Trade school background checks are essential screening processes that verify educational credentials, criminal history, and professional qualifications for vocational program graduates entering the workforce. These comprehensive evaluations help employers ensure candidates possess legitimate training and meet industry safety standards.
Key Takeaways
- Trade school background checks verify vocational education credentials, criminal history, and professional certifications to ensure qualified candidates.
- Employers conduct these screenings to meet industry regulations, reduce liability risks, and maintain workplace safety standards.
- Background check components include education verification, criminal records, drug testing, and license validation specific to skilled trades.
- FCRA compliance requires proper disclosure, authorization, and adverse action procedures when conducting employment screenings.
- Processing times typically range from 2-5 business days for basic checks, with specialized verifications taking up to 10 days.
- Costs vary from $25-150 per screening depending on scope, with comprehensive packages averaging $75-100 for trade positions.
Understanding Trade School Background Check Requirements
Trade school background checks serve as critical quality assurance measures in today's competitive skilled trades market. These comprehensive screenings validate that vocational graduates possess authentic credentials. Additionally, they maintain the professional standards expected in their respective fields. Employment verification processes have become increasingly sophisticated as employers recognize the importance of thorough candidate assessment.
The skilled trades industry faces unique challenges regarding workforce verification. This is particularly true for safety-sensitive positions and regulatory compliance requirements. Background screening protocols help mitigate risks associated with unqualified workers in construction, healthcare, automotive, and technical fields. Modern verification systems integrate multiple data sources to provide employers with comprehensive candidate profiles.
Educational credential verification remains the cornerstone of trade school background checks. This process ensures graduates completed legitimate programs from accredited institutions. Furthermore, it involves direct contact with educational institutions to confirm enrollment dates, program completion, and certification achievements. Advanced verification services now include digital transcript validation and real-time academic record access.
Modern employers must navigate complex regulatory environments while maintaining competitive hiring practices. Trade school background checks provide essential protection against negligent hiring claims. They also help organizations comply with industry-specific safety requirements and licensing standards. Technology integration has streamlined verification processes while improving accuracy and reducing costs.
Contemporary workforce verification encompasses multiple stakeholder perspectives including employers, candidates, and regulatory agencies. Employers seek reliable screening methods that balance thoroughness with efficiency. Candidates expect fair, transparent processes that protect their privacy rights. Regulatory agencies mandate compliance with federal and state employment laws. Effective background check programs address all these requirements simultaneously.
Types of Background Checks for Vocational Graduates
Criminal History Verification
Criminal background screening represents a fundamental component of employment verification for trade school graduates. Employers typically conduct county, state, and federal criminal searches. These searches identify any disqualifying offenses that might impact job performance or workplace safety. Criminal history verification involves multiple database searches and court record reviews. Automated systems cross-reference candidate information against extensive criminal repositories. However, manual verification often remains necessary for complete accuracy.
Different trades maintain varying tolerance levels for criminal history based on job responsibilities. Healthcare-related vocational positions often have zero-tolerance policies for certain offenses. Meanwhile, construction trades may focus primarily on violent crimes or theft-related convictions. Financial services positions require careful evaluation of fraud-related offenses. Transportation roles emphasize DUI convictions and traffic violations. Manufacturing sectors prioritize workplace violence indicators and substance abuse history.
Professional License and Certification Validation
Vocational education verification extends beyond basic diploma confirmation to include specialized licenses and industry certifications. Background check providers validate active license status, expiration dates, and any disciplinary actions through state regulatory boards. This verification process ensures candidates maintain current credentials required for their specific trade positions.
- Active license verification across multiple states
- Expiration date confirmation and renewal tracking
- Disciplinary action review and violation history
- Continuing education compliance verification
- Multi-state licensing validation for mobile workforce
Many skilled trades require ongoing certification maintenance through continuing education requirements. Verification services confirm not only initial certification achievement but also compliance with renewal obligations. Professional development standards vary significantly across different vocational sectors. Regulatory boards maintain different requirements for license renewal cycles. Some certifications require annual updates while others operate on multi-year schedules.
Drug Testing and Medical Clearances
Safety-sensitive trade positions often require comprehensive drug screening and medical evaluations. Pre-employment drug testing typically includes 5-panel or 10-panel urine analysis. Additionally, some positions require hair follicle testing for extended detection periods. Medical clearances ensure candidates can safely perform essential job functions. These evaluations may include physical examinations, vision tests, and hearing assessments.
DOT-regulated positions maintain specific testing requirements that exceed standard employment screening. These enhanced protocols ensure compliance with federal transportation safety regulations. Random drug testing programs continue throughout employment in many trade positions. Workplace safety incidents may trigger additional testing requirements. Post-accident testing protocols help determine whether substance use contributed to workplace incidents.
Employment History and Reference Verification
Previous work experience validation provides crucial insights into candidate reliability and performance. Background check services contact former employers to verify employment dates, job titles, and termination reasons. However, many companies limit information sharing due to legal liability concerns. Employment verification attempts to confirm basic factual information about work history.
Reference checks complement employment verification by gathering performance feedback from supervisors and colleagues. Professional references offer valuable perspectives on work quality, reliability, and interpersonal skills. Personal references may provide additional character insights but carry less weight in hiring decisions. Character references become more important for entry-level trade positions with limited work history. Academic references from instructors can provide valuable insights for recent graduates.
Education Transcript and Diploma Verification
Educational verification confirms graduation status and academic achievements from trade schools and vocational programs. This process involves direct contact with registrar offices to authenticate transcripts and diplomas. Verification services check graduation dates, program completion status, and GPA information when available. Digital verification systems have streamlined this process for many accredited institutions.
Fraudulent educational credentials remain a persistent problem in employment screening. Diploma mills and fake transcripts continue to challenge verification processes. Therefore, thorough educational verification protects employers from unqualified candidates. It also ensures legitimate graduates receive proper recognition for their achievements. Third-party verification services maintain databases of questionable institutions to help identify potential fraud.
Industry-Specific Background Check Considerations
Different vocational sectors require tailored background screening approaches based on regulatory requirements and safety considerations. Healthcare trades face the most stringent verification standards due to patient safety concerns. These positions mandate extensive criminal background checks, abuse registry searches, and ongoing monitoring requirements. Healthcare employers must comply with state licensing board requirements and federal regulations. Patient care responsibilities demand the highest level of candidate screening.
| Industry | Key Screening Elements | Regulatory Requirements |
| Healthcare | Criminal, abuse registries, licensing | State health department compliance |
| Construction | Safety records, workers' comp, drug testing | OSHA safety standards |
| Transportation | DOT physicals, driving records, criminal | Federal motor carrier regulations |
| Financial Services | Credit checks, regulatory licensing, criminal | FINRA and state securities compliance |
Construction and manufacturing trades focus primarily on safety-related background elements. These industries emphasize drug screening, workers' compensation history, and OSHA violation records. Transportation-related vocational programs require Department of Transportation physical examinations and driving record verification. Financial services trades necessitate credit history evaluation and regulatory registration verification. Each sector maintains unique risk factors that influence screening protocols.
Technology and cybersecurity vocational programs increasingly require enhanced screening protocols. These comprehensive checks help employers assess potential security risks in sensitive technical roles. Social media screening and digital footprint analysis have become standard practice for IT positions. Security clearance requirements add additional complexity to background verification processes. Government contracting positions may require federal background investigations.
Energy sector positions, including oil and gas operations, require specialized safety clearances and environmental compliance verification. Nuclear facility workers need extensive federal screening and ongoing security monitoring. Telecommunications positions may require security clearances for infrastructure protection roles. Emergency services training graduates need comprehensive background evaluation for public safety positions.
Legal Compliance and FCRA Requirements
Fair Credit Reporting Act compliance forms the legal foundation for all employment-related background screening activities. Employers must provide clear written disclosure about background check intentions before conducting verification. Additionally, they must obtain explicit written authorization from candidates. These requirements apply equally to trade school graduate screening and traditional degree-holder evaluation processes. FCRA violations can result in significant financial penalties and legal liability for employers.
Pre-adverse action procedures require employers to provide candidates with background check results before making negative employment decisions. This process includes furnishing a copy of the background report and a summary of FCRA rights. Final adverse action notifications must include specific reasons for employment denial and contact information for the background check provider. Candidates have rights to dispute inaccurate information and receive corrected reports.
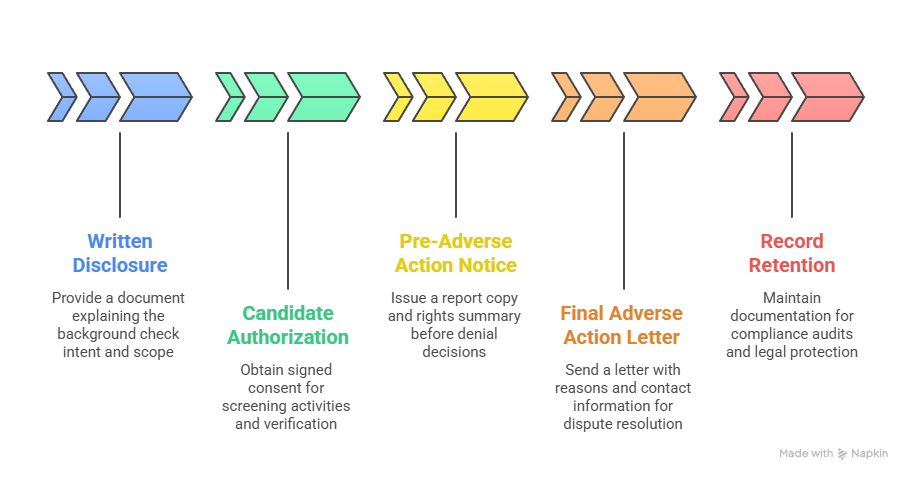
- Written disclosure requirements: Separate standalone document clearly stating background check intent and scope
- Candidate authorization: Signed consent for screening activities and ongoing verification processes throughout employment
- Pre-adverse action notices: Report copy and rights summary before employment denial decisions are finalized
- Final adverse action letters: Specific reasons and provider contact information for dispute resolution processes
- Record retention obligations: Documentation maintenance for compliance audit purposes and legal protection requirements
State and local ban-the-box legislation adds additional complexity to criminal history screening. These laws restrict timing of criminal background inquiries and require individualized assessment of conviction relevance. California's Fair Chance Act exemplifies comprehensive guidelines that many employers now follow nationwide. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission guidance emphasizes considering offense relevance, time elapsed, and rehabilitation evidence.
Additional state laws may restrict credit check usage, social media screening, and medical information collection. Employers must understand applicable state and local requirements in addition to federal compliance obligations. Multi-state employers face particular challenges navigating varying legal requirements across different jurisdictions. Legal counsel consultation becomes essential for complex compliance scenarios.
Background Check Process and Timeline Expectations
Trade school background check processing follows a standardized workflow designed to maximize accuracy while minimizing delays. Initial candidate information submission triggers automated database searches for criminal records. Simultaneously, education verification requests and reference contact attempts begin. Most background check providers offer online portals allowing real-time status monitoring throughout the verification process. Automated notifications keep employers informed of completion milestones and potential delays.
Education verification represents the most time-intensive component due to manual institutional contact requirements. Academic institutions often require 48-72 hours to respond to transcript requests and degree confirmation inquiries. Seasonal variations, including summer breaks and holiday periods, can extend verification timeframes significantly. Emergency hiring situations and time-sensitive project deadlines often necessitate accelerated background screening services. However, expedited processing may exclude certain verification components that require extended institutional response times.
International education verification presents unique challenges requiring specialized services and extended processing times. Foreign credential evaluation services help translate international qualifications into US equivalents. These services often require 7-14 business days for complete assessment. Language barriers and documentation differences can further complicate verification processes. Apostille documentation may be necessary for international academic records.
Quality assurance procedures ensure accuracy throughout the background check process. Manual reviews verify automated search results and identify potential discrepancies. Double-checking processes reduce false positive results that could unfairly impact candidates. Regular audits maintain system accuracy and compliance standards. Customer service teams handle candidate inquiries and dispute resolution processes.
Processing delays can occur due to various factors including incomplete candidate information, unresponsive references, and technical system issues. Court closures, institutional holidays, and natural disasters may impact verification timelines. Communication protocols keep all parties informed about potential delays and expected resolution timeframes. Contingency planning helps minimize disruption from unexpected processing complications.
Cost Factors and Budgeting Considerations
Background check pricing for trade school graduates varies considerably based on screening scope and geographic coverage. Basic packages including criminal history and education verification typically range from $25-50 per candidate. Comprehensive screening packages incorporating drug testing and specialized verifications can exceed $150 per individual. Volume discounts become available for employers conducting regular hiring activities or processing multiple candidates simultaneously. Service level agreements often provide predictable pricing structures for ongoing hiring needs.
Annual service agreements often provide 15-25% cost savings compared to individual screening purchases. Small businesses and occasional hirers might benefit from pay-per-use models despite higher per-screening costs. Hidden costs including re-screening for incomplete results and international verification charges can significantly impact budgeting projections. Rush processing fees can add 50-100% to standard screening costs.
- Basic screening packages: Criminal history checks, basic education verification, employment confirmation starting at $25-40
- Standard comprehensive packages: All basic elements plus drug testing, reference checks, license validation ranging $60-90
- Enhanced industry packages: Specialized verifications, regulatory compliance checks, ongoing monitoring services $90-150
- Premium rush services: Expedited processing with 24-48 hour turnaround guarantees and priority handling adding $25-75
Technology costs associated with background check integration can impact overall screening budgets. Application tracking system integration requires initial setup fees and ongoing maintenance costs. However, automation ultimately reduces administrative overhead and improves processing efficiency. Return on investment typically becomes apparent within 6-12 months of implementation. Staff training costs should be factored into budget planning.
Third-party verification services may charge additional fees for complex or international verifications. These costs vary based on verification complexity and geographic requirements. Employers should request detailed pricing breakdowns to understand all potential charges before engaging services. Volume pricing tiers often provide significant savings for larger organizations with regular hiring needs.
Common Challenges and Red Flags
Educational Verification Complications
Trade school closures and institutional changes create significant challenges for employment verification processes. When vocational schools cease operations or lose accreditation, confirming graduate credentials becomes extremely difficult. Third-party verification services maintain historical records for many closed institutions. However, gaps in documentation can delay or prevent complete verification. Name discrepancies between educational records and current legal names frequently cause verification delays. Marriage-related name changes, legal modifications, and international documentation often require additional verification steps.
Criminal Record Assessment Challenges
Understanding the relevance of criminal history to specific trade positions requires careful analysis and legal consideration. Minor offenses from years past may have minimal impact on current job performance. Conversely, recent violations might indicate ongoing risk factors. Employers must balance public safety concerns with fair hiring practices and second-chance employment opportunities. Legal counsel consultation helps ensure appropriate evaluation of criminal history information.
Key verification challenges include:
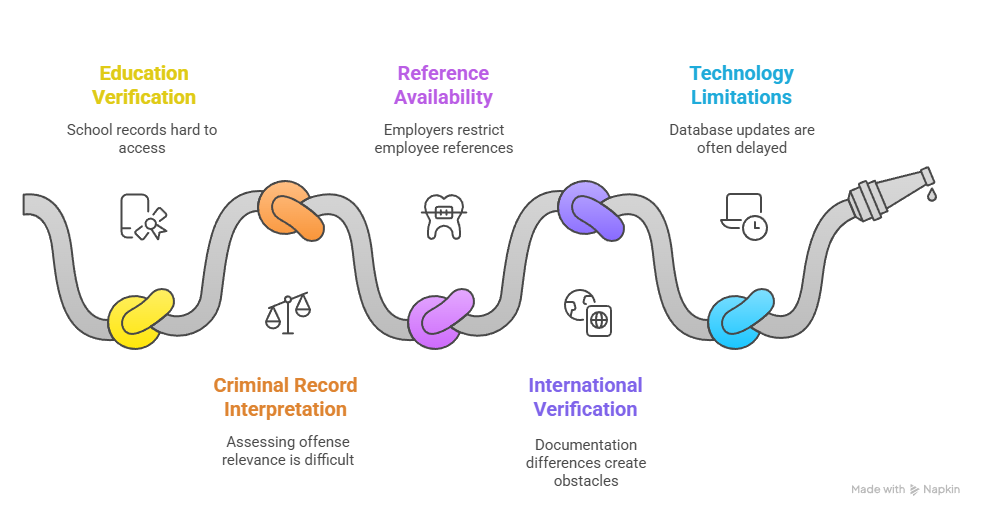
- Education verification complications: School closures, accreditation loss, record unavailability, name discrepancies, international credentials
- Criminal record interpretation challenges: Offense relevance assessment, timing considerations, rehabilitation evidence evaluation
- Reference availability issues: Former employer policy restrictions, contact information changes, response delays, privacy concerns
- International verification obstacles: Documentation differences, language barriers, credential evaluation requirements, apostille needs
- Technology limitations: Database update delays, interstate record sharing gaps, system maintenance periods, connectivity issues
Geographic and Identity Verification Issues
Geographic variations in criminal record availability can create incomplete background pictures for highly mobile candidates. Multi-state criminal searches help address these gaps but cannot guarantee comprehensive coverage of all jurisdictions. Additionally, international background verification presents unique challenges requiring specialized services and extended processing times. Court record access varies significantly between jurisdictions, affecting verification completeness.
Identity verification becomes crucial when discrepancies appear in background check results. Social Security number traces help confirm candidate identity and reveal address history. These traces can identify potential identity theft or documentation fraud. Address history verification helps ensure comprehensive geographic coverage for criminal searches. Alias and maiden name searches may be necessary for complete verification.
Incomplete candidate information can significantly delay background check processing. Missing Social Security numbers, incorrect dates of birth, or incomplete address histories create verification challenges. Candidate cooperation becomes essential for timely and accurate completion. Clear communication about required information helps prevent processing delays.
Best Practices for Employers and Candidates
Establishing Effective Policies and Procedures
Employers should establish clear, consistent background check policies that align with industry standards and legal requirements. These policies should specify which positions require screening and what verification components are necessary. Furthermore, they should outline the decision-making process for evaluating background check results. Regular policy updates ensure compliance with changing regulations and evolving industry practices. Training programs help hiring managers understand proper implementation procedures and legal boundaries.
Candidates can prepare for background checks by gathering necessary documentation in advance. This preparation includes obtaining official transcripts, collecting employment records, and preparing reference contact information. Additionally, candidates should review their own background information for accuracy. Being proactive about addressing potential issues demonstrates professionalism and transparency to prospective employers. Self-background checks can help identify potential problems before official screening begins.
Essential best practice areas:
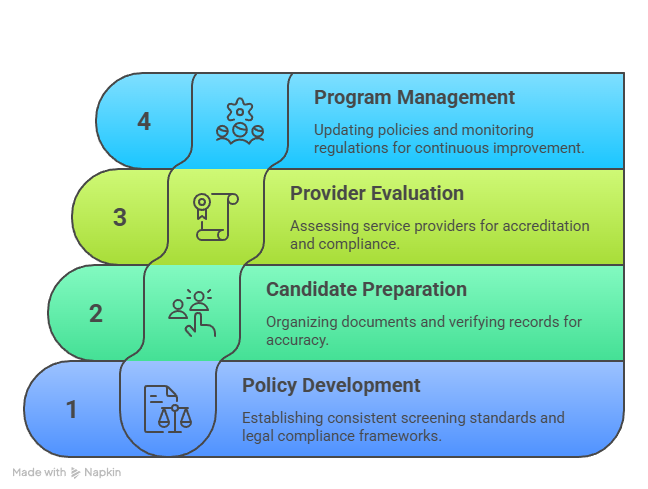
- Employer policy development: Consistent screening standards, legal compliance frameworks, fair evaluation criteria, appeal processes
- Candidate preparation strategies: Document organization, record accuracy verification, reference coordination, transparency maintenance
- Service provider evaluation: Accreditation verification, compliance standards assessment, technology capability review, customer support quality
- Ongoing program management: Policy updates, regulation monitoring, staff training, vendor performance evaluation, cost optimization
Service Provider Selection and Communication
Selecting qualified background check providers requires careful evaluation of accreditation, compliance standards, and technology capabilities. Reputable providers maintain Professional Background Screening Association membership and follow established industry best practices. Customer support quality and reporting capabilities also influence provider selection decisions. Service level agreements should clearly define turnaround times, accuracy standards, and dispute resolution procedures.
Communication strategies throughout the background check process help maintain positive candidate relationships. Regular status updates reduce anxiety and demonstrate employer professionalism. Clear explanations of any delays or complications help candidates understand the process. Prompt notification of results allows for efficient hiring decision implementation. Transparent communication builds trust and enhances employer brand reputation.
Program Management and Continuous Improvement
Ongoing monitoring programs help employers stay current with changing regulations and industry best practices. Regular audits of background check processes identify potential compliance gaps or improvement opportunities. Vendor performance reviews ensure service providers continue meeting established standards. Industry association participation provides access to training resources and regulatory updates.
Documentation management systems help maintain organized records for compliance purposes. Digital storage solutions provide secure access while protecting sensitive candidate information. Regular data purging schedules ensure compliance with retention requirements. Backup systems protect against data loss and ensure business continuity.
Training programs should cover legal requirements, fair hiring practices, and proper interpretation of background check results. Supervisory staff need understanding of adverse action procedures and candidate rights. Regular refresher training keeps staff current with evolving regulations and best practices. Scenario-based training helps staff handle complex situations appropriately.Add to Conversation
Conclusion
Trade school background checks represent essential risk management tools that protect employers while ensuring qualified candidates receive fair consideration for skilled trades positions. Comprehensive verification processes validate educational credentials, assess criminal history relevance, and confirm professional licensing requirements. Employers who implement thorough background screening protocols while maintaining FCRA compliance create safer workplaces and stronger hiring outcomes. As technology continues advancing verification capabilities, both efficiency and accuracy of trade school background checks will continue improving throughout 2024 and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a trade school background check include?Â
A comprehensive trade school background check typically includes education verification, criminal history searches, drug screening, employment history confirmation, and professional license validation. The specific components vary based on industry requirements and employer preferences.
How long does a trade school background check take?Â
Standard background checks for trade school graduates take 3-7 business days to complete. Expedited services can provide results within 24-48 hours, while comprehensive screenings requiring specialized verifications may take up to 10 business days.
Can a criminal record prevent trade school graduates from getting hired?Â
Criminal history impact depends on offense type, timing, and job relevance. Many employers consider factors like crime severity, time elapsed since conviction, and rehabilitation evidence. Some trades have specific disqualifying offenses while others focus on overall candidate qualifications.
Are employers required to tell candidates about background checks?Â
Yes, FCRA requirements mandate that employers provide written disclosure and obtain signed authorization before conducting background checks. Candidates must also receive copies of reports and adverse action notifications if employment is denied based on screening results.
How much do trade school background checks cost?
Background check costs range from $25-150 per candidate depending on screening scope and service level. Basic packages including criminal and education verification typically cost $50-75, while comprehensive screenings with drug testing and specialized checks can exceed $100.
What happens if there's an error in my background check?Â
Candidates have the right to dispute inaccurate background check information through the screening company and original data sources. The dispute process typically takes 30 days, during which employers cannot make adverse employment decisions based on contested information.
Additional Resources
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) Compliance Guide
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/using-consumer-reports-what-employers-need-know - Equal Employment Opportunity Commission Background Check Guidelines
https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/enforcement-guidance-consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment - Professional Background Screening Association Best Practices
https://www.professionalbackground.org/Resources/Best-Practices - Department of Transportation Background Check Requirements
https://www.fmcsa.dot.gov/regulations/title49/section/391.23 - National Association of Professional Background Screeners Certification Program
https://www.napbs.com/certification - State-by-State Background Check Law Database
https://www.nolo.com/legal-encyclopedia/state-laws-use-arrests-convictions-employment.html

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





