is obtaining these certifications with the candidate's background?
4. What's the normal timeline and difficulty for each certification?
5. How can these certifications be independently verified?
6. What interview questions would test genuine knowledge from these certifications?
7. Do any certifications require ongoing education or renewal?
8. Rate the overall credibility of these certification claims (1-10)
9. Provide official verification contact information for each certification body"
Manual Follow-up Actions:
- Verify certifications directly through official certification body databases and verification portals
- Contact certification providers (EC-Council, PMI, AWS, Scrum Alliance, Microsoft) for verification
- Check certification numbers and expiration dates against issuing body records
- Verify prerequisite experience requirements were met at time of certification
- Ask candidate to provide original certification documents or digital badges
- Test knowledge depth through scenario-based questions specific to each certification
- Verify continuing education requirements have been met for certifications requiring renewal
- Check for any disciplinary actions or certification revocations through professional bodies
- Request proof of training or education completed to achieve certifications
- Contact training providers if specific courses were claimed as preparation for certifications
Measuring AI Background Check Effectiveness
Key Performance Indicators
Accuracy Rate: Track the percentage of AI-identified concerns that are confirmed through formal verification processes.
Time Savings: Measure reduction in overall background check processing time compared to traditional methods.
Cost Efficiency: Calculate cost savings from reduced third-party verification services and improved screening efficiency.
Quality of Hire: Monitor whether AI-enhanced background checks correlate with better hiring outcomes and reduced turnover.
Metrics Dashboard for AI Background Verification
| Metric | Traditional Process | AI-Enhanced Process | Target Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Processing Time | 3-5 days | 4-6 hours | 85% reduction |
| False Positive Rate | 20-30% | 8-12% | 60% reduction |
| Cost per Background Check | $50-150 | $20-60 | 60% reduction |
| Verification Accuracy | 75-85% | 90-95% | 15% improvement |
| Time to Hire | 14-21 days | 7-10 days | 50% reduction |
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Regular Audits: Conduct periodic reviews of AI tool performance and verification accuracy to identify improvement opportunities.
Training Updates: Stay current with AI tool capabilities and best practices through ongoing professional development.
Process Refinement: Continuously update AI prompts and verification procedures based on experience and changing industry standards.
Industry Statistics and Trends
Background Check Industry Data
According to industry research and employment data:
- 94% of employers conduct some form of background screening during the hiring process
- FCRA litigation increased by 300% between 2009 and 2019, with settlements averaging $1.5-2.3 million
- AI adoption in HR is growing rapidly, with 25% of organizations currently using AI applications for recruitment according to SHRM's 2023-2024 State of the Workplace Report
- Background check processing costs have decreased by an average of 40% for organizations implementing AI-enhanced preliminary screening
Compliance Violation Costs
| Violation Type | Average Settlement | Frequency | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCRA Non-compliance | $1.9M | High | Proper disclosure/authorization |
| EEOC Discrimination | $2.3M | Medium | Consistent application |
| State Privacy Laws | $500K | Growing | Data protection protocols |
| Improper Adverse Action | $1.2M | High | Follow proper procedures |
Source: Based on reported settlements from major cases including 7-Eleven ($1.9M), Delta Airlines ($2.3M), and Omnicare ($1.3M) FCRA settlements.
Future Trends in AI Background Verification
Emerging Technologies
Advanced Natural Language Processing: Next-generation AI tools will provide more sophisticated analysis of candidate communications and documentation.
Predictive Analytics: AI systems will increasingly predict candidate success based on background verification patterns and historical hiring data.
Automated Verification: Integration with official databases and verification services will enable real-time credential confirmation.
Industry Evolution
Standardization: Industry standards for AI-powered background checks will continue to develop, providing clearer guidelines for implementation.
Regulatory Adaptation: Employment laws and regulations will evolve to address AI use in hiring processes, requiring ongoing compliance monitoring.
Integration Improvements: AI background check tools will increasingly integrate with existing HR systems and applicant tracking systems for seamless workflow.
Implementation Checklist for HR Professionals
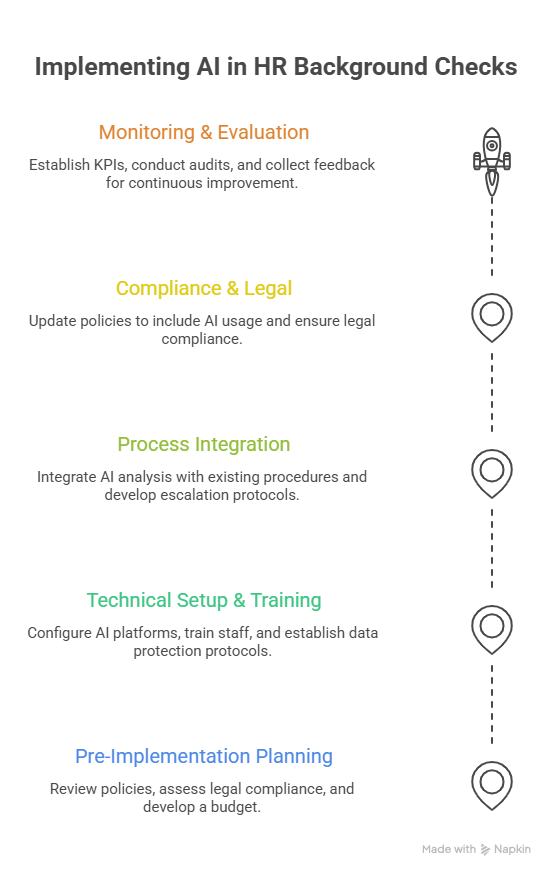
Pre-Implementation Planning
- Review current background check policies and procedures
- Assess legal compliance requirements (FCRA, EEOC, state laws)
- Identify AI tools and platforms that meet organizational needs
- Develop budget for AI tool licensing and training costs
- Create timeline for phased implementation
Technical Setup and Training
- Select and configure AI platforms with appropriate security measures
- Train HR staff on AI tool usage and prompt engineering
- Establish data protection and privacy protocols
- Create standardized AI prompts and workflows
- Test AI tools with sample candidate data
Process Integration
- Integrate AI analysis with existing background check procedures
- Develop escalation procedures for AI-identified concerns
- Create documentation templates for AI findings
- Establish quality assurance and audit procedures
- Implement feedback loops for continuous improvement
Compliance and Legal Considerations
- Update background check policies to include AI usage
- Ensure FCRA compliance documentation is current
- Review EEOC guidelines for consistent application
- Establish record retention policies for AI analysis
- Create procedures for candidate disputes and corrections
Monitoring and Evaluation
- Establish KPIs and metrics for AI effectiveness
- Implement regular accuracy audits and calibration
- Monitor legal developments affecting AI use in hiring
- Collect feedback from hiring managers and candidates
- Plan for regular policy and procedure updates
Conclusion
AI-powered employment background checks represent a significant advancement in HR technology, offering improved efficiency, consistency, and thoroughness in candidate evaluation. By implementing these tools strategically and maintaining proper oversight, HR professionals can enhance their screening processes while ensuring compliance and accuracy.
The key to successful AI integration lies in treating these tools as supplements to, rather than replacements for, traditional verification methods. When used appropriately, AI can help identify potential concerns early in the process, allowing HR teams to focus their verification efforts where they're most needed.
As AI technology continues to evolve, staying informed about best practices and maintaining a balance between automation and human judgment will be crucial for maximizing the benefits of AI-enhanced background verification while protecting both organizations and candidates throughout the hiring process.
Additional Resources and Citations
Legal and Regulatory Sources
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC): Background Checks: What Employers Need to Know - Official guidance on FCRA compliance for employment screening
- Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC): Background Checks: What Employers Need to Know - Joint FTC/EEOC publication on employment background checks and discrimination laws
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): Fair Credit Reporting; Background Screening - 2024 advisory opinion on reasonable procedures for accuracy in background screening
Industry Research and Statistics
- Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM): 2023-2024 State of the Workplace Report - Annual survey of HR professionals and workplace trends including AI adoption
- SHRM Getting Talent Back to Work Initiative: Second-chance hiring resources and best practices for employing individuals with criminal backgrounds
- FCRA Litigation Data: Based on reported cases and settlements including major employers' compliance failures and associated costs
Professional Development Resources
- SHRM Certification Programs: SHRM-CP and SHRM-SCP certifications provide competency-based HR knowledge including employment law and screening best practices
- Federal Trade Commission Business Guidance: Comprehensive resources for employers on background check compliance and best practices
- Equal Employment Opportunity Commission Training: Resources for understanding and implementing non-discriminatory hiring practices
Technical Implementation Guides
- Background Check Industry Standards: Professional organizations provide guidance on implementing AI tools while maintaining accuracy and compliance
- Data Privacy and Security: Resources for protecting candidate information during AI-powered screening processes
- Integration Best Practices: Guidelines for incorporating AI tools into existing HR systems and workflows
This article provides general guidance and should not be considered legal advice. Consult with qualified legal counsel for specific compliance requirements and implementation strategies appropriate to your organization's needs and jurisdiction.
References
HireVire. (2025). 5 Ways AI Interview Screening Reduces Time-to-Hire by 50%. https://hirevire.com/blog/ai-interview-screening-reduces-time-to-hire
Certn. (n.d.). Certn: The world's easiest background checks. https://www.certn.co

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.