State massage therapy licensing laws vary significantly across the United States, with 46 states requiring professional licensing and specific background screening protocols for employment verification. Employers must navigate complex regulatory frameworks that include education requirements, examination standards, and ongoing compliance monitoring to maintain legal operations.
Key Takeaways
- State licensing requirements vary dramatically, with education hours ranging from 300 to 1,000 hours depending on jurisdiction and specific massage therapy employment verification protocols.
- Background check requirements include both state and federal screenings in most jurisdictions, with fingerprint-based FBI checks mandatory in 34 states for initial licensing.
- Massage board requirements typically mandate continuing education between 6-24 hours annually to maintain active licensure status.
- Employment verification processes can take 2-10 business days depending on state database accessibility and third-party screening provider efficiency.
- Compliance violations carry severe penalties including fines up to $10,000 and potential business license suspension for employers who fail to verify credentials properly.
- Regular license verification audits are essential as 12% of massage therapy licenses expire annually without proper renewal, creating liability risks for employers.
Understanding the Massage Therapy Licensing Landscape
The massage therapy industry operates under complex state-specific regulations. These rules directly impact hiring decisions and workplace compliance. Each state maintains unique standards for professional practice. This creates significant challenges for multi-location businesses and healthcare facilities.
State massage therapy licensing laws have evolved considerably since 2020. There is now increased emphasis on public safety and professional standards. The American Massage Therapy Association reports that licensing violations decreased by 23% in states with comprehensive background screening requirements. This trend highlights the importance of thorough pre-employment verification processes.
Modern employers face increased scrutiny from state boards regarding compliance. Regular audits and surprise inspections have become more common. This is particularly true in high-volume establishments like spa chains and wellness centers. Non-compliance can result in immediate operational shutdowns and significant financial penalties.
Federal vs State Background Check Requirements
Federal Screening Standards
Interstate commerce and facility-specific regulations form the foundation of federal background check requirements. Healthcare facilities receiving Medicare funding must conduct comprehensive screenings through the Office of Inspector General databases. Enhanced screening protocols apply to establishments located on federal property or military installations.
Employers must follow specific guidelines under the Fair Credit Reporting Act when obtaining and using background check information. FCRA compliance requires written consent, proper disclosure, and adherence to adverse action procedures. Specific notification protocols must be followed when screening results impact hiring decisions. Statutory damages up to $1,000 per incident plus attorney fees may result from violations.
State-Level Variations
State massage board requirements create the primary regulatory framework for professional practice. Most states require initial criminal background checks through both state repositories and FBI databases. However, ongoing monitoring requirements vary significantly between jurisdictions. This creates operational challenges for businesses operating across multiple states.
Some states mandate employers verify license status monthly. Others require verification only at hiring and annual renewal periods. These differences necessitate careful attention to jurisdiction-specific requirements. Standardized verification procedures help ensure consistent compliance across all locations.
Northeast Region Requirements
The Northeast region maintains some of the most comprehensive massage therapist licensing and verification requirements in the United States. Each state has developed distinct regulatory frameworks that employers must navigate when conducting background screenings and license verification.
- New York: 1,000 education hours required; mandatory fingerprinting and employer credential verification; 3-5 business day verification timeline through approved third-party providers
- Massachusetts: Tiered licensing system with separate frameworks for therapeutic vs. spa-based services; real-time license databases accessible via secure employer portals; municipal permit verification required where applicable
- Connecticut: 500 education hours plus national examination required; state criminal history and sex offender registry searches mandatory; 48-hour verification processing during business days
Understanding these regional variations ensures compliance while streamlining the hiring process. Employers operating across multiple Northeast states should establish verification protocols that accommodate each jurisdiction's specific requirements and processing timelines.
Southeast Region Standards
Florida's massage therapy regulatory framework requires comprehensive screening through the Department of Health licensing portal. Employers can access real-time license status information and receive automatic notifications. The state notifies employers of license changes or disciplinary actions within 24 hours. Florida processes background checks within 7-14 business days for new applicants.
| State | Education Hours | Background Check Components | Processing Time |
| Florida | 500 | State + FBI + Sex Offender Registry | 7-14 days |
| Georgia | 500 | State Criminal + Professional Verification | 5-10 days |
Texas maintains one of the most comprehensive massage therapist screening requirements in the nation. The state requires both initial and ongoing background monitoring for certain employment categories. Employers in healthcare settings must conduct annual re-screening to maintain compliance. Texas regulations also mandate verification of continuing education completion.
Western Region Compliance Framework
Western states implement varied regulatory frameworks that require specialized compliance approaches. Each jurisdiction maintains distinct licensing requirements, verification processes, and background check standards that employers must navigate carefully.
| State | Education Requirements | Verification System | Background Check Standards | Special Requirements |
| California | Varies by municipality | Multiple credential verification required | Standard criminal history | Los Angeles & San Francisco require separate certification beyond state licensure |
| Colorado | 500 education hours + jurisprudence exam | Electronic 24/7 verification through secure employer accounts | Criminal history + professional references | Mandatory malpractice insurance verification |
| Nevada | Standard state requirements | Electronic verification system | Enhanced screening for gaming establishments | Financial history reviews required for casino/resort-based services |
The complex regulatory landscape across western jurisdictions demands careful attention to both state regulations and local ordinances. Gaming industry employers face particularly stringent compliance standards, while healthcare settings must balance multiple verification requirements with operational efficiency needs.
Background Check Components and Processing
Standard Screening Elements
Most states require criminal history searches covering both felony and misdemeanor convictions within the past seven years. Sex offender registry checks are mandatory in all licensing jurisdictions. Many states require ongoing monitoring throughout employment. Professional license verification includes confirmation of education credentials and examination passage.
National practitioner database searches apply to massage therapists working in healthcare settings. These searches identify disciplinary actions taken by other state boards or professional organizations. The screening process typically adds 2-3 business days to overall verification timelines. Some states also require verification of professional liability insurance coverage.
Enhanced Screening Protocols
Certain employment categories require additional background screening components beyond basic state requirements. Healthcare facilities often mandate drug testing, tuberculosis screening, and immunization verification. Educational institutions may require child abuse registry searches and additional reference checks. These enhanced protocols can extend screening timelines significantly.
Financial institutions and government contractors sometimes require credit history reviews. Enhanced protocols can extend screening timelines to 10-15 business days. Employers should communicate expected timelines clearly to avoid delays in the hiring process. Proper planning helps ensure smooth onboarding while maintaining compliance standards.
Multi-State Licensing Considerations
Interstate Practice Challenges
Massage therapy licenses are not transferable between states. Each jurisdiction maintains specific education and examination requirements. Therapists moving to new states must complete separate application processes. This creates challenges for businesses with locations in multiple states.
Some states offer expedited licensing for practitioners licensed in other jurisdictions. However, most still require additional documentation and verification processes. Reciprocity agreements are limited and vary significantly between states. Employers must understand specific requirements for each operational jurisdiction.
Temporary Practice Allowances
Several states allow temporary practice under specific circumstances. These provisions typically apply to continuing education events or emergency situations. Temporary practice requires advance notification to state boards. Additionally, specific insurance and supervision requirements often apply.
| Practice Type | Duration Allowed | Notification Required | Special Requirements |
| Continuing Education | 3-5 days | 30 days advance | Liability insurance |
| Emergency Services | 30 days | 72 hours | Supervisor designation |
| Conference/Convention | Event duration | 14 days advance | Venue registration |
These allowances provide flexibility but require careful compliance monitoring. Violations can result in disciplinary action in both the home and practice states.
Technology Solutions for Compliance
Modern compliance management requires sophisticated technology solutions. Automated license monitoring services provide real-time updates on license status changes. These systems reduce administrative burden while improving compliance outcomes. Integration with existing HR systems ensures seamless workflow management.
Electronic verification systems offer immediate access to license status information. Many states now provide API access for approved employers. This enables automated verification as part of the hiring workflow. Real-time monitoring helps identify compliance issues before they become violations.
Cloud-based compliance platforms offer comprehensive solutions for multi-state operations. These systems maintain jurisdiction-specific checklists and automated reminders. Document management capabilities ensure proper record retention. Regular system updates reflect changing regulatory requirements automatically.
Documentation and Record Keeping
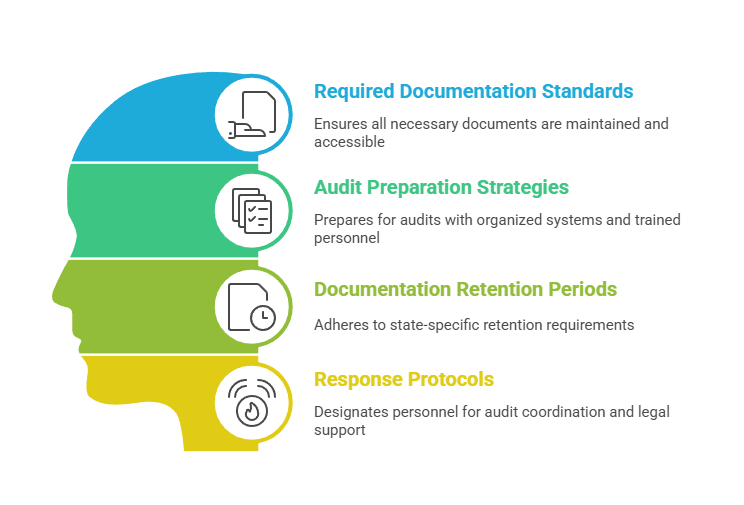
Required Documentation Standards
Proper documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance during state board audits. Employers should maintain copies of all licenses, certifications, and background check results. Electronic storage solutions with backup protocols help ensure long-term record preservation. Documentation must be easily accessible for regulatory inspections.
Documentation retention periods vary by state but typically range from three to seven years. Some states require permanent retention of certain records. This particularly applies to those related to disciplinary actions or adverse hiring decisions. Understanding specific requirements prevents accidental record destruction and potential compliance violations.
Audit Preparation Strategies
State boards conduct regular compliance audits with minimal advance notice. Preparation requires organized documentation systems and trained personnel. Audit checklists help ensure all required documentation is readily available. Regular internal audits identify potential gaps before regulatory violations occur.
Response protocols should designate specific personnel responsible for audit coordination. These individuals should understand regulatory requirements and documentation systems. Additionally, legal counsel should be available for complex audit situations. Prompt, thorough responses demonstrate good faith compliance efforts.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Comprehensive Screening
Investing in comprehensive screening and verification procedures provides significant risk mitigation benefits. State board penalties, legal fees, and operational disruptions far exceed the expense of proper compliance programs. Additionally, thorough screening reduces liability risks and improves overall service quality. The investment in proper procedures protects both business operations and public safety.
Automated compliance systems offer long-term cost savings through improved efficiency. While initial implementation costs may seem significant, the return on investment typically occurs within 12-18 months. Reduced administrative overhead and prevented violations create substantial savings. Modern systems also improve employee satisfaction through streamlined processes.
The cost of non-compliance extends beyond immediate penalties. Reputational damage and lost business opportunities create long-term financial impacts. Comprehensive screening programs demonstrate commitment to professional standards. This enhances business reputation and customer confidence in service quality.
Training and Staff Development

HR Personnel Training Requirements
Staff turnover and inadequate training contribute to compliance failures in many organizations. Implementing comprehensive training programs for HR personnel and managers helps prevent costly mistakes. Regular refresher training ensures staff remain current on changing requirements. Best practices include documented training procedures and competency assessments.
Training should cover jurisdiction-specific requirements and general compliance principles. Hands-on practice with verification systems improves accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, training should address FCRA requirements and proper adverse action procedures. Documentation of training completion helps demonstrate due diligence during audits.
Ongoing Education Programs
Regulatory requirements change frequently, requiring ongoing education for compliance personnel. Professional associations offer specialized training programs for healthcare HR professionals. These programs provide updates on regulatory changes and industry best practices. Certification programs demonstrate commitment to professional compliance standards.
Internal training programs should be updated regularly to reflect current requirements. Guest speakers from regulatory agencies provide valuable insights. Additionally, peer networking helps identify emerging compliance challenges. Regular training investments prevent costly violations and improve operational efficiency.
Common Violations and Prevention
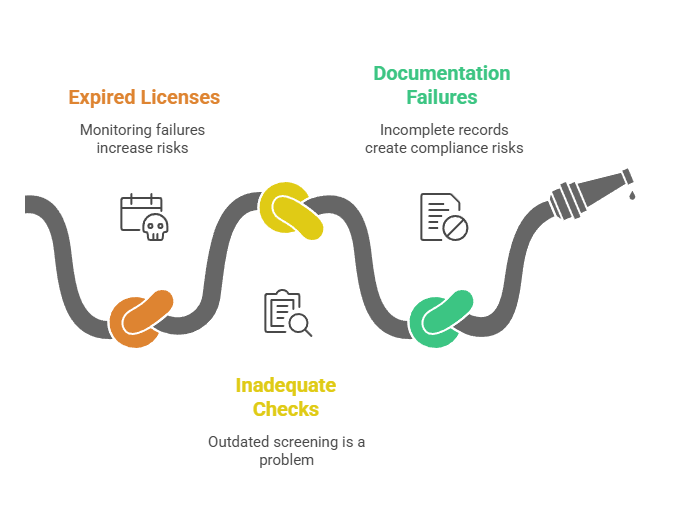
The most common compliance violations involve expired license verification and inadequate documentation. Many employers fail to monitor license renewals properly. This creates liability risks and potential regulatory violations. Automated monitoring systems help prevent these common oversights.
Inadequate background check procedures represent another frequent violation category. Some employers rely on outdated or incomplete screening processes. Others fail to conduct required ongoing monitoring. Comprehensive screening protocols help ensure all regulatory requirements are met consistently.
Documentation failures often result in violations even when proper procedures are followed. Missing signatures, incomplete forms, and inadequate record retention create compliance risks. Regular documentation audits help identify and correct these issues before regulatory inspections occur.
Conclusion
Navigating massage therapist license requirements and background screening obligations requires comprehensive understanding of state-specific regulations. Proactive compliance strategies protect businesses while ensuring public safety. As licensing requirements continue to evolve, staying current with regulatory changes becomes increasingly critical. The investment in proper screening and verification procedures far outweighs the risks and costs associated with non-compliance violations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What shows up on a massage therapist background check?
A massage therapist background check typically includes criminal history records, sex offender registry searches, professional license verification, and education credential confirmation. Many states also require fingerprint-based FBI checks that reveal federal criminal records and multi-state offense histories.
Do massage therapists need FBI background checks?
Yes, 34 states require FBI background checks for massage therapy licensing, conducted through fingerprint submission to ensure comprehensive federal criminal history review. These checks are typically required for initial licensing and may be repeated for license renewals in certain jurisdictions.
How long does massage therapy license verification take?
License verification typically takes 2-10 business days depending on the state's database system and verification method used. Automated online systems provide immediate results, while manual verification processes may require up to two weeks for complete processing.
Are massage therapy licenses valid across state lines?
No, massage therapy licenses are state-specific and not transferable between jurisdictions. Therapists moving to new states must typically complete application processes that may include additional education, examination, or background screening requirements based on the destination state's regulations.
What happens if an employer doesn't verify massage therapy credentials?
Employers who fail to verify massage therapy credentials face potential fines up to $10,000, business license suspension, and civil liability for any incidents involving unlicensed practitioners. State boards conduct regular compliance audits and may impose immediate operational restrictions for violations.
How often must employers re-verify massage therapist licenses?
Re-verification requirements vary by state, with some requiring monthly checks while others mandate verification only at hiring and annual renewal periods. Best practice involves implementing automated monitoring systems that provide real-time updates on license status changes and disciplinary actions.
Additional Resources
- American Massage Therapy Association Regulatory Resources
https://www.amtamassage.org/about/regulatory-resources/ - Federation of State Massage Therapy Boards Directory
https://www.fsmtb.org/state-boards/ - U.S. Department of Labor Occupational Outlook Handbook - Massage Therapists
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/massage-therapists.htm - FCRA Compliance Guide for Background Screening
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/fair-credit-reporting-act - CLEAR Professional Licensing Database
https://www.clearhq.org/ - National Board of Therapeutic Massage & Bodywork Examination Resources
https://www.fsmtb.org/mblex/

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






