California healthcare background check requirements are among the most comprehensive in the nation, mandated by the Department of Consumer Affairs (DCA) and individual licensing boards to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance. Healthcare professionals must undergo thorough screening processes that include criminal history checks, professional license verifications, and specific clearances depending on their role and practice setting.
Key Takeaways
- California healthcare background check requirements vary by profession but typically include DOJ criminal history checks, FBI fingerprinting, and license verification through the appropriate state board.
- California nursing license background check processes require LiveScan fingerprinting, criminal background screening, and submission through the California Board of Registered Nursing (BRN) or Board of Vocational Nursing and Psychiatric Technicians (BVNPT).
- California medical license background check procedures involve comprehensive screening through the Medical Board of California, including criminal history, malpractice claims, and disciplinary actions from other states.
- DCA background check requirements mandate that most healthcare licensing boards conduct thorough reviews of applicants' criminal history, with specific guidelines for disqualifying offenses and rehabilitation considerations.
- Healthcare employers must comply with Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) regulations when conducting background checks, including proper disclosure and consent procedures.
- Background check processing times typically range from 2-8 weeks, with expedited options available for certain healthcare positions during critical staffing shortages.
Understanding California's Healthcare Background Check Framework
California's healthcare background check system operates under a multi-layered regulatory framework. This system protects patient safety while ensuring fair employment practices. The Department of Consumer Affairs oversees most healthcare licensing boards. Each board has specific background check requirements for their profession's responsibilities and patient interaction levels.
The state's requirements cover both initial licensing and ongoing employment screening. Healthcare professionals must navigate federal FCRA compliance and state-specific DCA regulations. Individual licensing board requirements can vary significantly between different healthcare professions. Understanding these systems is crucial for both job seekers and employers. Non-compliance can result in licensing delays, employment termination, or legal complications.
California's approach has evolved significantly over the past decade. The state now uses new technologies like LiveScan fingerprinting and enhanced database connectivity. The DCA has streamlined many processes while maintaining rigorous standards. This creates more efficient screening procedures without compromising patient safety. This balance makes California's system a model for other states.
Regulatory Authority Structure
The Department of Consumer Affairs serves as the umbrella organization for most healthcare licensing boards. It provides oversight and standardization across diverse medical professions. Each licensing board operates with semi-autonomous authority. They establish profession-specific requirements while following DCA guidelines and state regulations.
Primary DCA Healthcare Licensing Boards:
- Medical Board of California - Physicians and surgeons
- California Board of Registered Nursing - Registered nurses and nurse practitioners
- Board of Vocational Nursing and Psychiatric Technicians - Licensed vocational nurses
- California State Board of Pharmacy - Pharmacists and pharmacy technicians
- Board of Behavioral Sciences - Mental health professionals and counselors
- Physical Therapy Board of California - Physical therapists and assistants
Coordination between these boards ensures consistent background check standards. It also allows for profession-specific modifications based on scope of practice and patient safety considerations.
Legal Foundation and Compliance Framework
California healthcare background check requirements come from multiple legal sources. These include state business and professions codes, federal regulations, and industry-specific statutes. The primary legal foundation stems from Business and Professions Code sections. These mandate character and fitness requirements for healthcare licensing.
Federal compliance requirements overlay state requirements. This creates a complex regulatory environment. Healthcare organizations must navigate both state licensing requirements and federal employment law. Their background check processes must meet all applicable standards.
DCA Background Check Requirements for Healthcare Licensing
The Department of Consumer Affairs has established comprehensive background check requirements. These serve as the foundation for most healthcare licensing in California. DCA background check requirements include mandatory criminal history screening through state and federal databases. They also have specific protocols for handling criminal convictions and professional disciplinary actions.
Core DCA Screening Components:
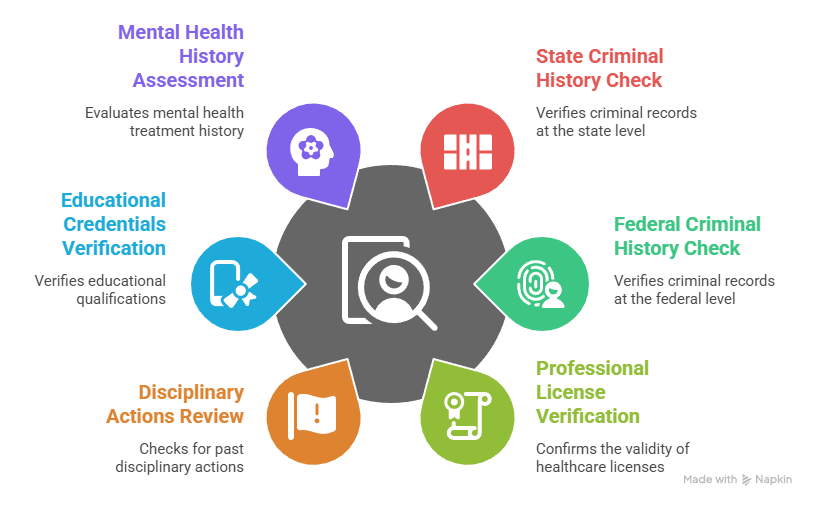
- State of California criminal history check through the Department of Justice
- Federal Bureau of Investigation criminal background screening via fingerprint submission
- Professional license verification from all jurisdictions where applicant held healthcare licenses
- Review of disciplinary actions, sanctions, or restrictions from any professional licensing authority
- Verification of educational credentials and clinical training completion
- Assessment of mental health or substance abuse treatment history when disclosed
The DCA has developed standardized procedures for evaluating background check results. These include specific guidelines for determining when criminal history or professional misconduct should result in license denial. These guidelines provide licensing boards with consistent frameworks while allowing for individualized assessment.
Processing times for DCA background check requirements typically range from four to twelve weeks. This depends on the complexity of an applicant's background and external verification sources. Applicants with extensive out-of-state history or criminal records may experience longer processing times.
Criminal History Evaluation Standards
DCA background check requirements include specific standards for evaluating criminal history. They pay particular attention to crimes that could impact patient safety or professional integrity. The evaluation process considers multiple factors. These include the nature and severity of offenses, the relationship between criminal conduct and healthcare practice, and evidence of rehabilitation since conviction.
| Crime Category | Evaluation Criteria | Typical Review Period |
| Violent Offenses | Patient safety impact assessment | 7-10 years |
| Financial Crimes | Trustworthiness evaluation | 5-7 years |
| Drug-Related Offenses | Substance abuse assessment | 3-5 years |
| Professional Misconduct | Direct practice relevance | Case-by-case |
The DCA recognizes that criminal history does not automatically disqualify individuals from healthcare practice. They must demonstrate rehabilitation and current fitness for professional responsibility. Licensing boards evaluate rehabilitation evidence. This includes completion of court-ordered programs, community service, employment history, and character references.
Professional License Verification Process
Professional license verification is a critical component of DCA background check requirements. It ensures that applicants have maintained good standing in all jurisdictions where they have held healthcare licenses. This process involves direct communication with licensing boards in other states and countries. It includes verification of license status and investigation of any disciplinary actions or restrictions.
Licensing boards pay particular attention to disciplinary actions involving patient safety, professional misconduct, or criminal behavior. Even minor disciplinary actions in other jurisdictions can trigger additional scrutiny and investigation in California. Applicants must provide complete and accurate information about all professional licenses held. Failure to disclose or misrepresentation can result in automatic license denial.
California Nursing License Background Check Procedures
California nursing license background check procedures involve comprehensive screening processes. Two primary licensing boards administer these with distinct requirements and evaluation criteria. The Board of Registered Nursing oversees registered nurses and nurse practitioners. The Board of Vocational Nursing and Psychiatric Technicians handles licensed vocational nurses and psychiatric technicians.
Registered Nursing Background Check Requirements:
- Comprehensive criminal history screening through LiveScan fingerprinting system
- Federal Bureau of Investigation background check covering all jurisdictions of residence
- Professional discipline verification from all states where nursing education or practice occurred
- Mental health evaluation requirements for applicants with history of substance abuse or disciplinary actions
- Continuing education compliance verification for license renewal applications
- Employer reference verification for recent nursing practice or clinical experience
Licensed Vocational Nursing Background Check Procedures:
- State and federal criminal background checks with enhanced scrutiny for patient care-related offenses
- Educational credential verification including clinical training site evaluations
- Previous healthcare employment verification with emphasis on patient care responsibilities
- Review of any healthcare-related criminal charges, regardless of disposition
- Assessment of rehabilitation efforts for applicants with disqualifying criminal history
The nursing license background check process typically requires 6-10 weeks for completion. Additional time is needed for complex cases involving criminal history or out-of-state education.
Board of Registered Nursing Screening Protocols
The Board of Registered Nursing has developed sophisticated screening protocols. These reflect the advanced practice responsibilities and patient safety obligations of registered nurses. The protocols include multi-layered review processes that evaluate criminal history, professional conduct, and clinical competency indicators.
Criminal history evaluation focuses particularly on offenses that could impact patient safety. This includes violent crimes, drug offenses, and crimes involving vulnerable populations. The board maintains specific guidelines for evaluating different types of criminal behavior. They consider factors such as offense severity, relationship to nursing practice, time elapsed since conviction, and evidence of rehabilitation efforts.
Professional conduct evaluation includes review of any previous nursing license disciplinary actions. It also covers employer disciplinary measures and clinical performance issues. The board coordinates with nursing education programs to identify students or graduates who experienced difficulties that could impact professional practice.
Vocational Nursing and Psychiatric Technician Requirements
The Board of Vocational Nursing and Psychiatric Technicians maintains specialized background check requirements. These address the unique patient care responsibilities of licensed vocational nurses and psychiatric technicians. Requirements include enhanced screening for offenses involving vulnerable populations. LVNs and psychiatric technicians often work with elderly, disabled, or mentally ill patients who require additional protection.
Specialized Screening Elements:
- Vulnerable Adult Abuse Registry: Mandatory screening through elder abuse and dependent adult abuse registries
- Mental Health Facility Background: Enhanced review for applicants seeking psychiatric technician licenses
- Medication Administration History: Review of any incidents involving medication errors or controlled substance violations
- Clinical Supervision Records: Evaluation of supervision requirements or restrictions from previous healthcare employment
The board's evaluation process includes specific consideration of rehabilitation efforts and current fitness for practice. This is particularly important for applicants with criminal history involving substance abuse or mental health issues.
California Medical License Background Check Standards

California medical license background check standards represent some of the most rigorous screening requirements in the healthcare industry. They reflect the significant autonomy and patient care responsibilities of physician practice. The Medical Board of California conducts comprehensive investigations. These extend far beyond basic criminal history checks.
The medical license background check process typically requires 12-20 weeks for completion. Complex cases require additional investigation time. International medical graduates may experience longer processing periods. This is due to additional verification requirements for foreign educational credentials and training programs.
Comprehensive Medical License Screening Components:
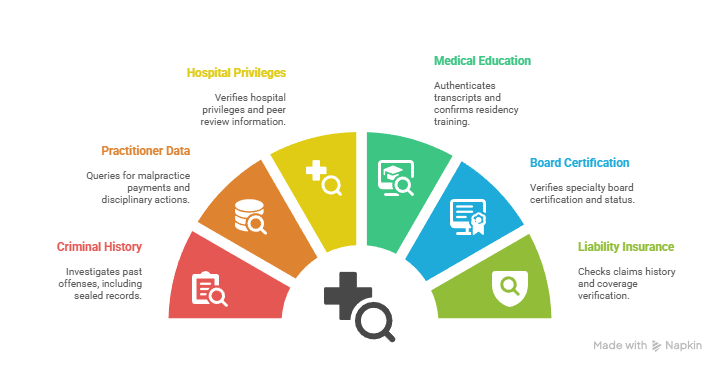
- Complete criminal history investigation including sealed or expunged records
- National Practitioner Data Bank query for malpractice payments and disciplinary actions
- Hospital privilege verification and peer review protected information when available
- Medical education transcript authentication and residency training confirmation
- Specialty board certification verification and maintenance of certification status
- Professional liability insurance claims history and coverage verification
The Medical Board employs specialized investigators and legal staff to conduct thorough background investigations. This is particularly important for applicants with complex histories or red flag indicators.
Malpractice and Professional Liability Review
Medical license background checks include exhaustive review of professional liability claims, settlements, and judgments. This covers any jurisdiction where the applicant has practiced medicine. The review process examines not only the financial aspects of malpractice claims but also the underlying clinical issues and quality of care concerns.
The board's evaluation considers multiple factors in assessing malpractice history. These include the severity of alleged misconduct, patient outcomes, the physician's response to claims, and implementation of practice improvements. Physicians with extensive malpractice history may be required to undergo peer review evaluation, additional training, or practice restrictions.
Professional liability review also encompasses hospital peer review activities, medical staff privilege restrictions, and voluntary practice limitations. The board investigates any restrictions on hospital privileges, clinical practice limitations, or required supervision arrangements.
International Medical Graduate Verification
International medical graduates face additional verification requirements. This includes authentication of foreign educational credentials and confirmation of training equivalency to U.S. standards. The process involves coordination with international medical education organizations, foreign medical licensing authorities, and credential verification services.
International Verification Components:
- Medical school transcript authentication through authorized credential verification services
- Foreign medical license status confirmation and any disciplinary history
- Clinical training documentation including internship and residency program completion
- English language proficiency demonstration through standardized testing
- Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates certification verification
The verification process for international medical graduates typically requires 16-24 weeks. This is due to communication delays with foreign institutions and the complexity of credential authentication.
Specialized Healthcare Background Check Requirements
California's diverse healthcare system encompasses numerous specialized roles. These require tailored background check procedures beyond standard licensing requirements. Specialized positions often involve particularly vulnerable patient populations, controlled substance access, or critical care environments. This necessitates enhanced screening protocols.
Specialized Healthcare Role Classifications:
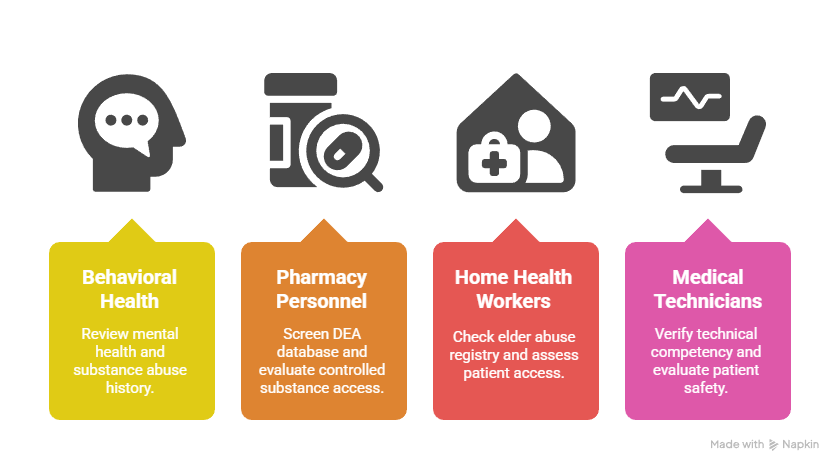
- Behavioral Health Professionals: Enhanced mental health and substance abuse history review
- Pharmacy Personnel: Drug Enforcement Administration database screening and controlled substance access evaluation
- Home Health and Personal Care Workers: Elder abuse registry checks and unsupervised patient access assessment
- Medical Device and Equipment Technicians: Technical competency verification and patient safety protocol evaluation
The specialized background check requirements often involve multiple regulatory authorities beyond the DCA. This includes federal agencies, local health departments, and facility-specific accreditation organizations. This creates complex compliance requirements that healthcare employers must navigate carefully.
Behavioral and Mental Health Professional Requirements
Mental health professionals face specialized background check requirements. These address the unique vulnerabilities and trust relationships inherent in behavioral health practice. The Board of Behavioral Sciences conducts enhanced screening. It focuses particularly on crimes involving abuse, exploitation, or boundary violations that could impact therapeutic relationships.
Enhanced Mental Health Screening Elements:
- Patient Abuse Registry Screening: Mandatory checks of vulnerable adult abuse registries and child abuse reporting databases
- Boundary Violation Assessment: Detailed review of any charges or allegations involving inappropriate professional relationships
- Substance Abuse Treatment History: Comprehensive evaluation of addiction treatment and recovery status
- Professional Ethics Violations: Review of any ethics complaints or professional conduct violations from other jurisdictions
Mental health professional background checks also include assessment of the applicant's own mental health treatment history. Personal mental health challenges do not automatically disqualify practice but may require ongoing monitoring or practice conditions.
Pharmacy and Controlled Substance Access Screening
Healthcare professionals who handle controlled substances undergo specialized screening through the Drug Enforcement Administration and state controlled substance monitoring programs. This enhanced screening addresses the significant public safety risks associated with controlled substance access and the potential for drug diversion or abuse.
| Position Type | DEA Screening Level | Monitoring Frequency |
| Pharmacist | Comprehensive background + ongoing monitoring | Annual review |
| Pharmacy Technician | Enhanced criminal history + drug offense focus | Bi-annual screening |
| Prescribing Physicians | DEA registration + prescription monitoring | Continuous monitoring |
The controlled substance screening process includes review of any drug-related criminal history. It also includes assessment of prescription monitoring database activity and evaluation of previous DEA registration issues or violations.
Employer Responsibilities and FCRA Compliance
Healthcare employers in California must navigate a complex regulatory landscape. This encompasses federal Fair Credit Reporting Act requirements, state employment discrimination laws, and industry-specific patient safety obligations. FCRA compliance requires specific procedures for disclosure, consent, and adverse action processes.
Essential FCRA Compliance Elements:
- Standalone Disclosure Requirements: Clear, separate documentation that background checks will be conducted for employment purposes
- Written Consent Procedures: Specific applicant authorization for each type of background screening conducted
- Adverse Action Protocols: Proper notice and dispute resolution procedures when background check results influence hiring decisions
- Consumer Reporting Agency Standards: Use of FCRA-compliant background check providers with appropriate certifications
California's additional employment protection laws create additional compliance requirements. These include the Fair Chance Act and local "Ban the Box" ordinances. These state and local laws limit when and how employers can inquire about criminal history. However, exceptions exist for positions requiring professional licensing or involving vulnerable populations.
Disclosure and Consent Procedures
FCRA compliance begins with proper disclosure and consent procedures. These inform applicants about the scope and purpose of background check screening. Healthcare employers must provide clear, standalone disclosure documents. These explain what types of screening will be conducted and how the results may be used in employment decisions.
Required Disclosure Elements:
- Scope of Background Check: Specific types of screening to be conducted (criminal history, education verification, license checks)
- Consumer Reporting Agency Information: Identity and contact information for background check provider
- Applicant Rights: Explanation of FCRA rights including dispute resolution procedures
- Decision Process: How background check results will be evaluated and used in hiring decisions
Consent procedures must ensure that applicants understand and voluntarily agree to background check screening before any investigation begins.
Adverse Action and Appeal Processes
When background check results lead to adverse employment decisions, FCRA requires specific notification and appeal procedures. These give applicants the opportunity to dispute inaccurate information or provide additional context about their background. Healthcare employers must provide pre-adverse action notices. These include copies of background check reports and summary of consumer rights before making final hiring decisions.
The adverse action process includes multiple steps designed to ensure fairness and accuracy in employment decisions. Applicants must receive reasonable time to review background check results and submit disputes or additional information before final adverse action occurs.
Common Disqualifying Factors and Rehabilitation Considerations
California's approach to healthcare background check evaluation emphasizes individualized assessment rather than categorical exclusions. However, certain types of criminal history and professional misconduct receive heightened scrutiny due to patient safety concerns. Common disqualifying factors include violent crimes, sexual offenses, financial crimes involving vulnerable populations, and drug-related felonies.
Primary Risk Categories for Healthcare Practice:
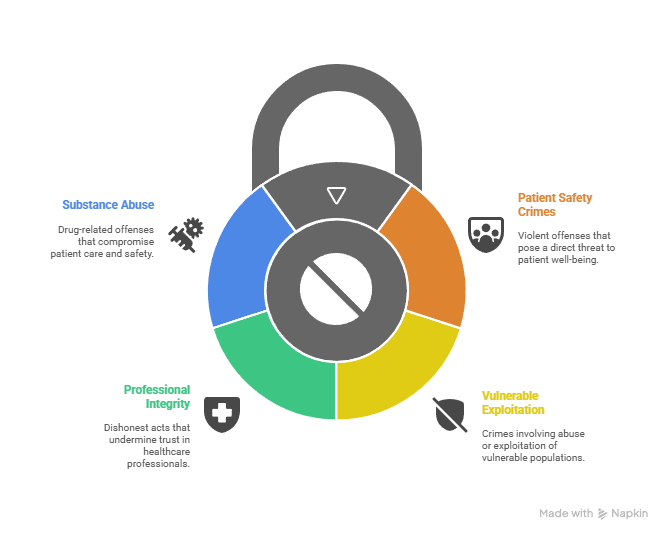
- Patient Safety Crimes: Assault, battery, domestic violence, and other violent offenses that suggest potential danger to patients
- Vulnerable Population Exploitation: Elder abuse, child abuse, dependent adult abuse, or financial exploitation of vulnerable individuals
- Professional Integrity Violations: Healthcare fraud, insurance fraud, identity theft, or other crimes indicating dishonesty
- Substance Abuse Offenses: Drug manufacturing, distribution, or possession with intent to distribute, particularly involving controlled substances
Rehabilitation Assessment Factors:
- Time Since Offense: Demonstration of sustained law-abiding behavior over significant time periods
- Completion of Legal Requirements: Successful completion of probation, parole, community service, and court-ordered programs
- Treatment and Recovery: Participation in substance abuse treatment, mental health counseling, or anger management programs
- Community Integration: Employment history, volunteer service, and community involvement demonstrating positive social reintegration
The rehabilitation assessment process recognizes that individuals can change and deserve opportunities to contribute positively to healthcare delivery.
Criminal History Evaluation Matrix
California healthcare licensing boards have developed sophisticated evaluation matrices. These consider multiple factors when assessing criminal history in relation to healthcare practice fitness. The matrices provide structured approaches to decision-making while allowing for individualized assessment.
| Offense Category | Evaluation Timeframe | Key Assessment Factors |
| Violent Felonies | 10+ years | Patient safety risk, anger management, rehabilitation evidence |
| Financial Crimes | 7-10 years | Trustworthiness, restitution completion, professional integrity |
| Drug Offenses | 5-7 years | Substance abuse treatment, recovery support, ongoing monitoring |
| Professional Misconduct | Case-by-case | Direct practice relevance, corrective action, professional development |
The matrix approach ensures consistent evaluation while recognizing that individual circumstances may warrant deviation from standard guidelines.
Appeals and Remediation Pathways
California provides multiple pathways for healthcare applicants to address background check issues. The appeals process allows applicants to present comprehensive evidence of rehabilitation. This includes documentation of treatment completion, community service, educational achievements, and character references.
Appeals Process Components:
- Administrative Review: Initial review by licensing board staff with authority to approve straightforward cases
- Board Hearing: Formal hearing before licensing board members for complex cases requiring detailed evaluation
- Conditional Licensure: Approval with practice conditions such as supervision, monitoring, or continuing education requirements
- Probationary Status: Limited-term licensure with regular review and compliance monitoring
The appeals process emphasizes applicant responsibility for demonstrating rehabilitation and current fitness.
Processing Timelines and Expedited Procedures
California healthcare background check processing timelines vary significantly. This is based on the complexity of applicant backgrounds, the specific licensing board involved, and current application volumes. Standard processing times range from 4-16 weeks for most healthcare licenses. Additional time is required for complex cases involving criminal history, out-of-state credentials, or international education.
Standard Processing Timeline Factors:
- Application Completeness: Complete applications with all required documentation process significantly faster
- Criminal History Complexity: Cases involving criminal records require additional investigation time
- Multi-State Verification: Applicants with education or practice history in multiple states face longer processing times
- International Credentials: Foreign-educated healthcare professionals require additional time for credential authentication
- Licensing Board Workload: Processing times fluctuate based on application volume and licensing board staffing levels
Expedited Processing Criteria:
- Critical Shortage Areas: Geographic regions or medical specialties experiencing severe healthcare workforce shortages
- Emergency Response Personnel: Healthcare professionals needed for disaster response or public health emergencies
- Military Spouse Considerations: Expedited processing for military spouses relocating to California
- Interstate Compact Participants: Streamlined procedures for licenses covered by interstate professional compacts
Factors Affecting Processing Speed
Multiple factors influence the speed of California healthcare background check processing. Application completeness and background complexity serve as primary determinants. Complete applications submitted with all required documentation, fees, and supporting materials process more quickly than those requiring follow-up correspondence.
Background complexity represents another major factor affecting processing speed. Clean backgrounds process through automated systems much faster than those requiring individual review and investigation. Criminal history, disciplinary actions, malpractice claims, or gaps in education or employment history all trigger additional review procedures.
External factors beyond applicant control also affect processing speed. These include licensing board staffing levels, application volume fluctuations, and coordination with other regulatory agencies.
Emergency and Critical Shortage Procedures
California has developed emergency and critical shortage procedures. These allow for expedited healthcare background check processing during urgent situations while maintaining essential safety standards. These procedures activate during declared emergencies, significant healthcare workforce shortages, or other circumstances where delayed licensing could impact public health and safety.
Emergency procedures may include temporary practice authorizations for qualified applicants while comprehensive background checks continue. They also include enhanced coordination between licensing boards and regulatory agencies to accelerate verification processes.
Critical shortage procedures recognize ongoing workforce challenges in certain medical specialties or geographic regions. They provide streamlined pathways for qualified professionals to enter practice more quickly.
Conclusion
California healthcare background check requirements represent a sophisticated regulatory framework. This balances rigorous patient safety protections with fair employment practices and rehabilitation opportunities. The Department of Consumer Affairs and individual licensing boards have created comprehensive screening procedures. These evaluate criminal history, professional conduct, and clinical competency while providing pathways for qualified individuals with past challenges to pursue meaningful healthcare careers. The state's emphasis on individualized assessment and rehabilitation recognition demonstrates a progressive approach that protects patients while supporting workforce development.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do California healthcare background checks take to complete?
California healthcare background checks typically take 2-8 weeks to complete, depending on the specific license type and complexity of the applicant's background. LiveScan fingerprinting results are usually available within 3-5 business days, but comprehensive reviews by licensing boards can extend the timeline, particularly for applicants with criminal history or out-of-state credentials.
Can I get a California nursing license with a criminal record?
Yes, you may still qualify for a California nursing license with a criminal record, as the state considers rehabilitation efforts and the relationship between offenses and nursing practice. The Board of Registered Nursing and Board of Vocational Nursing evaluate each case individually, considering factors such as the nature of the offense, time elapsed, and evidence of rehabilitation.
What crimes automatically disqualify healthcare workers in California?
California does not maintain a list of crimes that automatically disqualify healthcare workers, instead using an individualized assessment approach. However, violent crimes, sexual offenses, drug trafficking, and crimes involving patient abuse or professional misconduct receive heightened scrutiny and may result in license denial or employment disqualification.
Do California healthcare employers have to follow FCRA guidelines?
Yes, California healthcare employers must comply with Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) guidelines when conducting background checks, including providing proper disclosure, obtaining written consent, and following adverse action procedures. They must also comply with California's Fair Chance Act, which provides additional protections for applicants with criminal histories.
How often are healthcare background checks renewed in California?
Healthcare background check renewal requirements vary by profession and employer, with most licensing boards requiring updates every 2-4 years during license renewal. Some healthcare facilities conduct annual background check updates, while positions involving vulnerable populations may require more frequent screening.
What should I do if my California healthcare background check contains errors?
If your background check contains errors, immediately contact the background check provider to initiate a dispute process under FCRA guidelines. You should also notify the licensing board or employer and provide documentation supporting the correction. The background check company must investigate and correct any verified errors within 30 days.
Additional Resources
- California Department of Consumer Affairs - Healthcare Licensing Information
https://www.dca.ca.gov/ - California Board of Registered Nursing - License Application Guidelines
https://www.rn.ca.gov/ - Medical Board of California - Physician Licensing Requirements
https://www.mbc.ca.gov/ - Fair Credit Reporting Act Compliance Guide for Employers
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/using-consumer-reports-what-employers-need-know - California Fair Chance Act - Employment Background Check Regulations
https://www.dfeh.ca.gov/fairchance/ - LiveScan Fingerprinting Locations and Requirements
https://oag.ca.gov/fingerprints/locations - California Employment Development Department - Background Check Guidelines
https://edd.ca.gov/ - Board of Vocational Nursing and Psychiatric Technicians - LVN Licensing
https://www.bvnpt.ca.gov/

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





