In the fast-paced world of staffing and recruitment, compliance is king. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) outlines the obligations and duties that employers and staffing agencies must adhere to when conducting background checks on potential hires. A single infraction can lead to costly penalties, so being prepared and aware is crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the FCRA checklist for staffing, ensuring that recruiters can navigate the legal landscape with confidence while avoiding common pitfalls. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to implement effective FCRA compliance strategies in your recruitment process.
Key Takeaways
- FCRA compliance is crucial for all businesses conducting background checks through third-party agencies to avoid hefty fines and reputational damage.
- Every employer must have a legitimate reason for conducting a background check and must inform candidates and obtain their written consent.
- Clear and separate disclosure and authorization forms ensure transparency and respect the candidate's rights during the hiring process.
- Pre-adverse action procedures provide candidates with a fair chance to review and dispute background check findings before a final decision is made.
- Regular training on FCRA regulations and selecting compliant third-party screening services can help maintain legal adherence and enhance trust in your recruitment process.
EXPERT INSIGHT: I will never forget the day a candidate thanked us for walking them through the process of the FCRA. They noted it was the first time that anybody had spared a minute explaining the meaning of those notices and consent forms to them. It was a touching reminder that compliance is not about rules alone—it is about trust. When we go out of our way and are clear, candidates perceive a kind of respect, even if the end is disappointing. FCRA compliance, at its best, is proof that fairness and empathy can live at the heart of recruitment. - Charm Paz, CHRP
Introduction
FCRA compliance is critical in recruitment. It sets the legal standards for background checks. Ignoring these can result in hefty fines and damaged reputations. Your understanding of these rules can protect your business. But even deeper down the compliance rabbit hole, it is equally crucial to show candidates that their privacy and their rights are respected throughout the hiring process. Done with care, compliance wins trust—not just with the regulator, but with the very people you are trying to hire.
This article outlines the key aspects of the FCRA checklist for staffing. You will learn how to avoid violations, the importance of pre-adverse action notices, and how your staffing agency can remain compliant.
Understanding the FCRA: A Brief Overview
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a federal law that regulates the accuracy, fairness, and privacy of consumer information collected by credit reporting agencies. It plays a significant role in recruitment, especially when background checks are involved. Staffing agencies and employers who use consumer reports for hiring decisions must comply with FCRA regulations to protect applicants and employees.
Almost every business that hires needs to comply with FCRA. Specifically, if you're conducting background checks through third-party agencies, this law applies to you. This includes staffing agencies, large corporations, and small businesses alike. Any employer engaging consumer reporting agencies to gather background information must adhere to FCRA guidelines.
Non-compliance with the FCRA can lead to serious consequences. There are legal and financial repercussions, such as lawsuits and hefty fines. Employers might face civil liability for damages if they fail to follow the proper procedures outlined in the FCRA. Besides the financial impact, reputational damage and loss of trust are potential risks for organizations that overlook these legal priorities. Are you prepared to handle the implications of non-compliance?
Comprehensive FCRA Compliance Checklist for Staffing
Ensuring FCRA compliance during the staffing process is essential for protecting both your agency and the candidates. Here's what you need to focus on:
1. Pre-Employment Background Checks
- Identify the Permissible Purpose: Before you move forward with a background check, ensure there's a legitimate reason under FCRA guidelines. This typically includes employment decisions such as hiring or promotion.
- Notify the Candidate: You must inform the candidate that their background check will be used for employment purposes. Provide this information clearly, so there’s no room for misunderstanding.
- Get Written Consent: Always obtain written authorization from the candidate before you conduct a background check. This consent must be separate from any other paperwork, ensuring that the candidate is well aware of what they are agreeing to.
2. Disclosure and Authorization Forms
- Draft Clear and Conspicuous Disclosures: When preparing disclosures, focus on clarity and brevity. Avoid clutter and ensure the disclosure is stand-alone, not buried within other documents. This helps maintain transparency and legal compliance.
- Separate Authorization: Consent for a background check should be obtained on a document distinct from other employment materials. This tactic prevents legal issues arising from mixed purposes in a single document.
3. Pre-Adverse Action Procedures
- Pre-Adverse Action Notice: If a background check prompts you to consider adverse employment action, a pre-adverse action notice is necessary. This informs the candidate of potential negative outcomes motivated by their report.
- Include a Copy of the Report: Provide the candidate with a copy of their background check report. This transparency allows them to review the information, ensuring fairness.
- Summary of Rights: Along with the pre-adverse action notice, include a “Summary of Your Rights Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act.” This is a requirement, and it ensures the candidate knows their rights according to FCRA regulations.
4. Final Adverse Action Procedures
- Waiting Period: After sending a pre-adverse action notice, there’s a mandatory waiting period before making a final employment decision. This allows the candidate time to respond or dispute any information in their report.
- Send Final Adverse Action Notice: Should you decide against hiring based on the background check, send a final adverse action notice. Clearly state the decision and provide specific details about the agency that made the report and their contact information.
By sticking closely to these procedures, you minimize the risk of legal repercussions and uphold ethical hiring practices. Is your team ready for these actionable steps to maintain compliance? Consider reviewing your current processes and documentation to ensure they meet FCRA standards.
Avoiding FCRA Violations: Best Practices
Creating internal compliance policies that align with FCRA requirements is your first step. This ensures that every background check adheres to the law. You'll want clear guidelines for drafting, reviewing, and storing critical documents. Consistency is key.
Training is another critical area. Regularly update your recruitment teams on FCRA regulations to avoid inadvertent violations. Consider monthly or quarterly training sessions. This way, your team stays informed about any regulatory changes.
When it comes to choosing third-party screening services, select those with a strong compliance track record. Assess their understanding of FCRA mandates by asking for client testimonials or conducting brief interviews. This diligence minimizes risk in your background check processes.
FCRA Violations Penalties: What You Need to Know
Failing to comply with the FCRA can hit your wallet hard. Civil penalties for violations typically range from $100 to $1,000 per infraction. Consider a staffing agency running background checks on hundreds of candidates without proper consent; the penalties can add up quickly. On top of that, if there's willful non-compliance, criminal charges could come into play, leading to larger fines and even imprisonment.
Real-world examples bring these numbers to life. In 2014, a well-known company agreed to a $3 million settlement over FCRA violations due to improper consent forms. They didn't provide adequate disclosures to candidates undergoing background checks. Their oversight wasn't malicious, but it cost them significantly.
Think your company is too small to face such scrutiny? Think again. Any business using background checks for employment decisions is at risk. Even if your intentions are pure, mistakes can be costly. A small business once had to pay $100,000 because they failed to supply a candidate with their report before taking adverse action, violating FCRA protocols.
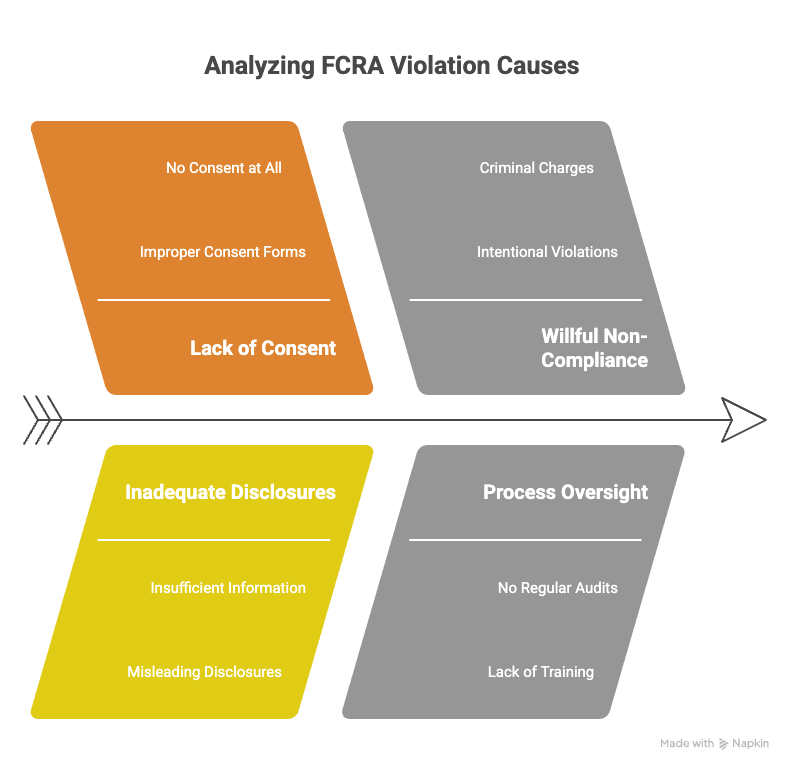
Have you revisited your FCRA processes lately? Regular audits could save you from costly penalties and ensure that you're always on the right side of the law.
Resources for Staffing Agency Compliance
Staying compliant with the FCRA demands vigilance and continuous learning. Here are some valuable resources to help you remain on track:
- GCheck Blog: A useful source for articles and updates related to background checks and compliance. The blog provides insights into industry trends and tips for maintaining FCRA compliance. Visit GCheck Blog for more information.
- EEOC Guidance on Background Checks: This official resource from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) helps employers understand legal requirements related to background checks for employment. The guidance offers comprehensive information on using background checks fairly and without discrimination. Check out the EEOC Guidance on Background Checks.
These resources serve as practical tools to guide you in navigating FCRA requirements effectively, mitigating risk, and ensuring fair hiring practices.
Conclusion
Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is more than just a legal obligation—it's a strategic component of responsible hiring. Understanding and applying a thorough compliance checklist is essential to protect your organization and candidates alike.
Key takeaways from the FCRA checklist include the necessity of having a legitimate purpose for conducting background checks and obtaining clear, written consent. The importance of transparency and communication in pre-adverse and adverse action procedures cannot be overstated.
Implementing proactive and rigorous compliance strategies is crucial. Beyond avoiding penalties, it enhances trust and credibility in your recruitment process. Regular training and updates on FCRA regulations should be part of your routine.
Stay informed and committed to ongoing learning to ensure seamless compliance and maintain the integrity of your hiring practices. Your diligence not only safeguards your agency but also ensures a fair experience for those seeking employment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens if a recruiter violates the FCRA?
A recruiter violating the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) faces legal consequences. Such violations can result in lawsuits, fines, and damaged business reputation. For instance, failing to provide necessary disclosures to candidates could land you in hot water legally.
How long must recruiters keep FCRA records?
Recruiters should retain FCRA records for at least five years. These documents might include consent forms and background check reports. Keeping accurate records helps in audits or disputes.
Can candidates sue for FCRA violations?
Yes, candidates can sue for FCRA violations. If a recruiter fails to comply with the FCRA, candidates may seek damages for violations. This can include statutory and punitive damages, as well as attorney fees.
What's included in an FCRA disclosure form?
An FCRA disclosure form includes a clear statement that a background check will be conducted. It should be separate from other employment documents. Candidates must understand what the check involves before signing.
How to handle disputes over background check errors?
Address disputes promptly by verifying the information with the background check provider. Correct any errors quickly and inform the candidate of the resolution. Open communication is key to resolving misunderstandings.
What should recruiters do if a candidate disputes the results of a background check?
If a candidate disputes the check, take it seriously. Verify the accuracy with the reporting agency and provide candidates with a clear process for resolving discrepancies.
Are there penalties for non-compliance with the FCRA?
Yes, non-compliance can lead to significant penalties. Fines, lawsuits, and loss of trust may occur. Ensuring compliance protects you legally and professionally.
Is it necessary to get written consent from candidates for background checks?
Absolutely, written consent is mandatory before conducting a background check. Without it, proceeding with a background check is a violation of the FCRA.
Do recruiters need to provide candidates a copy of their background check?
Yes, candidates have the right to request a copy of their background check. Providing them promptly ensures transparency and trust.
Can recruiters use third-party agencies for background checks?
Yes, third-party agencies can be used. Ensure they comply with FCRA requirements to avoid any indirect liabilities for violations.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






