Monthly OIG screening requirements represent a critical compliance framework that organizations must implement to avoid hiring excluded individuals and maintain federal program eligibility. Establishing systematic monthly screening processes protects healthcare organizations from potential penalties while ensuring continuous workforce compliance.
Key Takeaways
- Monthly screening frequency ensures continuous compliance with federal exclusion databases and reduces organizational liability risks significantly.
- Automated screening systems streamline the monthly OIG exclusion monitoring process while reducing human error and administrative burden.
- Documentation protocols for monthly screenings create essential audit trails that demonstrate ongoing compliance efforts to regulatory bodies.
- Multi-database screening beyond OIG includes SAM.gov and state-specific exclusion lists for comprehensive monthly compliance coverage.
- Immediate response procedures for positive screening results protect organizations from continued exposure to excluded individuals.
- Cost-benefit analysis consistently shows that monthly screening investments prevent substantially higher penalties and reputational damage.
Understanding Monthly OIG Screening Requirements
Healthcare organizations face stringent ongoing OIG exclusion monitoring obligations that extend far beyond initial hiring screenings. The Office of Inspector General expects employers to implement systematic processes that identify excluded individuals throughout the employment relationship. Monthly screening represents the gold standard for maintaining continuous compliance with federal healthcare program requirements in 2025.
Federal regulations don't explicitly mandate monthly screening frequency requirements. However, compliance experts consistently recommend this timeframe based on exclusion database update patterns. The OIG updates its List of Excluded Individuals and Entities (LEIE) monthly. Therefore, this screening interval proves logical for maintaining current compliance status.
Organizations that implement monthly screenings demonstrate proactive compliance efforts. Regulatory bodies view these efforts favorably during audits. Monthly screening requirements become particularly critical for healthcare organizations participating in Medicare, Medicaid, or other federal healthcare programs. These entities risk losing federal funding eligibility if they continue employing excluded individuals after exclusions take effect. The financial consequences of non-compliance far exceed the administrative costs of implementing monthly screening protocols.
Legal Framework for Continuous Screening
The legal foundation for ongoing screening stems from multiple federal regulations and guidance documents. These documents establish clear employer obligations for workforce monitoring. Healthcare organizations must understand that initial screening compliance doesn't satisfy their ongoing responsibilities for continuous surveillance.
OIG guidance documents consistently emphasize the importance of ongoing monitoring systems. These systems must identify excluded individuals promptly after their exclusion occurs. Organizations that fail to implement adequate screening frequencies face potential exclusion from federal healthcare programs themselves. This regulatory framework creates compelling business reasons for adopting monthly screening best practices.
Benefits of Monthly Screening Frequency
Organizations implementing monthly screening protocols experience significant compliance advantages compared to quarterly or annual screening approaches. Monthly frequency aligns with OIG database update schedules perfectly. This alignment ensures minimal delay between exclusion events and organizational awareness. Additionally, this alignment reduces the window of potential liability exposure while demonstrating commitment to compliance excellence.
| Screening Frequency | Risk Exposure Window | Compliance Rating | Administrative Burden |
| Monthly | 0-30 days | Excellent | Low |
| Quarterly | 0-90 days | Good | Medium |
| Annual | 0-365 days | Poor | High |
Monthly screening creates operational efficiencies that benefit HR departments and compliance teams significantly. Smaller monthly screening batches are easier to manage than large quarterly screening volumes. Large screening volumes can overwhelm administrative resources quickly. This approach enables more thorough review of screening results and faster response to positive findings.
Risk Mitigation Through Frequent Screening
Healthcare background screening frequency directly correlates with organizational risk exposure levels across multiple compliance domains. Monthly screening minimizes the duration of potential violations. Furthermore, monthly screening creates documentation that demonstrates ongoing compliance efforts to regulatory authorities.
This documentation proves invaluable during regulatory audits or investigations that examine organizational compliance practices. Organizations can show regulators their commitment to continuous monitoring rather than sporadic compliance efforts. Monthly screening frequency requirements also reduce the likelihood of regulatory penalties by catching violations early.
Implementing Automated Monthly Screening Systems
Modern compliance technology enables seamless automation of monthly OIG screening requirements without significant administrative burden. Automated systems can schedule, execute, and report screening results efficiently. These systems maintain comprehensive audit trails for compliance documentation. Additionally, these systems integrate with existing HR information systems to streamline workforce monitoring processes effectively.
Automation reduces human error risks while ensuring consistent screening execution. Staff availability and workload fluctuations won't impact screening consistency. Automated systems can process large employee databases efficiently. They also provide detailed reporting on screening results and compliance status. This technology investment pays dividends through reduced compliance costs and improved regulatory confidence.
Organizations should evaluate automated screening vendors based on specific criteria. Database coverage represents a critical evaluation factor. Update frequency and integration capabilities with existing systems also matter significantly. The best automated systems provide real-time alerts for positive screening results. They also maintain historical screening records for audit purposes. These capabilities transform monthly screening from administrative burden into strategic compliance advantage.
Technology Selection Criteria
Selecting appropriate automation technology requires careful evaluation of vendor capabilities, database coverage, and integration requirements. Organizations must ensure their chosen systems access current exclusion databases reliably. The systems should also provide dependable notification systems for positive results.
Technology investments should align with organizational size, complexity, and compliance requirements. This alignment maximizes the value and effectiveness of the screening system. Organizations should also consider scalability when selecting automated screening solutions for long-term success.
Multi-Database Screening Beyond OIG
Comprehensive monthly screening extends beyond OIG exclusion lists to include multiple databases. SAM.gov exclusions require monitoring for federal contracting compliance. State Medicaid exclusions and specialty database monitoring also demand attention. Continuous SAM screening ensures compliance with federal contracting requirements that may apply to healthcare organizations receiving government contracts.
State-specific exclusion lists capture additional excluded individuals who may not appear in federal databases. Therefore, organizations need comprehensive screening approaches that cover all relevant exclusion sources. Healthcare background check processes should incorporate these multiple database requirements systematically.
Healthcare organizations should screen against these key databases monthly:
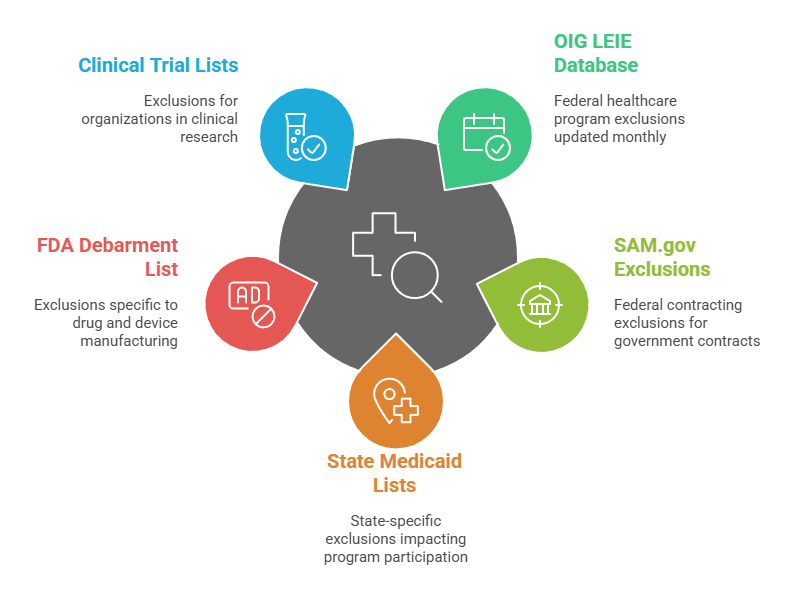
- OIG LEIE Database: Federal healthcare program exclusions updated monthly by the Office of Inspector General for all healthcare providers.
- SAM.gov Exclusions: Federal contracting exclusions that impact organizations receiving government contracts or grants from federal agencies.
- State Medicaid Lists: State-specific exclusions that may not appear in federal databases but impact state program participation significantly.
- FDA Debarment List: Exclusions specific to drug and device manufacturing that may impact certain healthcare organizations and suppliers.
- Clinical Trial Lists: Specialized exclusions for organizations conducting clinical research activities and pharmaceutical development work.
Multi-database screening creates comprehensive protection against excluded individuals. It also demonstrates thorough compliance efforts to regulatory authorities. Organizations that implement broad screening protocols show regulators their commitment to maintaining high compliance standards.
Database Integration Challenges
Different databases update on varying schedules with different data formats. This variation requires sophisticated integration approaches that can handle multiple data sources. Organizations need systems that can harmonize these diverse data sources into coherent screening workflows.
Technical challenges include data formatting inconsistencies and update timing variations. Administrative challenges involve managing multiple vendor relationships and ensuring comprehensive coverage. Organizations must address these challenges strategically to maintain effective screening programs.
Documentation and Audit Trail Requirements
Monthly screening programs must maintain detailed documentation that demonstrates ongoing compliance efforts. Proper documentation provides audit trails for regulatory review purposes. These records prove essential during compliance audits or investigations that examine organizational screening practices thoroughly.
Effective documentation protocols capture screening results and methodologies used for conducting screenings. Organizations should maintain records showing their screening frequency, database coverage, and response procedures. Documentation should also include the systems used for screening execution. This comprehensive documentation approach provides robust defense against compliance challenges. It also demonstrates commitment to regulatory requirements effectively.
Documentation systems should enable easy retrieval of screening records for specific employees, time periods, or compliance audits. Digital documentation systems with search capabilities streamline audit preparation significantly. These systems ensure record accessibility when regulators request information. The systems should integrate with existing HR records to provide comprehensive employee compliance profiles.
| Documentation Element | Retention Period | Regulatory Importance | Storage Method |
| Screening Results | 7 years minimum | Critical | Digital Archive |
| Response Actions | 7 years minimum | Critical | Digital Archive |
| System Logs | 3 years minimum | Important | Digital Archive |
Record Retention Best Practices
Healthcare organizations must establish record retention policies that exceed minimum regulatory requirements. Best practice retention periods account for potential investigation timeframes and statute of limitations considerations effectively. Organizations should balance storage costs against compliance risk when establishing retention schedules.
Digital storage solutions reduce retention costs while improving record accessibility for audit purposes. Cloud-based storage options provide additional security and backup capabilities that protect critical compliance documentation from loss or damage.
Response Procedures for Positive Screening Results
Organizations must establish immediate response protocols for positive monthly screening results. These protocols protect against continued compliance violations effectively. Effective response procedures include employee notification, work suspension protocols, and investigation processes. These procedures determine appropriate final actions while balancing compliance requirements with employment law obligations.
Positive screening results require immediate attention regardless of when they occur during the monthly screening cycle. Organizations should implement alert systems that notify compliance teams immediately. These alerts activate when excluded individuals are identified through screening processes. Rapid response capabilities minimize compliance violation periods. They also protect organizational interests effectively during critical compliance situations.
Response procedures should address these critical elements systematically:
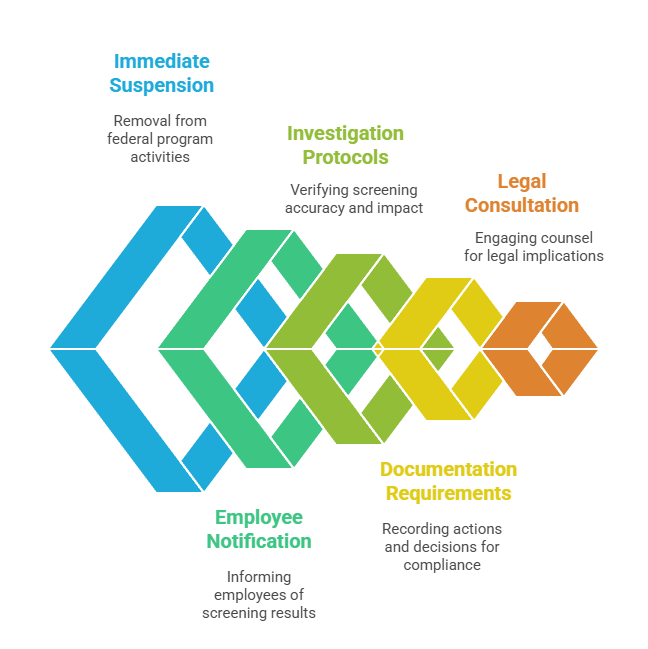
- Immediate Suspension: Remove excluded individuals from federal program-related activities immediately upon positive screening identification and verification.
- Employee Notification: Inform affected employees about screening results while providing opportunity for challenge, clarification, or appeal processes.
- Investigation Protocols: Verify screening accuracy and determine whether exclusion impacts specific job functions or entire employment relationships completely.
- Documentation Requirements: Record all response actions and decisions for audit trail purposes and comprehensive compliance demonstration to authorities.
- Legal Consultation: Engage employment counsel when positive results may impact employment decisions or create significant legal exposure risks.
Effective response procedures protect organizations from extended compliance violations. They also ensure fair treatment of affected employees throughout the resolution process. Organizations should train staff on response procedures to ensure consistent implementation across all departments.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Monthly Screening
Monthly OIG screening requirements represent significant compliance investments that organizations must evaluate carefully. These investments must be weighed against potential penalty exposure and operational disruption costs. Comprehensive cost-benefit analysis demonstrates that monthly screening investments typically generate substantial returns. These returns come through avoided penalties and reduced compliance risks over time.
Direct screening costs include vendor fees, staff time, and technology investments required for monthly screening implementation. These costs scale with employee population size. However, they benefit from economies of scale as screening volumes increase across the organization. Automated screening systems reduce per-employee costs significantly. They also provide enhanced compliance capabilities that justify technology investments fully.
Indirect benefits include penalty avoidance, reduced audit exposure, and enhanced regulatory relationships. These benefits provide long-term value beyond immediate compliance requirements. Organizations with strong compliance programs often receive favorable treatment during regulatory reviews. They also experience better outcomes during investigations. These reputational benefits compound over time while supporting business development and partnership opportunities.
| Cost Category | Monthly Investment | Annual Benefit | ROI Timeline |
| Technology Platform | $2,000-5,000 | $50,000-200,000 | 6-12 months |
| Staff Resources | $1,000-3,000 | $25,000-100,000 | 3-6 months |
| Vendor Services | $500-2,000 | $15,000-75,000 | 3-6 months |
ROI Calculation Methodologies
Healthcare organizations should calculate monthly screening return on investment using comprehensive methodologies. These methodologies must account for penalty avoidance, operational efficiency gains, and risk mitigation benefits accurately. Accurate ROI calculations support budget justification effectively. They also demonstrate compliance program value to organizational leadership clearly.
ROI calculations should incorporate both quantifiable benefits and strategic compliance advantages. Monthly screening provides measurable cost savings through penalty avoidance and operational efficiency improvements that justify program investments consistently.
Training and Staff Development Requirements
Successful monthly screening programs require comprehensive training for HR staff, compliance teams, and management personnel. Training ensures consistent implementation of screening procedures across all departments. Staff must understand their roles in the screening process clearly. They also need to know how to respond to positive screening results appropriately.
Training programs should cover database navigation, result interpretation, and documentation requirements thoroughly. Staff need to understand the legal implications of screening results. They must also know when to escalate issues to compliance leadership or legal counsel. Regular training updates ensure staff stay current with regulatory changes and best practices.
Organizations should develop training materials that address common screening scenarios. Role-playing exercises help staff practice response procedures safely. Documentation of training completion provides audit trail evidence of organizational commitment to compliance excellence. Ongoing education ensures staff maintain competency in screening procedures over time.
Competency Assessment Methods
Organizations should implement competency assessment methods to verify staff understanding of screening procedures. These assessments identify knowledge gaps before they impact compliance effectiveness. Regular competency evaluations ensure staff maintain required skill levels consistently.
Assessment methods can include written tests, practical demonstrations, and scenario-based evaluations. These methods should align with job responsibilities and organizational risk tolerance levels effectively.
Integration with Broader Compliance Programs
Monthly OIG screening requirements should integrate seamlessly with broader organizational compliance programs. This integration creates synergies that enhance overall compliance effectiveness. Screening data can inform other compliance activities like credentialing and privileging processes. Integration also reduces duplicate efforts and administrative burden across departments.
Compliance programs benefit from centralized screening data that supports multiple regulatory requirements simultaneously. Monthly screening results inform risk assessments for other compliance areas. They also provide early warning indicators for potential compliance issues. Integration with incident reporting systems creates comprehensive compliance monitoring capabilities.
Organizations should align screening schedules with other compliance activities where possible. This alignment maximizes administrative efficiency while ensuring comprehensive compliance coverage. Integrated reporting systems provide management with holistic views of organizational compliance status. These systems support data-driven decision making for compliance program improvements.
Regular compliance program reviews should evaluate screening integration effectiveness. Organizations should identify opportunities for additional integration that enhances compliance capabilities. Cross-functional compliance teams can identify synergies between screening and other compliance activities effectively.
Vendor Selection and Management
Choosing the right screening vendor significantly impacts monthly screening program success. Organizations must evaluate vendor capabilities thoroughly before making selection decisions. Vendor assessment should include database coverage, update frequency, and technical integration capabilities. Customer support quality and compliance expertise also matter significantly for long-term success.
Vendor management requires ongoing oversight to ensure service quality and compliance effectiveness. Organizations should establish service level agreements that define performance expectations clearly. Regular vendor performance reviews identify issues before they impact compliance effectiveness. Backup vendor arrangements provide continuity if primary vendors experience service disruptions.
Contract negotiations should address data security, privacy protection, and liability allocation comprehensively. Organizations must ensure vendors meet healthcare industry security standards consistently. Vendor contracts should include termination clauses that protect organizational interests appropriately. Regular contract reviews ensure terms remain favorable as business needs evolve.
Organizations should maintain relationships with multiple vendors when possible. This approach reduces dependency risks while providing leverage in contract negotiations. Vendor diversification also enables organizations to access specialized database coverage that single vendors might not provide comprehensively.
Conclusion
Monthly OIG exclusion screening represents essential compliance infrastructure for healthcare organizations committed to maintaining federal program eligibility in 2025. The combination of automated screening technology, comprehensive database coverage, and documented response procedures creates robust protection against excluded individual employment risks. Organizations that implement monthly screening best practices position themselves for long-term compliance success while minimizing regulatory exposure effectively. These investments in systematic compliance processes generate substantial returns through penalty avoidance and enhanced regulatory relationships that support organizational growth and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often are OIG exclusion databases updated?
The OIG updates its List of Excluded Individuals and Entities (LEIE) monthly, typically around the 15th of each month. This monthly update schedule forms the basis for recommending monthly screening frequency to ensure organizations identify newly excluded individuals promptly.
What happens if we find an excluded employee during monthly screening?
Upon discovering an excluded employee, immediately remove them from any federal healthcare program-related activities, notify the employee of the screening result, conduct a verification investigation, and document all actions taken. Consult employment counsel for guidance on employment decisions based on exclusion status.
Are monthly OIG screenings legally required?
While federal regulations don't specify exact screening frequencies, they require ongoing monitoring of workforce compliance. Monthly screening represents industry best practice that demonstrates reasonable compliance efforts and aligns with database update schedules.
Which databases should be included in monthly screening?
Comprehensive monthly screening should include OIG LEIE, SAM.gov exclusions, relevant state Medicaid exclusion lists, and any specialty databases applicable to your organization's activities, such as FDA debarment lists for organizations involved in pharmaceutical activities.
How long should we retain monthly screening documentation?
Maintain screening documentation for at least seven years, which exceeds most regulatory requirements and supports potential audit or investigation needs. Digital storage systems make long-term retention cost-effective while ensuring easy retrieval capabilities.
Can automated systems handle monthly OIG screening requirements?
Yes, automated screening systems can efficiently manage monthly screening requirements by scheduling screenings, accessing multiple databases, generating reports, and providing alerts for positive results. These systems reduce administrative burden while improving compliance consistency and documentation quality.
Additional Resources

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





