Hospitality hiring best practices in 2026 focus on developing systematic, retention-oriented recruitment frameworks that address chronic turnover through proactive talent pipeline management, cultural alignment assessment, and structured onboarding. This approach positions pre-employment screening as one element within a comprehensive hiring ecosystem designed for operational sustainability.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic hospitality hiring systems prioritize pipeline development over reactive vacancy filling, creating continuous talent relationships that reduce time-to-hire.
- Cultural alignment assessment during early screening stages significantly improves retention rates by identifying candidates whose values match organizational service standards.
- Multi-stage evaluation processes combining behavioral interviews, skill demonstrations, and reference verification produce more reliable hiring outcomes than single-method approaches.
- Retention-focused onboarding that begins before the first work shift establishes clear expectations and reduces early-stage turnover.
- Pre-employment screening hospitality workers requires understanding jurisdiction-specific regulations that vary by state and municipality regarding timing, scope, and disclosure requirements.
- Technology-assisted evaluation tools should complement rather than replace human judgment in assessing interpersonal skills critical to hospitality roles.
- Hospitality hiring during labor shortage conditions demands flexibility in qualification requirements while maintaining non-negotiable safety and compliance standards.
- Documented hiring protocols protect organizations from claims of inconsistent application while supporting continuous process improvement.
Developing a Strategic Hiring Framework for Hospitality Operations
Effective hospitality hiring best practices 2026 require moving beyond individual tactics toward integrated systems that address the industry's unique workforce challenges. Hospitality operations face distinctly high turnover rates, seasonal demand fluctuations, and roles requiring specific interpersonal competencies that are difficult to assess through traditional application reviews alone.
A strategic framework approach recognizes hiring as an ongoing operational function rather than an episodic activity triggered by vacancies. This perspective shifts organizational focus toward building relationships with potential candidates before positions open, maintaining structured evaluation criteria that produce consistent results, and designing onboarding experiences that improve early retention.
The foundation of this framework rests on three interconnected components:
- Proactive talent pipeline development that maintains continuous candidate relationships
- Systematic candidate evaluation using multiple assessment methods
- Retention-focused integration processes that begin before the first work shift
Building Continuous Talent Pipelines
Traditional hospitality hiring often operates in crisis mode, with managers scrambling to fill open positions as quickly as possible. This reactive approach typically results in lowered standards, inadequate screening, and poor cultural fit, which collectively contribute to the turnover cycle.
Proactive pipeline development maintains ongoing relationships with potential candidates regardless of immediate hiring needs. Organizations implementing pipeline strategies often maintain candidate pools of individuals who have expressed interest, completed preliminary applications, or participated in informational sessions.
| Pipeline Strategy | Implementation Approach | Primary Benefit |
| Educational partnerships | Establish connections with culinary schools and hospitality programs | Access to trained candidates before graduation |
| Open house events | Host facility tours and meet-the-team sessions without formal interviews | Allows mutual cultural fit assessment |
| Digital talent communities | Maintain communication through newsletters and social media groups | Reduces time-to-hire when positions open |
| Community organization relationships | Partner with workforce development agencies | Expands candidate pool diversity |
Digital talent communities represent another pipeline development approach. Organizations maintain communication with interested candidates through newsletters, social media groups, or dedicated platforms that share company updates, industry insights, and career development resources. When positions open, these pre-qualified individuals become the first outreach targets, dramatically reducing time-to-hire.
When I think about hospitality hiring, I realize that the strongest teams are rarely built through rushed decisions. As I continue to observe good operations, I am more and more convinced that consistent hiring processes are as important as speed in hiring. Technology can assist with hiring, but I still think people’s judgement is important to recognize potential, attitude, and cultural fit. In the end, thoughtful hiring often shapes the kind of service culture that guests experience every day.
Implementing Multi-Stage Evaluation Processes
Hospitality hiring process checklist systems should incorporate multiple evaluation methods that collectively assess different competency dimensions. Single-stage interviews rarely provide sufficient information to predict job performance in roles requiring complex interpersonal skills, stress management, and situational judgment.
Effective multi-stage processes typically begin with structured application screening that focuses on verifiable qualifications and experience relevant to specific position requirements. Subsequent stages might include phone screenings to assess communication skills, followed by in-person behavioral interviews using standardized question sets.
Practical skill demonstrations provide direct observation of job-relevant capabilities:
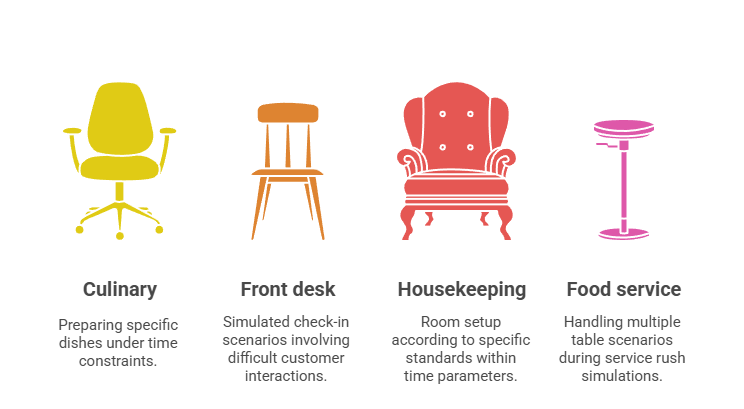
- Culinary positions: Preparing specific dishes under time constraints
- Front desk roles: Simulated check-in scenarios involving difficult customer interactions
- Housekeeping positions: Room setup according to specific standards within time parameters
- Food service roles: Handling multiple table scenarios during service rush simulations
Reference verification serves as an additional evaluation layer, though effectiveness depends on the quality of questions asked and the willingness of references to provide candid feedback. Structured reference check protocols that ask specific behavioral questions about past performance, reliability, and interpersonal conduct produce more useful information than general inquiries.
Integrating Pre-Employment Screening Within the Hiring Ecosystem
Pre-employment screening hospitality workers represents one component within comprehensive evaluation systems rather than a standalone solution. The scope, timing, and methods of screening vary based on position requirements, regulatory obligations, and organizational risk tolerance.
Screening considerations in hospitality contexts often include verification of identity and work authorization, criminal history review where permitted and relevant to position responsibilities (which may require use of consumer reports subject to FCRA requirements), and validation of credentials or licenses required for specific roles. The hospitality industry handles guest property, processes payment information, and often serves vulnerable populations, creating legitimate business interests in understanding candidate backgrounds.
However, screening implementation must comply with applicable federal, state, and local regulations that govern what information may be obtained, when in the hiring process screening may occur, and how results may be used in employment decisions. Employment screening that involves consumer reports typically occurs after conditional job offers in many jurisdictions, particularly those with ban-the-box or fair chance hiring regulations. When screening results inform employment decisions, FCRA adverse action procedures apply regardless of when screening occurs.
Addressing Hospitality Hiring During Labor Shortage Conditions

Persistent labor shortages in hospitality sectors have required organizations to reconsider traditional qualification requirements while maintaining standards critical for operational quality and regulatory compliance. This balance requires distinguishing between preferences and requirements.
Expanding Candidate Pool Parameters
Many hospitality operations historically required previous industry experience for most positions. Labor shortage conditions have prompted reconsideration of whether industry-specific experience is truly necessary or whether transferable skills from other sectors can meet operational needs with appropriate training.
Customer service skills developed in retail, healthcare, or call center environments often transfer effectively to hospitality contexts. Food preparation skills from institutional settings may translate to restaurant operations. Organizational abilities developed in administrative roles can support hotel operations or event coordination functions.
Flexible scheduling options attract candidates who cannot commit to traditional shift patterns, including parents with school-age children, students, or individuals with caregiving responsibilities. Operations that can accommodate varied availability may access labor pools unavailable to competitors requiring standard scheduling.
Maintaining Non-Negotiable Standards
Labor shortage pressures create temptation to accelerate hiring processes or overlook concerning information to fill immediate needs. This approach typically produces short-term relief followed by longer-term problems including performance issues, cultural disruption, or compliance violations.
Certain standards should remain non-negotiable regardless of hiring pressure:
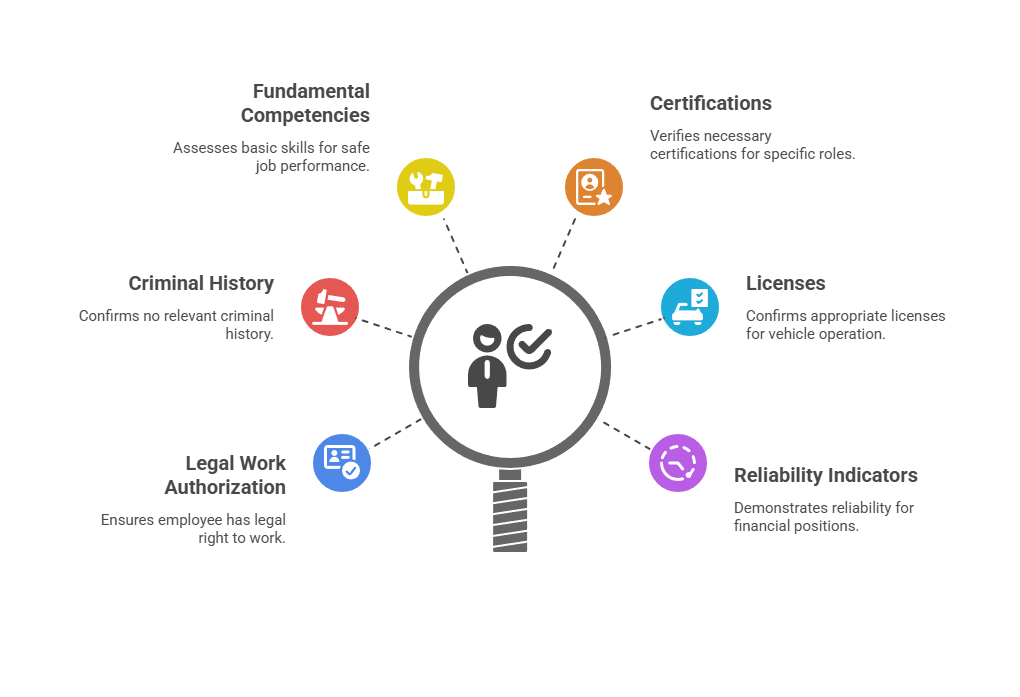
- Legal work authorization documentation
- Absence of disqualifying criminal history relevant to position responsibilities
- Fundamental competencies required for safe job performance
- Required certifications for alcohol service where applicable
- Appropriate licenses and clean driving records for vehicle operation roles
- Demonstrated reliability indicators for positions with financial responsibilities
Organizations should document which requirements are truly mandatory versus preferred, establishing clear decision criteria before recruitment begins. This advance planning prevents inconsistent application of standards across candidates and provides defensible rationale for hiring decisions.
Developing Internal Talent Through Advancement Pathways
Labor shortages make retention of existing employees increasingly valuable. Clear advancement pathways that allow entry-level workers to progress into roles with greater responsibility, compensation, and engagement create internal talent pipelines while improving retention.
| Development Strategy | Implementation | Retention Impact |
| Cross-training programs | Develop multi-functional capabilities across departments | Increases operational flexibility and employee value |
| Formal mentorship | Pair experienced employees with newer team members | Strengthens culture and accelerates skill development |
| Tuition assistance | Support hospitality management or culinary education | Demonstrates investment and builds loyalty |
| Promotional pathways | Document clear progression from entry to management roles | Creates motivation and reduces external recruiting needs |
Formal mentorship programs pair experienced employees with newer team members, accelerating skill development while strengthening organizational culture. Mentorship relationships often improve retention for both participants by increasing the mentor's sense of contribution and the mentee's integration into the team.
Assessing Cultural Alignment Throughout the Hiring Process
Cultural fit assessment has become increasingly recognized as a critical factor in hospitality hiring outcomes. Employees whose personal values and work preferences align with organizational culture demonstrate higher job satisfaction, better performance, and longer tenure than those hired based solely on technical qualifications.
Defining Organizational Culture Explicitly
Effective cultural assessment requires first articulating what organizational culture actually is. Many hospitality operations rely on vague concepts like "family atmosphere" or "service excellence" without defining the specific behaviors, values, and expectations these terms represent.
Useful culture definitions identify observable behaviors that exemplify cultural values. If "teamwork" is a stated value, the definition should specify what teamwork looks like in practice, such as proactively assisting colleagues during service rushes without being asked, or sharing knowledge freely with newer team members.
Culture definitions should acknowledge both positive attributes the organization cultivates and negative characteristics it explicitly rejects. Some hospitality operations emphasize creativity and flexibility, accepting occasional procedural variations in service of guest satisfaction. Others prioritize consistency and standardization, expecting strict adherence to established protocols.
Evaluating Cultural Fit Through Behavioral Questions
Structured behavioral interview questions can effectively assess cultural alignment when designed to reveal candidate values and preferences. These questions should focus on past experiences rather than hypothetical scenarios, as candidates may provide aspirational answers to hypothetical questions that don't reflect actual behavior patterns.
Sample behavioral question frameworks by cultural priority:
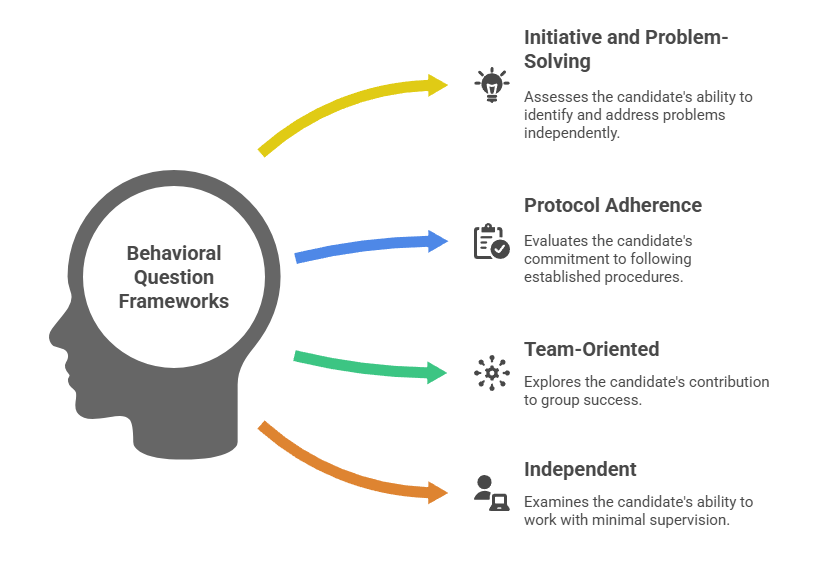
- Initiative and problem-solving cultures: "Describe a situation where you identified and addressed a problem without explicit direction from management."
- Protocol adherence cultures: "Tell me about a time when you faced pressure to deviate from established procedures. How did you respond?"
- Team-oriented cultures: "Give an example of how you contributed to a group success. What was your specific role?"
- Independent cultures: "Describe a project you completed with minimal supervision. What was your approach?"
Service recovery scenarios provide particularly useful cultural assessment opportunities in hospitality contexts. How candidates describe handling dissatisfied customers, their emotional responses to criticism, and their problem-solving approaches reveal important cultural fit indicators.
Providing Realistic Job Previews
Realistic job previews that honestly represent both positive and challenging aspects of positions allow candidates to self-select based on accurate information. This transparency reduces turnover by preventing surprises that lead to early departure.
Hospitality work often involves irregular schedules, weekend and holiday requirements, physically demanding tasks, and emotionally challenging customer interactions. Candidates who understand these realities before accepting positions are less likely to experience regret and resignation shortly after starting.
Some organizations incorporate job shadowing into their hiring processes, allowing candidates to observe typical work conditions for several hours before final hiring decisions. Video or virtual reality tools can provide realistic previews when in-person observation is impractical.
Designing Retention-Focused Onboarding Experiences
The period between job acceptance and the end of the first 90 days represents the highest-risk window for turnover in hospitality operations. Structured onboarding that begins before the first work shift significantly improves retention by establishing clear expectations, building relationships, and creating early success experiences.
Pre-Start Engagement
Effective onboarding begins immediately after job acceptance rather than on the first scheduled work day. The period between acceptance and start date presents risks that candidates will accept competing offers or experience anxiety that leads to reconsideration.
Maintaining regular communication during this period keeps new hires engaged and excited:
- Welcome messages from team members and supervisors
- Information about what to expect on the first day
- Preliminary paperwork completion that reduces administrative burden
- Invitations to voluntary social events before official start dates
- Facility tours that help new hires visualize their work environment
Pre-start facility tours for positions that weren't initially recruited through in-person processes help new hires visualize their work environment and reduce first-day uncertainty. Virtual tours can serve similar purposes when in-person visits are impractical.
Structured First-Week Experiences
First-week onboarding should balance necessary administrative and compliance training with meaningful work that allows new employees to contribute and experience success quickly. Overwhelming new hires with policies and procedures without opportunities for practical application creates frustration and disengagement.
| Onboarding Component | Timing | Purpose |
| Essential compliance training | Day 1 | Safety procedures and harassment prevention |
| Observation periods | Days 1-2 | Familiarization with workflows and standards |
| Simple task assignments | Days 2-3 | Early success experiences and confidence building |
| Mentor/buddy assignment | Day 1 | Accessible resource for questions and guidance |
| Daily supervisor check-ins | Days 1-5 | Early identification of confusion or concerns |
Assigned mentors or buddies provide new hires with accessible resources for questions and guidance without requiring constant supervisor attention. Peer mentors often prove more approachable than managers for questions new employees perceive as basic or potentially embarrassing.
30-60-90 Day Integration Milestones
Extended onboarding that continues through the first 90 days establishes clear performance expectations while providing structured support for achieving them. Milestone-based approaches create checkpoints that both employees and supervisors can use to assess progress and address gaps.
Thirty-day milestones might focus on mastery of basic job functions, familiarity with standard operating procedures, and successful relationship building with immediate team members. Sixty-day milestones could emphasize independent task completion and problem-solving in routine situations. Ninety-day milestones often include demonstrated ability to handle complex situations and full integration into organizational culture.
Leveraging Technology While Maintaining Human Judgment
Technology tools have proliferated in recruitment and hiring contexts, offering capabilities ranging from automated application screening to video interview analysis to scheduling optimization. These tools can improve efficiency and consistency when implemented thoughtfully as complements to human decision-making rather than replacements. Organizations can benefit the most when technology takes over the structured steps, while the final decision rests with the hiring experts. This will ensure that the efficiency gains do not compromise the hiring decisions.
Application Screening and Matching Systems
Applicant tracking systems that automatically screen applications based on specified criteria can process high volumes efficiently, identifying candidates who meet threshold qualifications. These systems work most effectively when screening for objective, verifiable requirements such as specific certifications, experience duration, or education credentials.
Automated screening becomes more problematic when attempting to evaluate subjective qualities or make nuanced judgments about qualification relevance. Systems that reject applications for minor keyword absences or formatting variations may eliminate qualified candidates whose applications don't match precise algorithmic expectations.
Some platforms use matching algorithms that compare candidate profiles against job requirements or successful employee characteristics, generating fit scores. These tools can identify promising candidates who might be overlooked in manual reviews, but should not be the sole basis for advancement decisions.
Interview and Assessment Technologies
Video interviewing platforms that allow asynchronous candidate responses to standardized questions provide scheduling flexibility while ensuring consistent question administration. Some platforms offer analysis features that claim to assess candidate suitability based on word choice, facial expressions, or vocal characteristics.
The validity and fairness of automated interview analysis remains subject to debate and ongoing research. These tools may reflect biases present in training data or make inferences not supported by industrial-organizational psychology research. Regulations in some jurisdictions restrict or require disclosure of automated employment decision tools.
Organizations using such technologies should treat automated assessments as one input among several rather than determinative factors, maintain human review of results, and monitor outcomes across demographic groups to identify potential disparate impact.
Scheduling and Coordination Tools
Hiring coordination technologies that automate interview scheduling, send reminder communications, and track candidate progress through hiring stages reduce administrative burden and improve candidate experience through timely, consistent communication.
These tools prove particularly valuable in high-volume hiring environments common to hospitality operations, where recruiting teams may manage dozens of candidates simultaneously across multiple positions. Automated status updates keep candidates informed about their application progress, reducing uncertainty and the likelihood of accepting competing offers.
Developing Hospitality-Specific Hiring Process Checklists
Standardized hiring process checklists ensure consistent application of evaluation criteria, reduce oversight risk, and support continuous improvement through documentation of decision-making rationale. Effective checklists should be position-specific while maintaining core elements common across hiring activities.
Pre-Recruitment Planning Components
Before initiating candidate recruitment, hiring checklists should prompt completion of foundational planning tasks. These include documented position requirements distinguishing mandatory qualifications from preferences, defined evaluation criteria with relative weighting, and identified assessment methods appropriate for competency evaluation.
Budget confirmation ensures necessary resources exist for competitive compensation, recruiting activities, and screening procedures. Timeline establishment creates realistic expectations for hiring completion while preventing artificial urgency that compromises evaluation quality.
| Planning Element | Required Documentation | Compliance Purpose |
| Position requirements | Mandatory vs. preferred qualifications | Prevents inconsistent application |
| Evaluation criteria | Weighted scoring rubrics | Supports defensible decisions |
| Assessment methods | Stage-specific evaluation tools | Ensures job-relevant testing |
| Regulatory review | Applicable federal, state, and local laws | Confirms legal compliance |
| Budget allocation | Compensation and screening costs | Prevents mid-process constraints |
Compliance review verifies that planned hiring procedures align with applicable regulations regarding timing of background screening, prohibited inquiries, and required disclosures. This review should consider federal laws, state statutes, and any municipal ordinances relevant to the hiring location.
Candidate Evaluation Stage Checklists
Each evaluation stage should have associated checklists that ensure consistent process application. Application review checklists specify required qualifications that must be present for advancement, formatting requirements for documentation, and prohibited considerations.
Interview stage checklists include standardized question sets with guidance on acceptable answer characteristics, rating scales for consistent evaluation, and required documentation of responses and interviewer assessments. Skills assessment checklists detail the exact tasks candidates will perform, evaluation criteria for successful completion, and scoring rubrics for objective assessment.
Post-Selection Process Checklists
After candidate selection but before final hiring, checklists should ensure completion of all conditional offer requirements, background screening procedures where applicable, verification of work authorization, and documentation of hiring decision rationale.
Onboarding preparation checklists confirm that necessary resources are available:
- Workspace and equipment setup
- System access credentials and login information
- Training materials and orientation schedules
- Mentor assignments and first-week itineraries
- Supervisor availability confirmation
Documentation checklists ensure that required hiring records are complete and properly stored, including applications, interview notes, assessment results, offer letters, and acknowledgment of receipt of required notices. Retention schedules should be applied based on regulatory requirements and potential litigation timelines.
Conclusion
Implementing hospitality hiring best practices 2026 requires systematic approaches that integrate talent pipeline development, structured evaluation, and retention-focused onboarding. Success depends on treating hiring as a continuous strategic function rather than reactive crisis response, with pre-employment screening hospitality workers positioned as one component within comprehensive systems subject to jurisdiction-specific regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important hospitality hiring best practices 2026 for reducing turnover?
Proactive talent pipeline development, structured cultural fit assessment during interviews, realistic job previews that set accurate expectations, and retention-focused onboarding that begins before the first work day represent the most effective turnover reduction strategies. These practices collectively address the primary causes of early departure including poor cultural alignment, unmet expectations, and inadequate initial support.
How should pre-employment screening hospitality workers be integrated into the hiring process?
Pre-employment screening should occur after preliminary qualification assessment and typically follows conditional job offers, particularly in jurisdictions with ban-the-box or fair chance hiring regulations. Screening scope should be limited to information relevant to specific position responsibilities, with results evaluated through individualized assessment rather than blanket disqualification rules. Requirements vary significantly by state and local jurisdiction.
What should a comprehensive hospitality hiring process checklist include?
Effective checklists include pre-recruitment planning components such as documented position requirements and compliance review, stage-specific evaluation procedures with standardized questions and scoring criteria, reference verification protocols, and post-selection steps including background screening authorization and work authorization verification. Checklists should be position-specific while maintaining core consistency across hiring activities.
How can hospitality operations hire effectively during labor shortage conditions?
Labor shortage hiring requires expanding candidate pool parameters by considering transferable skills from other industries, broadening geographic recruitment ranges, and offering scheduling flexibility. Organizations should distinguish between preferred and truly required qualifications while maintaining non-negotiable standards related to legal work authorization, safety-critical competencies, and regulatory compliance requirements. Internal talent development through clear advancement pathways also addresses shortage conditions.
What role should technology play in hospitality hiring decisions?
Technology tools including applicant tracking systems, video interview platforms, and automated scheduling improve efficiency and consistency when used as complements to human judgment rather than replacements. Automated screening works best for objective criteria verification, while complex interpersonal skill assessment required for hospitality roles benefits from direct human evaluation. Organizations should maintain human review of technology-generated assessments and monitor for potential algorithmic bias.
How can cultural fit be assessed during the hospitality hiring process?
Cultural fit assessment requires first explicitly defining organizational culture through observable behaviors rather than abstract concepts, then developing behavioral interview questions that reveal candidate values and past behavior in relevant situations. Realistic job previews allow candidates to self-assess fit, while job shadowing provides direct experience of work environment and team dynamics before final hiring decisions.
What are the key components of retention-focused onboarding in hospitality?
Retention-focused onboarding begins with pre-start engagement that maintains candidate connection between acceptance and first work day, continues with structured first-week experiences balancing compliance training with meaningful work contributions, and extends through 30-60-90 day milestone achievement with regular feedback conversations. Assigned peer mentors and supervisor check-ins provide ongoing support during the highest-risk turnover period.
How do hiring regulations vary by location for hospitality operations?
Hiring regulations differ significantly across federal, state, and municipal jurisdictions regarding permissible screening timing, types of background information that may be considered, required notices and disclosures, and lookback period limitations for certain records. Organizations operating in multiple locations must develop protocols complying with the most restrictive applicable regulations or implement jurisdiction-specific variations. Legal requirements continue to evolve and require ongoing monitoring.
Additional Resources
- Fair Credit Reporting Act Summary of Rights
https://www.consumer.ftc.gov/articles/pdf-0096-fair-credit-reporting-act.pdf - U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission - Prohibited Employment Policies/Practices
https://www.eeoc.gov/prohibited-employment-policiespractices - Department of Labor - Employment Law Guide
https://www.dol.gov/agencies/odep/publications/fact-sheets/employment-laws-assistance-for-workers-with-disabilities - Society for Human Resource Management - Background Check State Laws
https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/state-and-local-updates - Federal Trade Commission - Using Consumer Reports for Employment Purposes
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/using-consumer-reports-employment-purposes

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





