In today's increasingly digital world, background checks have become an essential tool for employers across various industries. From staffing agencies and healthcare providers to technology firms and hospitality businesses, understanding the nuances of data privacy in background checks is essential. Not only can it protect the individual’s peace of mind, but it also shields businesses from potential legal issues and reputational harm.
Key Takeaways
- Safeguarding personal information in background checks is crucial for building trust and maintaining the integrity of the hiring process.
- Legal frameworks like GDPR, CCPA, and FCRA provide strict guidelines for ensuring data privacy during background checks.
- Common data privacy issues include unauthorized access, data breaches, inaccurate data, and improper data storage and disposal.
- Best practices for data privacy include using reputable vendors, implementing data encryption, controlling access, conducting regular audits, and obtaining clear consent.
- HR professionals, recruiters, and job seekers must proactively understand and adhere to data privacy laws to protect sensitive information.
Introduction
Privacy can't be an afterthought in a world where data reigns supreme. It’s a front-and-center concern, especially when it comes to background checks. Safeguarding personal information isn't just about avoiding hefty fines or dodging lawsuits; it’s about building trust and maintaining the integrity of the hiring process and the workplace environment.
The stakes are high for business owners, HR professionals, and recruiters—from bustling staffing agencies and tech innovators to healthcare providers and non-profits. Data privacy isn't some abstract concept; it’s a real-world, everyday challenge that affects hiring decisions, company reputation, and, ultimately, the bottom line. And let’s not forget the job seekers, the individuals whose private histories and personal details are at the center of this scrutiny. Each sector—be it transportation, tenant screening, retail, or hospitality—faces its own unique set of challenges and considerations when handling sensitive information. Understanding the importance of data privacy in background checks enables everyone involved to navigate this complex landscape more securely and confidently.
EXPERT INSIGHT: In the background check process, it is not only essential to verify the information provided but also to collect only the necessary data for a specific purpose and ensure its proper safekeeping. In today's digital and virtual environment, with the increasing capabilities of technology, this task has become increasingly challenging. Previously, appropriate filing, storing, and shredding of hard copies were sufficient measures. However, this is now only a part of the process. We must also consider data storage, cloud storage, encryption, and secure deletion, among other factors. The information shared by candidates is personal and confidential, and a significant amount of trust is placed in the process by both candidates and companies, as well as between companies and background check agencies. The key question then becomes: How do we maintain this trust? Read on to learn more. - Emile Garcia, SHRM-SCP, CHRP, CHRBP
What is Data Privacy in Background Checks?
Data privacy concerns background checks and safeguards the personal information collected during these procedures. This means ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and security of sensitive data such as social security numbers, criminal and credit histories, and employment records.
Definition
Data privacy in background checks refers to the practices and protocols used to protect personal information from unauthorized access, misuse, or public exposure. It ensures the data collected has its well-defined purpose. This approach guarantees that only relevant information is gathered, minimizing the risk of unnecessary or invasive data collection. By adhering to these guidelines, organizations can maintain the trust of their employees and candidates, while also upholding the principles of transparency and accountability. Furthermore, this clarity in data usage reinforces the overall integrity and effectiveness of the background check process. It involves maintaining the confidentiality of the data so that only authorized personnel can access it, ensuring the integrity of the data so that it's accurate and unaltered, and securing the data against breaches and cyber threats. This is especially critical given that background checks often pull from various sensitive data sources to build a comprehensive profile of the individual.
Legal Frameworks
Several legal frameworks provide guidelines and regulations for maintaining data privacy in background checks. Key among these are:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This is a comprehensive data protection law that applies to all entities handling the personal data of European Union (EU) citizens. It mandates strict data protection requirements, including obtaining explicit consent, ensuring data accuracy, and giving individuals the right to access and delete their information.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This legislation enhances privacy rights and consumer protection for California residents. Under CCPA, individuals have the right to be informed about what personal data is being collected, the purposes for which it is used, and with whom it is shared. It also provides the right to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of personal information.
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): A U.S. federal law that regulates how consumer reporting agencies use individuals' information, FCRA requires that background checks be conducted with an individual's knowledge and consent, that the information provided be accurate and up-to-date, and that there are processes for disputing errors found within these reports.
Understanding and adhering to these legal frameworks is crucial for anyone conducting or subjecting themselves to a background check. These laws uphold privacy rights, ensure data accuracy, and foster trust between individuals and organizations.
Why Data Privacy is Crucial in Background Checks
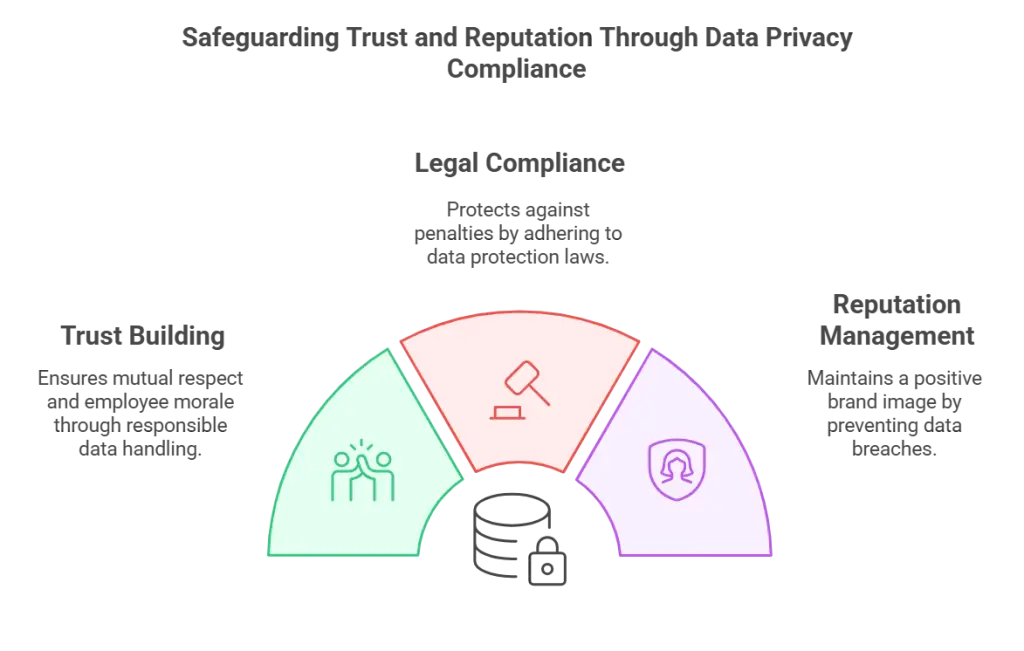
Trust Building
Building trust between employers and employees hinges on handling personal information responsibly. Employees want reassurance that their sensitive data, from social security numbers to financial history, won't be compromised. Employers' strong commitment to data privacy fosters a sense of security and mutual respect. This trust not only improves employee morale but can also enhance retention rates and encourage a more transparent work environment.
Legal Compliance
Adhering to legal requirements isn’t just a matter of ethical practice—it's a crucial legal obligation. Legislation such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) impose stringent standards on how personal data must be handled. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and potential lawsuits. By embedding data privacy into background checks, companies safeguard themselves against costly legal repercussions and ensure adherence to best practices.
Reputation Management
A single data breach can wreak havoc on a company's reputation. News of compromised personal information spreads quickly, eroding trust from current employees, prospective hires, and clients. Reputational damage can lead to lost business opportunities and a tarnished brand image that may take years to rebuild. Companies that prioritize data privacy in their background checks, on the other hand, project a culture of accountability and reliability, securing their standing in the marketplace and setting themselves apart as trustworthy organizations.
Common Data Privacy Issues in Background Checks
When it comes to background checks, safeguarding personal data is paramount. However, several common issues often arise, jeopardizing data privacy. First off, unauthorized access poses a significant threat. When sensitive information falls into the wrong hands, it can lead to identity theft or data misuse. Businesses must implement stringent access controls to limit who can view or handle such information.
Another prevalent issue is data breaches. Often caused by weak cybersecurity measures, hacking, or even insider threats, breaches can have severe implications—financial losses, legal ramifications, and a tarnished reputation. To mitigate these risks, companies must invest in robust cybersecurity protocols and regular vulnerability assessments.
Another critical concern is the use of inaccurate data during background checks. Relying on outdated or incorrect information can lead to unfair employment decisions and legal complications. Ensuring that data is accurate and up-to-date requires ongoing monitoring and verification processes.
Lastly, improper data storage and disposal practices can compromise data privacy. Failing to store data securely exposes it to unauthorized access, while improper disposal—such as neglecting to shred sensitive documents or deleting digital records—can lead to data leaks. Hence, a well-defined data management policy is indispensable; it should outline secure storage solutions and standardized procedures for data disposal.
Proactively addressing these common data privacy issues can significantly reduce risks and safeguard the integrity of the background check process.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Privacy in Background Checks
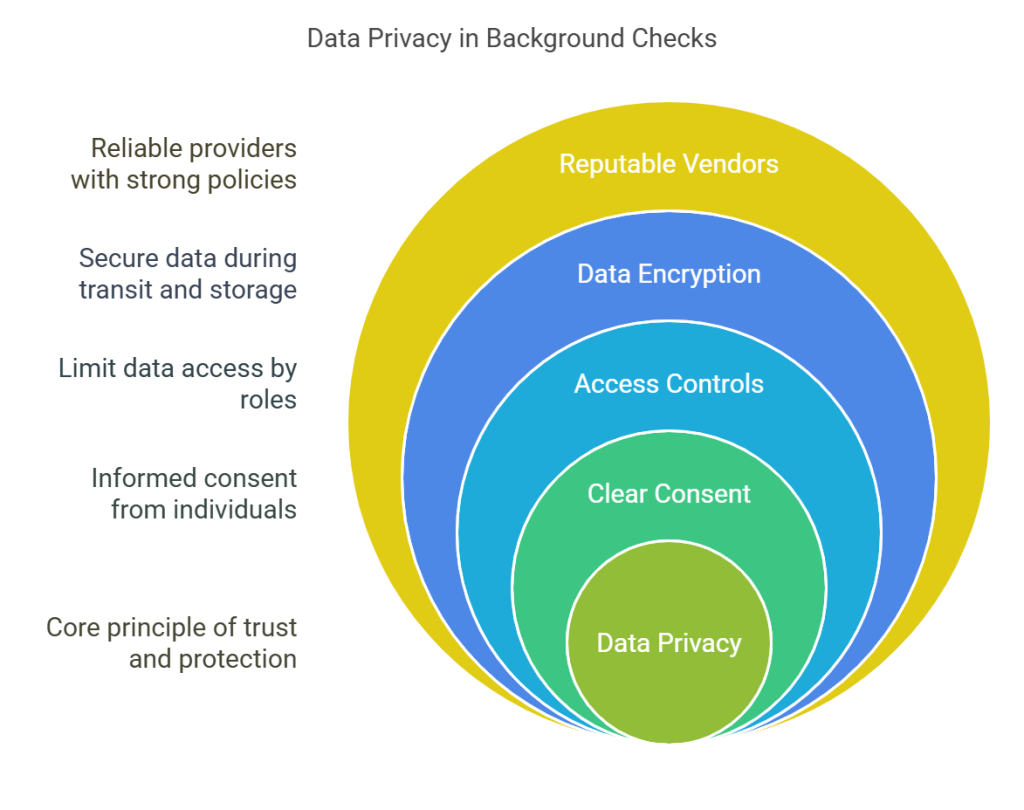
Ensuring data privacy in background checks isn't just about following the letter of the law—it's about cultivating trust and protecting the rights of individuals. Here are some concrete steps to take:
Choose Reputable Vendors
Why it matters: The first line of defense is selecting a reliable background check provider. Vendors with robust privacy policies and proven compliance records reduce the risk of data mishandling.
Actionable advice: Research vendors thoroughly. Look for third-party certifications, read reviews, and ask for references. Don't hesitate to press them on their security protocols and compliance measures.
Data Encryption
Why it matters: Encryption transforms data into a secure format that can only be read with the appropriate decryption key. This ensures that sensitive information remains protected during transmission and storage.
Actionable advice: Always use end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest. Ensure your vendors do the same. Implementing strong encryption protocols (e.g., Advanced Encryption Standard with a 256-bit key [AES-256]) is non-negotiable.
Access Controls
Why it matters: Not everyone in the organization needs access to all data. Limiting access minimizes the risk of unauthorized use and potential leaks.
Actionable advice: Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to restrict data access to only those employees who need it for their roles. Regularly review and update permissions as roles change.
Regular Audits
Why it matters: Regular audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure ongoing compliance with data privacy policies and regulations.
Actionable advice: Schedule periodic internal and third-party audits. Review access logs, encryption practices, and vendor compliance. Document findings and remediate issues promptly.
Clear Consent
Why it matters: Obtaining explicit, informed consent from individuals before conducting background checks is a legal requirement and an ethical best practice.
Actionable advice: Develop clear, easy-to-understand consent forms. Explain what data will be collected, how it will be used, and the measures to protect it. Ensure that consent is given freely and can be withdrawn at any time.
By integrating these best practices into your background check process, you comply with legal standards and build a foundation of trust and integrity. Ensuring data privacy isn't just about sidestepping fines—it's about fostering a culture of respect and responsibility.
Legal Considerations for Employers
Navigating the legal landscape of background checks is no small feat. Employers must know various legislative requirements to maintain compliance and uphold data privacy standards.
FCRA Compliance
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a cornerstone in regulating background checks in the United States. It mandates that employers must:
- Provide Disclosure and Obtain Consent: Before conducting a background check, employers must inform applicants of their intentions and obtain written consent. This disclosure must be clear and conspicuous, typically in a stand-alone document.
- Pre-Adverse Action Protocol: If the background check reveals information that may lead to an adverse employment decision, the employer must provide the candidate with a pre-adverse action disclosure. This includes a copy of the report and a summary of the individual's rights under the FCRA.
- Adverse Action Notices: Should the employer decide to take adverse action (e.g., not hiring the candidate based on the background check), they must issue an adverse action notice. This should include contact information for the Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA), a statement that the CRA did not make the adverse decision, and information about the candidate's right to dispute inaccuracies in the report.
GDPR and CCPA
While the FCRA dominates the U.S. landscape, employers handling data from European or Californian residents must consider the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
- GDPR: This European regulation emphasizes stringent data protection and privacy for individuals. Key considerations include:
- Data Minimization: Only collect data that is necessary for the background check.
- Consent: Obtain explicit consent from the candidate and ensure they are informed of how their data will be used.
- Right to Access and Erasure: Candidates can access the data held by the employer and request its deletion under certain circumstances.
- CCPA: This regulation focuses on giving California residents more control over their personal information. Employers must:
- Notify: Inform candidates at or before data collection about the types of personal data being collected and the purposes for which it will be used.
- Rights to Opt-Out: Ensure candidates can opt out of having their data sold or shared.
- Access and Deletion: Allow candidates to request access to their personal information and request its deletion.
State-Specific Laws
Beyond federal and international regulations, various states have specific laws and regulations concerning background checks and data privacy. For example:
- Ban-the-Box Laws: Several states and localities have implemented “ban-the-box” laws, prohibiting employers from asking about criminal history on job applications. Employers need to be aware of whether such laws apply in their location.
- Identity Theft Protection Laws: States like New York have laws requiring businesses to implement safeguards for sensitive information to prevent identity theft.
- Salary History Bans: Some states restrict employers from inquiring about a candidate's salary history to promote fair pay practices.
Maintaining compliance with these varied legal requirements isn’t just about avoiding penalties. It’s about fostering trust and demonstrating a commitment to ethical practices. Employers should stay informed and continually review their policies to align with evolving legislation. Adhering to these laws protects individuals’ privacy and fortifies the organization's reputation and legal standing.

Role of Technology in Enhancing Data Privacy
Secure Software Solutions
Modern software solutions have become indispensable in ensuring the privacy of data collected during background checks. Secure platforms employ state-of-the-art encryption methods to safeguard personal information against unauthorized access. These solutions also include features like multi-factor authentication, which adds an extra layer of security. Regular updates and patches further help protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. In a nutshell, leveraging cutting-edge software can significantly mitigate the risks associated with data breaches.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing the background check process by offering enhanced accuracy and security. AI algorithms can sift through vast amounts of data to identify inconsistencies or fraudulent information more efficiently than manual methods. These technologies can also flag potential red flags without exposing sensitive data to unnecessary viewing, thus maintaining privacy. Moreover, machine learning models continuously improve over time, ensuring that the background checks are precise and conducted in a manner that prioritizes data protection.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is emerging as a potential game-changer for maintaining data integrity and privacy. Its decentralized nature ensures that no single entity controls the entire data set, reducing the likelihood of targeted attacks. Each piece of data is securely encrypted and linked to the previous one, creating an immutable ledger that is incredibly difficult to tamper with. This makes blockchain an attractive option for storing and verifying the data used in background checks, offering unparalleled security and transparency.
Responsibilities of HR Professionals and Recruiters
Training and Awareness
In the realm of data privacy, knowledge is power. For HR professionals and recruiters, it starts with comprehensive training sessions that cover data privacy principles and the specific requirements of key legislation like GDPR, CCPA, and FCRA. These sessions should be mandatory and regularly updated to keep pace with evolving regulations and emerging threats. By fostering a culture of awareness, you reduce the risk of data breaches and build a workforce that understands the importance of protecting sensitive information.
Developing Policies
Clear, well-crafted policies are the backbone of any successful data privacy strategy. HR professionals and recruiters should collaborate with legal teams to draft policies that are not only compliant with current laws but also tailored to their organization's unique needs and values. These policies should outline procedures for conducting background checks, managing data, and responding to potential breaches. They should be communicated effectively to all employees, ensuring everyone is on the same page and knows their role in safeguarding personal information.
Incident Response Plan
Despite best efforts, data breaches can and do occur. That's why having an incident response plan is crucial. This plan should detail the steps immediately following a breach, including notifying affected individuals, cooperating with regulatory bodies, and mitigating further risks. Proactively developing and rehearsing this plan ensures that HR professionals and recruiters can act decisively and efficiently when faced with a data privacy issue, minimizing damage and maintaining trust.
Privacy Protection Tips for Job Seekers
Know Your Rights
Understanding your rights is the first line of defense when protecting your privacy during background checks. Laws such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) in the U.S. and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union grant specific protections regarding personal data. For instance, under FCRA, you must be notified if a background check is being conducted and can receive a copy of the report. Familiarize yourself with these rights to ensure you are not blindsided during the hiring process.
Check Privacy Policies
Before consenting to any background check, review the privacy policies of the companies conducting them. These policies should outline how your data will be collected, stored, shared, and disposed of. Ensure the company adheres to industry-standard security protocols. If the privacy policy is unclear or raises concerns, it might be worth reconsidering your involvement with that employer or background check service.
Ask Questions
Don’t be afraid to directly ask potential employers how they will handle and protect your data. Questions can include: What specific data will be collected? Who will have access to this information? How long will my data be stored? What steps are you taking to ensure my data remains secure? These questions not only demonstrate your awareness and concern about data privacy but can also provide crucial information about the employer’s commitment to safeguarding your data.
What is a Cyber Background Check?
A cyber background check, also sometimes referred to as an online background check or digital footprint analysis, involves gathering information about an individual from publicly accessible online sources. This can include social media profiles, news articles, blog posts, forum discussions, and other digital records. The goal is often to assess a person's character, reputation, and online behavior, potentially for employment, tenant screening, or other vetting purposes.
However, the increasing use of cyber background checks raises significant data privacy concerns. The sheer volume of personal information available online makes it challenging to ensure accuracy and fairness. Information found online may be outdated, misleading, or taken out of context. Furthermore, the collection and storage of such data can expose individuals to risks like identity theft and discrimination.
Key privacy concerns associated with cyber background checks include:
- Accuracy and Reliability: Online information isn't always accurate or verified.
- Context and Interpretation: Social media posts or online comments can be easily misinterpreted.
- Scope and Consent: Individuals may not be aware of or consent to the extent of online data collection.
- Data Security: Storing large amounts of personal data increases the risk of breaches.
- Discrimination: Information found online could lead to unfair biases and discriminatory practices.
- Right to be forgotten: Many online records remain forever, and there is little recourse to have these removed.
Therefore, it's crucial for both individuals and organizations to be aware of the implications of cyber background checks. Individuals should manage their online presence carefully, while organizations must adhere to strict ethical guidelines and legal regulations regarding data collection and usage. Transparency, consent, and data security are paramount in mitigating the privacy risks associated with this increasingly common practice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What kind of personal data is collected in a background check?
During a background check, various types of personal data can be collected depending on the purpose and scope. Generally, this includes full name, date of birth, social security number, previous addresses, employment history, educational qualifications, criminal records, credit history, and sometimes even social media profiles. The specific data collected may also depend on industry requirements and job-specific needs.
How can I ensure my personal information is protected during a background check?
To ensure your personal information is protected during a background check, look for companies that follow stringent data privacy protocols and comply with relevant legal frameworks like GDPR and CCPA. Request to see their privacy policies and how they manage data protection. Additionally, make sure the background check process includes encryption methods for data transmission and storage and that only authorized individuals have access to your information. Always give clear, informed consent before your data is collected.
What steps should an employer take if there’s a data breach?
If a data breach occurs, employers should act swiftly and follow a pre-established incident response plan. The immediate steps include:
- Identifying and containing the breach to prevent further data loss.
- Notifying affected individuals and regulatory bodies as required by law.
- Conducting a thorough investigation to ascertain the cause of the breach.
- Remediating vulnerabilities to prevent future incidents.
- Reviewing and updating data privacy policies and procedures to strengthen overall security measures.
Failing to respond adequately to a data breach can result in significant legal penalties and damage to the company’s reputation.
Are there penalties for non-compliance with data privacy laws?
Yes, there are substantial penalties for non-compliance with data privacy laws. For example, under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), organizations can face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their annual global turnover, whichever is higher. In the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) imposes fines ranging from $2,500 to $7,500 per violation. Similarly, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) includes penalties that can result in statutory penalties, actual damages, and punitive damages. Non-compliance brings financial repercussions and risks severe reputational damage and loss of trust among stakeholders.
Conclusion
Recapping the critical points, data privacy is not just a compliance checkbox but a fundamental aspect of trust-building in background checks. For businesses, adhering to privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, and FCRA secures more than just legal standing—it defends their reputation and fosters a positive employee-employer relationship. For job seekers, knowing one's rights and scrutinizing privacy policies is a gateway to safeguarding personal data.
Employers must prioritize data privacy in their background check processes. This can be achieved by implementing stringent access controls, conducting regular audits, using reputable vendors, and obtaining clear consent before gathering sensitive information. On the other hand, job seekers should be proactive about understanding how their data will be managed and protected during the hiring process.
By embracing these practices and staying vigilant about the latest trends and requirements, businesses and individuals can confidently and honestly navigate the complex landscape of data privacy in background checks.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






