Navigating the hiring process can be complex, especially when trying to ensure you bring on trustworthy and competent employees. Pre-hire background checks play a crucial role in making informed hiring decisions. Whether you're a business owner, HR professional, recruiter, or job seeker, understanding the intricacies of these checks can provide valuable insights and help you navigate the hiring landscape more effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Pre-hire background checks are essential for verifying qualifications, ensuring workplace safety, and maintaining legal compliance.
- Different checks include employment history, education verification, criminal records, credit history, driving records, drug testing, reference checks, and social media screening.
- Legal frameworks like the FCRA, EEOC, Ban-the-Box laws, and data privacy regulations guide the proper conduct of these checks.
- Best practices include notifying candidates, using reputable screening companies, maintaining consistent policies, focusing on relevant information, and documenting the process.
- Both employers and job seekers benefit from a transparent, fair, and informed approach to pre-hire background checks, leading to better hiring outcomes and a more secure work environment.
Introduction
Did you know that 94% of employers conduct at least one background check during hiring? This statistic might surprise you, but it underscores the critical role that pre-hire background checks play in modern recruitment.
Pre-hire background checks are systematic investigations into a potential employee's history. They're not just about catching red flags; they're crucial for verifying qualifications, ensuring workplace safety, and maintaining legal compliance. For employers, these checks provide peace of mind that their new hire is exactly who they say they are. For job seekers, understanding these checks can help demystify the hiring process and make the journey smoother.
This guide will unravel everything you need to know about pre-hire background checks. From various types of checks to legal considerations and best practices, we've got you covered. Whether you're an employer looking to make better hiring decisions or a job seeker preparing for your next opportunity, this guide will be invaluable.

What Are Pre-Hire Background Checks?
Pre-hire background checks are a routine part of the hiring process where potential employers gather and review information about a candidate’s past. These checks serve several critical functions. Primarily, they verify the accuracy of a candidate’s qualifications, ensuring the applicant has the skills and experience they claim. Ensuring workplace safety is another key objective; employers aim to maintain a secure environment for all employees by examining an individual's criminal history or substance use. Additionally, legal compliance is a major factor—employers must adhere to various regulations, such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), which dictate how background checks should be conducted and what information can be used.
EXPERT INSIGHT: As a practicing HR pro, I've realized a resume only speaks a half-truth—it's what we learn off the page that is most important. Pre-employment background scanning is not exclusion, it's responsibility, using smart decisions that keep both the workplace—and everyone who comes through the workplace—safe. I've seen firsthand how thoughtful screening—with fairness, context, and empathy—is not only about assembling teams, it's about establishing trust. When we weigh caution against dignity, we create safer workplaces, stronger teams, and provide everyone who comes through the door a fair chance. It's not process—it's people, and it makes a difference. - Charm Paz, CHRP
Types of Pre-Hire Background Checks
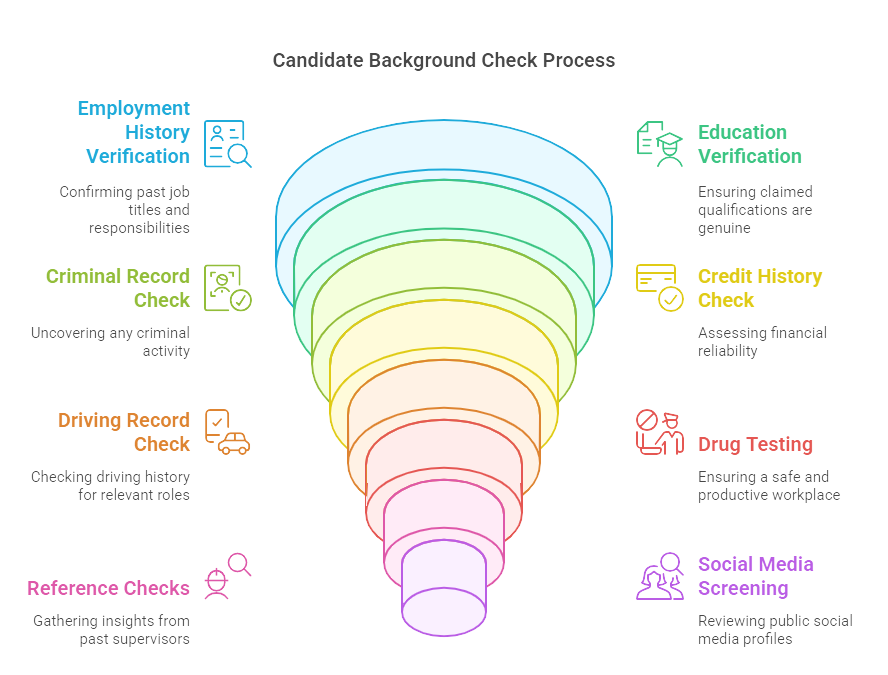
Background checks come in various flavors, each designed to gather specific information about a candidate. Here’s a closer look at the primary types:
- Employment History Verification: This check essentially calls a candidate's bluff. It verifies past job titles, responsibilities, and dates of employment. It’s about ensuring that your candidate isn't padding their resume – confirming what’s written is what took place.
- Education Verification: Think of this as a diploma detective. It confirms that the diplomas, degrees, or certifications the candidate claims to have earned are genuine. If a job requires specific qualifications, you must ensure the candidate has achieved them.
- Criminal Record Check: This delves into the candidate's past to uncover any criminal activity relevant to the job role. This check can be particularly crucial for roles involving trust and safety—like those in education, healthcare, or finance.
- Credit History Check: This check, often used for positions of financial responsibility, examines the candidate's credit history. It’s an indicator of financial reliability and can flag potential risks like excessive debt that could lead to conflicts of interest.
- Driving Record Check: If the job involves driving, you must ensure your candidate has a clean driving history. Points on a license, DUIs, and accidents are critical information for roles involving company vehicles.
- Drug Testing: Drug testing is important for maintaining a safe and productive workplace. Many companies require potential employees to pass a drug test before hiring, particularly for safety-sensitive positions.
- Reference Checks: Think of these as personal reviews. Speaking with past supervisors or colleagues can give you a perspective on the candidate's work habits, strengths, and weaknesses. It’s about getting the real scoop beyond the polished resume and rehearsed interview responses.
- Social Media Screening: More controversial yet increasingly common, this check reviews a candidate’s public social media profiles for any red flags. Inconsistent professional information, inappropriate behavior, or controversial opinions shared online can give employers pause.
Understanding these checks and when to use them can make your hiring process more robust and well-informed. Each type offers a different lens to view a candidate’s history and fit for your organization.
Legal Considerations
Navigating the legal landscape of pre-hire background checks can be a minefield for employers. Below, we address the critical legal frameworks you need to be aware of:
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
At the federal level, the FCRA outlines specific requirements for conducting background checks through third-party agencies. To stay compliant, employers must:
- Notify applicants in writing: Inform candidates that a background check will be performed. This notification should be separate from other application documents.
- Obtain written consent: Candidates must provide written permission before conducting any checks.
- Pre-adverse action process: If you find something concerning, send the candidate a pre-adverse action notice, a copy of the report, and a summary of their rights under the FCRA.
- Adverse action notice: Should you decide not to hire the candidate based on the background report, you must provide an adverse action notice detailing the decision and informing them of their right to dispute the findings. For in-depth guidelines, refer to the FTC Guidelines.
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
EEOC regulations help prevent discriminatory practices in the hiring process:
- Avoid disparate treatment: Ensure that all candidates are subject to the same screening procedures, irrespective of race, color, national origin, sex, or religion.
- Disparate impact: Avoid enforcing policies that could unintentionally discriminate against specific groups. For example, a blanket policy of not hiring anyone with a criminal record may disproportionately affect certain demographics.
Ban-the-Box Laws
These laws, which are enacted in various states and municipalities, prohibit employers from asking about criminal history on job applications:
- Delay timing: Inquiries about criminal records can often only be made after a conditional job offer has been extended.
- State-specific compliance: Be aware of local regulations requiring more nuanced approaches to handling criminal history information.
Data Privacy
Handling candidates' personal information requires careful attention:
- Secure storage: Keep all background check information securely and confidentially.
- Transparency: Be upfront with candidates about what information will be collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it.
- Minimize data: Only collect information directly applicable to the job role.
Adhering to these legal guidelines safeguards your organization and ensures a fair and respectful hiring process for all candidates.
Best Practices for Conducting Background Checks
A methodical approach ensures fairness, accuracy, and compliance when conducting pre-hire background checks. Below are some best practices to keep in mind:
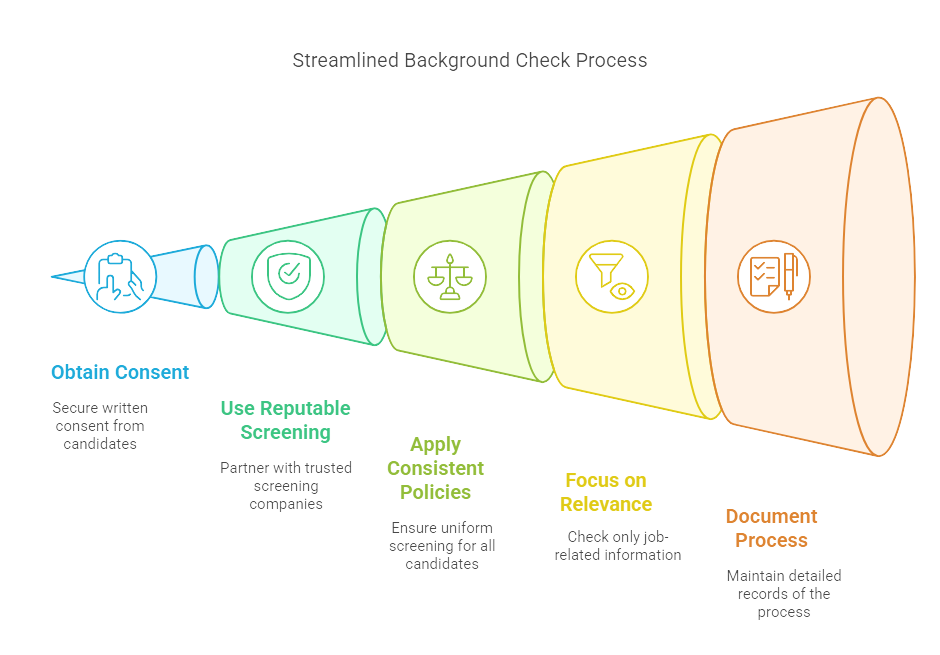
Notify Candidates
Transparency is key. Always inform candidates that a background check will be part of the hiring process and obtain their written consent before proceeding. This step adheres to legal requirements, and fosters trust between you and the prospective employee.
Use Reputable Screening Companies
The accuracy of your background checks depends largely on the quality of your screening provider. Partner with reputable background screening companies known for their thoroughness and compliance with legal standards. This minimizes the risk of errors and legal complications.
Consistent Screening Policies
To ensure fairness and reduce bias, apply the same screening process for all candidates applying for the same position. This consistency ensures that all candidates are evaluated equally and reinforces your company’s commitment to non-discriminatory practices.
Focus on Relevance
Concentrate only on information pertinent to the job role in question. For instance, a driving record check may be critical for a delivery driver position but irrelevant for a software developer. Focusing on relevant criteria helps avoid intrusions into a candidate's private life and keeps the process efficient.
Document the Process
Maintain detailed records of the background check process, including the consent forms, the information obtained, and the decisions made. This documentation is vital for both audit trails and resolving any future disputes. It also demonstrates your commitment to a thorough and legally compliant hiring process.
By adhering to these best practices, employers can create a consistent, transparent, and fair background check process that protects the organization and respects the rights and dignity of job candidates.
How to Handle Negative Findings
Negative findings on a background check can be a tough nut to crack, but it’s not the end of the road for either the employer or the candidate.
Context Matters
First off, context is king. Not every red flag is equal, and understanding the specifics can help you make a balanced decision. Was the misdemeanor from a decade ago, or is it something more recent? Is it relevant to the job function? A traffic violation might matter for a delivery driver but not for someone in sales.
Individual Assessment
Avoid one-size-fits-all policies. Each situation should be evaluated on its own merits. Blanket decisions can lead to missed opportunities and potential legal pitfalls. Assess factors like the type of offense, how much time has passed, and if there's been any rehabilitation since the incident.
Communicate with Candidates
Transparency goes a long way. If you find negative information, discuss it openly with the candidate. Sometimes, there are misunderstandings or errors in the report. Give the candidate a chance to explain or dispute the findings. This step not only builds trust but can also clarify any discrepancies.
Make Informed Decisions
Ultimately, hiring decisions shouldn't hinge solely on background check results. Weigh all available information—interviews, references, skills assessments—alongside the background check. A holistic view offers a clearer picture of the candidate's suitability for the role.
Handling negative findings carefully ensures you make informed, fair hiring decisions, all while maintaining respect and transparency with your candidates.
The Impact of Background Checks on Job Seekers
In most hiring processes, pre-hire background checks are conducted after a conditional job offer is extended. This stage is often called "contingency," where the offer hinges on passing the background check. For job seekers, there’s still a crucial step to make or break the final employment decision, even after the interview.
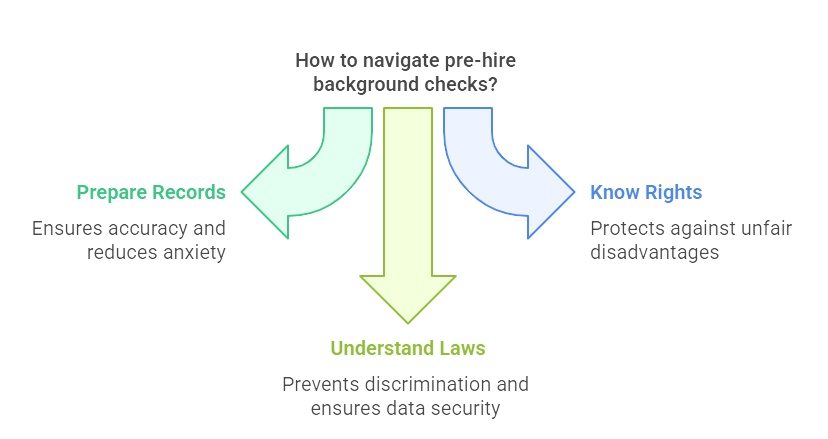
Preparation is Key
For job seekers, being prepared for a background check can significantly reduce anxiety and increase the likelihood of passing this hurdle smoothly. Start by maintaining accurate and up-to-date records of your employment history, educational qualifications, and any other relevant credentials. Misrepresentations or discrepancies can lead to delays or even revocation of the job offer. It’s also wise to request a copy of your background check periodically. This allows you to identify and address any inaccuracies before they become problematic.
Know Your Rights and Recourse
Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), job seekers have specific rights during the background check process. You are entitled to know if information in your background check has been used against you. You also have the right to receive a copy of the report and dispute any inaccuracies. It’s important to familiarize yourself with these protections to ensure potential errors in the report do not unfairly disadvantage you.
Understanding the laws and regulations, such as ban-the-box and data privacy rules, can also give you an edge. These laws protect candidates from discrimination and ensure personal information is handled securely. If a background check results in a negative finding, employers must provide you with a copy of the report and a summary of your rights. Use this opportunity to explain any issues or provide context that may not be immediately apparent from the report alone.
Being proactive and informed can significantly affect how you navigate the pre-hire background check process. For employers, understanding the impact of these checks on job seekers can lead to a more compassionate and comprehensive approach, ultimately contributing to a fair and effective hiring process.
Conclusion
Navigating pre-hire background checks effectively involves more than just ticking boxes on a list. To recap, we have covered the diverse types of background checks, their purposes, and critical legal considerations. Each element is vital in the hiring landscape, from verifying employment and education history to running criminal and credit checks.
Understanding and implementing best practices can make a world of difference. Notify candidates upfront, use reputable screening companies, maintain consistent policies, and focus only on relevant information. Handling negative findings with care and context creates a more equitable process.
Pre-hire background checks are crucial in fostering a safe, compliant, and productive workplace. For employers, it's about refining and updating your policies for optimal results. Preparation and awareness can ease any anxiety surrounding this stage for job seekers.
By adhering to these guidelines, both parties can approach the hiring process with confidence and clarity, contributing to better employment outcomes and a more secure work environment.

