Navigating the realm of pre-employment screenings can be a maze for both employers and job seekers. The question of whether "do pre-employment drug screens test for alcohol?" is both common and crucial. In this guide, we'll dive deep into the intricacies of drug and alcohol testing, providing you with essential knowledge to navigate this aspect of the hiring process. Whether you're a business owner, HR professional, recruiter, or job seeker, this comprehensive overview will answer your questions and outline practical considerations for everyone involved.
Key Takeaways
- Pre-employment drug screens are crucial for workplace safety and compliance, often including tests for substances like THC, opiates, amphetamines, cocaine, and PCP.
- Alcohol is typically not included in standard drug panels but may be tested for in safety-sensitive industries like transportation, as mandated by the Department of Transportation (DOT).
- Various methods such as breath, urine, blood, and mouth swab tests are available for alcohol detection, each with its strengths and appropriate use cases.
- Employers and job seekers should clearly understand the testing policies and prepare accordingly, ensuring both compliance with legal standards and the maintenance of workplace safety.
- Industry-specific considerations dictate the necessity and scope of drug and alcohol testing, with heightened importance in sectors like healthcare, transportation, retail, and hospitality.
Introduction
In today's workplace, ensuring safety and compliance is paramount, and pre-employment drug and alcohol testing plays a critical role in that effort. Employers need to safeguard their work environment, while job seekers must be aware of what these tests entail. This article aims to unravel the complexities surrounding pre-employment drug screens, particularly examining whether they test for alcohol.
We'll cover the essentials: what substances are typically checked, the inclusion (or exclusion) of alcohol in these tests, and industry-specific considerations. If you're involved in the hiring process, whether as an employer, HR professional, recruiter, or job seeker, understanding these aspects can pave the way for smoother, more informed decisions.
By breaking down the specifics of pre-employment drug screens and their implications, we offer you a clear roadmap to navigate this often-confusing territory.

Understanding Pre-Employment Drug Screens
Pre-employment drug screens are a standard part of the hiring process for many companies. These tests are designed to screen potential employees for the presence of illegal substances and, in some cases, alcohol.
Definition and Purpose
A pre-employment drug screen is a test that employers use to detect the presence of drugs or alcohol in a candidate’s system before they are officially hired. The purpose is multi-faceted: it helps ensure workplace safety, maintain productivity, and comply with legal and regulatory standards. For instance, in safety-sensitive roles such as those involving heavy machinery or public transportation, ensuring employees are sober and drug-free is paramount.
Being able to rotate in different facets of HR, I can say that the hiring and selection process is among the toughest processes in the field of Human Resources. But hey, we must not forget as well the pre-employment screenings which others might think is just for the sake of ticking the box for compliance. I’ve seen firsthand how confusion around alcohol testing can lead to misunderstandings. The reality is, that alcohol isn’t typically part of standard drug panels. However, there are additional layers of checking for some safety-sensitive positions. As we go through twists and turns related to this experience, I have learned that open communication is the key to attaining success in this initiative. After all, we have one goal which is not only to help the organization but also the people we bring into the organization.
Components of a Drug Screen
Typically, a standard pre-employment drug screen tests for several common substances. These often include:
- THC (marijuana)
- Opiates (e.g., heroin, morphine)
- Amphetamines (e.g., methamphetamine)
- Cocaine
- Phencyclidine (PCP)
Employers may opt for different panel tests (e.g., 5-panel, 10-panel) that vary in the number of substances they test for. Some may also include prescription medications that can impair one's ability to perform job duties safely and effectively.
Importance in Various Industries
The necessity of pre-employment drug screens can vary significantly depending on the industry:
- Healthcare: Ensuring that medical professionals are not under the influence is critical to patient safety.
- Transportation: Federal regulations often mandate drug screenings for jobs involving driving or operating heavy equipment, underscoring the sector’s focus on public safety.
- Technology: While not always legally required, companies in this sector may still conduct drug tests to maintain high levels of performance and innovation.
By understanding the components and importance of pre-employment drug screens, both employers and job seekers can better navigate this vital aspect of the hiring process.
Do Pre-Employment Drug Screens Test for Alcohol?
Standard Drug Panels
In the world of pre-employment screenings, most potential employees are familiar with the standard drug panels, which typically test for substances like THC, opiates, amphetamines, cocaine, and PCP. However, alcohol is not usually included in these standard panels, which can be a surprise for many.
Alcohol Testing in Pre-Employment Screens
When it comes to alcohol testing, the approach can vary considerably. While many standard drug screens don't include alcohol, there are specific situations where testing for alcohol may be mandatory or considered a best practice.
DOT and Non-DOT Testing
For employers regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT), alcohol testing is a requirement. The DOT mandates alcohol and drug testing for safety-sensitive employees, such as pilots, truck drivers, and train operators, given the critical nature of their roles. This ensures a zero-tolerance stance on intoxication, which could jeopardize public safety.
On the other hand, Non-DOT regulated industries have more flexibility. They may choose to include alcohol testing based on their specific policies and the nature of the job. For instance, positions where safety is a concern or where employees represent the company in a public capacity might have more stringent testing policies that include alcohol. This can contribute to creating a safe and professional work environment and minimize the risk of accidents or liability issues.
In essence, while alcohol isn't a staple in all pre-employment drug screens, there are circumstances and industries where its inclusion is crucial. Whether you're an employer seeking to create robust screening policies or a job seeker preparing for a drug test, understanding these nuances can help you navigate the process with greater confidence.
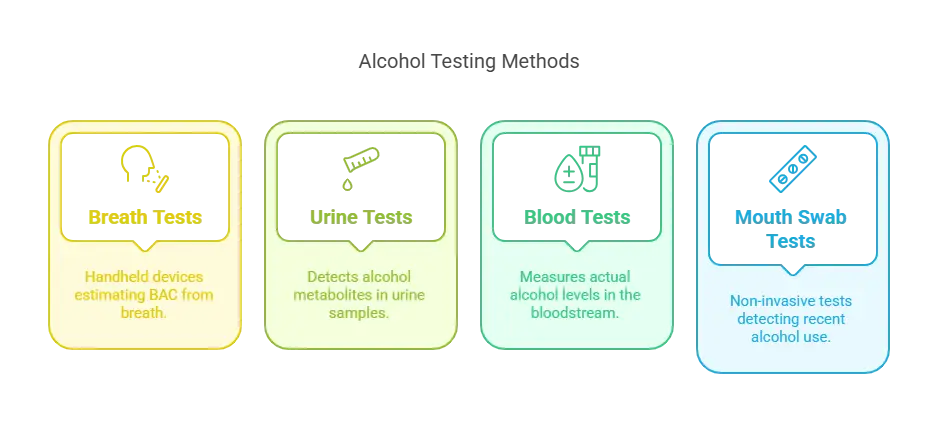
Types of Alcohol Testing Methods
When it comes to pre-employment alcohol testing, there are several methods available. Each has its strengths and potential applications within the hiring process. Here’s a breakdown:
Breath Tests
Breathalyzers are perhaps the most well-known tool for measuring blood alcohol concentration (BAC). These handheld devices estimate BAC by analyzing a person's breath. In pre-employment settings, breath tests are less common but might be used in industries where immediate alcohol detection is critical, such as transportation and law enforcement.
Urine Tests
Urine tests are frequently employed in pre-employment drug screens and can detect alcohol metabolites, such as ethyl glucuronide (EtG). These tests are relatively affordable and simple to administer. While urine tests are better known for detecting drugs, they can also identify alcohol use within the past 12 to 48 hours. This makes them useful for employers looking to ensure that potential hires are free from recent alcohol use.
Blood Tests
Blood tests measure the actual amount of alcohol in the bloodstream, providing a highly accurate BAC reading. These tests are more invasive and expensive compared to other methods, which makes them less common in standard pre-employment checks. However, they might be used in specific scenarios where precise quantification of alcohol levels is required.
Mouth Swab Tests
Mouth swab tests, or saliva tests, can detect alcohol use that has occurred within the past 24 hours. These tests are non-invasive, easy to administer, and provide quick results. Their ability to detect recent alcohol use makes them particularly useful for industries where immediate sobriety is essential, such as healthcare and transportation.
By understanding the different methods of alcohol testing, employers can make informed decisions about which type of test best fits their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
FAQs Surrounding Alcohol Testing in Pre-Employment Drug Screens
Why include alcohol testing in pre-employment screens?
Including alcohol testing in pre-employment drug screens can be crucial for employers looking to maintain a safe and productive workplace. Alcohol impairment can lead to accidents, lower productivity, and compromise workplace safety. For roles that involve operating heavy machinery, driving, or healthcare, even a slight impairment can have serious consequences. Employers may also aim to promote a culture of responsibility and professionalism.
What are the costs for pre-employment drug screens?
One of the common concerns around pre-employment screens is cost. The cost of a basic urine drug screen typically ranges between $30 to $60. However, adding alcohol testing can increase the cost marginally, depending on the method used. For example, urine alcohol tests might add an extra $10 to $20 per test, whereas more sophisticated methods like blood tests can be more expensive. Employers must weigh these costs against the potential risks and benefits of including alcohol testing in their pre-employment screening process.
What are the employer policies in pre-employment drug testing?
Employer policies around alcohol testing can vary widely. Some companies have zero-tolerance policies and include alcohol testing as a standard part of the pre-employment screening. Others may only include it for certain positions deemed safety-sensitive. It’s vital for employers to clearly communicate their policies to job applicants and ensure they comply with relevant laws and regulations. Employers should also consider periodic reviews and updates to their policies to ensure they remain relevant and legally compliant.
Preparing for Pre-Employment Drug Screens
Job Seekers
What to Expect
Stepping into the world of pre-employment screenings can feel daunting, but knowledge is power. Typically, you’ll be asked to provide a sample—often urine, but it could also be hair, blood, or saliva—either at your potential employer's location or a designated testing facility. The test aims to check for illicit drugs and, occasionally, alcohol.
Preparation Tips
Preparation isn’t about "beating" the test but rather understanding it. Avoid consuming substances that could yield a positive result, and be cautious with over-the-counter medications and foods that might be flagged. Staying hydrated and well-rested won't influence the outcome, but it will help you feel more at ease during the process.
Failing the Test
Failing a pre-employment drug test can feel like a major setback, but it's not the end of the road. Different employers have different policies; some might allow a retest after a period of time, especially if the substance detected is legally prescribed. Knowing the policy of the company you're applying to will help you navigate the next steps.
Employers
Policy Development
For employers, creating a clear and fair drug and alcohol testing policy is fundamental. The policy should articulate the types of tests used, substances screened for, and the consequences of failing a test. This transparency helps ensure that all employees and candidates are aware of the expectations.
Legal Considerations
Navigating the legal landscape can be tricky. Staying compliant with federal, state, and local laws is crucial to avoid legal consequences. Consult resources like the EEOC guidelines to ensure that your testing policies don't inadvertently lead to discrimination or violate privacy laws.
Implementing Tests
Implementation should be systematic and documented. Choose reputable testing providers and ensure that all test administration is conducted under consistent conditions. Training for those administering the tests can help maintain ethical standards and ensure accurate results. Establishing a chain of custody for samples is also vital in maintaining the integrity of the results.
By understanding and preparing for pre-employment drug screenings, both job seekers and employers can approach the process with confidence and clarity, ensuring a fair and transparent experience for all involved.
Drug and Alcohol Testing Myths and Facts
Let's cut through the noise and get to the core of some prevalent myths surrounding drug and alcohol testing in the pre-employment context.
Common Myths
"Employment drug tests always include alcohol testing."
While it might seem logical to lump alcohol in with other substances, the reality is a bit different. Standard pre-employment drug screens often do not include alcohol testing. Typical drug panels focus on substances like THC, opiates, amphetamines, and cocaine. Including an alcohol test is up to the discretion of the employer and is more common in specific industries, such as transportation, where safety is paramount.
"CBD will cause you to fail a drug test."
This myth has been circulating, especially with the increasing popularity of CBD products. Most standard drug tests look for THC, the psychoactive component of cannabis, not CBD. That said, some CBD products may contain trace amounts of THC. Therefore, it's critical for consumers to choose high-quality, lab-tested products to avoid unexpected results.
Facts and Realities
Alcohol testing is industry-dependent.
In safety-sensitive roles, especially those regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT), alcohol screening is more likely to be a part of the pre-employment process. The DOT mandates alcohol tests for transportation workers, but for many non-DOT roles, alcohol testing is not a given.
Alcohol presence is short-lived in the body.
One reason alcohol is often excluded from pre-employment panels is its transient nature. After consumption, alcohol leaves the bloodstream relatively quickly compared to drugs like marijuana or cocaine. Tests like breathalyzers and saliva swabs can detect recent use, but their detection window is shorter, making them less useful for routine pre-employment checks.
Employers have the final say.
Ultimately, the inclusion of alcohol in pre-employment drug screens comes down to employer policy. Some employers choose to test for alcohol to maintain a stringent standard, particularly in roles involving heavy machinery, driving, or high responsibility. It's crucial for candidates to be aware of each company's specific drug and alcohol policies.
Clearing up these misconceptions ensures that both employers and job seekers approach pre-employment screenings with a more accurate understanding, eliminating unnecessary stress and confusion.
Special Considerations for Specific Industries
When it comes to pre-employment drug and alcohol testing, not all industries are created equal. The importance and methods of testing can vary significantly depending on the nature of the work and the potential risks involved.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, the stakes are particularly high. Employees are often in close contact with patients and are responsible for their wellbeing. Any impairment due to substance use can have dire consequences. Thus, rigorous drug and alcohol testing is a common practice. Not only does it ensure patient safety, but it also maintains the integrity of the healthcare environment. Tests in this field often include a comprehensive panel that screens for a wide array of substances, including alcohol. Enhanced scrutiny is applied to roles such as surgeons, anesthesiologists, and emergency response professionals.
Transportation
For the transportation industry, maintaining sobriety is paramount due to the safety-sensitive nature of the work. This is especially true for roles that fall under the Department of Transportation (DOT) guidelines, which mandate regular alcohol testing. Non-CDL (Commercial Driver's License) positions may not be legally bound by DOT regulations, but many companies still enforce stringent policies to minimize risk. Tests for alcohol are common, given the severe implications of an accident caused by an impaired driver. Regular testing helps ensure not just the safety of the employee, but also that of passengers, other road users, and the general public.
Retail and Hospitality
Although these industries may not seem as high-risk as healthcare or transportation, maintaining a drug-free workplace is crucial for other reasons. Customer-facing roles demand a high level of professionalism and alertness. The use of substances, including alcohol, can impair judgment, reduce efficiency, and negatively affect customer interactions. Many retail and hospitality businesses opt to include alcohol testing in their pre-employment screens to foster a reliable and productive workforce. This not only helps in maintaining the desired level of service but also reduces the likelihood of workplace incidents, which can lead to costly legal issues and damage to the business's reputation.
In summary, while the importance of pre-employment drug and alcohol testing is universally acknowledged, its implementation is tailored to fit the specific needs and risks of different industries. From ensuring patient safety in healthcare to preventing accidents in transportation and maintaining high standards in customer-facing roles, these tailored approaches help create safer, more productive workplaces.
Conclusion
Pre-employment drug and alcohol testing is a vital component of workplace safety and compliance, especially in industries where precision and alertness are paramount. By understanding what these tests typically include, and why alcohol testing may or may not be part of them, employers and job seekers can better navigate the hiring process with confidence.
For job seekers, knowing what to expect and preparing adequately can make a significant difference. Awareness of an employer's policies and the legal framework surrounding these tests ensures that both rights and responsibilities are upheld. Employers, on the other hand, should focus on developing transparent, fair, and compliant testing policies that reflect industry standards and regulatory requirements.
As you move forward, whether you're looking to secure a new job or streamline your company's hiring practices, remember that clear communication and adherence to best practices are key. For further insights and detailed guidance, check out resources like the GCheck Blog, the Department of Labor, or the EEOC.
Equipped with the right information, you can approach pre-employment drug and alcohol testing processes in a manner that is both ethically sound and practically effective.
Additional Resources
- Virginia Background Check Laws: A Practical Guide for HR
- Non-CDL DOT Physical and Drug Test Requirements: What You Need to Know
- How Much Does a Urine Drug Screen Cost? Factors and Pricing
- Ohio Background Check Laws: What Employers Need to Know
- Understanding Mississippi Background Check Laws for HR
- Oklahoma Background Check Laws: Ensuring Compliance in Your Business
- Missouri Background Check Laws: A Practical Guide for Businesses
- Georgia Background Check Laws: Ensuring Compliance in Your Business
- Iowa Background Check Laws: Ensuring Business Compliance
- New Jersey Employment Background Check Laws: What to Expect in 2025 (and Beyond)
- What Does a SLED Background Check Include?
- Which States Require 10-Year Background Checks?
- What Questions Can’t You Ask in a Job Interview?
- How to Conclude a Phone Interview Professionally
- How to Check If Someone Graduated College: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How Long Does It Take to Pass a Mouth Swab Drug Test?
- Best Practices for Conducting Employee Background Checks in Texas
- Do Employers Really Check College Degrees?
- Do Pre-Employment Drug Screens Test for Alcohol? What You Should Know

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






