Active warrants typically appear on employment background checks when employers conduct comprehensive criminal history screenings. However, warrant visibility depends on the specific type of background check performed, jurisdiction policies, and the screening company's database access.
Key Takeaways
- Active warrants generally show up on thorough employment background checks that include criminal record searches and court database queries.
- The type of background screening determines warrant visibility. Basic checks may miss warrant information while comprehensive screenings typically capture active warrants.
- Federal warrants and felony warrants are more likely to appear on background checks than minor misdemeanor warrants. This occurs due to database integration differences.
- Employers must follow FCRA compliance guidelines when using warrant information in hiring decisions. This includes providing proper disclosure and adverse action notices.
- Job applicants have legal rights regarding background check accuracy. Additionally, they can dispute incorrect warrant information through formal procedures.
- Some jurisdictions limit how employers can use pending criminal matters in employment decisions. These restrictions include active warrants through "ban the box" legislation.
Understanding Active Warrants in Employment Screening
Active warrants are legal documents issued by courts. They allow law enforcement to arrest individuals for criminal activity or failure to appear in court. When employers conduct background checks, these warrant records often show up through database searches. Furthermore, screening companies use multiple sources to gather this information.
Employment screening involves many factors that affect job seekers and hiring organizations. Legal requirements, technical systems, and procedures all play important roles. As a result, both employers and applicants need to understand how warrants appear in background checks. Moreover, knowing these details helps everyone make better decisions.
Background check companies gather information from many sources to create reports on job candidates. These sources include court records, law enforcement databases, and criminal justice systems. Consequently, screening services often include active warrant details in their reports. However, warrant information accuracy can vary greatly. This depends on how well databases are maintained, how jurisdictions report information, and which screening methods are used.
The Fair Credit Reporting Act controls how employers use background check information. This includes active warrant data in hiring decisions. This federal law requires employers to follow specific steps when they make negative employment decisions based on background check results. Therefore, understanding these legal rules helps both employers and job applicants handle warrant-related screening issues better.
Employment background checks have become more thorough over time. Similarly, warrant detection methods have improved with better technology. Nevertheless, gaps in information still exist due to system limitations. Additionally, different screening companies may have varying levels of access to warrant databases.
Types of Background Checks That Reveal Warrant Information
Different types of background checks have varying abilities to detect active warrants. Basic employment verifications typically focus on work history and education only. In contrast, comprehensive criminal screenings search multiple databases for legal issues. Therefore, understanding which type of screening reveals warrant information is crucial for both employers and job seekers.
Employment screening packages range from simple reference checks to extensive investigations. Meanwhile, the depth of warrant searching depends on the specific services purchased. Furthermore, screening companies offer different levels of database access based on their capabilities and client needs.
Comprehensive Criminal History Searches
Comprehensive criminal background checks offer the most thorough screening option available to employers. They typically include active warrant searches across multiple jurisdictions. These extensive investigations check federal, state, and local criminal justice databases. As a result, they can identify outstanding legal issues including pending warrants, criminal charges, and court proceedings.
Professional screening companies often have direct access to court management systems. They also connect to law enforcement databases that contain current warrant information. The scope of comprehensive criminal searches goes beyond simple conviction records. Instead, they include pending cases, active warrants, and other legal matters that may affect job suitability.
Court Record Database Searches
Court record searches focus specifically on judicial system databases where warrant information is stored. Court staff regularly update these databases with new information. These searches can find active bench warrants, arrest warrants, and other court-issued legal documents. Furthermore, they may discover warrants that don't show up in other types of screening.
The success of court record searches varies by location. Some courts keep better digital records than others. Additionally, database access and connection capabilities differ across different areas.
| Search Type | Warrant Detection Rate | Database Sources |
| Federal Court Search | 95% for federal warrants | PACER, FBI databases |
| State Court Search | 80-90% for state warrants | State court management systems |
| County Court Search | 70-85% for local warrants | County clerk databases |
Court database integration affects how well warrants are detected during screenings. Moreover, the timing of when searches are conducted can impact results. Some databases update more frequently than others, which creates differences in information availability.
Factors Affecting Warrant Visibility on Background Checks
Many factors determine whether active warrants appear on employment background checks. These technical and procedural issues can affect how accurate and complete screening results are. Database connection problems create significant challenges. Similarly, different reporting methods between jurisdictions affect warrant detection. Additionally, screening company abilities influence whether warrant information shows up in final reports.
The timing of database updates affects warrant visibility. Moreover, specific search settings used during screening can impact detection rates. These factors work together to determine how effective warrant searches will be. Consequently, understanding these limitations helps explain why some warrants may not appear on certain background checks.
Different areas have significant differences in warrant reporting methods. Some states have centralized criminal justice systems that make comprehensive warrant searches easier. In contrast, others rely on separate local systems. These separate systems may not work well with commercial screening databases. As a result, technical limitations can cause incomplete warrant information to appear on background checks.
Database maintenance schedules vary widely between different criminal justice systems. Furthermore, data sharing agreements between agencies can be complex and sometimes incomplete. Meanwhile, screening companies must navigate these various systems to gather accurate information. Therefore, some warrant information may be missed due to system limitations rather than screening company errors.
Database Update Frequencies and Timing Issues
Criminal justice databases work on different update schedules. These schedules can affect how current and accurate warrant information is in background check reports. Some systems update warrant status immediately. However, others may have delays of several days or weeks before new warrant information becomes available. As a result, these timing differences can create problematic situations.
Recently issued warrants may not show up on background checks right away. Conversely, resolved warrants may continue to appear as active even after they have been handled. Therefore, understanding these timing issues is important for correctly interpreting background check results.
The coordination between court systems, law enforcement agencies, and commercial screening databases involves complicated processes. These include data sharing agreements and technical connections between systems. When these systems have delays or technical problems, warrant information may become temporarily unavailable. Additionally, information may become incorrect during system disruptions.
System integration challenges affect warrant reporting consistency across different jurisdictions. Moreover, budget constraints may limit how often some databases are updated. Meanwhile, technological differences between older and newer systems can create compatibility issues. Consequently, these factors contribute to variations in warrant detection rates.
Legal Rights and FCRA Compliance in Warrant-Related Screening
The legal framework surrounding warrant information in employment screening is complex but important. Federal and state laws provide protections for job applicants while also allowing employers to make informed hiring decisions. Understanding these legal requirements helps both parties navigate the screening process appropriately. Moreover, compliance with these laws is mandatory for employers who conduct background checks.
Employment law continues to evolve regarding how warrant information can be used in hiring decisions. Similarly, court interpretations of existing laws provide additional guidance. Nevertheless, the basic principles of fair treatment and accurate information remain constant. Additionally, recent legislative changes in some areas have created new requirements for employers.
Employee Rights Under Federal Law
The Fair Credit Reporting Act provides strong protections for job applicants. These protections apply when employers use background check information, including active warrant data, in employment decisions. Candidates have the right to receive proper notice before background checks are conducted. They also have the right to get copies of their background check reports. Furthermore, they can dispute incorrect information that appears in screening results.
These rights specifically cover warrant-related information. This includes data that may be outdated, incorrect, or improperly reported. When warrant information appears on background checks, applicants can challenge how accurate this data is. They can do this through formal dispute procedures with both the screening company and the original data sources.
The dispute process requires screening companies to investigate challenged information. They must fix any errors within reasonable time periods. However, warrant-related disputes can be complicated and often need legal help to handle effectively.
Applicant rights also include protection from discrimination based on arrest records in many jurisdictions. Furthermore, some areas have specific laws about how pending legal matters can be considered. Meanwhile, employers must balance their need for safety with applicant privacy rights. Therefore, understanding these legal protections is essential for all parties involved.
Employer Obligations and Adverse Action Procedures
Employers must follow specific FCRA procedures when using warrant information from background checks. This applies when making negative employment decisions. These requirements include providing pre-adverse action notices. These notices allow candidates to review and dispute background check results before final employment decisions are made.
The adverse action process also requires employers to provide specific information. This includes details about the screening company used and the candidate's rights to dispute incorrect information. Compliance with these requirements is required under federal law.
FCRA Compliance Requirements for Warrant-Related Decisions:
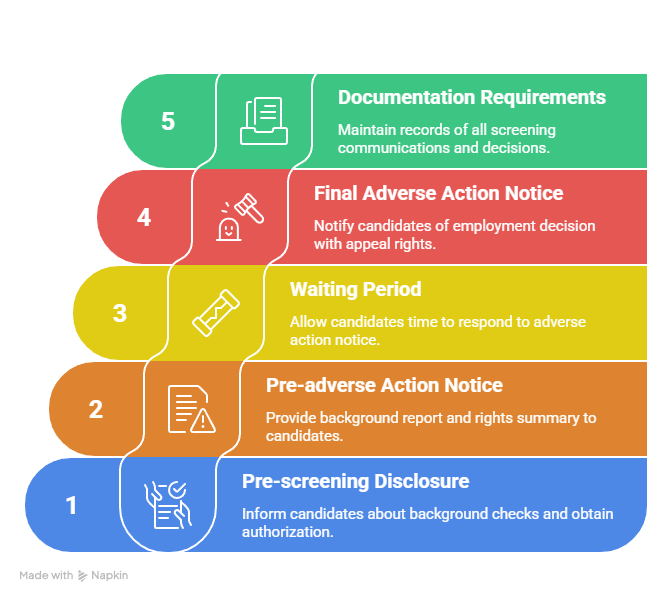
- Pre-screening disclosure: Clear written notice of background check intent and candidate authorization
- Pre-adverse action notice: Copy of background report and summary of rights when considering negative action
- Waiting period: Reasonable time for candidate to respond to adverse action notice
- Final adverse action notice: Formal notification of employment decision with appeal rights information
- Documentation requirements: Proper record-keeping of all screening-related communications and decisions
FCRA compliance becomes more complex when warrant information is involved. Employers must tell the difference between pending legal matters and actual criminal convictions. Many areas have implemented "ban the box" legislation. This legislation further limits how employers can use pending criminal matters, including active warrants, in initial screening decisions.
Employer training on FCRA requirements is essential for proper compliance. Additionally, regular policy updates help ensure continued adherence to legal requirements. Meanwhile, documentation of all screening-related decisions protects employers from potential legal challenges. Furthermore, working with experienced screening companies can help ensure proper procedures are followed.
Industry-Specific Considerations for Warrant Screening
Different industries face varying rules and risk management needs. This applies when conducting background checks that may reveal active warrant information. Financial services, healthcare, transportation, and government contractors often work under enhanced screening requirements. These requirements need comprehensive criminal history investigations, including active warrant searches. Consequently, these industry-specific requirements can affect both how deep screening goes and how warrant information is evaluated.
Professional licensing boards and regulatory agencies may also require disclosure. This includes active warrants or pending criminal matters as part of licensing maintenance or renewal processes. This creates additional considerations for employers in regulated industries. Hiring individuals with active warrants could potentially affect the organization's licensing status or regulatory compliance.
Industry standards continue to evolve as technology and legal requirements change. Similarly, professional organizations often provide guidance on best practices for their sectors. Nevertheless, employers must stay current with both industry-specific and general legal requirements. Additionally, regular policy reviews help ensure continued compliance with changing standards.
High-Security and Sensitive Position Requirements
Positions involving access to sensitive information require enhanced background screening. This includes roles involving financial assets or vulnerable populations. These screenings typically include active warrant searches. Government security clearance investigations, financial industry background checks, and healthcare credential verification processes often require comprehensive criminal history reviews. Therefore, these enhanced screening requirements would identify active warrant status.
The evaluation standards for warrant-related findings in sensitive positions often differ from standard employment screening. Some organizations use zero-tolerance policies for any active legal issues. However, these policies must still comply with applicable employment laws and FCRA requirements. This creates complex legal and procedural considerations for employers in high-security industries.
High-security positions may also require ongoing monitoring rather than just initial screening. Furthermore, security clearance requirements can change based on the level of access needed. Meanwhile, some positions may allow for conditional employment pending warrant resolution. Therefore, employers in these industries need detailed policies and procedures for handling warrant-related issues.
Geographic and Jurisdictional Variations in Warrant Reporting
Geographic location significantly affects how well active warrants appear on background checks. Different states, counties, and municipalities have varying systems for maintaining and sharing warrant information. Understanding these geographic differences helps explain why warrant detection rates can vary greatly depending on where screening is conducted. Moreover, these variations affect both the accuracy and completeness of background check results.
Regional differences in technology infrastructure also impact warrant reporting capabilities. Similarly, funding levels for court systems and law enforcement agencies vary widely across different areas. Nevertheless, efforts to improve information sharing continue at all levels of government. Additionally, federal initiatives aim to standardize certain aspects of criminal justice information systems.

State-Level Database Integration Differences
State criminal justice information systems vary greatly in their connection capabilities. They also differ in data sharing agreements with commercial background screening companies. Some states have comprehensive, centralized databases. These databases make thorough warrant searches possible across all areas within the state. In contrast, others rely on separated systems. These systems may not capture warrant information from all local courts and law enforcement agencies.
These differences can create significant gaps in warrant detection rates. The gaps depend on where the screening is done and where the warrants were issued. Interstate data sharing agreements and federal database integration also affect warrant visibility on background checks.
The National Crime Information Center (NCIC) keeps certain warrant information at the federal level. However, access to this database is limited to law enforcement agencies and authorized screening companies. Commercial screening companies may have different levels of access to federal warrant information. This can affect how complete their reports are.
State-level initiatives to improve database integration continue to develop. Furthermore, federal funding sometimes supports these improvement efforts. Meanwhile, privacy concerns must be balanced with the need for accurate information sharing. Therefore, progress in this area often involves complex negotiations between various stakeholders.
Local Court System Variations
Local court systems work under different administrative procedures. They also have varying technology capabilities that can significantly affect warrant reporting accuracy and timeliness. Urban areas with well-funded court systems typically keep more comprehensive digital records. They also have faster database update procedures compared to rural courts with limited technology resources.
These differences can result in warrant information being more easily available from some areas. Meanwhile, information from other areas remains difficult to access. Understanding these local variations helps explain inconsistencies in background check results.
Jurisdictional Factors Affecting Warrant Detection:
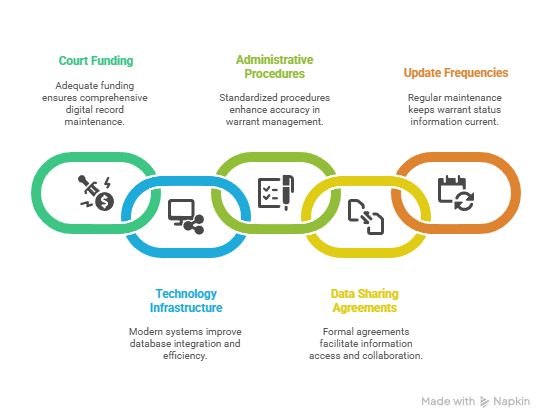
- Court system funding levels: Better-funded courts maintain more comprehensive digital records
- Technology infrastructure: Modern case management systems provide better database integration
- Administrative procedures: Standardized warrant entry and update procedures improve accuracy
- Data sharing agreements: Formal agreements with screening companies facilitate information access
- Update frequencies: Regular database maintenance ensures current warrant status information
Local government budget priorities significantly impact court system technology capabilities. Additionally, staff training levels affect how accurately information is entered and maintained. Meanwhile, some smaller jurisdictions may lack dedicated IT support for their systems. Furthermore, geographic isolation can create additional challenges for system connectivity and maintenance.
Accuracy and Dispute Resolution for Warrant Information
Background check accuracy issues are especially problematic when they involve active warrant information. These records can significantly affect employment opportunities and personal reputation. Common accuracy problems include outdated warrant status, incorrect personal identification information, and warrants that have been resolved but continue to appear as active. The technical complexity of criminal justice data systems contributes to these challenges. Additionally, the multiple agencies involved in warrant processing create additional complications.
The dispute resolution process for warrant-related background check errors requires coordination. This coordination involves screening companies, court systems, and law enforcement agencies. The process aims to verify current warrant status and correct inaccurate information. This process can be time-consuming and complex. This is particularly true when warrants were issued by courts in different areas or when court records are incomplete.
Accuracy issues can have serious consequences for job seekers and employers alike. Similarly, incorrect warrant information can lead to wrongful denial of employment opportunities. Nevertheless, proper dispute procedures can help resolve these issues when they occur. Additionally, ongoing improvements in database technology continue to reduce accuracy problems over time.
Common Warrant-Related Accuracy Issues
Identity mismatching represents one of the most significant accuracy problems. This occurs in warrant-related background check information, particularly when individuals share similar names, birth dates, or other identifying information. Criminal justice databases may contain incomplete or outdated personal information. This can result in warrant records being incorrectly assigned to the wrong individuals.
These misidentification issues can be especially problematic in background screening contexts. Employers may make negative employment decisions based on inaccurate warrant information. Therefore, proper identity verification is crucial for accurate screening results.
Resolved warrant status often fails to update quickly in screening databases. This results in situations where warrants that have been satisfied, dismissed, or otherwise resolved continue to appear as active. Court administrative delays contribute to these status update problems. Additionally, database synchronization issues and inadequate data sharing procedures between agencies create further complications.
| Accuracy Issue Type | Frequency Rate | Resolution Timeframe |
| Identity Mismatch | 15-20% of warrant reports | 30-60 days |
| Outdated Status | 25-30% of warrant reports | 14-45 days |
| Jurisdiction Errors | 10-15% of warrant reports | 21-90 days |
Technical improvements in identity verification continue to reduce mismatching problems. Furthermore, standardized data formats help improve accuracy across different systems. Meanwhile, regular database audits can identify and correct systemic accuracy issues. Therefore, the overall accuracy of warrant-related information continues to improve gradually.
Best Practices for Employers and Job Seekers
Both employers and job seekers can take steps to handle warrant-related background check issues more effectively. Employers should develop clear policies about how they evaluate warrant information in hiring decisions. Meanwhile, job seekers should be proactive about understanding their background check rights and addressing any accuracy issues. Therefore, preparation and knowledge help both parties navigate these situations successfully.
Clear communication between employers and job seekers helps prevent misunderstandings about warrant-related findings. Similarly, transparency about screening procedures and evaluation criteria promotes fairness in the hiring process. Nevertheless, legal requirements must always be followed regardless of informal agreements. Additionally, documentation of all interactions protects both parties from potential disputes.
Employers benefit from working with experienced screening companies that understand warrant-related complexities. Furthermore, regular training for HR staff helps ensure proper handling of sensitive background check information. Meanwhile, job seekers should consider conducting self-background checks to identify potential issues before applying for positions. Therefore, proactive approaches help prevent problems and facilitate smoother hiring processes.
Professional development in background screening continues to evolve with changing technology and legal requirements. Additionally, industry associations provide valuable resources for staying current with best practices. Meanwhile, legal counsel can help both employers and job seekers understand their rights and obligations. Furthermore, regular policy reviews ensure continued compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Conclusion
Active warrants typically appear on comprehensive employment background checks. However, visibility depends on screening depth, database access, and location factors. Employers must navigate FCRA compliance requirements when using warrant information in hiring decisions. Meanwhile, job applicants retain rights to dispute inaccurate information. The complexity of warrant-related screening requires careful attention to legal requirements, accuracy verification, and industry-specific considerations. Understanding these factors helps all parties make informed decisions about employment screening involving active warrant information.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do all background checks show active warrants?
Not all background checks reveal active warrants. Basic employment screenings that only verify employment history or education typically won't include warrant information. However, comprehensive criminal background checks that search court records and law enforcement databases will usually identify active warrants. The scope of warrant detection depends on the specific screening package purchased by the employer. Additionally, it depends on the screening company's database access capabilities.
How long do active warrants stay on background checks?
Active warrants remain on background checks indefinitely until they are resolved through the court system. Unlike some criminal records that may be sealed or expunged after certain timeframes, warrants continue to appear on screenings until the underlying legal matter is addressed. Once a warrant is satisfied, dismissed, or otherwise resolved, it should be removed from active status. However, database updates may take several weeks to reflect the change.
Can I get a job if I have an active warrant?
Having an active warrant doesn't automatically disqualify you from employment. Hiring decisions depend on various factors including the nature of the warrant, job requirements, and employer policies. Many employers consider the relevance of legal issues to job responsibilities. Some positions have stricter requirements than others. However, FCRA regulations require employers to follow specific procedures before making adverse employment decisions based on background check findings, including active warrants.
Are bench warrants different from arrest warrants on background checks?
Background check reports may distinguish between different warrant types. However, both bench warrants and arrest warrants typically appear on comprehensive criminal screenings. Bench warrants are usually issued for failure to appear in court. In contrast, arrest warrants authorize law enforcement to arrest individuals for alleged criminal activity. Some employers may view these warrant types differently when making employment decisions. They consider factors such as the underlying charges and circumstances.
Do active warrants from other states show up on background checks?
Interstate warrant information can appear on background checks. This depends on database integration and information sharing agreements between jurisdictions. Federal warrant databases and interstate criminal justice information systems facilitate cross-border warrant reporting. However, coverage may be incomplete for some local jurisdictions. Comprehensive background checks often include multi-state searches that can identify warrants from various jurisdictions. Nevertheless, smaller counties or specialized courts may have limited database connectivity.
How do I remove incorrect warrant information from my background check?
Correcting inaccurate warrant information requires disputing the errors with both the screening company and the original data sources. The FCRA provides specific procedures for challenging background check accuracy. This includes formal dispute notifications that require investigation and correction of inaccurate information. You'll typically need documentation proving the warrant information is incorrect. This includes court records showing case dismissal or warrant satisfaction. The dispute process can take 30-60 days. Additionally, it may require legal assistance for complex cases.
Additional Resources
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) Compliance Guide
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/fair-credit-reporting-act - Equal Employment Opportunity Commission Background Check Guidelines
https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment-decisions - National Association of Professional Background Screeners Best Practices
https://www.napbs.com/best-practices - Consumer Financial Protection Bureau Background Check Rights
https://www.consumerfinance.gov/consumer-tools/background-checks/ - Society for Human Resource Management Background Screening Resources
https://www.shrm.org/topics-tools/tools/toolkits/background-investigations - Legal Aid Foundation Criminal Record Resources
https://www.legalaid.org/issues/criminal-justice/criminal-records

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





