California dental practices must navigate a complex web of state-specific screening requirements that extend far beyond standard background checks, including Dental Board of California regulations, OSHA bloodborne pathogen standards, and state employment law provisions that directly impact patient safety and practice liability. Understanding these specialized requirements is essential for dental office managers and practice owners who face potential penalties, malpractice exposure, and patient trust violations when hiring staff without proper verification protocols.
Key Takeaways
- California dental practices must comply with Dental Board of California regulations requiring criminal background checks for registered dental assistants (RDA) and registered dental assistants in extended functions (RDAEF) through Live Scan fingerprinting.
- Office managers should implement multi-layered screening that includes credential verification, criminal history review, reference checks, and drug testing to meet healthcare industry standards and reduce liability exposure.
- The California Fair Chance Act limits how employers can use criminal history in hiring decisions, requiring individualized assessments and specific timing for background check inquiries.
- Dental practices must verify professional licenses through the Dental Board of California's online portal and confirm that dental hygienists, RDAs, and RDAEFs maintain current, unrestricted credentials.
- FCRA compliance requires dental practices to obtain written authorization before conducting background checks, provide pre-adverse action notices, and follow specific procedures before rejecting candidates based on screening results.
- Practices hiring unlicensed dental assistants face fewer regulatory screening requirements but should still conduct thorough background checks to protect patients and minimize negligent hiring liability.
- Annual re-screening of existing employees helps dental practices identify license suspensions, criminal convictions, or other issues that could compromise patient safety or practice reputation.
- Understanding the distinction between direct patient care roles and administrative positions allows practices to implement risk-appropriate screening protocols that balance thoroughness with cost-effectiveness.
Understanding California's Unique Dental Assistant Screening Landscape
California operates under one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks for dental professionals in the United States. Unlike many states with minimal oversight of dental support staff, California requires specific categories of dental assistants to obtain state registration. This registration triggers mandatory screening requirements that dental practices must understand before extending employment offers.
The Dental Board of California oversees approximately 150,000 licensed professionals, including dentists, registered dental assistants, dental hygienists, and other auxiliary personnel. This regulatory authority extends beyond initial licensing to encompass employment verification responsibilities. These responsibilities fall directly on dental practice owners and office managers who hire and supervise dental staff.
The Three-Tier Regulatory Framework
Three primary regulatory bodies govern screening requirements for California dental practices. First, the Dental Board of California establishes profession-specific standards for registered positions. Second, the California Department of Public Health enforces infection control and safety protocols. Third, the California Department of Fair Employment and Housing oversees employment discrimination and fair chance hiring laws.
This multi-agency oversight creates compliance challenges that generic background check services often fail to address. Dental office hiring background checks must satisfy healthcare-specific standards while respecting candidate rights. California's employee-friendly legal environment adds additional layers of complexity to the screening process.
Why Specialized Dental Screening Matters
Dental assistants handle sensitive patient information and access controlled substances. They operate sterilization equipment and work in close proximity to vulnerable populations. These populations include children, elderly patients, and immunocompromised individuals who require additional safety protections.
A 2024 Dental Economics survey found that 73% of dental practices experienced at least one hiring-related challenge in the previous year. Credential verification issues and background check delays ranked among the top concerns. Improper screening exposes practices to negligent hiring liability, which occurs when an employer fails to exercise reasonable care. California courts have awarded substantial damages in negligent hiring cases, particularly when employers ignored red flags or failed to conduct industry-standard background verification.
Mandatory Screening for Registered Dental Assistants
California law creates distinct credential categories for dental assistants, each with different screening requirements. Registered Dental Assistants (RDA) and Registered Dental Assistants in Extended Functions (RDAEF) must complete state-approved education programs. They must pass written and practical examinations. They must also submit to criminal background checks before the Dental Board issues registration. Understanding these requirements prevents costly hiring mistakes and regulatory violations.
Live Scan Fingerprinting Requirements
The Dental Board of California requires RDA and RDAEF applicants to complete Live Scan fingerprinting. This process involves submission through the California Department of Justice and FBI databases. The fingerprinting generates a comprehensive criminal history report that the Board reviews before granting registration.
Applicants with certain criminal convictions face potential denial or conditional approval with practice restrictions. Dental practices should verify that RDA and RDAEF candidates have completed this process successfully. Always check registration status through the Dental Board's online license verification portal before hiring.
Credential Verification Best Practices
The Dental Board of California maintains a public database accessible at dbc.ca.gov that allows employers to verify licenses in real-time. Office managers should verify credentials before the first day of employment. Documentation of verification dates should be maintained in personnel files. This creates an audit trail that demonstrates compliance with healthcare industry standards.
When verifying credentials, dental practices should check for five critical elements:
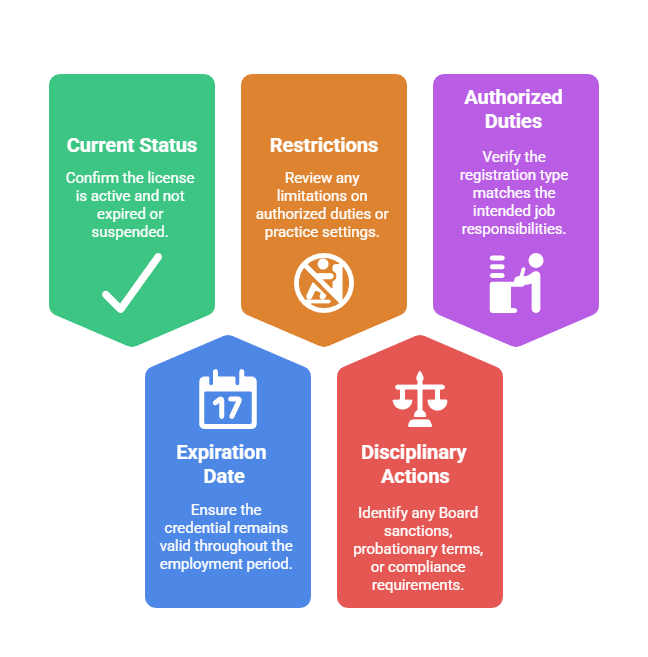
- Current registration status: Confirm the license is active and not expired or suspended
- Expiration date: Ensure the credential remains valid throughout the employment period
- License restrictions or conditions: Review any limitations on authorized duties or practice settings
- Disciplinary actions: Identify any Board sanctions, probationary terms, or compliance requirements
- Authorized duties scope: Verify the registration type matches the intended job responsibilities
Some dental assistants hold registrations from other states and assume California will recognize their credentials. California does not participate in dental assistant interstate compacts. This means out-of-state registered assistants must complete California's separate registration process, including new background screening through Live Scan fingerprinting.
Background Check Requirements for Unlicensed Dental Assistants
California permits dental practices to hire unlicensed dental assistants who perform basic supportive duties under direct dentist supervision. These positions include reception, appointment scheduling, basic chairside assistance, and sterilization tasks. While the Dental Board doesn't mandate specific screening for unlicensed assistants, dental practice owners should implement comprehensive background checks to protect patients and reduce liability.
Essential Components of Unlicensed Assistant Screening
A thorough background check for unlicensed dental assistants should include multiple verification layers. Start with seven-year criminal history searches at county and state levels. Add verification of identity and employment eligibility through I-9 documentation. Include reference checks with previous healthcare employers who can speak to job performance and patient interaction skills.
Education verification for claimed diplomas or certificates ensures candidates possess the foundational knowledge they claim. Drug screening for positions involving equipment operation or controlled substance proximity adds another safety layer. These combined screenings create a comprehensive profile that helps practices make informed hiring decisions.
Criminal history searches should focus on offenses relevant to patient safety and healthcare settings. Theft or fraud convictions suggest potential dishonesty with patient information or practice finances. Violent crimes indicate possible patient safety risks. Drug-related offenses matter for positions with controlled substance access. Crimes of moral turpitude can undermine patient trust and practice reputation.
California Fair Chance Act Compliance
The California Fair Chance Act restricts when employers can inquire about criminal history. It also limits how they can use conviction information in hiring decisions. Dental practices cannot ask about criminal history on initial applications. They must wait until after making a conditional employment offer to conduct criminal background checks.
When a background check reveals disqualifying information, practices must follow a specific five-step process:
| Step | Required Action | Timing |
| 1. Provide background report | Send candidate a copy of the full background check | Immediately upon receipt |
| 2. Pre-adverse action notice | Deliver written notice explaining the disqualifying information | Same time as report |
| 3. Candidate response period | Allow time for candidate to provide clarifying information | Minimum 5 business days |
| 4. Individualized assessment | Consider offense nature, time elapsed, and job relationship | Before final decision |
| 5. Final adverse action notice | Provide written notice if proceeding with rejection | After assessment completion |
This process protects candidate rights while allowing employers to make informed decisions. Documentation of each step demonstrates compliance with California employment law. It also provides evidence of reasonable care in the hiring process.
Dental Board Background Check Requirements and Ongoing Monitoring

The Dental Board of California maintains continuing jurisdiction over registered dental professionals throughout their careers. Understanding these ongoing dental board background check requirements helps practices avoid hiring professionals with hidden disciplinary issues. License restrictions can create patient safety risks and regulatory violations that expose practices to liability.
Primary Source Verification Standards
Healthcare accreditation bodies and professional liability insurers require primary source verification for all licensed staff. This means confirming credentials directly with the issuing agency rather than relying on candidate-provided documentation. Primary source verification protects practices from resume fraud and ensures staff qualifications meet regulatory standards.
For dental practices, primary source verification includes four essential checks:
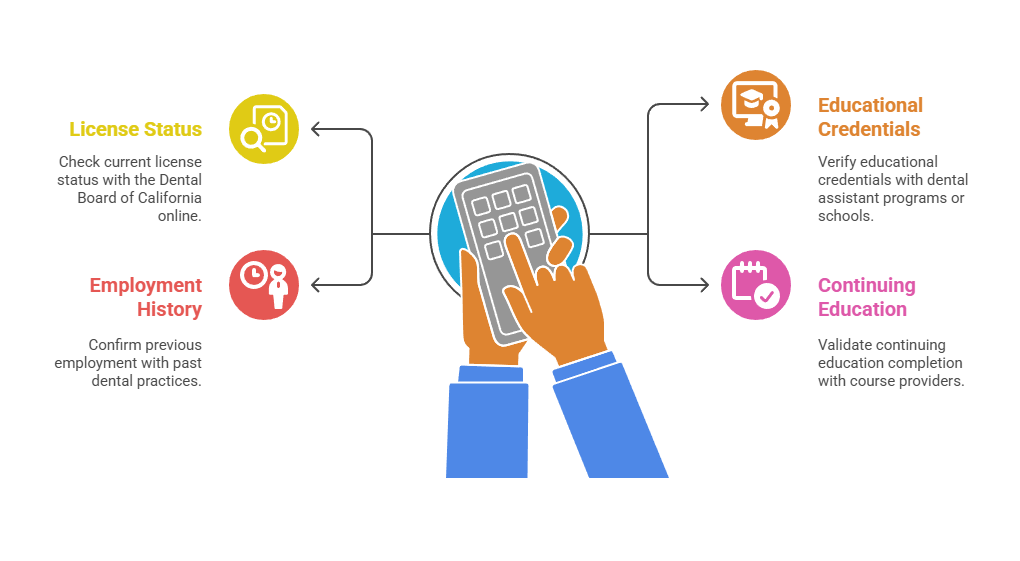
- Checking current license status with the Dental Board of California through the official online portal
- Verifying educational credentials with dental assistant programs, community colleges, or dental schools
- Confirming previous employment with past dental practices to validate experience claims
- Validating continuing education completion with course providers to ensure compliance with renewal requirements
The Dental Board's online verification system provides instant access to licensure information. However, it may not reflect pending investigations or recent complaints under review. Consider requesting comprehensive license history reports for finalists in hiring processes. This additional step matters particularly for positions involving extensive patient contact or controlled substance access.
Annual Re-Screening Protocols
Leading dental practices implement annual re-screening protocols for all patient-facing staff. This ongoing monitoring identifies license suspensions, new criminal convictions, or disciplinary actions. These issues can occur after initial hiring and may go undetected without systematic review processes.
The California Dental Practice Act allows the Board to suspend or revoke licenses based on several post-registration factors. Substance abuse issues, unprofessional conduct, and conviction of crimes substantially related to dental practice all trigger potential disciplinary action. Practice owners and office managers should establish calendar reminders to re-verify licenses 30 days before expiration dates. Review Dental Board disciplinary action reports quarterly and conduct annual criminal background updates for staff in positions of trust.
FCRA Compliance for Dental Practice Background Checks
The federal Fair Credit Reporting Act governs how employers use consumer reporting agencies for background checks. California dental practices using third-party screening services must comply with FCRA requirements. Violations can result in statutory damages up to $1,000 per violation plus attorney fees. Understanding these requirements protects practices from costly litigation and regulatory penalties.
Authorization and Disclosure Requirements
Before ordering background checks through consumer reporting agencies, dental practices must provide candidates with specific documentation. First, provide a clear and conspicuous written disclosure that a background report may be obtained for employment purposes. This disclosure must appear as a standalone document—not buried within employment applications or offer letters.
Candidates must provide written authorization before the practice orders background reports. California law adds extra requirements beyond federal FCRA standards. The disclosure must include a checkbox where candidates can request a copy of any background report. Practices must also notify applicants that records may be checked through federal and state criminal justice databases. These additional requirements demonstrate California's commitment to candidate rights and transparency in hiring.
Adverse Action Procedures
When background check results lead to rejection of a candidate, FCRA requires a specific adverse action process. Dental practices must provide a pre-adverse action notice. This notice must include a copy of the background check report. It must also include the FTC's "Summary of Your Rights Under the FCRA."
After allowing reasonable time for the candidate to dispute inaccuracies (five business days under California law), the practice can proceed with final action. The final adverse action notice must identify the consumer reporting agency used. It must clarify that the agency didn't make the adverse decision. It must explain the candidate's right to dispute report accuracy within 60 days.
Many dental practices violate FCRA by failing to provide proper pre-adverse action notice. Others reject candidates immediately upon receiving unfavorable background reports. These violations expose practices to statutory damages and attorney fees. They also create potential discrimination claims if adverse actions disproportionately affect protected classes.
Drug Screening and Health Clearances for Dental Staff
Dental practices operate as healthcare facilities subject to OSHA bloodborne pathogen standards and infection control protocols. These requirements create legitimate grounds for pre-employment drug screening and health clearances. Such screenings extend beyond typical employment screening to address specific healthcare environment risks.
Legal Drug Testing Standards in California
California generally allows pre-employment drug testing for positions involving safety-sensitive duties. Equipment operation and controlled substance access qualify as safety-sensitive functions. Dental assistant positions typically meet these criteria due to instrument handling and infection control responsibilities. Patient care involvement further supports drug testing justification.
Dental practices should implement consistent drug screening policies applied to all candidates for similar positions. The policy should specify tested substances using standardized panels. It should explain testing methodology and laboratory standards. It should outline consequences of positive results and prescription medication disclosure procedures. Always obtain candidate consent before drug testing. Use certified laboratories that follow chain-of-custody protocols to ensure result accuracy and legal defensibility.
Health Screening and Immunization Verification
California requires healthcare workers to provide proof of immunity or vaccination against specific diseases. Measles, pertussis, and influenza (during flu season) requirements apply under defined conditions. Dental practice employee verification should include documentation of immunity and vaccination status to protect patients and staff.
Required health documentation includes four core elements:
| Immunization/Screening | Requirement | Documentation |
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) | Proof of immunity | Vaccination records or titer test results |
| Pertussis (Tdap) | Within past 10 years | Vaccination record with date |
| Influenza | Annual during flu season | Current year vaccination or declination form |
| Tuberculosis | Baseline at hire | TB test results (PPD or blood test) |
Some dental practices require hepatitis B vaccination documentation. However, this vaccine is offered post-hire under OSHA bloodborne pathogen standards. It is not required as a pre-employment condition. Document all health screening results in confidential medical files separate from general personnel records. This maintains compliance with ADA confidentiality requirements and protects employee privacy.
Creating Compliant Screening Policies for California Dental Practices
Developing written screening policies protects dental practices from discrimination claims. It ensures consistent application of hiring standards. It demonstrates reasonable care in negligent hiring defense scenarios. Effective dental practice staff background verification policies balance thoroughness with legal compliance while remaining practical for daily operations.
A comprehensive screening policy should address eight key components. First, identify which positions require background checks and what type of screening applies to each role. Second, establish timing of background checks in the hiring process. Third, define criminal conviction categories that create disqualification. Fourth, outline individualized assessment procedures for candidates with criminal history.
Fifth, specify credential verification requirements and re-verification schedules. Sixth, detail drug testing protocols and circumstances. Seventh, establish reference check procedures and documentation requirements. Eighth, assign responsibility for policy implementation and compliance monitoring. Document your policy rationale by connecting screening requirements to legitimate business needs. Patient safety, regulatory compliance, controlled substance security, and liability management all support screening policies. This documented rationale supports legal defensibility if candidates challenge screening practices.
Staff Training and Implementation
Office managers responsible for hiring should receive training on compliance requirements. Training topics should include California Fair Chance Act requirements and FCRA adverse action procedures. Cover appropriate interview questions about criminal history (none until after conditional offers). Address discriminatory screening practices to avoid and confidential handling of background check information.
Create standardized workflows that ensure consistent screening application across all candidates. Use checklists to verify that each hiring step complies with legal requirements:
- Application review: Conduct without criminal history questions or inquiries
- Interview process: Avoid prohibited inquiries about arrests, convictions, or incarceration
- Conditional offer letter: Clearly state employment is contingent on screening results
- Authorization forms: Ensure FCRA and California requirement compliance
- Adverse action process: Follow proper procedures if screening reveals disqualifying information
These standardized workflows reduce compliance errors. They create consistency across hiring managers. They generate documentation that demonstrates good-faith compliance efforts in case of legal challenges.
Common Screening Mistakes California Dental Practices Must Avoid
Even well-intentioned dental practices make screening errors that create legal liability or allow problematic hires. Understanding these common mistakes helps office managers implement more effective background verification protocols. Avoiding these pitfalls protects practices from regulatory penalties and negligent hiring claims.
Common screening violations include:
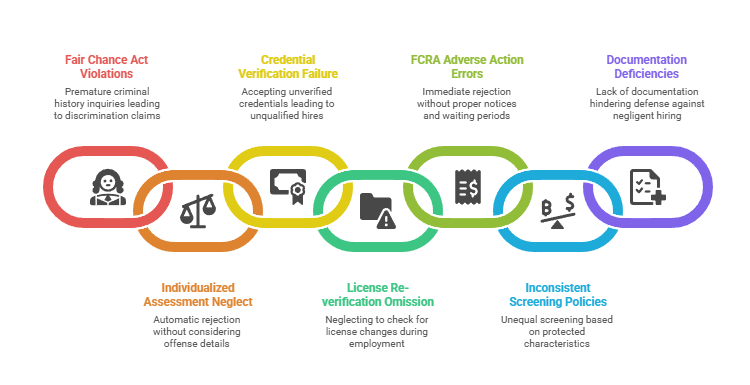
- Premature criminal history inquiries: Asking about criminal background on applications or during interviews before conditional offers violates California's Fair Chance Act and exposes practices to discrimination claims.
- Skipping individualized assessments: Automatically rejecting candidates with criminal records without considering offense nature, time elapsed, and job relationship violates state law and requires documented analysis for each case.
- Relying on candidate-provided credentials: Accepting license copies or certificates without verifying through the Dental Board of California or educational institutions allows resume fraud and hiring of unqualified staff.
- Failing to re-verify licenses: Never checking credentials after initial hire misses license suspensions, restrictions, or disciplinary actions that occur during employment and violate regulatory requirements.
- Inadequate FCRA adverse action procedures: Rejecting candidates immediately after receiving background reports without proper pre-adverse action notices and waiting periods creates statutory liability up to $1,000 per violation.
- Inconsistent policy application: Screening some candidates more thoroughly than others based on protected characteristics rather than position requirements creates discrimination exposure and undermines legal defensibility.
- Poor documentation practices: Failing to document screening decisions, individualized assessments, or policy rationale leaves practices unable to demonstrate reasonable care in negligent hiring defense scenarios.
Time pressure and staffing shortages tempt practices to cut corners, but the risks far outweigh short-term conveniences. Implement quarterly license verification checks for all registered staff and document reviews in personnel files. These systematic processes demonstrate ongoing commitment to patient safety and regulatory compliance that protects practice reputation and financial stability.
Conclusion
California dental assistant screening requirements demand specialized knowledge that extends beyond generic background check services. Dental practice owners and office managers must balance comprehensive screening protocols with California's employee-protective laws. Multi-layered verification satisfies Dental Board regulations, FCRA requirements, and fair chance hiring standards simultaneously. By establishing written policies, conducting primary source credential verification, following proper adverse action procedures, and implementing ongoing monitoring protocols, dental practices protect patients and reduce liability exposure. The investment in thorough, compliant screening processes pays dividends through reduced turnover, stronger patient safety, and demonstrated commitment to regulatory compliance that protects practice reputation and financial stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What background checks are required for dental assistants in California?
Registered Dental Assistants (RDA) and Registered Dental Assistants in Extended Functions (RDAEF) must complete Live Scan fingerprinting through the California Department of Justice and FBI as part of their credential application process. Unlicensed dental assistants are not subject to mandatory state background checks. However, dental practices should conduct thorough screening including criminal history searches, reference checks, and credential verification to ensure patient safety and reduce negligent hiring liability.
Can California dental practices ask about criminal history on job applications?
No, the California Fair Chance Act prohibits employers from inquiring about criminal history on initial job applications or during preliminary interviews. Dental practices must wait until after making a conditional employment offer before asking about criminal background or conducting background checks. When criminal history is discovered, employers must conduct an individualized assessment considering the nature of the offense, time elapsed, and relationship to job duties before making final hiring decisions.
How often should dental practices verify employee licenses and credentials?
Dental practices should verify professional licenses through the Dental Board of California's online portal before the first day of employment and conduct re-verification at least annually thereafter. Since California dental licenses renew every two years, quarterly verification checks help identify suspensions, restrictions, or disciplinary actions that occur between renewal periods. Document all verification activities in personnel files to demonstrate ongoing compliance with healthcare industry standards.
What disqualifies someone from working as a dental assistant in California?
The Dental Board of California may deny RDA or RDAEF registration based on criminal convictions substantially related to dental practice duties, including crimes involving dishonesty, fraud, theft, substance abuse, or violence. For unlicensed dental assistants, individual dental practices establish their own disqualification criteria within legal limits. Most practices exclude candidates with recent violent offenses, theft convictions, or drug-related crimes for positions involving controlled substance access.
Do California dental practices need FCRA compliance for background checks?
Yes, dental practices using third-party consumer reporting agencies for background checks must comply with federal Fair Credit Reporting Act requirements. This includes providing standalone written disclosure before obtaining reports, securing written candidate authorization, following specific adverse action procedures when background information leads to rejection, and providing candidates with copies of reports and notices of rights. FCRA violations can result in statutory damages of up to $1,000 per violation plus attorney fees.
Are drug tests required for dental assistant positions in California?
California law does not mandate pre-employment drug testing for dental assistants, but dental practices may require drug screening for positions involving safety-sensitive duties, equipment operation, or controlled substance access. Drug testing policies must be applied consistently to all candidates for similar positions, require candidate consent, and use certified laboratories. Always document legitimate business justifications for drug testing requirements to demonstrate compliance with California employment law.
How should dental practices handle candidates with criminal records?
After discovering criminal history through post-conditional offer background checks, California dental practices must conduct individualized assessments before rejecting candidates. Consider the nature and severity of the offense, time elapsed since conviction or sentence completion, evidence of rehabilitation, and the relationship between criminal conduct and specific job duties. Provide written pre-adverse action notices, allow at least five business days for candidates to respond, and document the assessment process to demonstrate compliance with fair chance hiring laws.
What credentials must California dental hygienists and RDAs maintain?
Registered Dental Hygienists must hold current California dental hygiene licenses issued by the Dental Board of California, renewed every two years. Registered Dental Assistants and Registered Dental Assistants in Extended Functions must maintain current registration with the Dental Board, also renewed biennially. All registered professionals must complete continuing education requirements, maintain current CPR certification, and comply with infection control training standards to ensure licenses remain active and unrestricted.
Additional Resources
- Dental Board of California License Verification Portal
https://www.dbc.ca.gov/lookup.shtml - California Fair Employment and Housing Council Fair Chance Act Regulations
https://calcivilrights.ca.gov/fair-chance-act/ - Federal Trade Commission FCRA Compliance Guide for Employers
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/using-consumer-reports-what-employers-need-know - California Dental Practice Act (Business and Professions Code Division 2, Chapter 4)
https://www.dbc.ca.gov/lawsregs/dpa.shtml - OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard for Dental Settings
https://www.osha.gov/bloodborne-pathogens - California Department of Justice Live Scan Information
https://oag.ca.gov/fingerprints/locations

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





