Agricultural worker background checks are essential compliance requirements during harvest season. Employers must follow H-2A visa regulations, state-specific screening mandates, and FCRA guidelines when hiring seasonal farm workers. Proper implementation of agricultural hiring compliance programs protects both employers and workers while ensuring regulatory adherence across federal and state jurisdictions.
Key Takeaways
- Agricultural worker background checks must comply with H-2A visa requirements, state regulations, and Fair Credit Reporting Act provisions for seasonal hiring programs.
- Farm worker screening requirements vary significantly by state, with some requiring criminal history checks while others mandate drug testing and employment verification procedures.
- Harvest season employee checks should be initiated 30-45 days before seasonal work begins to accommodate processing delays and documentation requirements.
- Migrant worker background screening involves additional federal oversight, including Form I-9 verification and potential Department of Labor reporting obligations.
- Agricultural hiring compliance programs reduce liability exposure while improving worker retention rates and workplace safety standards during peak harvest periods.
- Staffing agencies specializing in agricultural placements must maintain separate compliance protocols for temporary worker screening versus direct-hire employee background checks.
As harvest season approaches, agricultural employers face mounting pressure to secure reliable workforce solutions. They must maintain strict compliance standards during this critical period. The intersection of federal immigration law, state employment regulations, and industry-specific safety requirements creates a complex landscape for farm worker screening requirements. Understanding these obligations is crucial for agricultural operations seeking to protect their business interests and maintain operational continuity during critical harvest periods.
Agricultural operations depend heavily on seasonal labor during peak harvest times. The temporary nature of this work creates unique challenges for background screening programs. Employers must balance thorough due diligence with operational urgency while often requiring expedited processing options and contingency planning for screening delays. The consequences of inadequate screening can be severe for agricultural employers, as poor hiring decisions during harvest season can disrupt operations and create safety hazards.
Compliance failures may result in federal penalties and program suspensions. These risks make comprehensive agricultural worker background checks an essential business practice. Modern agricultural operations increasingly rely on migrant workers and H-2A visa holders, requiring specialized screening approaches and enhanced documentation requirements. Understanding the regulatory framework governing these programs is essential for compliance success and operational sustainability during critical harvest periods.
Understanding Federal H-2A Visa Background Check Requirements
The H-2A temporary agricultural worker program serves as the primary legal pathway for hiring foreign seasonal workers in American agriculture. Federal regulations mandate specific screening protocols that extend beyond basic employment verification procedures. These requirements include criminal background investigations, employment history validation, and ongoing compliance monitoring throughout the worker's authorized stay.
Under current Department of Labor guidelines, employers must demonstrate that domestic workers are unavailable before accessing H-2A labor pools. This process involves advertising positions through state workforce agencies and maintaining detailed records of recruitment efforts. Additionally, employers must provide housing, transportation, and guarantee minimum work hours as specified in their labor certification applications. Agricultural operations utilizing H-2A workers face enhanced scrutiny from federal agencies, including potential worksite inspections and audit procedures.
Documentation and Record-Keeping Standards
H-2A employers must maintain comprehensive personnel files for each worker, including original visa documentation, housing inspection reports, and wage payment records. These files remain subject to federal inspection for three years following the worker's departure.
Record-keeping requirements extend beyond basic employment documentation to include detailed recruitment records showing efforts to hire domestic workers. Transportation and housing records must demonstrate compliance with federal standards, while wage records must show payment of prevailing wages and required benefits.
State-Specific Farm Worker Screening Regulations

Agricultural hiring compliance varies dramatically across different states, with some jurisdictions imposing minimal requirements while others mandating comprehensive background investigations. California requires agricultural employers to conduct criminal history checks for workers handling pesticides or operating heavy machinery. Texas focuses primarily on immigration status verification and basic safety training documentation. Understanding regional variations becomes critical during harvest season when agricultural operations frequently recruit workers from multiple states.
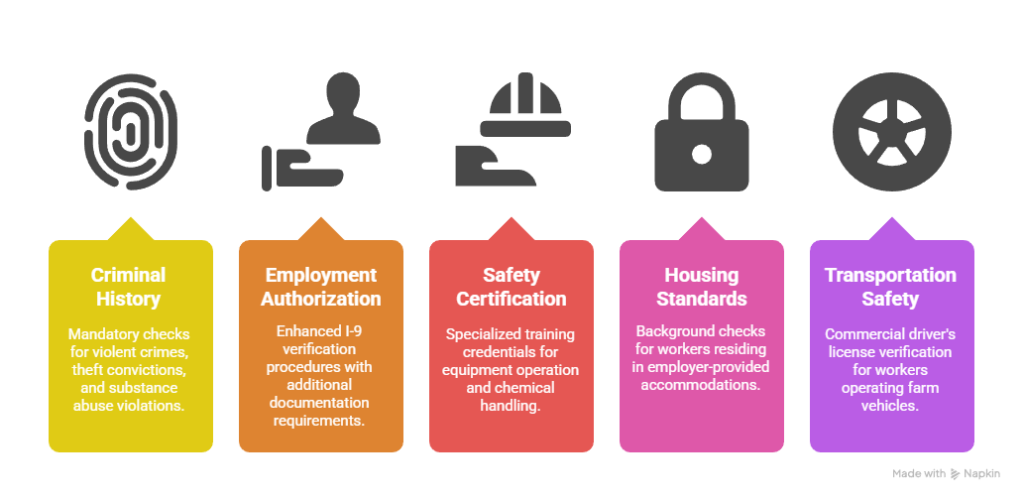
- Criminal History Verification: Mandatory checks for violent crimes, theft convictions, and substance abuse violations in most agricultural states
- Employment Authorization: Enhanced I-9 verification procedures with additional documentation requirements beyond federal minimums
- Safety Certification: Specialized training credentials for equipment operation and chemical handling specific to agricultural applications
- Housing Standards: Background checks for workers residing in employer-provided accommodations with enhanced tenant screening requirements
- Transportation Safety: Commercial driver's license verification for workers operating farm vehicles and equipment transport
Compliance with state-specific regulations often requires engaging local background screening providers familiar with jurisdictional requirements. This approach ensures accurate interpretation of applicable laws while maintaining processing efficiency during peak hiring periods.
Implementing Effective Harvest Season Employee Screening Programs
Successful agricultural worker background check programs require careful planning and early implementation to accommodate seasonal hiring timelines. Most background investigations require 7-14 business days for completion, though complex cases involving multiple jurisdictions may extend processing times significantly. Early initiation of screening procedures prevents last-minute compliance issues that could disrupt harvest operations.
| Screening Component | Timeline | Cost Range | Compliance Impact |
| Criminal History Check | 3-7 days | $15-$45 | Federal/State Required |
| Employment Verification | 5-10 days | $25-$60 | H-2A Mandatory |
| Drug Testing | 1-3 days | $30-$80 | State Dependent |
| Reference Verification | 7-14 days | $20-$50 | Best Practice |
Agricultural employers should establish standardized screening protocols that apply consistently across all seasonal hires. This approach ensures equal treatment of applicants while simplifying compliance monitoring and audit preparation.
Technology Integration and Digital Workflows
Modern background screening platforms offer integrated solutions specifically designed for agricultural seasonal hiring. These systems provide automated workflow management, compliance tracking, and real-time status updates that streamline high-volume processing during peak recruitment periods.
Migrant Worker Background Screening Compliance
Migrant worker populations present unique challenges for agricultural background screening programs due to limited credit histories, frequent address changes, and potential language barriers. Traditional screening methods may prove inadequate for workers who have lived in multiple states or countries. These circumstances require specialized investigation techniques and alternative verification sources to ensure comprehensive risk assessment.
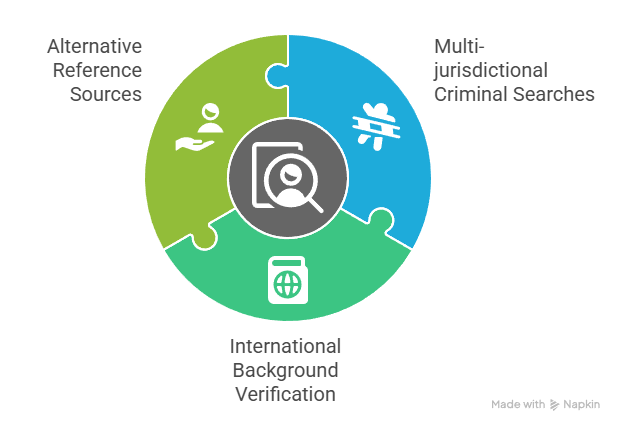
- Multi-jurisdictional Criminal Searches: Comprehensive coverage of previous residence locations and work sites across state boundaries requiring coordination with multiple court systems and law enforcement agencies. These searches often involve manual research processes that extend processing times but provide essential coverage for transient worker populations. Specialized vendors with multi-state capabilities typically deliver more accurate and complete results than standard screening providers.
- International Background Verification: Coordination with foreign agencies when workers have recent overseas residence requiring specialized protocols and extended processing timelines. This process often involves translation services and understanding of different legal systems and documentation practices. Cultural competency becomes essential when interpreting results from international background investigations.
- Alternative Reference Sources: Community organizations, religious institutions, and agricultural cooperatives familiar with workers providing verification support when traditional employment references are unavailable. These sources often maintain closer relationships with seasonal workers than conventional employers. Professional outreach and relationship-building with these organizations improves reference quality and verification accuracy.
These enhanced procedures require additional time and resources but provide essential protection against compliance violations and workplace safety risks. The investment in comprehensive screening typically generates positive returns through improved safety records and reduced turnover rates.
Cultural Sensitivity in Screening Procedures
Effective migrant worker screening requires cultural competency and sensitivity to diverse backgrounds and experiences. Screening professionals should receive training on cultural differences that may impact background investigations, including naming conventions, documentation availability, and communication styles.
Seasonal Timing and Workflow Management
Harvest season scheduling creates compressed timeframes that challenge traditional background screening workflows. Agricultural employers must balance thorough due diligence with operational urgency, often requiring expedited processing options and contingency planning for screening delays. Strategic planning and early engagement with screening providers can mitigate these timing pressures effectively while maintaining compliance standards throughout the hiring process.
Emergency Hiring Procedures
Agricultural operations occasionally face emergency hiring situations during harvest season when workers leave unexpectedly or additional labor becomes necessary. These situations require expedited screening procedures that maintain compliance standards while accommodating operational urgency.
Emergency hiring protocols may include expedited screening options with higher processing fees and conditional employment offers subject to satisfactory background check completion. These approaches require careful legal review to ensure compliance with applicable employment laws and screening regulations.
Cost Management and Budget Planning for Agricultural Background Checks
Agricultural operations face unique cost pressures when implementing comprehensive background screening programs for seasonal workers. The temporary nature of harvest employment creates challenges in justifying screening expenses compared to permanent employee hiring costs. However, proper budget planning can optimize screening investments while maintaining necessary compliance standards throughout the organization.
Cost-effective screening approaches focus on risk-based assessments that prioritize higher-level checks for positions with greater responsibility or safety implications. Entry-level field workers may require only basic criminal history and eligibility verification, while equipment operators and supervisory personnel undergo more comprehensive investigations. This tiered approach balances cost control with appropriate risk management strategies while maintaining regulatory compliance across all worker categories.
Volume pricing arrangements with screening providers can significantly reduce per-unit costs for large seasonal hiring programs. Many providers offer graduated pricing scales based on annual screening volumes, often including additional services such as expedited processing and dedicated account management. Long-term contracts may provide additional cost savings and service guarantees during peak demand periods when screening capacity becomes constrained across the agricultural industry.
Return on Investment Analysis
Comprehensive background screening programs typically generate positive returns through reduced turnover, improved safety records, and decreased liability exposure. Agricultural employers report average ROI ratios of 3 to 5 when comparing screening costs to avoided losses from problematic hires.
Cost-benefit analysis should include quantifiable benefits such as reduced workers' compensation claims and decreased equipment damage rates. Intangible benefits include improved workplace safety culture and enhanced operational reliability during critical harvest periods.
Legal Compliance and Risk Management
Agricultural worker background check programs must navigate complex legal requirements spanning employment law, immigration regulation, and fair credit reporting standards. The Fair Credit Reporting Act imposes specific obligations when third-party screening companies conduct background investigations. These obligations include disclosure requirements and adverse action procedures that apply to all agricultural employers regardless of operation size or worker status.
| Compliance Area | Key Requirements | Penalties for Violations |
| FCRA | Written consent, adverse action procedures | Up to $1,000 per violation |
| Title VII | Non-discriminatory screening criteria | Unlimited monetary damages |
| State Laws | Varies by jurisdiction | Criminal penalties possible |
FCRA compliance requires employers to obtain written consent before conducting background checks and provide specific disclosures about screening activities to all applicants. Employment discrimination laws add additional complexity to agricultural screening programs through Title VII requirements and state-specific anti-discrimination statutes. Agricultural employers must ensure their screening criteria do not have disparate impact on protected groups while maintaining job-related qualification standards.
Discrimination Prevention Strategies
Agricultural employers must ensure their background screening programs do not discriminate against protected classes of workers. Consistent application of screening criteria and job-related qualification standards help prevent discrimination claims while maintaining workplace safety and security requirements.
Technology Solutions and Digital Integration
Modern agricultural screening programs increasingly rely on technology solutions to manage high-volume seasonal hiring efficiently. Digital platforms provide automated workflow management, real-time status tracking, and integrated compliance monitoring capabilities. These systems reduce administrative burden while improving accuracy and consistency in screening processes, becoming particularly valuable during compressed harvest season hiring periods when manual processes cannot keep pace with operational demands.
Cloud-based screening platforms offer scalability that matches agricultural hiring patterns throughout the year, handling low-volume background processing during off-seasons while scaling up for peak harvest hiring periods. Automated workflow management reduces manual intervention requirements and minimizes processing errors that could compromise compliance or operational efficiency. Real-time dashboards provide visibility into screening progress and potential bottlenecks requiring management attention during critical hiring periods.
Mobile applications enable field supervisors and HR personnel to initiate background screenings from remote locations, particularly valuable for agricultural operations spanning large geographic areas. Mobile access allows immediate screening initiation when suitable candidates are identified in the field. Digital document collection streamlines the consent and authorization process for applicants while ensuring proper documentation and record retention throughout the screening lifecycle.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
Agricultural screening programs must maintain robust data security measures to protect sensitive employee information. Background check data includes personal identifiers, criminal history information, and employment records requiring careful protection throughout the screening process.
Data breaches can result in significant legal liability and regulatory penalties for agricultural employers. Screening vendors should maintain appropriate cybersecurity certifications and insurance coverage to protect client data and ensure business continuity during security incidents.
Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement
Effective agricultural screening programs require ongoing quality assurance measures to maintain accuracy and compliance standards throughout the operational lifecycle. Regular audit procedures help identify processing errors, compliance gaps, and improvement opportunities that could impact program effectiveness. Quality control measures become particularly important during high-volume harvest season hiring when processing pressures may compromise attention to detail and regulatory compliance.
- Statistical Analysis: Tracking metrics such as processing times, accuracy rates, and compliance violations helps identify trends requiring management attention and process improvements.
- Feedback Collection: Regular surveys and interviews with hiring managers, HR personnel, and screened applicants provide valuable program improvement insights and identify potential issues.
- Training Programs: Regular updates address changing regulations and best practices in agricultural screening while ensuring consistent application of procedures.
- Vendor Management: Regular performance reviews evaluate processing times, accuracy rates, and customer service quality to ensure screening providers maintain acceptable service levels.
- Documentation Standards: Standardized forms and procedures reduce variability and improve compliance consistency across all screening activities and personnel interactions.
Statistical analysis of screening outcomes provides valuable insights for program optimization and strategic planning. Tracking processing times, accuracy rates, and compliance violations helps identify trends requiring management attention and resource allocation. Comparative analysis across different screening providers or time periods reveals performance variations requiring investigation and potential corrective action.
Performance Metrics and Key Performance Indicators
Agricultural screening programs should establish clear performance metrics to measure effectiveness and identify improvement opportunities throughout the operational cycle. Processing time metrics track how quickly screenings are completed relative to operational requirements and seasonal deadlines.
Accuracy measurements evaluate the quality of screening results and frequency of errors requiring correction or additional investigation. Cost per hire metrics help evaluate program efficiency and budget performance while supporting strategic planning and vendor selection decisions.
Industry Best Practices and Benchmarking Standards
Agricultural screening programs benefit from adopting industry best practices and benchmarking against established standards to ensure optimal performance and compliance. Leading agricultural employers typically implement tiered screening approaches that match investigation depth to position risk levels and responsibilities. Entry-level positions receive basic criminal history and eligibility verification, while supervisory and equipment operator roles undergo comprehensive investigations including reference checks and skills assessments.
Best practice programs incorporate seasonal planning cycles that align screening activities with agricultural production schedules and labor demand patterns. Early engagement with screening providers secures adequate capacity during peak hiring periods while allowing sufficient time for thorough investigations. Contingency planning addresses potential screening delays or adverse findings that could impact harvest operations and workforce availability during critical periods.
Professional agricultural associations and industry groups provide valuable resources for screening program development and compliance guidance. These organizations often publish screening guidelines specific to agricultural operations and seasonal workforce management. Participation in industry forums and conferences provides opportunities to learn from other employers' experiences and stay current with regulatory developments affecting agricultural hiring practices.
Regulatory Updates and Compliance Monitoring
Agricultural employers must stay current with changing regulations affecting background screening requirements and procedures. Federal agencies periodically update H-2A program requirements and compliance standards that impact screening protocols.
State legislatures frequently modify employment laws and fair credit reporting requirements that affect agricultural screening programs. Regular monitoring of regulatory developments ensures programs remain compliant and avoid potential violations or penalties.
Vendor Selection and Partnership Management
Successful agricultural screening programs depend on effective partnerships with qualified background screening vendors who understand agricultural industry requirements and seasonal operational demands. Vendor selection should prioritize providers with demonstrated experience in agricultural hiring and familiarity with H-2A program requirements. Specialized agricultural screening vendors often provide superior service quality and compliance support compared to general employment screening companies.
Key vendor evaluation criteria include processing capacity during peak agricultural hiring seasons, accuracy and completeness of screening results, and compliance with federal and state regulatory requirements. Cost considerations should balance per-unit screening fees with service quality and reliability during critical harvest periods. Volume pricing arrangements and long-term contracts can provide cost savings while ensuring adequate service capacity when needed most.
Service level agreements should specify processing timelines, accuracy standards, and customer service response requirements that align with agricultural operational needs. Clear escalation procedures address urgent screening requests and processing delays that could impact harvest operations. Regular performance reviews evaluate vendor compliance with service agreements and identify opportunities for improvement or contract modification.
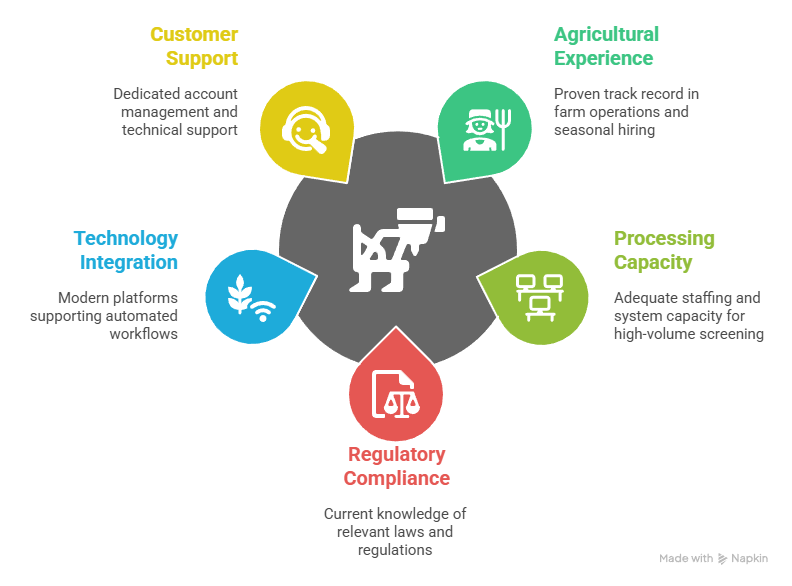
- Agricultural Industry Experience: Proven track record with farm operations, seasonal hiring, and H-2A program compliance requirements ensuring specialized expertise and understanding of unique operational challenges.
- Processing Capacity: Adequate staffing and system capacity to handle high-volume screening during peak agricultural hiring seasons without compromising quality or processing timelines.
- Regulatory Compliance: Current knowledge of federal immigration laws, state employment regulations, and FCRA requirements affecting agricultural screening programs and seasonal workforce management.
- Technology Integration: Modern platforms supporting automated workflows, real-time status tracking, and mobile access for field-based agricultural operations spanning large geographic areas.
- Customer Support: Dedicated account management and responsive technical support addressing urgent screening needs and operational requirements during critical harvest periods.
Long-term vendor partnerships provide stability and institutional knowledge that improve screening program effectiveness over time. Established relationships facilitate better communication and service customization that addresses specific operational requirements. However, periodic vendor evaluation ensures continued competitive pricing and service quality while identifying potential improvements or alternative solutions.
Contract Negotiation and Service Agreements
Effective vendor contracts should address agricultural industry-specific requirements and seasonal operational patterns that differ from standard employment screening arrangements. Service level agreements must account for peak hiring periods and processing volume fluctuations throughout the agricultural calendar.
Contract terms should include provisions for expedited processing during harvest seasons, volume discounts for large screening programs, and performance guarantees that protect agricultural employers from service disruptions. Clear data security and privacy protection requirements ensure compliance with applicable regulations and protect sensitive employee information.
Conclusion
Agricultural seasonal worker screening represents a critical component of successful harvest operations requiring careful balance between compliance obligations and operational efficiency. Effective programs incorporate federal H-2A requirements, state-specific regulations, and industry best practices while maintaining cost-effective approaches suitable for seasonal employment patterns. As regulatory scrutiny continues increasing across agricultural industries, employers who invest in comprehensive screening programs position themselves for sustainable success while protecting their workers and communities. The complexity of these requirements makes professional guidance essential, particularly for operations spanning multiple states or utilizing diverse worker populations during peak harvest periods.
Frequently Asked Questions
How far in advance should agricultural employers begin background screening for harvest season workers?
Agricultural employers should initiate background screening 30-45 days before harvest season begins to accommodate processing delays and potential complications. This timeline allows sufficient time for thorough investigations while providing flexibility to address adverse findings or find replacement workers if necessary.
What specific background checks are required for H-2A agricultural workers?
H-2A workers must undergo criminal background checks, employment verification, and eligibility confirmation as part of the federal visa process. Additional requirements may include drug testing, reference checks, and specialized certifications depending on job duties and state regulations where work will be performed.
Do agricultural background check requirements vary by state?
Yes, agricultural background check requirements vary significantly by state, with some jurisdictions requiring comprehensive criminal history checks while others focus primarily on employment eligibility verification. Employers must research applicable laws in both their operational state and workers' states of residence.
How much do agricultural worker background checks typically cost?
Agricultural worker background checks typically cost between $50-$150 per worker depending on the scope of investigation required. Basic criminal history and employment verification checks cost less, while comprehensive packages including drug testing and multiple verification components cost more.
What happens if a seasonal agricultural worker fails a background check during harvest season?
When seasonal workers fail background checks during harvest season, employers must follow proper adverse action procedures under the Fair Credit Reporting Act, including providing required notices and appeal opportunities. Employers should maintain pre-screened backup candidates to minimize operational disruptions.
Are there special considerations for screening migrant agricultural workers?
Migrant agricultural workers require enhanced screening procedures including multi-jurisdictional criminal searches, alternative reference verification methods, and potentially international background checks. Language barriers and limited documentation history may require specialized investigation techniques and extended processing times.
Can agricultural employers use the same background screening provider for both H-2A and domestic workers?
Agricultural employers can use the same background screening provider for H-2A and domestic workers, but must ensure the provider understands different compliance requirements for each worker category. H-2A workers require specific federal compliance elements while domestic workers may be subject to different state-specific requirements.
What records must agricultural employers maintain for seasonal worker background checks?
Agricultural employers must maintain complete background check records including consent forms, screening reports, and adverse action documentation for at least three years. H-2A employers face additional federal record-keeping requirements that may extend retention periods and include specific documentation elements.
Additional Resources
- Department of Labor H-2A Temporary Agricultural Workers Program Guide
https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/immigration/h2a - Fair Credit Reporting Act Compliance Guide for Employers
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/using-consumer-reports-what-employers-need-know - USCIS Form I-9 Employment Eligibility Verification Instructions
https://www.uscis.gov/i-9 - National Agricultural Workers Survey Reports
https://www.dol.gov/agencies/eta/national-agricultural-workers-survey - State-by-State Agricultural Employment Law Summaries
https://www.ncsl.org/labor-and-employment/agricultural-worker-protection - Agricultural Safety and Health Best Practices Guide
https://www.osha.gov/agriculture - Migrant and Seasonal Agricultural Worker Protection Act Overview
https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/agriculture/mspa - Background Screening Industry Association Agricultural Guidelines
https://www.bsiaonline.org/Industry-Guidelines

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





