Maryland healthcare background checks are mandatory for most healthcare positions and must comply with both federal CMS requirements and state COMAR regulations. The process typically takes 5-15 business days and includes criminal history, licensing verification, and exclusion database searches.
Key Takeaways
- Maryland healthcare workers must undergo comprehensive background checks that include criminal history, professional licensing verification, and federal exclusion database searches before employment.
- The background check process typically takes 5-15 business days depending on the screening company, position requirements, and whether additional verification is needed.
- Disqualifying factors include felony convictions within 7 years, certain misdemeanors, professional license sanctions, and inclusion on federal or state exclusion lists.
- CNAs and other licensed healthcare professionals must complete additional licensing-specific background checks through the Maryland Board of Nursing or relevant licensing board.
- Employers must follow both CMS and COMAR compliance requirements when conducting healthcare employment screening to maintain Medicare/Medicaid participation and state licensing.
- Job seekers can expedite the process by obtaining their own background check reports and ensuring all professional licenses are current before applying.
Maryland Healthcare Background Check Requirements
Maryland healthcare facilities must conduct thorough background checks on all employees with patient access or administrative responsibilities. These requirements stem from federal regulations, particularly the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) guidelines. Additionally, state regulations outlined in the Code of Maryland Regulations (COMAR) provide specific compliance standards.
Healthcare employers face strict compliance obligations to maintain their operating licenses. Furthermore, they must meet federal funding eligibility requirements. The state's healthcare licensing background check requirements apply to multiple facility types including hospitals, nursing homes, home health agencies, and assisted living facilities.
Maryland's approach differs from other states by requiring both pre-employment screening and ongoing monitoring for certain positions. Healthcare staffing agencies operating in Maryland must also ensure compliance with these regulations when placing temporary workers. Moreover, contract workers face the same screening requirements as permanent employees.
Federal and state regulators conduct regular audits of healthcare facilities to ensure proper background check procedures. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, including loss of Medicare/Medicaid reimbursement. Additionally, facilities may face state licensing sanctions for inadequate screening practices.
Legal Framework and Regulatory Compliance
The Maryland healthcare background check system operates under multiple layers of federal and state regulations. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs how employers conduct background checks and handle applicant information. Meanwhile, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services establishes minimum screening standards for healthcare facilities.
State-specific regulations include Maryland's fair hiring laws and healthcare facility licensing requirements. These laws balance patient safety concerns with employment rights protections. Additionally, the Maryland Department of Health provides guidance on proper screening procedures for different healthcare positions.
Healthcare facilities must maintain detailed documentation of their screening processes. This includes written policies, staff training records, and individual screening documentation. Furthermore, facilities must demonstrate compliance during routine inspections and audits.
| Regulatory Authority | Primary Requirements |
| Federal CMS | Criminal background checks, exclusion list verification |
| Maryland COMAR | State-specific screening standards, licensing verification |
| FCRA | Consumer rights protection, proper disclosure procedures |
Compliance failures can result in serious consequences including facility closure and criminal charges. Therefore, healthcare employers invest significantly in compliance programs and staff training.
Types of Background Checks for Healthcare Workers
Maryland healthcare employers must conduct comprehensive screening that covers multiple areas of an applicant's background. The screening process examines criminal history, professional credentials, and employment eligibility. Additionally, specialized positions may require enhanced screening elements.
Most healthcare positions require a multi-faceted approach to background verification. This includes both automated database searches and manual verification processes. Furthermore, certain roles demand ongoing monitoring throughout the employment period.
The screening process typically begins after a conditional job offer is extended to the candidate. However, some facilities conduct preliminary screening during the application review process. Moreover, emergency hiring situations may require expedited screening procedures.
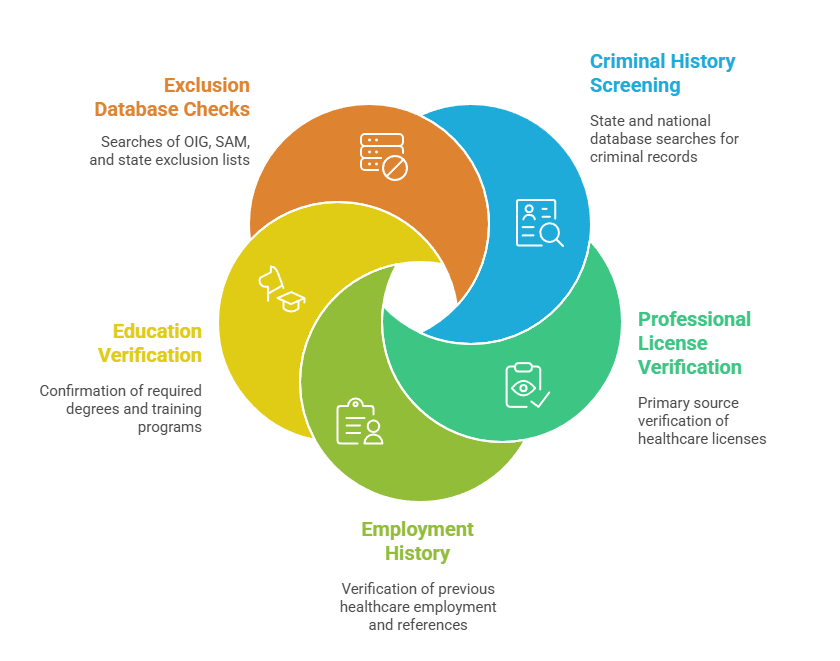
- Criminal History Screening: State and national criminal database searches
- Professional License Verification: Primary source verification of all healthcare licenses
- Employment History: Previous healthcare employment verification and reference checks
- Education Verification: Confirmation of required degrees and training programs
- Exclusion Database Checks: OIG, SAM, and state exclusion list searches
Healthcare facilities often partner with specialized screening companies that understand healthcare compliance requirements. These companies provide comprehensive packages designed specifically for healthcare employers. Consequently, facilities can ensure thorough screening while maintaining efficiency.
Criminal History Screening
Criminal background checks for healthcare workers in Maryland examine both state and national databases for disqualifying convictions. The screening process looks at felony and misdemeanor convictions within specified timeframes. Additionally, some positions require review of pending charges and arrest records.
Maryland healthcare employers typically use a seven-year lookback period for criminal history screening. However, certain violent crimes and drug-related offenses may have longer consideration periods. Furthermore, positions involving controlled substances often require enhanced criminal screening.
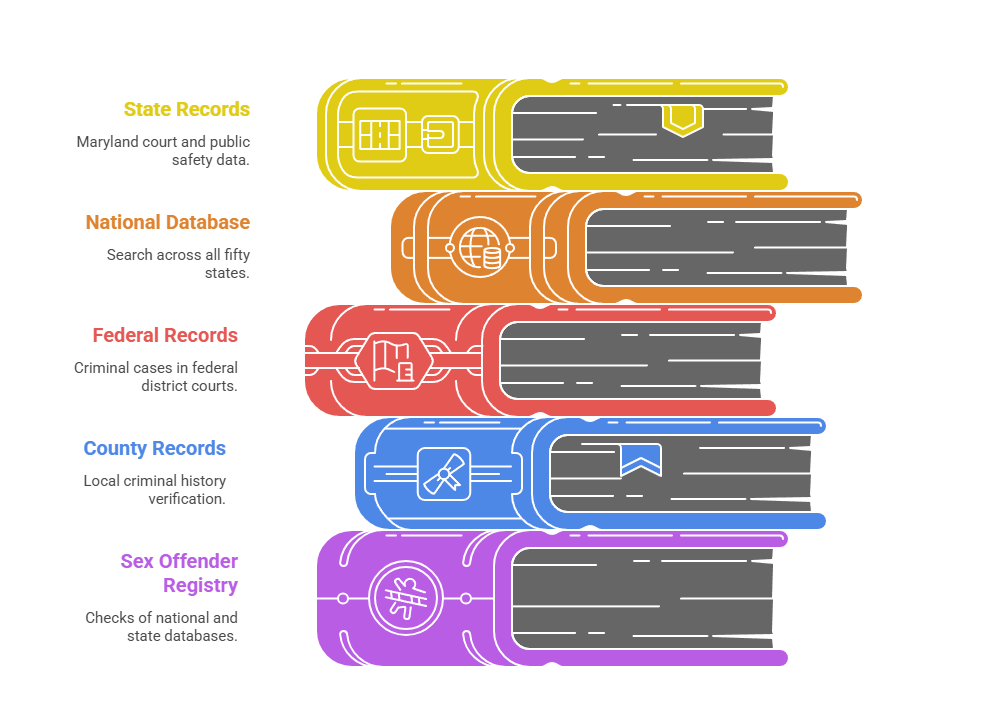
- State Criminal Records: Maryland court databases and Department of Public Safety records
- National Criminal Database: Multi-jurisdictional search covering 50 states
- Federal Criminal Records: Federal district court criminal case searches
- County Criminal Records: Local jurisdiction criminal history verification
- Sex Offender Registry: National and Maryland sex offender database checks
The criminal screening process must comply with both federal and state fair hiring requirements. Additionally, employers must provide proper disclosures and follow adverse action procedures when criminal history impacts hiring decisions.
Professional License Verification
Healthcare licensing background checks in Maryland involve comprehensive verification of all professional credentials and certifications. The process includes checking for active license status, disciplinary actions, and continuing education compliance. Additionally, employers must verify licenses from other states where applicants previously worked.
Primary source verification is required for all healthcare licenses, meaning employers must contact licensing boards directly. This process ensures accuracy and identifies any restrictions or sanctions on professional licenses. Furthermore, employers must verify that licenses will remain active throughout the employment period.
The Maryland Department of Health oversees most healthcare professional licensing through various specialized boards. Each profession has specific requirements for initial licensing, renewal, and disciplinary procedures. Moreover, some positions require verification of specialty certifications and continuing education credits.
CNA Background Check Requirements in Maryland
Certified Nursing Assistants face specific background check requirements through both state licensing and employment screening processes. The Maryland Board of Nursing oversees CNA certification and maintains the Maryland Nurse Aide Registry. Additionally, individual healthcare facilities conduct their own employment-based screening for CNAs.
CNA background checks include criminal history screening, abuse registry checks, and training verification. The state requires background checks for initial CNA certification, registry renewal, and employment at healthcare facilities. Furthermore, CNAs must undergo additional screening when transferring certifications from other states.
Maryland's CNA screening process includes checking the National Nurse Aide Abuse Registry for substantiated findings. State-specific abuse registries are also reviewed during the screening process. Moreover, employers must verify completion of approved training programs and competency testing requirements.
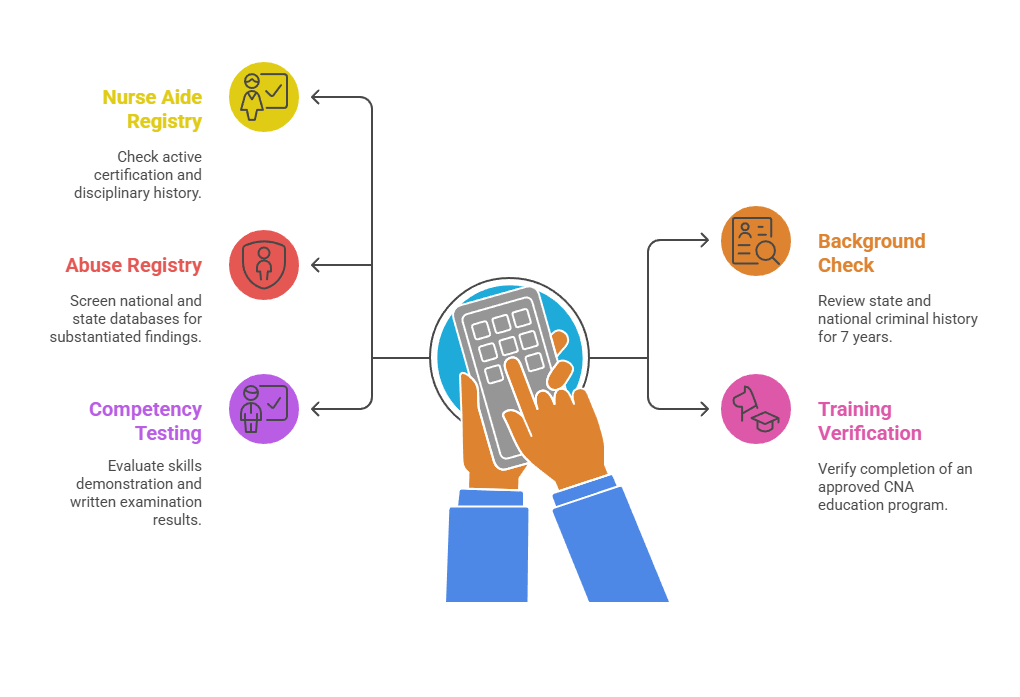
- Maryland Nurse Aide Registry: Active certification status and disciplinary history
- Criminal Background Check: State and national criminal history within 7 years
- Abuse Registry Screening: National and state databases for substantiated findings
- Training Program Verification: Approved CNA education program completion
- Competency Testing: Skills demonstration and written examination results
CNA background checks typically process faster than other healthcare positions due to streamlined registry systems. However, additional verification requirements may extend processing times. Therefore, CNAs should ensure all documentation is current before beginning the employment process.
Maryland Hospital Employment Screening Process
Maryland hospitals follow comprehensive employment screening protocols that exceed basic background check requirements due to federal program participation. The screening process includes criminal background checks, professional license verification, and specialized screenings for specific departments. Additionally, hospitals must comply with Joint Commission standards and Medicare/Medicaid participation requirements.
Hospital employment screening begins after a conditional job offer and must be completed before work begins. The process includes employment eligibility verification, drug screening, and health clearances beyond standard background checks. Furthermore, department-specific roles may require additional screening elements such as financial background checks for billing staff.
Large hospital systems often maintain internal compliance departments to oversee screening processes. These departments ensure consistent application of screening standards across all facilities. Moreover, they provide guidance on handling complex screening situations and regulatory changes.
Hospital employment screening must address multiple regulatory requirements simultaneously. This includes federal CMS standards, state licensing regulations, and accreditation body requirements. Additionally, hospitals must maintain detailed documentation of all screening activities for audit purposes.
| Screening Component | Processing Time | Documentation Required |
| Criminal Background Check | 3-5 business days | Government-issued photo ID |
| Professional License Verification | 2-3 business days | Current license numbers and states |
| Employment Reference Verification | 5-7 business days | Previous supervisor contact information |
| Education Verification | 3-5 business days | Official transcripts or certificates |
| Drug Screening | 1-2 business days | Valid ID and chain of custody forms |
Hospital screening processes include ongoing monitoring requirements for licensed professionals. This involves periodic re-screening and continuous monitoring of licensing boards for disciplinary actions. Consequently, hospitals can identify issues that arise during employment and take appropriate action.
Disqualifying Factors for Healthcare Employment
Maryland healthcare employment screening identifies specific factors that may disqualify candidates from healthcare positions. Criminal convictions within certain timeframes typically result in automatic disqualification from most healthcare roles. Additionally, professional licensing issues and inclusion on federal exclusion lists prevent healthcare employment.
Healthcare facilities must evaluate each disqualifying factor in context with job requirements and patient safety considerations. Some facilities provide appeals processes for candidates who can demonstrate rehabilitation or dispute screening results. However, certain serious offenses may result in permanent disqualification from healthcare employment.
The evaluation process must comply with federal and state fair hiring practices while prioritizing patient safety. Employers must document their decision-making process and provide proper notifications to affected candidates. Furthermore, facilities must ensure consistent application of disqualification standards across all positions.
Criminal Convictions and Timeframes
Felony convictions within the past seven years typically result in automatic disqualification from healthcare positions in Maryland. Violent crimes, sexual offenses, and crimes against vulnerable populations may have longer disqualification periods. Additionally, drug-related felonies often result in permanent disqualification from positions involving controlled substances.
Misdemeanor convictions may also impact healthcare employment eligibility depending on their nature and relevance to healthcare duties. Theft, fraud, and assault convictions are particularly concerning for healthcare employers. Moreover, multiple misdemeanor convictions may be viewed as seriously as single felony convictions.
Maryland follows federal guidance on considering rehabilitation efforts, time since conviction, and job relevance when evaluating criminal history. Candidates may provide evidence of rehabilitation, community service, or other factors that demonstrate fitness for healthcare employment. However, employers retain discretion in making final hiring decisions based on their patient safety policies.
Professional License Issues
Professional licensing problems can disqualify healthcare workers from employment even without criminal convictions. License suspensions, revocations, or disciplinary actions create significant barriers to healthcare employment in Maryland. Additionally, failure to maintain current licensing or continuing education requirements may result in employment disqualification.
Disciplinary actions on professional licenses include formal reprimands, practice restrictions, and mandatory education requirements. The severity and relevance of disciplinary actions to the proposed position influence employment decisions. Furthermore, patterns of licensing problems across multiple states raise additional concerns for employers.
Healthcare facilities must verify that all licensed professionals maintain good standing throughout their employment period. This includes ongoing monitoring of licensing boards for new disciplinary actions or license status changes. Consequently, employees may face termination if licensing issues arise during employment.
Background Check Processing Timeframes and Expediting Options
Healthcare background check processing times in Maryland vary based on screening complexity and the chosen screening provider's efficiency. Standard criminal background checks typically complete within 3-5 business days for most candidates. However, comprehensive healthcare screening packages may take 7-15 business days to complete all required elements.
Several factors can extend background check processing timeframes beyond standard estimates. Multiple state license verifications add 2-3 days per state to the overall timeline. Additionally, international background checks, education verification from foreign institutions, or situations requiring additional documentation may significantly extend processing times.
Healthcare facilities often work with specialized screening companies that understand healthcare compliance requirements and can expedite processing when necessary. Rush processing options are available for critical positions, though they typically incur additional fees. Furthermore, some screening companies offer status tracking systems that provide real-time updates on screening progress.
Job seekers can help expedite the background check process by ensuring all personal information is accurate and complete. Providing comprehensive work history, current contact information for references, and necessary documentation in advance reduces processing delays. Moreover, healthcare facilities should communicate expected timeframes to candidates and provide regular updates during lengthy screening processes.
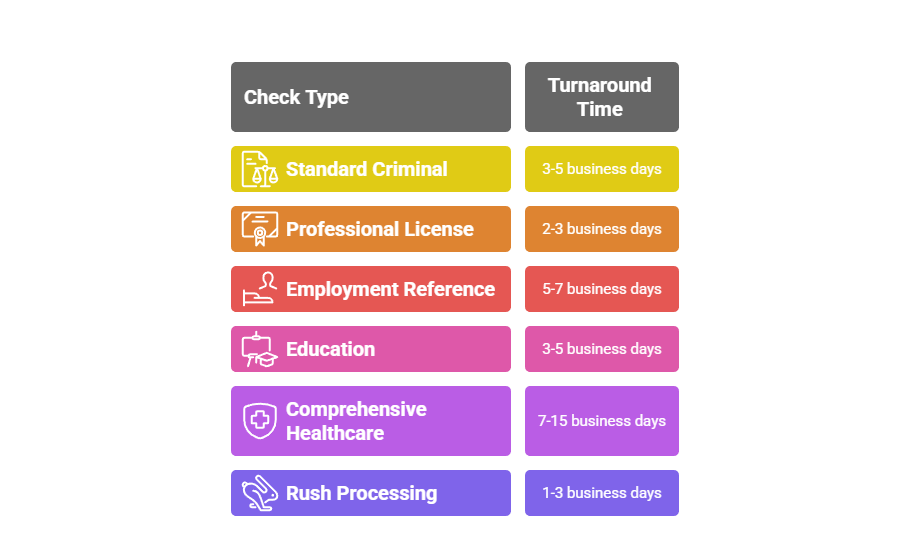
- Standard Criminal Check: 3-5 business days for state and national database searches
- Professional License Verification: 2-3 business days per licensing jurisdiction
- Employment Reference Checks: 5-7 business days depending on employer responsiveness
- Education Verification: 3-5 business days for domestic institutions
- Comprehensive Healthcare Package: 7-15 business days for complete screening
- Rush Processing: 1-3 business days with expedited service fees
Healthcare employers should plan screening timeframes into their hiring processes to avoid delays in filling critical positions. Additionally, maintaining relationships with reliable screening providers helps ensure consistent processing times and quality results.
Cost Considerations for Healthcare Background Checks
Healthcare background check costs in Maryland vary significantly based on the comprehensiveness of screening requirements and the chosen screening provider. Basic criminal background checks typically cost $25-50 per candidate. However, comprehensive healthcare screening packages including multiple verification elements may cost $100-200 per screening.
Employers must balance screening costs with compliance requirements and risk management needs. While more comprehensive screening costs more upfront, it can prevent costly compliance violations and patient safety incidents. Additionally, volume pricing arrangements with screening providers can reduce per-screening costs for large healthcare facilities.
Healthcare facilities should budget for ongoing screening costs beyond initial pre-employment checks. This includes periodic re-screening requirements, ongoing monitoring services, and additional screening for promotions or role changes. Furthermore, rush processing fees and international screening elements can significantly increase costs.
| Screening Component | Typical Cost Range | Processing Time |
| Basic Criminal Check | $25-40 | 2-3 business days |
| Professional License Verification | $15-25 per license | 2-3 business days |
| Employment Reference Check | $20-35 per employer | 3-5 business days |
| Education Verification | $25-40 per institution | 3-5 business days |
| Comprehensive Package | $100-200 | 7-15 business days |
| Rush Processing Fee | $50-100 additional | 1-2 business days |
Cost-effective screening strategies include bundling multiple screening elements with single providers and negotiating volume discounts. Additionally, some facilities conduct preliminary screening internally before ordering comprehensive third-party screenings to reduce overall costs.
Compliance Requirements for Healthcare Employers
Maryland healthcare employers must maintain comprehensive compliance programs to meet federal and state background check requirements. These programs involve establishing written policies, training staff on proper procedures, and maintaining detailed documentation of all screening activities. Additionally, facilities must ensure equal treatment of all candidates while following Fair Credit Reporting Act requirements.
Compliance frameworks must address multiple regulatory requirements simultaneously including CMS standards, state licensing regulations, and federal employment laws. Healthcare employers must balance patient safety requirements with candidate rights and fair employment practices. Furthermore, facilities must implement ongoing monitoring programs for licensed professionals and establish procedures for addressing background check issues during employment.
Documentation requirements include maintaining screening records, adverse action notices, and evidence of policy compliance for specified retention periods. Healthcare facilities participate in regular audits by state licensing agencies, federal regulators, and accreditation organizations. Moreover, compliance programs should include regular policy updates to reflect changing regulations and industry best practices.
- Written Policies and Procedures: Comprehensive screening policies covering all position types and screening elements
- Staff Training Programs: Regular training on FCRA compliance, fair hiring practices, and screening procedures
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Systematic maintenance of screening records and compliance documentation
- Audit Preparation: Regular internal audits and preparation for regulatory inspections
- Policy Updates: Ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes and policy adjustments
Effective compliance programs help healthcare facilities avoid penalties while maintaining efficient hiring processes. Additionally, strong compliance frameworks protect facilities during regulatory audits and demonstrate commitment to patient safety standards.
Best Practices for Job Seekers

Healthcare job seekers in Maryland can improve their employment prospects by understanding background check requirements and preparing accordingly. Obtaining personal background check reports before applying helps identify potential issues and allows time to address them proactively. Additionally, ensuring all professional licenses are current and in good standing prevents delays during the screening process.
Transparency about background issues during the application process often works in candidates' favor compared to attempting to hide problems. Many healthcare employers appreciate honesty and may work with candidates who demonstrate rehabilitation and fitness for healthcare work. Furthermore, candidates should be prepared to provide detailed explanations and supporting documentation for any background issues.
Job seekers should maintain organized records of their employment history, education credentials, and professional licenses. Having complete contact information for previous employers and references expedites the screening process. Moreover, candidates should respond promptly to screening company requests for additional information or documentation.
Professional development activities and community involvement can help offset minor background issues for healthcare job seekers. Continuing education, volunteer work, and professional certifications demonstrate ongoing commitment to healthcare careers. Additionally, obtaining letters of recommendation from healthcare professionals can support employment applications despite background concerns.
Resources and Support for Healthcare Employers
Maryland healthcare employers can access multiple resources to support their background check compliance efforts. The Maryland Hospital Association provides guidance and training on employment screening best practices for hospital members. Additionally, professional associations for different healthcare sectors offer specialized compliance resources and networking opportunities.
Third-party screening companies specializing in healthcare can provide comprehensive compliance support beyond basic background check services. These companies offer policy development assistance, staff training, and ongoing compliance monitoring. Furthermore, many screening providers offer online portals that streamline the screening process and provide real-time status updates.
Legal counsel specializing in healthcare employment law can provide valuable guidance on complex screening situations and regulatory compliance. Employment attorneys help healthcare facilities navigate fair hiring requirements while maintaining patient safety standards. Moreover, legal professionals can assist with policy development and audit preparation.
State and federal regulatory agencies provide official guidance documents and training opportunities for healthcare employers. The Maryland Department of Health offers resources specific to state licensing requirements and healthcare facility compliance. Additionally, CMS provides detailed guidance on federal background check requirements and compliance expectations.
- Maryland Hospital Association: Industry-specific compliance guidance and training programs
- Healthcare Screening Companies: Specialized services and compliance support for healthcare employers
- Employment Law Attorneys: Legal guidance on complex screening and compliance issues
- State Licensing Agencies: Official regulatory guidance and compliance resources
- Professional Associations: Networking and best practice sharing opportunities
Regular participation in industry training and networking events helps healthcare employers stay current on regulatory changes and best practices. Additionally, maintaining relationships with compliance professionals and screening providers ensures access to expert guidance when needed.
Conclusion
Maryland healthcare background checks represent a critical component of patient safety and regulatory compliance for healthcare employers. The process requires careful attention to both federal CMS requirements and state COMAR regulations while balancing thoroughness with efficiency. Healthcare facilities must invest in comprehensive compliance programs that address multiple regulatory requirements while maintaining fair employment practices. Job seekers can improve their success by understanding requirements, maintaining current credentials, and being transparent about background issues. Effective background check programs protect patients while supporting healthcare facilities in attracting qualified professionals who meet the highest safety and professional standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a healthcare background check take in Maryland?
Healthcare background checks in Maryland typically take 5-15 business days, depending on the comprehensiveness of screening requirements and whether additional verification is needed for licenses or employment history.
What disqualifies you from healthcare work in Maryland?
Disqualifying factors include felony convictions within 7 years, certain misdemeanors involving violence or fraud, professional license sanctions, inclusion on federal exclusion lists, and substantiated abuse or neglect findings.
Do CNAs need background checks in Maryland?
Yes, CNAs in Maryland must undergo background checks for initial certification, employment at healthcare facilities, and license renewals, including criminal history and nurse aide registry verification.
Are fingerprints required for Maryland healthcare background checks?
Fingerprint-based background checks are required for certain healthcare positions and licensing applications, particularly for roles involving vulnerable populations or controlled substances.
Can you work in healthcare with a criminal record in Maryland?
Healthcare employment with a criminal record depends on the nature of convictions, timeframe, rehabilitation efforts, and specific job requirements, with some convictions resulting in permanent disqualification.
How much do healthcare background checks cost in Maryland?
Healthcare background check costs in Maryland range from $50-150 depending on screening components, with comprehensive packages including multiple verifications typically costing more than basic criminal checks.
What is included in a Maryland healthcare background check?
Maryland healthcare background checks include criminal history screening, professional license verification, employment history checks, education verification, and federal exclusion database searches.
Who pays for healthcare background checks in Maryland?
Healthcare employers typically pay for background checks as part of their hiring process, though some candidates may choose to obtain their own screening reports to expedite employment.
Additional Resources
- Maryland Department of Health Professional Licensing Information
https://health.maryland.gov/pages/licensing.aspx - Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Background Check Requirements
https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Provider-Enrollment-and-Certification/SurveyCertificationGenInfo/Background-Checks - Maryland Board of Nursing CNA Registry
https://www.mbon.maryland.gov/Pages/cna.aspx - Code of Maryland Regulations Healthcare Facility Requirements
https://www.dsd.state.md.us/COMAR/SubtitleSearch.aspx - Fair Credit Reporting Act Compliance Guidelines
https://www.ftc.gov/enforcement/rules/rulemaking-regulatory-reform-proceedings/fair-credit-reporting-act - Maryland Hospital Association Resources
https://www.mhaonline.org - Office of Inspector General Exclusion Database
https://exclusions.oig.hhs.gov

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





