Prescription drug users have specific legal protections during employment drug testing. This includes the right to Medical Review Officer (MRO) consultation and confidential disclosure processes. Understanding these rights and proper disclosure strategies helps job seekers navigate employment screening while maintaining medical privacy.
Key Takeaways
- Medical Review Officer (MRO) verification is mandatory for all positive drug tests in most employment contexts, providing prescription drug users a confidential appeal process.
- Federal ADA and state disability laws protect employees taking legally prescribed medications from discrimination based on their medical conditions.
- Timing of prescription disclosure matters significantly – revealing medications after a positive test through the MRO process is typically more protective than pre-test disclosure.
- Documentation requirements include valid prescriptions from licensed physicians, matching names, and current dosage information to verify legitimate medical use.
- Employer drug testing policies must comply with federal DOT regulations, state employment laws, and disability accommodation requirements.
- Safety-sensitive positions have stricter requirements but still maintain MRO review processes and reasonable accommodation obligations under disability laws.
Understanding Employment Drug Testing Laws
The landscape of employment drug testing laws creates a complex framework. Prescription drug users must navigate both federal regulations and state-specific protections. The Drug-Free Workplace Act of 1988 established baseline requirements for federal contractors. Meanwhile, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides crucial protections for individuals taking prescription medications for qualifying disabilities.
Most employment drug screening policies must balance workplace safety concerns with individual medical privacy rights. Federal Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations govern transportation workers. Non-DOT employees fall under varying state employment drug testing laws. These state laws often provide broader protections than federal requirements.
State-by-State Compliance Requirements:
| State Category | Disclosure Requirements | MRO Process | Additional Protections |
| Strict Compliance States | Pre-test disclosure optional | Mandatory MRO review | Strong disability protections |
| Moderate Regulation States | Employer policy dependent | MRO required for positives | Standard ADA compliance |
Understanding these legal frameworks helps job seekers make informed decisions. The variation in state laws means that rights and protections differ significantly. Geographic location and industry sector both play important roles in determining available protections.
The Medical Review Officer (MRO) Process Explained
Medical Review Officers serve as independent physicians. They evaluate positive drug test results to determine if legitimate medical explanations exist. The MRO process provides prescription drug users with a confidential avenue to explain positive test results. This happens without initially disclosing sensitive medical information to employers.
When a laboratory reports a positive drug test result, the MRO must contact the tested individual within specific timeframes. This contact typically happens within 72 hours. During this confidential consultation, individuals can provide prescription documentation. They can also give medical explanations for the positive result. The MRO then conducts a medical interview to verify the legitimacy of the prescription use.
MRO Interview Preparation Steps:
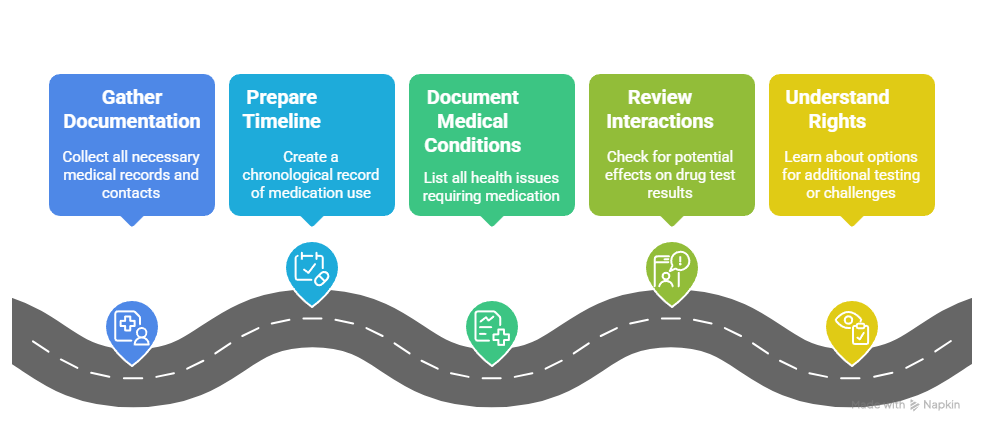
- Gather all relevant prescription documentation including bottles, pharmacy records, and physician contact information
- Prepare a clear timeline of when medications were prescribed and dosage changes
- Document any medical conditions that necessitate the prescription medications
- Review medication interactions that might affect drug test results beyond the prescribed substance
- Understand your rights to request additional testing or challenge laboratory procedures
The MRO process typically concludes with either a "negative" result or a "positive" result. A negative result means prescription use is verified. A positive result means no legitimate medical explanation exists. This determination significantly impacts whether employers receive information about prescription drug use. They may simply receive a standard negative test result instead.
MRO Interview Timeline and Expectations
The MRO interview follows strict timeline requirements to protect employee rights. Most MROs attempt initial contact within 24-48 hours of receiving positive results. Employees typically have 72 hours to respond to contact attempts. After this period, the MRO may report a positive result to the employer.
During the interview, the MRO will ask specific questions about prescription use. They want to verify the medication was prescribed by a licensed physician. They also confirm the dosage matches what would produce the test results. The MRO may contact your prescribing physician to verify information. This contact happens only with your written permission.
Legal Prescription Drugs in Workplace Context
Legal prescription drugs workplace policies must distinguish between legitimate medical use and substance abuse. These policies must also maintain compliance with disability accommodation laws. Commonly prescribed medications may trigger positive drug tests. These include opioid pain relievers, benzodiazepines for anxiety disorders, ADHD stimulant medications, and certain sleep aids.
The legitimacy of prescription drug use in employment contexts depends on several factors. These include a valid prescription from a licensed physician and appropriate dosage levels. The person must have a legitimate medical condition. There should be an absence of impairment or safety concerns. Employers cannot automatically disqualify applicants solely based on prescription drug use. They must demonstrate direct safety risks or essential job function conflicts.
Protected Prescription Categories:
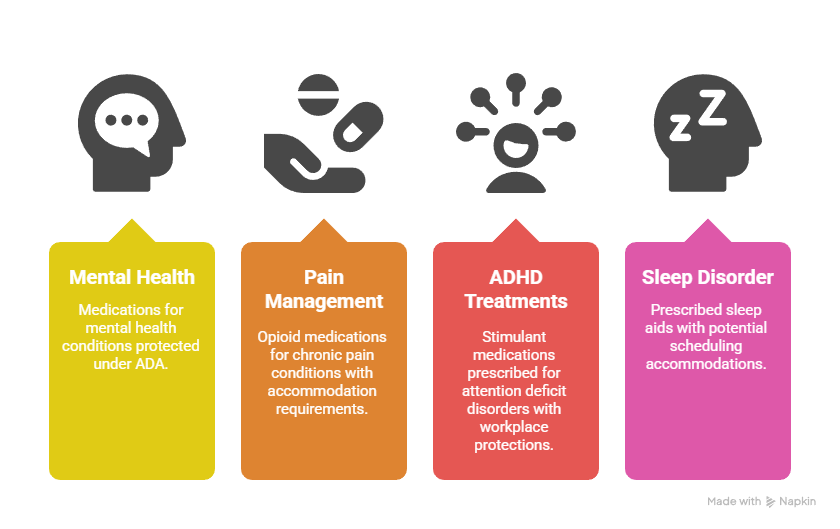
- Mental health medications: Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, mood stabilizers protected under ADA
- Pain management prescriptions: Opioid medications for chronic pain conditions with accommodation requirements
- ADHD treatments: Stimulant medications prescribed for attention deficit disorders with workplace protections
- Sleep disorder medications: Prescribed sleep aids with potential scheduling accommodations
Employment screening background check processes must separate prescription drug testing from other screening components. This separation helps maintain medical privacy. Legitimate prescription use cannot serve as grounds for employment discrimination. This applies when reasonable accommodations allow safe job performance.
Common Medications That Trigger Positive Tests
Many everyday prescription medications can cause positive drug test results. Opioid pain medications like oxycodone and hydrocodone will test positive for opiates. Benzodiazepines such as Xanax and Ativan show up on standard drug panels. ADHD medications like Adderall and Ritalin test positive for amphetamines.
Other medications can also cause unexpected positive results. Some over-the-counter medications may trigger false positives. Cold medicines containing pseudoephedrine can test positive for methamphetamines. Poppy seeds can cause positive opiate results. This is why the MRO review process is so important for accurate result interpretation.
Drug Test Disclosure Rights and Strategies
Drug test disclosure rights vary significantly based on timing, state laws, and employer policies. This makes strategic disclosure decisions crucial for protecting both employment opportunities and medical privacy. Pre-test disclosure involves revealing prescription medications before testing occurs. Post-test disclosure happens through the MRO process after positive results.
Pre-test disclosure strategies offer transparency. However, they may create unconscious bias or premature accommodation discussions. Many employment law attorneys recommend avoiding pre-test disclosure. This recommendation applies unless specifically required by employer policies. This approach maintains maximum privacy protection while preserving all legal rights.
Post-test disclosure through MRO channels provides the strongest legal protections. This approach allows individuals to maintain medical privacy unless drug test results necessitate explanation. The MRO process creates a confidential medical review. This often results in negative test reports to employers when legitimate prescriptions explain positive results.
Strategic Disclosure Considerations:
| Timing | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use Cases |
| Pre-test | Shows honesty, allows early accommodations | May create bias, unnecessary disclosure | Safety-sensitive roles |
| Post-test (MRO) | Maximum privacy, legal protections | No early accommodation planning | Most employment situations |
| No disclosure | Complete privacy | Risk if discovered later | Non-detectable medications |
Successful disclosure strategies require understanding specific state employment drug testing laws and individual employer policies. Documentation preparation and legal consultation can significantly improve outcomes. This is especially true when prescription drug disclosure becomes necessary.
State-Specific Disclosure Protections
State employment laws create varying levels of protection for prescription drug disclosure. Some states provide comprehensive privacy protections. Others offer minimal safeguards beyond federal requirements. California, New York, and several other states have enacted specific employment drug testing laws. These laws strengthen worker protections and limit employer discretion.
Enhanced Protection States:
- California: Strict MRO requirements, limited employer access to medical information
- New York: Comprehensive disability protections, restricted pre-employment testing
- Connecticut: Strong privacy protections, detailed accommodation processes
These enhanced protection jurisdictions typically require employers to demonstrate legitimate business necessity for drug testing. They also provide robust appeal processes and accommodation requirements.
Prescription Drug Testing Policy Compliance
Prescription drug testing policy compliance requires employers to balance workplace safety obligations with disability accommodation requirements. They must also maintain medical privacy protections. Comprehensive policies must address testing procedures, MRO processes, and accommodation protocols. They should also include appeals mechanisms while maintaining consistency with federal and state employment laws.
Effective workplace drug screening laws implementation includes clear policy communication. It also requires consistent application across all employees and proper training for supervisory personnel. Employers must establish specific protocols for handling prescription drug disclosures and accommodation requests. They must maintain confidentiality of medical information throughout these processes.
Policy Compliance Checklist:
- Establish clear testing procedures with detailed timelines and notification requirements
- Implement MRO processes with qualified medical professionals and confidentiality protections
- Create accommodation frameworks for prescription drug users with disabilities
- Develop appeal mechanisms for disputed test results or policy violations
- Maintain documentation standards for all testing and accommodation activities
- Provide supervisor training on disability accommodation and medical privacy requirements
Legal medication employment policies should include specific provisions for prescription drug use. They should also cover accommodation procedures and non-discrimination protections. Regular policy updates ensure continued compliance with evolving employment drug testing laws. They also help maintain compliance with disability rights legislation.
Employer Responsibilities and Limitations
Employers have specific responsibilities when implementing drug testing policies. They must provide clear written policies to all employees. They must use certified laboratories for testing. They must also ensure proper chain of custody procedures. Most importantly, they must respect employee medical privacy rights.
However, employers also face limitations on what they can do. They cannot discriminate against employees taking legally prescribed medications. They cannot ask about prescription drug use during interviews. They also cannot refuse to hire someone solely because they take prescription medications for a disability.
Workplace Drug Screening Laws by Industry
Industry-specific workplace drug screening laws create different compliance requirements. Transportation, healthcare, and safety-sensitive positions are subject to stricter federal regulations. Other sectors operate under more flexible state-based frameworks. DOT-regulated industries maintain mandatory testing protocols with limited accommodation options. Non-regulated employers have greater flexibility in policy development.
Transportation industry workers face the most restrictive prescription drug policies. This is due to safety concerns and federal oversight. However, even DOT regulations include MRO review processes. They also have specific accommodation procedures for certain prescription medications. These accommodations apply to medications that don't impair safety-sensitive functions.
Industry-Specific Requirements:
- Transportation (DOT): Mandatory testing, strict medication restrictions, limited accommodations
- Healthcare: Patient safety focus, professional licensing considerations, accommodation flexibility
- Manufacturing: Safety-sensitive position identification, equipment operation restrictions, case-by-case review
- Office/Professional: Minimal restrictions, broad accommodation requirements, privacy protections
Understanding industry-specific drug testing compliance helps job seekers prepare appropriate disclosure strategies. It also helps with accommodation requests. Each sector's unique safety concerns and regulatory framework influence available protections. They also affect employer discretion levels.
Safety-Sensitive Position Considerations
Safety-sensitive positions require careful evaluation of prescription drug effects on job performance. This evaluation must maintain compliance with disability accommodation laws. These roles typically involve operation of heavy machinery or transportation responsibilities. They may also include positions where impairment could endanger public safety.
Employers must conduct individualized assessments rather than blanket exclusions based on prescription drug use. This evaluation process considers specific job functions and medication effects. It also looks at accommodation possibilities and alternative assignment options. All of this must happen while maintaining safety standards.
DOT Regulated vs. Non-DOT Positions
DOT regulated positions have much stricter requirements than non-DOT jobs. DOT workers must follow federal transportation drug testing rules. These rules limit which prescription medications are acceptable. They also have very limited accommodation options for certain medications.
Non-DOT positions follow state employment laws and ADA requirements. These typically provide more flexibility for prescription drug users. Employers in non-DOT industries have more discretion to provide accommodations. They can often find ways to allow prescription drug use while maintaining workplace safety.
Drug Testing Compliance Documentation Requirements
Drug testing compliance documentation creates essential protection for both employees and employers. It establishes clear records of testing procedures, results, and accommodation requests. It also documents policy adherence. Proper documentation standards help prevent discrimination claims. They also ensure consistent application of employment drug testing policies.
Employee documentation should include prescription bottles with matching names. It should have current physician contact information. Medical records supporting legitimate use may be necessary in some cases. Maintaining organized medical documentation helps streamline MRO consultations. It also facilitates accommodation discussions while protecting privacy rights.
Essential Documentation Elements:
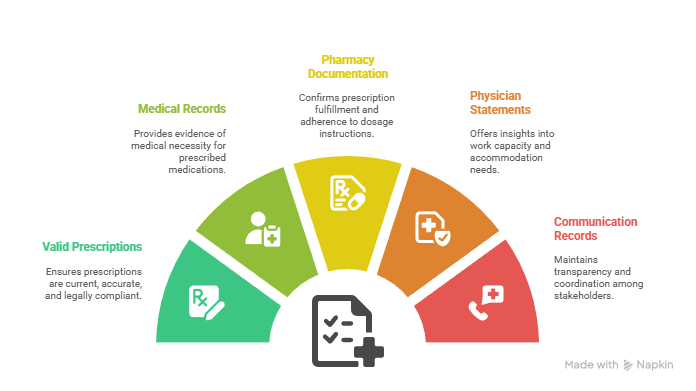
- Valid prescriptions with current dates, proper dosages, and licensed physician information
- Medical records supporting the necessity of prescription medications for legitimate conditions
- Pharmacy documentation confirming prescription fills and dosage compliance
- Physician statements regarding work capacity and accommodation needs when requested
- Communication records with MROs, employers, and accommodation coordinators
Employer documentation requirements include testing procedures and policy communications. They also cover accommodation decisions and appeals processes. Comprehensive record-keeping demonstrates good faith compliance efforts. It also supports legal defense against discrimination claims.
Employee Record-Keeping Best Practices
Employees should maintain their own records of all prescription medications and medical treatments. Keep copies of all prescriptions, including expired ones that might still show up in drug tests. Document all communications with healthcare providers about work accommodations. Also keep records of any workplace discussions about prescription drug use.
Store these documents securely but make them easily accessible. You may need them quickly during an MRO consultation. Digital copies stored in secure cloud services can be helpful. However, also maintain physical copies of important documents as backup options.
Preparing for MRO Consultations
MRO consultation preparation significantly influences outcomes when prescription drugs trigger positive employment drug test results. These confidential medical interviews allow individuals to present legitimate medical explanations. They also maintain privacy protections and legal rights throughout the process.
Successful MRO consultations require gathering complete prescription documentation and preparing clear medical explanations. You must also understand the consultation process timeline. Most MROs conduct telephone interviews within 72 hours of receiving positive test results. This makes rapid documentation assembly crucial for favorable outcomes.
MRO Interview Success Strategies:
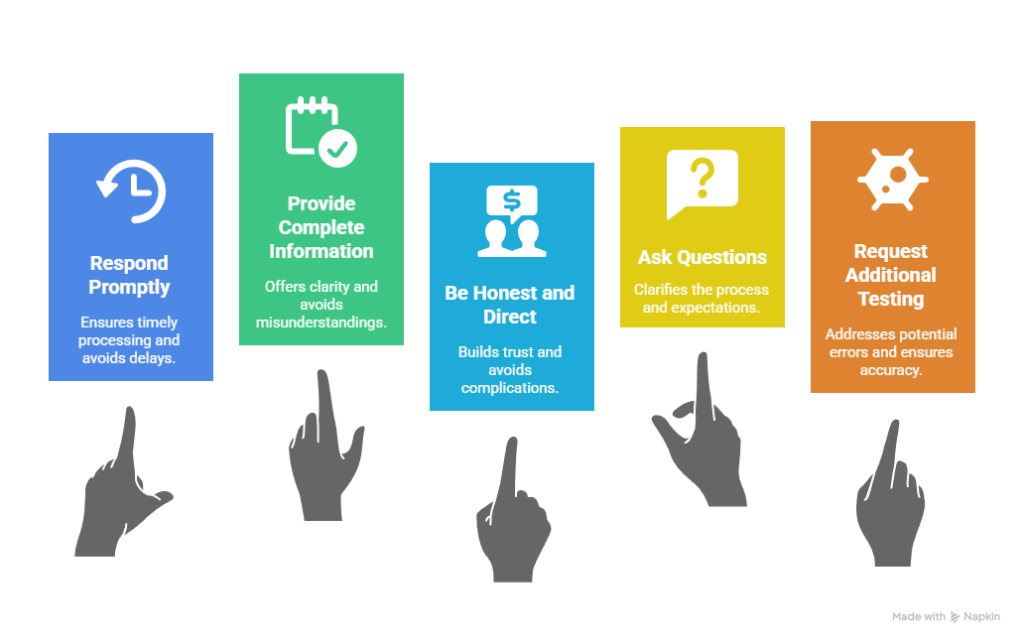
- Respond promptly to MRO contact attempts to avoid delayed processing
- Provide complete information including all relevant prescriptions and medical conditions
- Be honest and direct about prescription use and medical necessity
- Ask questions about the process, timeline, and potential outcomes
- Request additional testing if you believe laboratory errors occurred
Effective MRO consultation preparation includes understanding your rights to confidential medical review. It also includes the potential for negative test result reporting. This can happen when legitimate prescriptions explain positive results.
Documentation Organization Tips
Organizing medical documentation before employment drug testing begins helps ensure smooth MRO consultations. It also helps with accommodation processes. Create a comprehensive medical file with current prescriptions and physician contacts. Include relevant medical records that support your prescription use.
Digital documentation storage with secure cloud backup ensures access to medical records during time-sensitive MRO consultations. Physical copies provide backup options for important prescription verification documents. Make sure all prescription bottles have current labels with your name and prescribing physician information.
What to Expect During the MRO Call
The MRO will typically call you within 24-72 hours of receiving a positive test result. They will verify your identity and explain the purpose of the call. Be prepared to provide detailed information about your prescription medications. This includes dosage, frequency, and prescribing physician information.
The MRO may ask about when you last took the medication. They want to ensure the timing matches the test results. Be honest about any missed doses or changes in medication timing. The MRO may also ask about other medications or supplements you're taking. Some combinations can affect drug test results.
Understanding Your Rights During Drug Testing
Employment drug test rights encompass federal disability protections and state employment law safeguards. They also include specific procedural requirements that protect workers from discrimination while ensuring workplace safety. These rights include confidential medical review and accommodation considerations. They also cover appeals processes for disputed results.
The Americans with Disabilities Act provides foundational protections for individuals taking prescription medications for qualifying disabilities. It requires employers to engage in interactive accommodation processes rather than automatic disqualification. State employment laws often enhance these federal protections. They add additional privacy safeguards and procedural requirements.
Fundamental Testing Rights:
- Confidential MRO review for all positive drug test results
- Medical privacy protection during disclosure and accommodation processes
- Reasonable accommodation consideration for prescription drug use related to disabilities
- Appeals processes for disputed test results or policy violations
- Non-discrimination protection based on legitimate prescription drug use
- Documentation access to test results and procedural records
Understanding these rights helps job seekers navigate employment screening processes. It also helps maintain legal protections and medical privacy. Proper rights assertion can prevent discrimination. It can also ensure fair treatment during drug testing procedures.
ADA Protections for Prescription Drug Users
The Americans with Disabilities Act provides strong protections for people taking prescription medications for disabilities. Employers cannot discriminate against you solely because you take prescription medications. They must consider reasonable accommodations that allow you to perform essential job functions safely.
However, ADA protections have some limitations. The law doesn't protect current illegal drug use. It also allows employers to prohibit alcohol use in the workplace. Employers can still enforce safety requirements. But they must show that prescription drug use actually impairs your ability to do the job safely.
State Law Variations and Additional Protections
State employment laws vary widely in their protection of prescription drug users. Some states have very strong privacy protections and accommodation requirements. Others provide only minimal protections beyond federal requirements. Research your state's specific employment drug testing laws before job searching.
Many states require employers to follow specific procedures for drug testing. Some limit when testing can occur. Others require specific notification procedures. Some states also provide additional appeals processes beyond the federal MRO requirement.
Accommodation Requests and Workplace Solutions
Reasonable accommodation requests provide prescription drug users with options for maintaining employment while managing medical conditions. The accommodation process requires interactive dialogue between employees and employers. It aims to find solutions that meet both medical needs and workplace safety requirements.
Successful accommodations might include modified work schedules to account for medication timing. They could involve alternative job assignments that don't conflict with prescription drug effects. Some accommodations might include additional safety measures or modified equipment. The key is finding solutions that work for both parties.
Common Accommodation Examples:
- Schedule modifications to account for medication timing or medical appointments
- Alternative assignments to positions that don't conflict with medication effects
- Safety equipment or additional training to address potential impairment concerns
- Work environment changes such as lighting or noise modifications
- Leave time for medical appointments or medication adjustments
The accommodation process should begin as soon as a potential conflict is identified. Early engagement often leads to better solutions for everyone involved. Employers must engage in good faith discussions about possible accommodations.
Interactive Process Requirements
The ADA requires employers to engage in an interactive process when accommodation requests are made. This means both parties must work together in good faith to find solutions. Employers cannot simply deny requests without exploring options. They must show that accommodations would create undue hardship.
The interactive process should involve open communication about job requirements and medical limitations. Employers may request medical documentation to support accommodation needs. However, they cannot ask for complete medical records or unnecessary personal information.
Legal Resources and Support Options
Legal resources and support options provide crucial assistance for prescription drug users facing employment discrimination or drug testing issues. Employment law attorneys specializing in disability rights can provide guidance on complex situations. Many attorneys offer free consultations for discrimination cases.
State and federal agencies also provide support and enforcement of employment drug testing laws. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) handles federal disability discrimination complaints. State fair employment agencies handle state-level violations and provide additional resources.
Available Support Resources:
- Employment law attorneys specializing in disability discrimination and drug testing issues
- EEOC complaints for federal disability discrimination violations
- State employment agencies for state-specific law violations and guidance
- Disability rights organizations providing advocacy and legal support
- Professional associations offering industry-specific guidance and resources
These resources can help navigate complex legal issues and protect your rights. They can also provide guidance on documentation and procedure requirements. Early consultation often prevents problems from escalating.
When to Consult an Attorney
Consider consulting an employment law attorney if you believe you've faced discrimination based on legitimate prescription drug use. Also consult an attorney if an employer refuses to engage in the accommodation process. If you're facing termination or discipline related to prescription drug use, legal advice can be valuable.
Many employment attorneys work on contingency fees for discrimination cases. This means you don't pay unless you win your case. Most attorneys offer free initial consultations to evaluate your situation. Even if you don't hire an attorney, the consultation can help you understand your rights and options.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating employment drug testing while taking prescription medications requires understanding legal protections and strategic disclosure timing. It also requires proper MRO process preparation. The combination of federal ADA protections and varying state employment laws creates a complex but navigable framework for prescription drug users seeking employment. By maintaining proper documentation and understanding industry-specific requirements, job seekers can protect their opportunities. Utilizing MRO consultation rights also helps protect both employment opportunities and medical privacy. Most importantly, legitimate prescription drug use should not automatically disqualify individuals from employment opportunities when proper procedures are followed and reasonable accommodations are possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I have to disclose prescription medications before taking an employment drug test?
No, you are not required to disclose prescription medications before testing in most situations. The MRO process provides a confidential post-test disclosure option that often provides better privacy protection while maintaining all legal rights to medical review and accommodation.
Can employers refuse to hire me because I take prescription medications?
Employers cannot automatically refuse hiring based solely on legitimate prescription drug use. They must demonstrate that your medication use creates direct safety risks or prevents essential job function performance, and must consider reasonable accommodations under disability laws.
What happens during an MRO consultation after a positive drug test?
The Medical Review Officer will contact you within 72 hours to conduct a confidential medical interview. You'll provide prescription documentation and medical explanations for the positive result. The MRO then determines whether to report a negative or positive result to your employer based on legitimate medical use.
Which prescription medications commonly cause positive drug test results?
Common medications that trigger positive results include opioid pain relievers (oxycodone, hydrocodone), benzodiazepines (Xanax, Ativan), stimulants for ADHD (Adderall, Ritalin), and certain sleep medications. Always maintain current prescription documentation for any controlled substances.
Are there different rules for safety-sensitive jobs like transportation or healthcare?
Yes, DOT-regulated transportation positions have stricter federal requirements with limited accommodation options, though MRO review processes still apply. Healthcare positions often have professional licensing considerations, but generally allow more accommodation flexibility than transportation roles.
Can I request a retest if I believe my drug test results are wrong?
Yes, you have the right to request additional testing during the MRO consultation process. This may include testing split samples or requesting review of laboratory procedures. The MRO can order additional testing when legitimate concerns about accuracy exist.
How long do employers keep drug test results and medical information?
Employers must maintain drug testing records according to federal and state requirements, typically 1-5 years depending on the industry. Medical information disclosed during accommodation processes must be kept confidential and separate from general personnel files under ADA requirements.
What should I do if an employer discriminates against me for legitimate prescription use?
Document all interactions, maintain medical records, and consider consulting with an employment law attorney. File complaints with appropriate state agencies or the EEOC for disability discrimination. Many attorneys offer free consultations for employment discrimination cases involving prescription drug use.
Additional Resources
- U.S. Department of Transportation - Drug Testing Regulations
https://www.transportation.gov/odapc - EEOC Guidance on Disability Discrimination and Drug Testing
https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance - National Association of Medical Review Officers
https://www.namro.org - Americans with Disabilities Act - Employment Resources
https://www.ada.gov/topics/employment - State Employment Drug Testing Laws Database
https://www.ncsl.org/labor-and-employment/drug-testing - Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration - Workplace Guidelines
https://www.samhsa.gov/workplace - Employment Law Attorney Directory for Drug Testing Issues
https://www.nela.org/find-attorney - Prescription Drug Information and Employment Rights
https://www.dol.gov/general/topic/disability/ada

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





