Verifying a high school diploma for employment requires a systematic approach involving direct contact with educational institutions, third-party verification services, or official document requests that comply with FERPA regulations. Employers who implement proper diploma verification processes reduce hiring risks by up to 78% while ensuring FCRA compliance throughout the employment screening process.
Key Takeaways
- Direct school verification remains the most reliable method, requiring contact with the registrar's office or district records department for official confirmation of graduation status.
- Third-party verification services like National Student Clearinghouse provide faster results within 24-48 hours for employers conducting bulk employment screening education checks.
- Required documentation typically includes the candidate's full legal name, graduation year, school name, and written authorization per Fair Credit Reporting Act guidelines.
- Verification timeframes range from 2-5 business days for direct school contact to immediate results for online diploma verification systems.
- Cost considerations vary from free direct verification to $15-50 per verification through professional screening services depending on urgency and volume requirements.
- Legal compliance mandates following FCRA adverse action procedures if diploma verification reveals discrepancies that impact hiring decisions.
Why Diploma Verification Matters for Employment
Employment screening education has become a critical component of modern hiring practices. According to recent statistics, 34% of job applications contain some form of educational misrepresentation. This alarming trend makes understanding how to verify a high school diploma for employment essential for protecting your organization. Educational verification serves multiple purposes beyond simple credential confirmation.
The diploma verification process establishes candidate honesty and ensures minimum job requirements are met. Additionally, it protects companies from negligent hiring lawsuits. Furthermore, the process demonstrates due diligence in your hiring practices. Modern employment verification has evolved significantly due to sophisticated resume fraud.
Today's employers face challenges including fake diplomas purchased online and altered transcripts. These sophisticated deception methods make comprehensive verification strategies more important than ever. Therefore, employers must adapt their screening processes accordingly. Consequently, understanding proper verification procedures becomes essential for all hiring professionals.
Legal Requirements and FCRA Compliance
The Fair Credit Reporting Act governs educational background checks when conducted by third-party screening companies. Employers must obtain written consent before initiating any diploma verification process. This consent should clearly state that educational verification is part of the background screening. FCRA compliance extends to adverse action procedures as well.
If diploma verification reveals discrepancies leading to hiring rejection, employers must provide pre-adverse action notices. These notices must include copies of the background check report and the candidate's rights under FCRA. Additionally, employers must follow specific timing requirements for adverse actions. Furthermore, maintaining proper documentation throughout the process is essential.
FCRA Compliance Requirements:
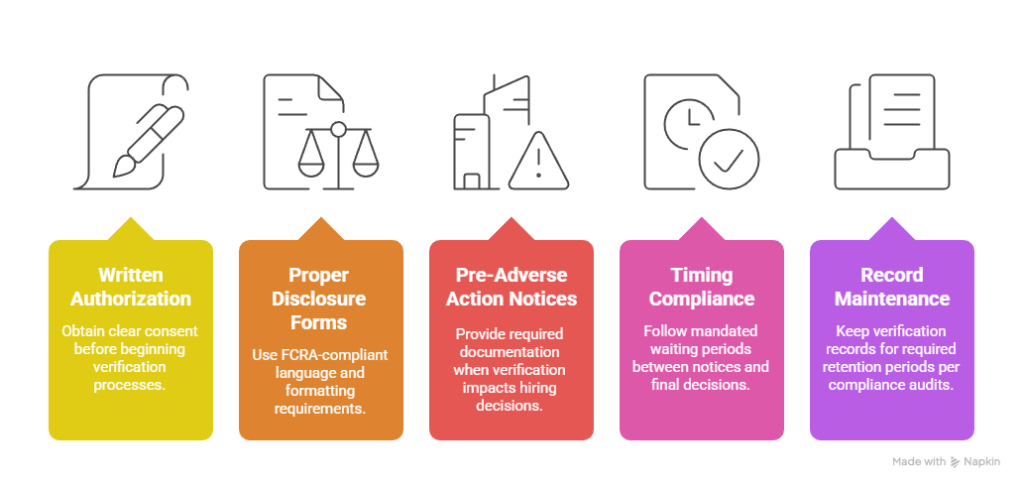
- Written Authorization: Obtain clear consent before beginning verification processes
- Proper Disclosure Forms: Use FCRA-compliant language and formatting requirements
- Pre-Adverse Action Notices: Provide required documentation when verification impacts hiring decisions
- Timing Compliance: Follow mandated waiting periods between notices and final decisions
- Record Maintenance: Keep verification records for required retention periods per compliance audits
State-specific requirements may impose additional obligations beyond federal FCRA mandates. Some states require specific language in disclosure forms or have unique timing requirements for adverse actions. Therefore, employers should consult employment law experts familiar with their jurisdiction's requirements.
Methods to Verify High School Diplomas
Direct School Verification
Direct contact with educational institutions provides the most authoritative diploma verification available. Most high schools maintain permanent records through their registrar's office or district administration. This method requires patience but offers definitive results that stand up to legal scrutiny.
Contact the school's main office or registrar department first during normal business hours. Provide the graduate's full legal name, approximate graduation year, and your verification purpose clearly. Many schools require written requests or specific forms to release educational information per privacy regulations.
| Verification Method | Average Timeframe | Typical Cost | Reliability Score |
| Direct School Contact | 3-7 business days | Free-$10 | 95% |
| District Records Office | 2-5 business days | Free-$15 | 98% |
School closures present unique challenges in the diploma verification process requiring alternative approaches. When schools close, records typically transfer to the district office or state education department for long-term storage. Contact the state's Department of Education for guidance on accessing closed school records effectively.
Third-Party Verification Services
Professional background screening companies streamline the verify employee education process for busy employers. Services like National Student Clearinghouse and Sterling offer comprehensive educational verification with faster turnaround times. These services maintain extensive databases of educational institutions and graduation records nationwide.
They can verify multiple educational credentials simultaneously, making them ideal for employers with high-volume hiring needs. Third-party services excel at verifying diplomas from closed schools or institutions with limited administrative resources. These services maintain historical records and established relationships with educational archives. Consequently, they can often locate records when direct school contact fails.
Key Service Features:
- Database Coverage: Access to comprehensive institutional records and historical graduation data
- Turnaround Speed: Faster processing times compared to direct school verification methods
- Volume Handling: Ability to process multiple verification requests simultaneously for efficiency
- Historical Records: Access to records from closed or merged educational institutions
- Standardized Reporting: Consistent format and presentation of verification results for HR systems
Professional verification services provide standardized reporting formats that integrate easily with HR systems. Moreover, they offer customer support throughout the verification process. Additionally, many services provide online portals for tracking verification status and results in real-time.
Online Diploma Verification Systems
Many modern school districts offer online diploma verification systems for immediate results. These platforms allow employers to instantly verify graduation status using the graduate's information. Additionally, they require a verification code or reference number for security purposes.
Online systems provide immediate results but aren't universally available across all institutions. Larger districts and states with centralized education systems are more likely to offer these services. The verification typically requires the graduate's consent and specific identifying information for privacy protection.
Online System Benefits:
- Instant verification results
- 24/7 availability for employers
- Cost-effective verification option
- Reduced administrative burden
- Standardized verification format
However, these systems have limitations that employers must consider. Not all schools participate in online verification programs currently. Furthermore, some systems may have limited historical data availability. Therefore, alternative verification methods may still be necessary for comprehensive screening processes.
Required Documentation and Information
Successful diploma verification requires specific information about the graduate and their educational background for accurate results. Incomplete or inaccurate information can delay the verification process or result in failed searches. Therefore, gathering comprehensive details upfront saves time and improves success rates. Additionally, proper documentation ensures FCRA compliance throughout the process.
Essential Information Categories:
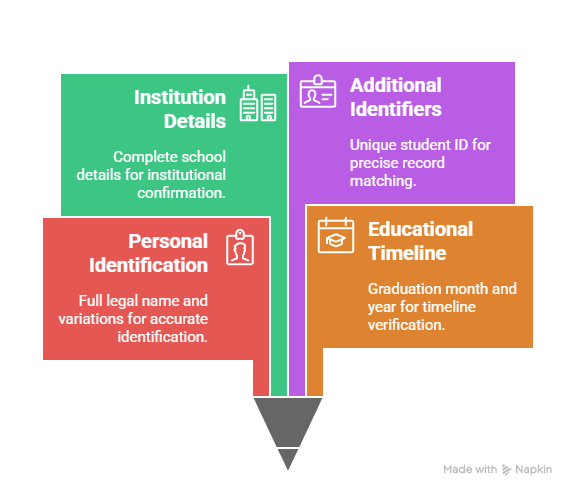
- Personal Identification: Full legal name including any variations or maiden names used during attendance
- Educational Timeline: Graduation month and year, or approximate timeframe if exact dates are unknown
- Institution Details: Complete school name, city, state, and district name when available
- Additional Identifiers: Student ID number or other unique identifiers from original school records
Additional documentation may be required depending on the verification method chosen by employers. Some schools request government-issued identification or signed authorization forms before releasing educational information. Furthermore, having backup documentation can expedite the verification process when primary information is incomplete.
Supporting Documents That Expedite Verification:
- Official Diplomas: Original or certified copies of graduation certificates or diplomas
- Academic Transcripts: High school transcripts showing completed coursework and graduation confirmation
- Yearbook Records: Class photos or graduation listings from official school publications
- Authorization Forms: Written permission from graduates allowing information release to employers
- Government ID: Photo identification confirming candidate identity for verification purposes
The more accurate information provided initially, the faster and more reliable the verification process becomes overall. Employers should request comprehensive educational information during the application process to facilitate smooth verification procedures. Consequently, this approach reduces delays and improves hiring timeline efficiency.
Step-by-Step Verification Process
Initial Preparation Phase
Begin by gathering all necessary information about the candidate's educational background from application materials. Review the job application or resume for educational details carefully. Note any inconsistencies or incomplete information that requires clarification before proceeding.
Obtain proper authorization from the candidate before initiating verification procedures per legal requirements. This authorization should be in writing and clearly state the purpose of the educational background check. FCRA compliance requires explicit consent for third-party verifications to protect candidate privacy rights.
Conducting the Actual Verification
Contact the appropriate verification source using your chosen method during business hours. For direct school verification, call and speak with registrar staff directly. Explain your employment verification needs clearly and provide the candidate's complete information systematically.
Submit required documentation promptly to avoid processing delays that impact hiring timelines. Many schools have specific forms or procedures for employment verifications that must be followed exactly. Follow their requirements precisely to avoid delays or rejected requests that slow the process.
Effective Verification Communication Script:
- Opening Statement: "Hello, I'm calling to verify a high school diploma for employment purposes"
- Candidate Information: "The candidate's name is [Full Name], and they reportedly graduated in [Year]"
- Information Request: "What information do you need from me to process this verification request"
- Timeline Inquiry: "What is your typical turnaround time for employment verification requests"
- Follow-up Procedures: "How will you provide the verification results to our organization"
Document all communication during the verification process meticulously for compliance purposes. Record who you spoke with, when the conversation occurred, and what information was exchanged. This documentation protects your organization and ensures proper record-keeping for audits.
Following Up on Verification Results
Monitor verification requests actively, especially those with tight hiring timelines that cannot accommodate delays. Contact verification sources if responses are delayed beyond their stated timeframes significantly. Professional follow-up demonstrates urgency while maintaining positive relationships with verification sources.
Review verification results carefully when received to ensure accuracy and completeness. Compare the verified information against what the candidate provided on their application materials. Note any discrepancies in graduation dates, school names, or other details that require further investigation or clarification from candidates.
Industries Where High School Diploma Verification is Critical
Healthcare and Medical Services
Healthcare organizations routinely verify high school diplomas due to strict regulatory requirements and patient safety concerns. Medical assistants, pharmacy technicians, and administrative staff must demonstrate basic educational qualifications before handling patient information. Additionally, healthcare employers face significant liability risks that make thorough verification essential.
The healthcare industry maintains rigorous standards for all employees regardless of their direct patient interaction levels. Even support staff like medical receptionists and billing specialists require verified educational credentials. Furthermore, healthcare organizations must comply with various state licensing requirements that mandate educational verification.
Healthcare Verification Requirements:
- Patient Safety Compliance: Ensuring all staff meet minimum educational standards for safe patient care
- Regulatory Mandates: Meeting state and federal requirements for healthcare facility staffing qualifications
- Professional Licensing: Supporting license applications and renewals that require educational verification
- Accreditation Standards: Satisfying healthcare organization accreditation requirements for staff qualifications
Healthcare employers often use third-party verification services due to high hiring volumes and strict compliance requirements. Consequently, they invest in comprehensive background screening that includes educational verification as a standard component.
Education Sector Employment
Educational institutions extensively verify high school diplomas for all positions from teachers to support staff. School districts must ensure their employees meet minimum educational requirements regardless of their specific roles. Additionally, educational employers serve as role models for students and communities requiring verified qualifications.
Even non-teaching positions like bus drivers, cafeteria workers, and administrative assistants undergo diploma verification in educational settings. Furthermore, substitute teachers and temporary staff require the same verification standards as permanent employees. Educational institutions cannot risk employing individuals who misrepresented their basic qualifications.
Educational Sector Verification Standards:
- Role Model Requirements: All employees must demonstrate truthfulness in their educational backgrounds
- District Policy Compliance: Meeting standardized hiring requirements across all school district positions
- State Certification Support: Providing verified education records for teaching license applications
- Community Trust: Maintaining public confidence in educational institution hiring practices
School districts often maintain relationships with verification services to process large volumes of background checks efficiently. Therefore, they prioritize accuracy and thoroughness in their educational verification procedures.
Financial Services Industry
Banks, credit unions, and financial institutions require high school diploma verification due to regulatory oversight and fiduciary responsibilities. Financial services employees handle sensitive customer information and significant monetary transactions daily. Additionally, regulatory agencies expect financial institutions to verify the basic qualifications of all employees thoroughly.
Entry-level positions like bank tellers, customer service representatives, and loan processors must demonstrate verified educational credentials. Furthermore, financial institutions face regular audits that examine their hiring practices and employee qualification verification procedures. Therefore, comprehensive verification protects against regulatory violations and potential penalties.
The financial services industry maintains strict hiring standards that extend beyond educational verification to comprehensive background screening. However, diploma verification remains a fundamental component of their screening process. Moreover, financial institutions often require ongoing verification for promotions and role changes.
Government and Public Service
Government agencies at federal, state, and local levels routinely verify high school diplomas for virtually all positions. Public service employment requires transparency and accountability that begins with honest educational credentials. Additionally, government employers must demonstrate fair and consistent hiring practices that include thorough verification procedures.
Civil service positions, law enforcement roles, and administrative positions all require verified high school education as minimum qualifications. Furthermore, government agencies face public scrutiny regarding their hiring practices and employee qualifications. Therefore, comprehensive verification protects against criticism and ensures public trust in government institutions.
Government Verification Protocols:
- Public Accountability: Demonstrating thorough vetting of employees who serve the public interest
- Security Clearance Requirements: Supporting background investigations for positions requiring security clearances
- Civil Service Standards: Meeting standardized qualifications for government employment opportunities
- Transparency Obligations: Maintaining open and verifiable hiring practices subject to public records requests
Government agencies often have standardized verification procedures that apply across all departments and positions consistently. Consequently, they maintain detailed documentation of all verification activities for audit and transparency purposes.
Timeline and Costs
Verification timeframes vary significantly based on the method chosen and the responsiveness of educational institutions involved. Planning adequate time for diploma verification prevents hiring delays and ensures thorough vetting of candidates. Additionally, understanding typical timelines helps employers set realistic expectations with candidates and hiring managers.
Comprehensive Timeline Breakdown:
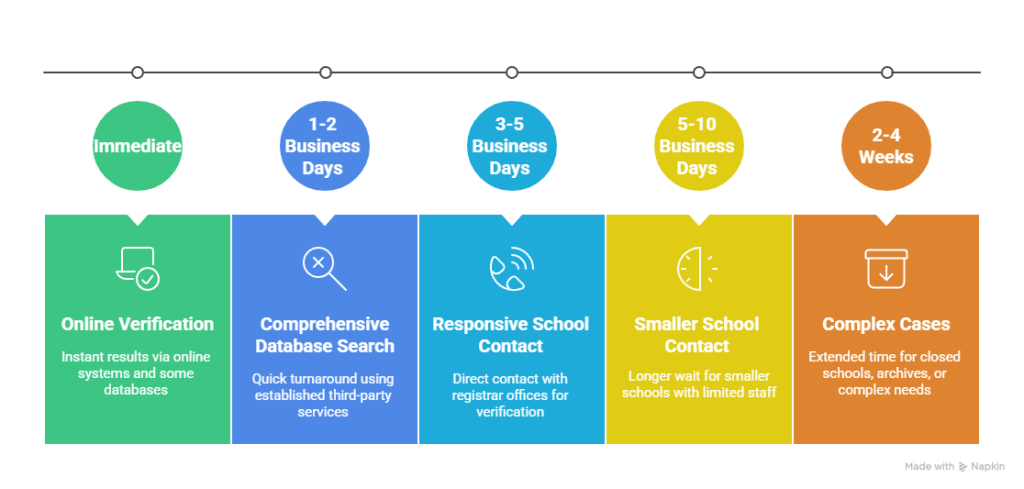
- Immediate Results: Online verification systems and some third-party database searches
- 1-2 Business Days: Established third-party services with comprehensive database access
- 3-5 Business Days: Direct school contact with responsive registrar offices
- 5-10 Business Days: Smaller schools or districts with limited administrative staff
- 2-4 Weeks: Closed schools, archived records, or complex verification requirements
Cost considerations should factor into your overall employment screening budget realistically. While direct verification costs less per candidate, the staff time required may exceed third-party service fees. Furthermore, high-volume hiring operations benefit from the efficiency of professional verification services despite higher per-verification costs.
| Volume Level | Recommended Approach | Cost Per Verification | Administrative Time |
| 1-10 Monthly | Direct School Contact | $0-15 | 2-4 hours per verification |
| 11-50 Monthly | Hybrid Approach | $10-25 | 1-2 hours per verification |
| 50+ Monthly | Third-Party Service | $15-35 | 15-30 minutes per verification |
Budget for rush verifications when hiring timelines are compressed due to business needs. Many third-party services offer expedited processing for additional fees ranging from $10-50 per verification request. However, not all verification types can be expedited, particularly those involving closed schools or archived records.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Closed Schools and Merged Districts
School closures complicate the diploma verification process significantly for employers and verification services alike. When schools close, their records typically transfer to the district office, state education department, or designated successor institution. However, identifying the correct records custodian requires research and persistence from verification professionals.
Start with the state Department of Education when dealing with closed schools in your verification process. Most states maintain databases of closed institutions and can direct you to the appropriate records custodian efficiently. Some states offer centralized verification services for closed school records that streamline the process considerably.
Closed School Verification Resources:
- State Education Departments: Primary custodians of closed school records and transfer information
- Regional Service Centers: Educational cooperatives that may house historical records from multiple districts
- Successor Districts: School districts that absorbed students and records from closed institutions
- Archive Services: Professional record management companies contracted by states for historical document storage
- University Archives: Higher education institutions that may house historical K-12 records in their archives
Historical research may be necessary for very old closures that predate modern record-keeping systems. Local libraries, historical societies, and newspaper archives can provide information about school closures and record transfers. Therefore, persistence and creativity often lead to successful verification of older credentials.
Name Changes and Variations
Name discrepancies between application information and school records cause frequent verification delays and complications. Marriage, divorce, legal name changes, and nickname usage can all impact record searches significantly. Additionally, cultural naming conventions may create confusion in verification processes.
Request comprehensive name information during the application process to minimize verification delays. Ask candidates to provide any names they may have used during high school attendance periods. Furthermore, include maiden names, nicknames, or legal name changes that occurred after graduation in your information gathering.
Name Verification Strategy:
- Legal Names: Current legal name and name used during high school attendance
- Maiden Names: Pre-marriage names for candidates who married after graduation
- Nicknames: Common names or shortened versions used in school records
- Cultural Variations: Different spelling conventions or name order variations
- Legal Changes: Court-ordered name changes with documentation timeline
Always verify using the candidate's legal name at the time of graduation for accurate results. School records reflect the name on official enrollment documents, which may differ significantly from current legal names. Therefore, obtaining historical name information improves verification success rates substantially.
Incomplete or Missing Records
Some educational institutions have incomplete records due to fires, floods, administrative changes, or poor record-keeping practices historically. These situations require creative verification approaches and alternative documentation methods. Additionally, very old records may be stored in formats that require special handling or conversion.
Consider alternative verification methods when primary records are unavailable through traditional channels. Yearbooks, newspaper graduation announcements, class reunion records, or testimonials from school staff may provide supporting evidence. However, alternative methods may not satisfy all employment requirements depending on your organization's policies.
Alternative Documentation Sources:
- Yearbook Records: School or public library copies showing graduation class lists and student photos
- Newspaper Archives: Local newspaper graduation announcements or academic honor roll listings
- Alumni Databases: School alumni association membership records or reunion documentation
- Athletic Records: High school sports participation records that span the candidate's senior year
- Academic Awards: Scholarship or academic recognition records from community organizations
Document any alternative verification methods used and maintain copies of supporting evidence carefully. These alternative approaches may not satisfy all employment requirements but can provide valuable supporting information. Furthermore, combining multiple alternative sources strengthens the overall verification evidence significantly.
Best Practices for Employers
Develop standardized verification procedures that ensure consistency across all hiring decisions and protect against discrimination claims. Written policies should specify which positions require diploma verification clearly. Additionally, outline acceptable verification methods and compliance requirements that staff must follow consistently.
Train hiring managers on proper verification procedures and legal requirements regularly to ensure compliance. Consistent application of verification policies protects against discrimination claims and ensures FCRA compliance throughout your organization. Furthermore, regular training updates keep staff informed of changing regulations and best practices.
Comprehensive Employer Best Practices:
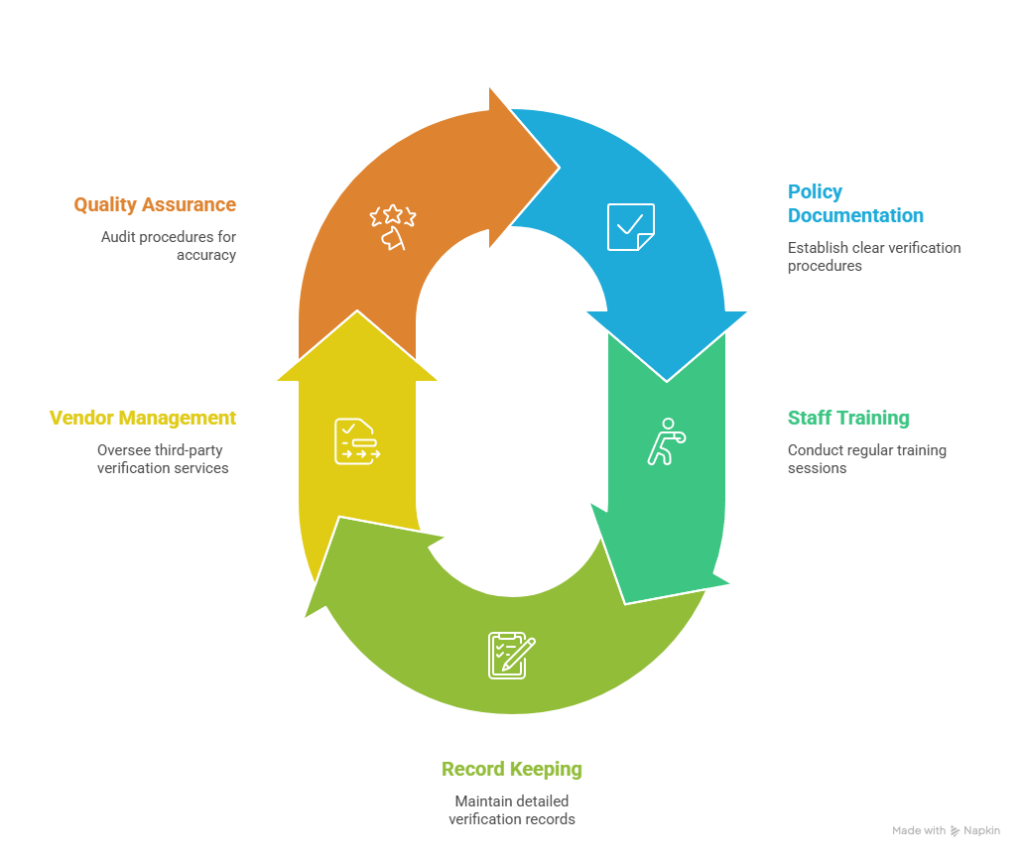
- Policy Documentation: Written procedures specifying verification requirements for different position types and levels
- Staff Training Programs: Regular training sessions on verification procedures, legal compliance, and update notifications
- Systematic Record Keeping: Detailed documentation of all verification activities, results, and compliance measures
- Vendor Management: Due diligence on third-party verification service providers including compliance verification and performance monitoring
- Quality Assurance: Regular audits of verification procedures and outcomes to ensure consistency and accuracy
Maintain detailed records of all verification activities for legal protection and audit purposes. These records serve as evidence of due diligence in hiring decisions and may be required for legal compliance. Additionally, comprehensive documentation protects your organization during employment-related disputes or regulatory examinations.
Consider implementing verification tracking systems that monitor turnaround times, success rates, and compliance metrics regularly. Furthermore, establish relationships with multiple verification providers to ensure backup options when primary sources are unavailable. Therefore, redundancy in verification capabilities prevents hiring delays and ensures consistent service delivery.
Conclusion
Effective diploma verification for employment requires balancing thoroughness, efficiency, and legal compliance throughout the entire process. The methods outlined in this comprehensive guide provide employers with multiple options for verifying high school diplomas based on their specific needs and operational constraints. Whether using direct school contact, third-party services, or online verification platforms, the key is implementing consistent procedures that protect your organization while respecting candidate rights. As educational verification continues evolving with new technologies and regulations, staying informed about emerging solutions and legal requirements ensures your hiring processes remain both effective and fully compliant with current standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it typically take to verify a high school diploma for employment?
Diploma verification timeframes vary by method: online systems provide immediate results, third-party services typically take 1-3 business days, and direct school contact usually requires 3-7 business days. Factors like school responsiveness, record availability, and verification complexity can affect these timelines.
What documents are needed to verify a high school diploma?
Essential documentation includes the graduate's full legal name, graduation year, complete school name and location, and written authorization from the candidate. Additional helpful documents include student ID numbers, copies of diplomas or transcripts, and any name variations used during school attendance.
Can employers verify high school diplomas online?
Yes, many school districts offer online verification systems, and third-party services like National Student Clearinghouse provide digital verification platforms. However, not all schools participate in online systems, and some verifications still require traditional contact methods.
Is it legal for employers to verify employee education without consent?
No, employers must obtain written consent before conducting educational background checks, especially when using third-party screening services. FCRA regulations require explicit authorization and proper disclosure forms before initiating any verification process.
How much does diploma verification cost for employers?
Costs vary by method: direct school verification is often free to $15, while third-party services typically charge $15-50 per verification. Volume discounts and service packages can reduce per-verification costs for employers with high hiring volumes.
What happens if a diploma verification reveals discrepancies?
Employers must follow FCRA adverse action procedures if verification discrepancies impact hiring decisions. This includes providing pre-adverse action notices, copies of the verification report, and information about candidate rights to dispute findings.
How do you verify diplomas from closed high schools?
Contact the state Department of Education, which typically maintains records from closed schools or can direct you to the appropriate custodian. District offices, regional education centers, or designated successor institutions may also house these records.
Can international high school diplomas be verified for US employment?
Yes, but verification requires specialized services familiar with international educational systems. Third-party screening companies often offer international verification services, though timelines and costs are typically higher than domestic verifications.
Additional Resources
- National Student Clearinghouse - Educational Verification Services
https://www.studentclearinghouse.org/employers/ - Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) Compliance Guidelines
https://www.ftc.gov/enforcement/rules/rulemaking-regulatory-reform-proceedings/fair-credit-reporting-act - Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) - Background Check Guidelines
https://www.shrm.org/topics-tools/tools/how-to-guides/conduct-background-checks - U.S. Department of Education - Verification Resources
https://www.ed.gov/category/program/verification - Professional Background Screening Association (PBSA) - Best Practices
https://www.thepbsa.org/ - Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) - Background Check Guidelines
https://www.eeoc.gov/newsroom/eeoc-enforcement-guidance-consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





