FCRA Compliance for Small Businesses: Avoid Costly Background Check Mistakes

Small businesses conducting employment background screening must navigate complex FCRA compliance requirements to avoid penalties that can reach $1,000 per violation. Understanding federal regulations, proper disclosure procedures, and candidate rights protects your business while ensuring effective hiring practices.
Key Takeaways
- FCRA compliance for small business requirements apply to any employer using third-party background check services, regardless of company size or industry.
- Proper written disclosure and authorization procedures must occur before conducting any employment background screening on potential employees.
- Small business background checks require adverse action protocols when unfavorable information influences hiring decisions, including pre-adverse and final adverse action notices.
- FCRA violations penalties range from $100 to $1,000 per violation, with potential class-action lawsuits costing businesses millions in settlements.
- Employment background screening companies must be Consumer Reporting Agencies (CRAs) certified under federal regulations to provide compliant services.
- Regular training and documentation of FCRA background check requirements helps small businesses maintain consistent compliance across all hiring processes.
Understanding FCRA Requirements for Small Business Hiring
The Fair Credit Reporting Act governs how small businesses conduct employment background screening. Moreover, these rules apply regardless of company size or industry sector. Originally designed to regulate credit reporting, FCRA expanded to cover employment-related consumer reports in 1997.
Small business owners often mistakenly believe FCRA compliance rules only apply to large corporations. However, federal regulations clearly state that any employer using third-party services must follow these requirements. Additionally, state laws may impose even stricter standards for background screening procedures.
FCRA background check requirements activate whenever you use external services to investigate job applicants. This includes criminal history checks, employment verification, education confirmation, and reference checks. Even businesses with fewer than five employees must follow federal guidelines when outsourcing background investigations.
Essential FCRA Compliance Steps for Employment Screening
Pre-Screening Disclosure and Authorization Process
Small businesses must obtain written consent before conducting employment background screening. The disclosure must appear on a standalone document, separate from job applications or other hiring paperwork. Furthermore, FCRA regulations require clear, conspicuous language that informs candidates about the background check process.
| Disclosure Requirement | Compliance Standard | Common Mistakes |
| Standalone Document | Separate from all other forms | Combined with job applications |
| Clear Language | Plain English, readable format | Legal jargon or fine print |
| Specific Purposes | Detail types of screening | Generic "background check" terms |
Authorization forms should specify the types of screening you'll conduct. Generic language like "background check" may not satisfy compliance requirements.
Selecting FCRA-Compliant Background Check Providers
Consumer Reporting Agencies must maintain proper certification to provide compliant small business background checks. Therefore, verify your provider's credentials and compliance procedures before establishing partnerships. Reputable CRAs offer standardized processes that help small businesses meet federal requirements.
Your chosen provider should offer adverse action support and training resources. Additionally, they should provide updated forms that reflect current regulatory standards. This partnership approach reduces FCRA violations penalties while streamlining your hiring workflow.
Adverse Action Protocol Implementation
Adverse action procedures protect candidates when background information influences hiring decisions. Small businesses must follow specific notification timelines and provide required documentation. Consequently, the process involves two distinct phases: pre-adverse action and final adverse action notices.
Pre-adverse action requires providing candidates with background report copies and Federal Trade Commission rights summaries. Allow reasonable time for candidates to dispute inaccurate information. Furthermore, final adverse action notices must include specific reasons for employment decisions and contact information for the reporting agency.
Industry-Specific FCRA Compliance Considerations
Different small business sectors face unique employment background screening challenges. Healthcare providers must conduct more extensive checks due to patient safety requirements. Meanwhile, financial services companies need credit history reviews for positions involving money handling. Understanding industry-specific needs helps tailor compliant screening programs while avoiding unnecessary procedures.
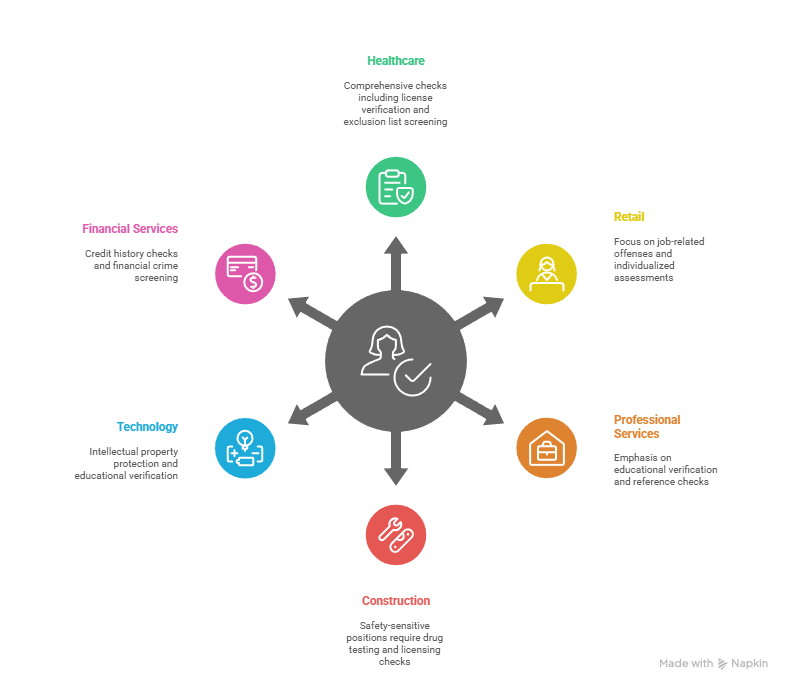
- Healthcare and Medical Practices: Medical facilities require comprehensive criminal background checks, professional license verifications, and exclusion list screenings. State regulations often mandate additional requirements beyond federal FCRA compliance in small business standards. Therefore, consider ongoing monitoring for licensed professionals to maintain continuous compliance.
- Retail and Restaurant Operations: Customer-facing positions may warrant criminal history screening, but avoid blanket exclusions that could violate Equal Employment Opportunity Commission guidelines. Focus on job-related offenses and follow individualized assessment protocols. Additionally, credit checks typically aren't appropriate unless positions involve cash handling or financial responsibilities.
- Professional Services and Consulting: Educational verification and professional reference checks help validate candidate qualifications. Criminal screening may be less critical unless client work involves sensitive information or vulnerable populations. However, maintain consistent screening standards across similar position types.
- Construction and Trade Services: Safety-sensitive positions may require drug testing alongside traditional background screening. Workers' compensation history and professional licensing checks protect both employees and customers. Furthermore, consider ongoing screening for positions requiring specialized certifications or licenses.
- Technology and Startups: Software development and technical positions often require intellectual property protection measures. Educational verification becomes crucial for positions requiring specific technical degrees or certifications. Additionally, previous employment verification helps confirm claimed experience levels and project involvement.
- Financial Services and Accounting: Credit history checks are often necessary for positions involving financial responsibilities or client money handling. Professional licensing verification ensures compliance with industry regulations. Moreover, criminal background screening should focus on financial crimes and fraud-related offenses.
Common FCRA Violations and Prevention Strategies
Small businesses frequently make costly mistakes during employment background screening processes. Understanding common violations helps prevent expensive penalties and legal challenges. FCRA violations penalties compound quickly when multiple candidates are affected by the same compliance failures.
Inadequate Disclosure Procedures: Many small businesses combine background check disclosures with job applications or other documents. FCRA requires standalone disclosure forms with clear, understandable language. Therefore, avoid burying disclosure language in lengthy employment agreements or policy manuals.
Improper Adverse Action Handling: Failing to provide required notices or rushing through adverse action timelines creates significant liability. Candidates must receive copies of background reports and adequate time to respond to negative findings. Additionally, document all adverse action communications and maintain compliance records.
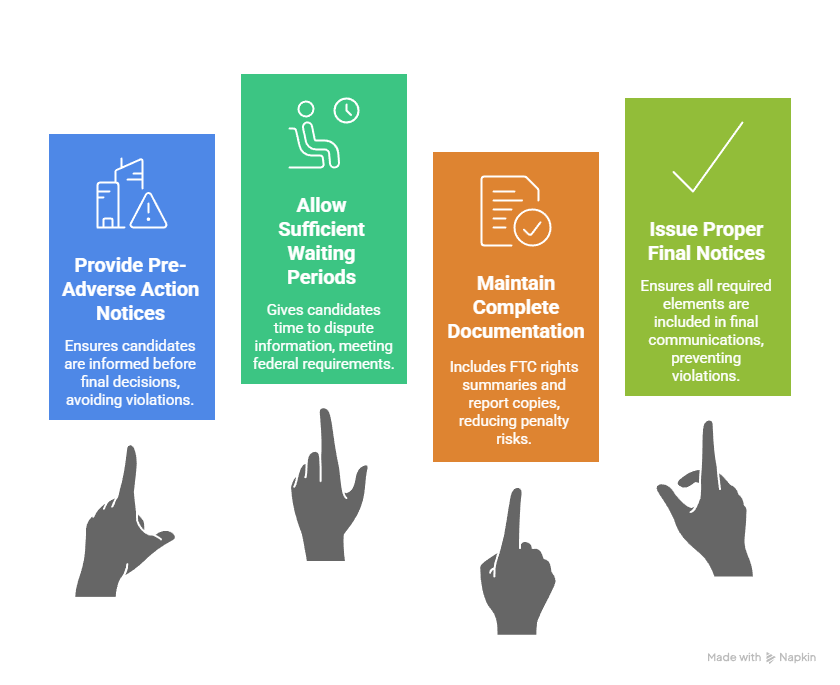
- Missing pre-adverse action notices: Skipping the initial notification phase before making final hiring decisions creates immediate FCRA violations
- Inadequate waiting periods: Not allowing sufficient time for candidates to dispute background report information violates federal requirements
- Incomplete documentation: Failing to provide FTC rights summaries or background report copies exposes businesses to penalty risks
- Improper final notices: Missing required elements in final adverse action communications creates additional violation opportunities
Systematic compliance procedures reduce violation risks while protecting your business reputation. Regular training updates ensure consistent application across all hiring team members.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of FCRA Compliance Investment
Implementing proper FCRA compliance for small business procedures requires upfront investment but prevents costly violations. Background screening expenses typically range from $50 to $200 per candidate, depending on investigation scope. However, compare this cost against potential penalties and legal fees from non-compliance situations.
FCRA violations penalties start at $100 per violation but can reach $1,000 for willful non-compliance. Class-action lawsuits involving multiple candidates have resulted in million-dollar settlements for small businesses. Therefore, investment in compliant procedures and provider relationships pays for itself through risk reduction.
| Compliance Investment | Annual Cost Range | Potential Savings |
| Compliant CRA Services | $2,000-10,000 | $50,000+ in violations |
| Legal Consultation | $1,000-5,000 | $100,000+ in lawsuits |
| Staff Training Programs | $500-2,500 | Ongoing violation prevention |
Consider compliance costs as insurance against business-threatening penalties. Proper small business background checks protect your company while supporting effective hiring decisions. Additionally, compliant processes improve candidate experience and employer branding efforts.
Technology Solutions for FCRA Compliance Management
Modern employment background screening platforms integrate FCRA compliance features that streamline small business processes. Automated disclosure generation, electronic consent collection, and adverse action management reduce manual compliance burdens. Furthermore, cloud-based systems provide audit trails and documentation storage that support compliance verification during regulatory reviews.
Automated Compliance Features: Look for platforms that generate compliant disclosure forms and manage consent collection electronically. Automated adverse action workflows ensure proper timing and documentation requirements. Additionally, integration with applicant tracking systems creates seamless compliance processes that reduce administrative overhead.
Documentation and Record Management: Digital platforms maintain comprehensive audit trails for all background screening activities. Electronic storage systems organize required documentation according to FCRA retention requirements. Moreover, automated compliance reporting identifies potential issues before they become violations.
- Electronic disclosure delivery: Automated generation and delivery of FCRA-compliant disclosure documents with candidate acknowledgment tracking
- Consent management systems: Digital signature collection with comprehensive audit trail documentation for regulatory compliance verification
- Adverse action workflow automation: Systematic notice generation with proper timing controls and required documentation delivery
- Comprehensive compliance reporting: Regular audit reports showing process adherence, violation risks, and improvement opportunities for ongoing optimization
Technology investments reduce compliance workload while improving documentation quality and consistency. Choose solutions that scale with your business growth and increasing hiring volume requirements.
Implementing Ongoing FCRA Compliance Programs
Sustainable FCRA compliance requires systematic procedures and regular training updates throughout your organization. Assign specific team members to oversee employment background screening processes and maintain current knowledge of regulatory changes. Furthermore, document all procedures and create comprehensive audit trails for compliance verification during potential regulatory reviews.
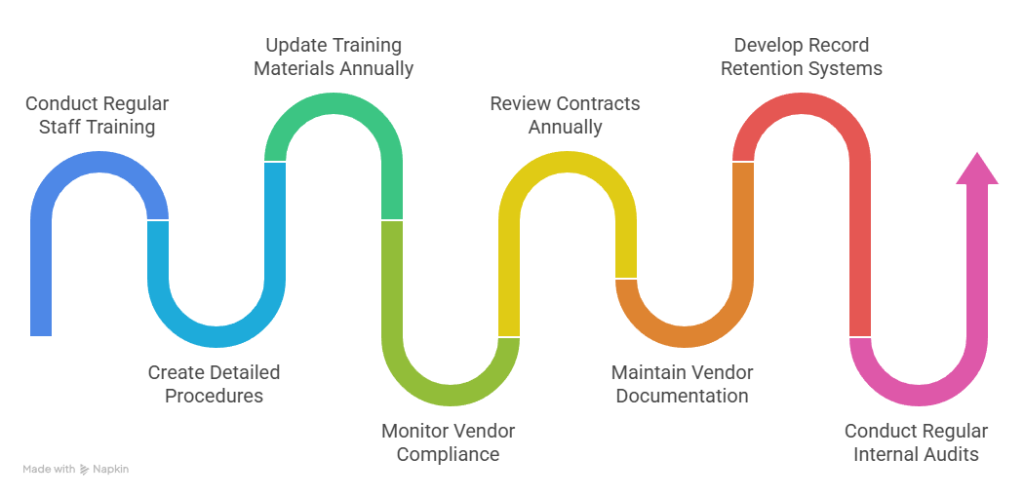
- Staff Training and Documentation Systems: Regular training ensures consistent application of FCRA background check requirements across your hiring team members. Create detailed written procedures that outline each compliance step from initial disclosure through final adverse action protocols. Additionally, update training materials annually to reflect regulatory changes and emerging best practices in the industry.
- Vendor Management and Oversight Procedures: Monitor your Consumer Reporting Agency's compliance standards and service quality on an ongoing basis. Review contracts annually and evaluate new providers when necessary for improved services or cost optimization. Moreover, maintain comprehensive documentation of vendor certifications and compliance procedures for audit purposes and regulatory inquiries.
- Record Retention and Internal Audit Systems: FCRA requires specific record retention periods for background check documentation and related communications. Develop organized filing systems that separate personnel records from background screening materials according to federal requirements. Furthermore, regular internal audits help identify compliance gaps before they become costly violations or regulatory issues.
Conclusion
FCRA compliance for small businesses requires systematic attention to disclosure procedures, vendor selection, and adverse action protocols throughout the hiring process. Understanding federal requirements and implementing consistent processes protects your business from costly violations while supporting effective hiring decisions. Regular training, proper documentation, and technology solutions create sustainable compliance programs that grow with your business expansion. Investment in FCRA compliance pays significant dividends through reduced legal risk and improved hiring outcomes for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do FCRA compliance requirements apply to small businesses with fewer than 15 employees?
Yes, FCRA compliance for small business requirements apply to all employers regardless of size when using third-party background check services. Company size doesn't exempt businesses from federal consumer reporting regulations.
Can I conduct background checks using free online databases instead of certified providers?
Free databases don't provide FCRA-compliant reports and may contain inaccurate information. Small business background checks must use certified Consumer Reporting Agencies to ensure compliance and accuracy.
How long should I wait between pre-adverse action notice and final hiring decisions?
FCRA doesn't specify exact timeframes, but allows reasonable time for candidates to respond to negative findings. Most compliance experts recommend 5-7 business days minimum for employment background screening decisions.
What's the difference between background checks for employees versus independent contractors?
FCRA background check requirements typically don't apply to independent contractors since they're not employees. However, some client contracts or industry regulations may require contractor screening.
Are there any positions exempt from FCRA compliance requirements?
FCRA compliance applies to all employment background screening conducted through third-party providers. Some positions may have additional requirements, but none are exempt from basic federal regulations.
How often should small businesses update their FCRA compliance procedures?
Review FCRA compliance procedures annually and update them whenever regulations change. Subscribe to Federal Trade Commission updates and maintain relationships with employment law attorneys for current guidance.
Additional Resources
- Federal Trade Commission FCRA Guidance for Employers
https://www.ftc.gov/tips-advice/business-center/guidance/using-consumer-reports-what-employers-need-know - Equal Employment Opportunity Commission Background Check Guidelines
https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment-decisions-under-title-vii - Society for Human Resource Management FCRA Compliance Toolkit
https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/fcracompliancetoolkit.aspx - National Association of Professional Background Screeners Best Practices
https://www.napbs.com/resource-center/background-screening-best-practices - California Employment Law Consultation Services
https://www.dir.ca.gov/dlse/DistrictOffices.htm - Professional Background Screening Association Compliance Resources
https://www.thepbsa.org/compliance-resources