Ensuring compliance with background check laws is crucial for HR professionals, business owners, and recruiters across various industries. While federal regulations such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) play a significant role, each state also has specific requirements that companies must adhere to. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Arkansas background check laws to ensure your hiring practices are effective and compliant.
Key Takeaways
- Compliance with federal and Arkansas-specific background check laws is crucial for businesses to avoid legal issues.
- Key components of a background check include criminal records, credit history, employment verification, education verification, and reference checks.
- Ensuring FCRA compliance involves clear disclosure, obtaining candidate consent, and following the adverse action process.
- Different industries have unique background check requirements and best practices, necessitating tailored compliance strategies.
- Overcoming common challenges like inaccurate records, candidate pushback, and staying updated on laws helps streamline and legalize the background check process.
Introduction
Compliance with background check laws is not just a regulatory obligation—it's a critical step in safeguarding your business and ensuring fair hiring practices. For HR professionals in Arkansas, a thorough understanding of federal and state-specific regulations is essential to avoid legal pitfalls and maintain the integrity of your hiring processes.
Our target audience includes professionals from a spectrum of industries, such as staffing agencies, healthcare, transportation, tenant screening, non-profits, retail, technology, and hospitality. Each sector faces unique challenges and has specific requirements regarding background checks, making tailored compliance strategies all the more important.
This guide is your go-to resource for navigating Arkansas's background check laws. It provides industry-specific recommendations and highlights best practices to streamline your compliance efforts.

In the United States, each state enforces its own distinct set of laws and HR procedures, particularly when it comes to background check practices. These variations pose unique challenges for HR practitioners striving to remain compliant and respectful of local regulations. To achieve full compliance, HR professionals must first delve into the nuances of each state's legal framework and then craft tailored company policies that align with these regional requirements. This meticulous approach not only ensures adherence to the law but also fosters a culture of respect and integrity within the organization.
Understanding Arkansas Background Check Laws
Navigating the maze of Arkansas background check laws can feel daunting, but it's a crucial step to ensure your hiring practices are compliant and fair. Here are the key areas you need to focus on:
- State-Specific Regulations: While the FCRA sets the foundation for background checks nationally, Arkansas adds its unique twists. In Arkansas, employers must adhere to both federal and state laws, which means understanding the specific stipulations and how they differ. For example, Arkansas law may impose additional restrictions on the type of information requested or how that information can be used in hiring decisions.
- Consent Requirements: Before investigating a candidate's background, obtaining their consent is non-negotiable. In Arkansas, this means clearly and conspicuously disclosing that a background check will be performed and obtaining the candidate's written authorization. Failing to do so can result in legal complications and damage your company's reputation.
- Use of Criminal Records: Arkansas has specific guidelines on how criminal records can influence hiring decisions. While it's permissible to consider criminal history, the state mandates that the nature of the crime, the time elapsed since the offense, and the relevance to the job must be considered. This balanced approach aims to offer fair opportunities to all candidates without compromising workplace safety and integrity.
- Arkansas Ban the Box: The "Ban the Box" initiative, implemented in Arkansas, removes the checkbox asking whether applicants have a criminal record from initial job applications. This initiative doesn't prevent background checks but ensures that candidates are evaluated on their qualifications first, rather than dismissed outright due to past convictions. Employers in Arkansas must ensure compliance with this initiative to promote equal employment opportunities and avoid potential penalties.
Understanding these core aspects of Arkansas background check laws is essential for building a compliant hiring process. It protects your company from legal issues and ensures a fair and respectful approach toward all potential employees.
Key Components of a Background Check
When assembling a thorough background check, it’s essential to focus on key components to ensure you're compliant with Arkansas laws and making informed hiring decisions. Here’s a breakdown:
Criminal Records
First, criminal records. You can access these in Arkansas through state repositories and specific county courthouses. It's crucial to ensure you follow the state's consent requirements. Always get the applicant's written permission before digging into their criminal history. When you have the data, be conscious of state laws regarding using this information. For example, Arkansas has restrictions on considering arrests that didn’t lead to convictions.
Credit History
Credit history checks can be a bit tricky. While they’re not as commonly used, they’re allowed under Arkansas law but have certain limitations. Ensure the role you're hiring for justifies the need to check credit. Usually, this pertains to positions involving financial responsibilities. As always, get explicit consent before pulling these reports and have a solid reason for their relevance to the job.
Employment Verification
When validating past employment, you want to contact previous employers to confirm job titles, employment dates, and, if possible, reasons for leaving. This step is crucial to ensure the applicant’s resume matches their real work history. Getting detailed feedback is not always easy, but even the basics can help confirm whether they have the experience they claim.
Education Verification
Similar to employment verification, education checks involve confirming your candidate's educational background. Contact the institutions directly or use third-party services to verify degrees, certifications, and other educational qualifications. In Arkansas, like elsewhere, this helps you ensure the candidate has the necessary credentials and avoids issues with falsified information.
Reference Checks
Lastly, reference checks are your chance to get deeper insights from people who've worked directly with your candidate. Ask for professional references and prepare pointed questions that give you a better picture of the candidate's abilities, work style, and suitability for the role. Always document these discussions well to have a record of the information obtained and to support your final hiring decision.
By meticulously covering these key background check components, you can ensure your hiring process complies with Arkansas law and helps you make informed choices.
Ensuring FCRA Compliance
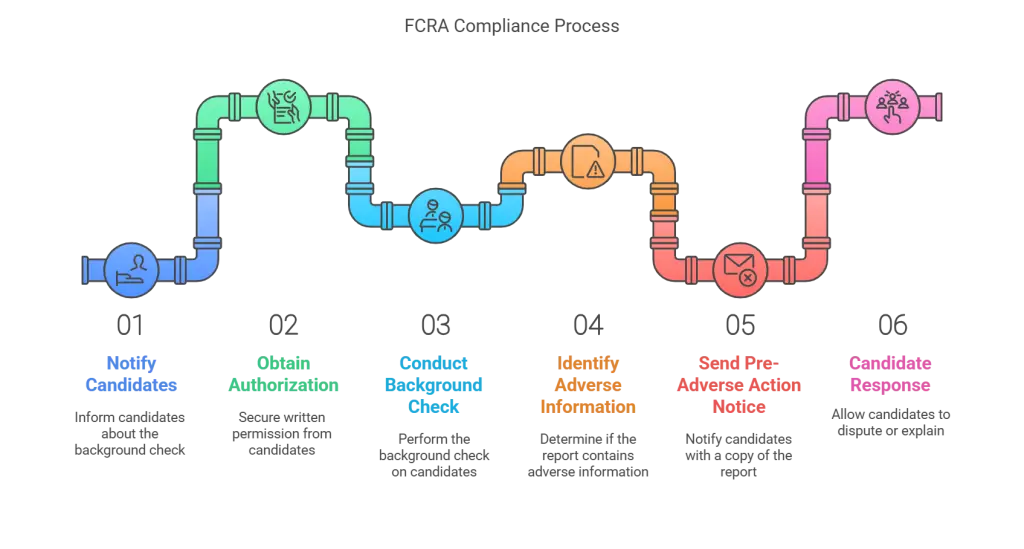
Summary of FCRA Requirements
Navigating the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) can seem daunting, but it boils down to a few key mandates. First, always notify candidates that you intend to run a background check. This isn't just a courtesy—it's the law. The candidate must also authorize the background check in writing.
Disclosure and Authorization
Before you conduct a background check, you must follow two crucial steps: disclosure and authorization. The disclosure must be clear and stand-alone—essentially, it can't be buried in the fine print of an application. Once disclosed, you must get written permission from the candidate. Simple enough, but missing this step can land you in hot water.
Adverse Action Process
If something in the background check makes you rethink hiring the candidate, you must follow the FCRA's adverse action process. This involves two steps: sending a pre-adverse action notice and a final adverse action notice if you decide to proceed. The pre-adverse action notice should include a copy of the report and a summary of the candidate's rights. Give the candidate a chance to dispute the report. If everything checks out and you decide against hiring, send a final adverse action notice.
Ensuring fairness throughout this process is paramount. It's essential to approach each background check and any subsequent decisions with transparency and empathy. Fairness means not only following legal protocols but also considering the context of any findings and their relevance to the role. Candidates deserve a fair chance to explain or correct any discrepancies in their reports. By maintaining an open and respectful dialogue, you reinforce a culture of trust and fairness, which benefits both the candidate and the organization.
Internal Resources
Keeping up with FCRA compliance is ongoing, but having the right resources can make it easier. Stay vigilant, follow these steps, and your background checks will stay within legal bounds while helping you make informed hiring decisions.
Arkansas Background Check Resources
Here is a table of related Arkansas government websites that would be useful for Arkansas business owners interested in background checks:
| Website Name | URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Labor and Licensing (Arkansas) | https://www.labor.arkansas.gov | Offers resources on labor laws, employment regulations, and licensing impacting background checks. |
| Department of Public Safety (Arkansas) | https://www.dps.arkansas.gov | Provides access to criminal history records and background check information. |
| Administrative Office of the Courts (Arkansas) | https://www.arcourts.gov | Access to court records and legal information relevant to background checks. |
| Department of Corrections (Arkansas) | https://doc.arkansas.gov | Information on criminal records, parolees, and public safety concerns. |
| Office of the Attorney General (Arkansas) | https://arkansasag.gov | Offers guidance on legal matters, including consumer protection and employment law. |
| Economic Development Commission (Arkansas) | https://www.arkansasedc.com | Provides resources for business development and compliance with state regulations. |
| Arkansas General Assembly | https://www.arkleg.state.ar.us | Stay updated on laws and regulations passed by the state legislature that may affect background checks. |
| Department of Health (Arkansas) | https://www.healthy.arkansas.gov | Information on health regulations and requirements impacting employee screenings and background checks. |
These websites provide valuable resources and information to ensure Arkansas business owners comply with state laws and regulations when conducting background checks.
Specific State Laws Governing Background Checks in Arkansas
Arkansas Code Annotated 11-2-124
This statute restricts employers from requesting or requiring access to an employee’s personal social media accounts. Employers cannot ask employees or prospective hires to disclose usernames or passwords or add the employer to their contacts.
This law ensures that employers respect the privacy of employees and job applicants. Compliance helps avoid potential legal issues related to invasion of privacy and maintains a respectful boundary between personal and professional life.
Arkansas Human Rights Act (AHRA)
Enacted in 1993, the AHRA prohibits employment discrimination based on race, religion, national origin, gender, disability, and other protected characteristics. This state law mirrors federal anti-discrimination laws and provides additional protections.
Adherence to the AHRA is essential for fostering a fair and inclusive workplace. Non-compliance can lead to significant legal consequences, including fines, lawsuits, and damage to the business's reputation.
Arkansas Code 12-12-1005
This statute mandates that certain employers conduct criminal background checks using fingerprinting. It applies to roles involving care for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with disabilities.
Ensuring compliance with this law is critical for businesses in sensitive sectors. It helps make informed hiring decisions, thereby protecting vulnerable individuals and reducing the risk of liability for negligent hiring.
Sealing and Expungement of Criminal Records
In Arkansas, individuals may petition to have their criminal records sealed or expunged, removing them from public access. Once sealed or expunged, employers cannot use these records during the hiring process.
Understanding the process and implications of record sealing and expungement is vital for employers. It ensures they do not unlawfully discriminate against applicants with sealed or expunged records, thus avoiding potential legal challenges.
For more detailed information on Arkansas background check laws, visit the Arkansas Department of Public Safety and review the Arkansas Code.
Industry-Specific Requirements and Best Practices
Navigating background check regulations can be tricky, especially when different industries have unique requirements. Here’s a streamlined breakdown:
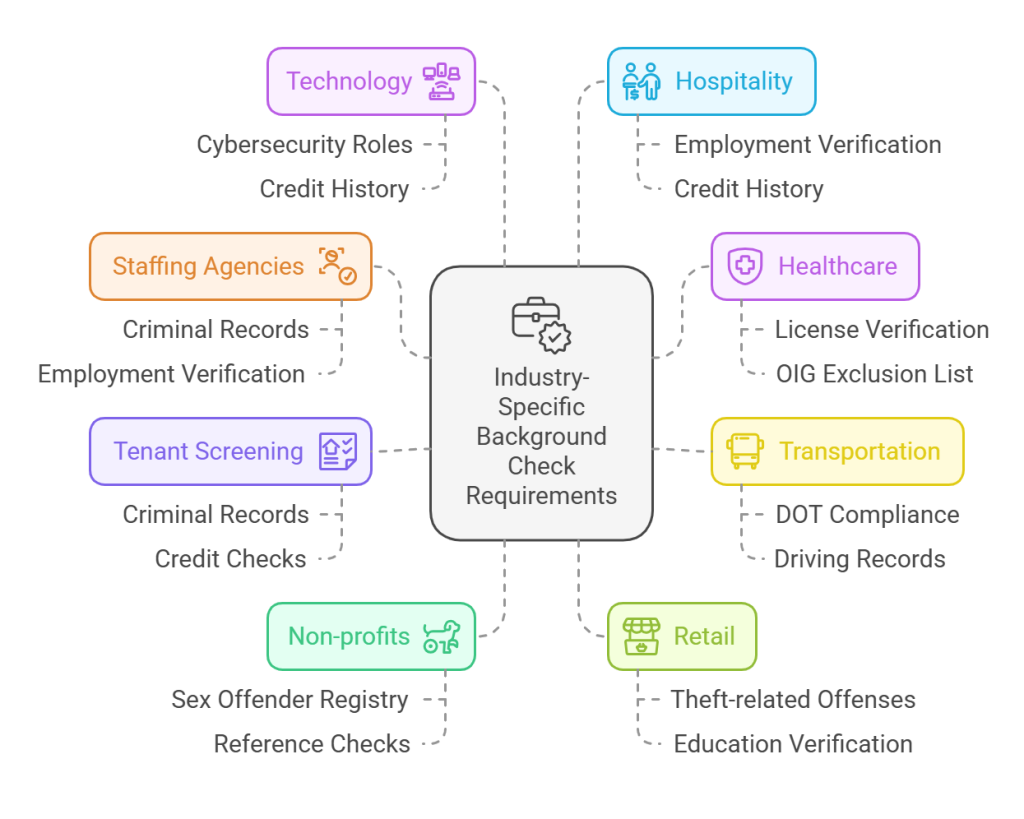
Staffing Agencies
For staffing agencies, efficiency and thoroughness go hand in hand. Prioritize quick, compliant checks that include criminal records, employment verification, and reference checks. Ensure signed candidate consent forms are obtained and always stay updated on federal and state-specific guidelines.
Healthcare
Healthcare settings demand stringent adherence to background checks due to direct patient care. In addition to standard checks, include license verification and OIG exclusion list checks. Regularly audit your processes to comply with federal health regulations and Arkansas state laws.
Transportation
Transportation industry roles often involve public safety, making comprehensive checks essential. Department of Transportation (DOT) compliance is necessary for commercial drivers, focusing on driving records, alcohol and drug testing histories, and criminal records. Keep accurate logs for auditors and stay aligned with the FMCSA's clearinghouse database.
Tenant Screening
When screening tenants, focus on criminal records, eviction history, and credit checks while adhering to Arkansas-specific rules on notice and consent. Follow the FCRA guidelines to ensure fair treatment and avoid discrimination claims. Clear documentation and transparent communication with prospective tenants are crucial.
Non-profits
Non-profits often operate with vulnerable populations, requiring extra diligence in background checks. Beyond criminal records, including sex offender registry checks and comprehensive reference checks. Volunteer roles should not be exempt from background screening. Be transparent about your screening processes with both staff and volunteers.
Retail
Retail environments face high turnover, making efficient yet comprehensive checks essential. Criminal background checks, particularly for theft-related offenses, are critical. Employment and education verification can be scaled based on role sensitivity. If you handle data from EU nationals, ensure GDPR compliance.
Technology
Tech companies should prioritize strong background checks for positions with access to sensitive data or intellectual property. These checks should include criminal records, education, and employment verification. Cybersecurity roles may necessitate additional checks, such as a credit history, to evaluate risk factors.
Hospitality
Given the customer-facing nature of hospitality roles, criminal background checks are crucial. Verify past employment to ensure candidates' reliability and trustworthiness. Consider additional checks like credit history for roles that handle payments or sensitive customer information.
You can maintain compliance and build a trustworthy and competent team by tailoring your approach to industry-specific requirements and following best practices. Keep detailed records and stay updated with ongoing legislative changes to help streamline your background check process.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Inaccurate Records
One of the main pain points in the background check process is dealing with report inaccuracies. Imagine going through the entire hiring process only to hit a snag because of erroneous information—it’s frustrating for everyone involved. To mitigate this, first, ensure your background check provider is reputable and adheres to high standards of accuracy. In cases where inaccuracies arise, promptly notify the candidate and the reporting agency. The FCRA requires that candidates have an opportunity to dispute and correct these errors, so ensure that you have a clear, swift mechanism in place to handle these disputes.
Candidate Pushback
Not every candidate will be thrilled about going through a background check. Some may have past issues they're worried will surface; others may see it as an invasion of privacy. To navigate this, transparency is key. Ensure you explain the reasons for the background check early in the hiring process and provide detailed information about what will be checked. This openness can alleviate much anxiety and increase compliance. If pushback still occurs, listen to their concerns and, if appropriate, adjust your process or provide additional reassurances.
Staying Updated
Regulations are always changing, and staying compliant isn't a one-and-done affair. Maintain a proactive stance on regulatory changes by subscribing to updates from credible sources such as the Professional Background Screening Association (PBSA) and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). Regular training sessions and workshops for your HR team can also be incredibly beneficial in keeping everyone on the same page. Create a compliance checklist that reflects the most current legal requirements and review it quarterly.
By addressing these common hurdles head-on, you can streamline your background check process and ensure it's both effective and compliant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can employers in Arkansas use arrest records in hiring decisions?
Employers in Arkansas are permitted to consider arrest records, but they must tread carefully. The FCRA and state laws require that any criminal records used in hiring decisions be accurate and relevant to the job. It’s also essential to ensure that the use of such records does not inadvertently result in discrimination, violating Title VII of the Civil Rights Act. An arrest without a conviction shouldn’t carry undue weight in the hiring process.
What should be included in a background check disclosure form?
A compliant background check disclosure form should be clear and conspicuous. It must inform the candidate that a background check will be conducted and specify the nature of the checks. This form has to be standalone—not embedded within other employment documents. Additionally, the form should include a "Summary of Your Rights Under the FCRA" and obtain the candidate’s written authorization before proceeding with the background check.
Are there specific industries in Arkansas where additional checks are mandatory?
Yes, some industries in Arkansas are subject to stricter background check requirements. For example, positions in healthcare may require more extensive checks due to the sensitive nature of the work and the need to protect vulnerable populations. Similarly, roles in transportation, education, and positions involving children or the elderly often have additional mandated checks. Always verify industry-specific regulations to ensure full compliance.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with Arkansas background check laws?
Non-compliance with background check laws in Arkansas can result in severe consequences. Penalties may include fines, potential lawsuits, and damage to your organization's reputation. Violating the FCRA can lead to statutory damages ranging from $100 to $1,000 per violation, actual damages, attorney's fees, and punitive damages for willful misconduct. Ensuring compliance is a legal obligation and critical to maintaining a fair and transparent hiring process.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, it's critical to emphasize the core aspects of complying with Arkansas background check laws. The main takeaways focus on knowing and integrating state-specific regulations, securing proper consent, respecting the "Ban the Box" initiative, and interpreting the lawful use of criminal records.
The key advice for HR professionals and business owners is straightforward: stay vigilant, apply best practices, and stay informed about legal changes. To stay on the right side of the law, regularly review and update your background check processes. Utilize resources like the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) guidelines and insights from HR professionals.
Staying compliant isn't just about avoiding penalties—it's about fostering a transparent, ethical hiring environment that benefits your organization and prospective employees.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






