In today's competitive job market, where talent acquisition is pivotal to organizational success, the role of background checks in the hiring process cannot be overstated. According to the Society for Human Resource Management, 90% of HR professionals utilize background checks to vet potential candidates. This statistic underscores the significance of thorough pre-employment screening in safeguarding against potential risks and liabilities.
Key Takeaways
- Employment History Discrepancies: Inconsistencies such as inaccurate employment dates, misrepresented job titles, or unexplained gaps can indicate potential issues with a candidate's honesty or reliability.
- Criminal Records: Past convictions, especially those relevant to the job role, may raise concerns about a candidate's suitability and the safety of the workplace.
- Educational Misrepresentations: Falsified degrees or certifications suggest dishonesty and a possible lack of necessary skills for the position.
- Credit History Issues: For roles involving financial responsibilities, a poor credit history or bankruptcies can signal financial instability or irresponsibility.
- Failed Drug Tests: Positive drug test results may indicate substance abuse issues, potentially affecting job performance and workplace safety.
Understanding Red Flags
Red flags serve as warning signs within background checks that warrant closer examination. These indicators can range from discrepancies in employment history to criminal convictions and financial troubles. Identifying red flags is crucial as they may signify potential risks or discrepancies that could impact the hiring process and organizational integrity.
Background checks are more than just a procedural step that HR professionals should follow. They are an essential aspect of the hiring process that nurtures trust among the people involved -- the HR, organization, and candidates. In this ever-changing work ecosystem, it is important to not only fill the open positions but to ensure that whom we bring into the organization resonates with the core values of the company. Therefore, thoughtful evaluation and bias-free decision-making play a great role.
What are Background Checks?
Background checks encompass a comprehensive review of an individual's past experiences, behaviors, and qualifications. These checks typically involve scrutinizing various aspects such as criminal history, employment verification, and education credentials. By delving into an applicant's background, employers aim to verify the accuracy of provided information, assess suitability for the role, and mitigate potential risks associated with hiring decisions.
Legal Considerations (FCRA)
HR professionals must navigate background checks within the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) framework. Enacted to promote consumer information's accuracy, fairness, and privacy, the FCRA imposes specific obligations on employers conducting background checks. Key provisions include obtaining candidate consent, ensuring data accuracy, providing adverse action notices, and allowing candidates to dispute inaccuracies.
Common Types of Red Flags on a Background Check
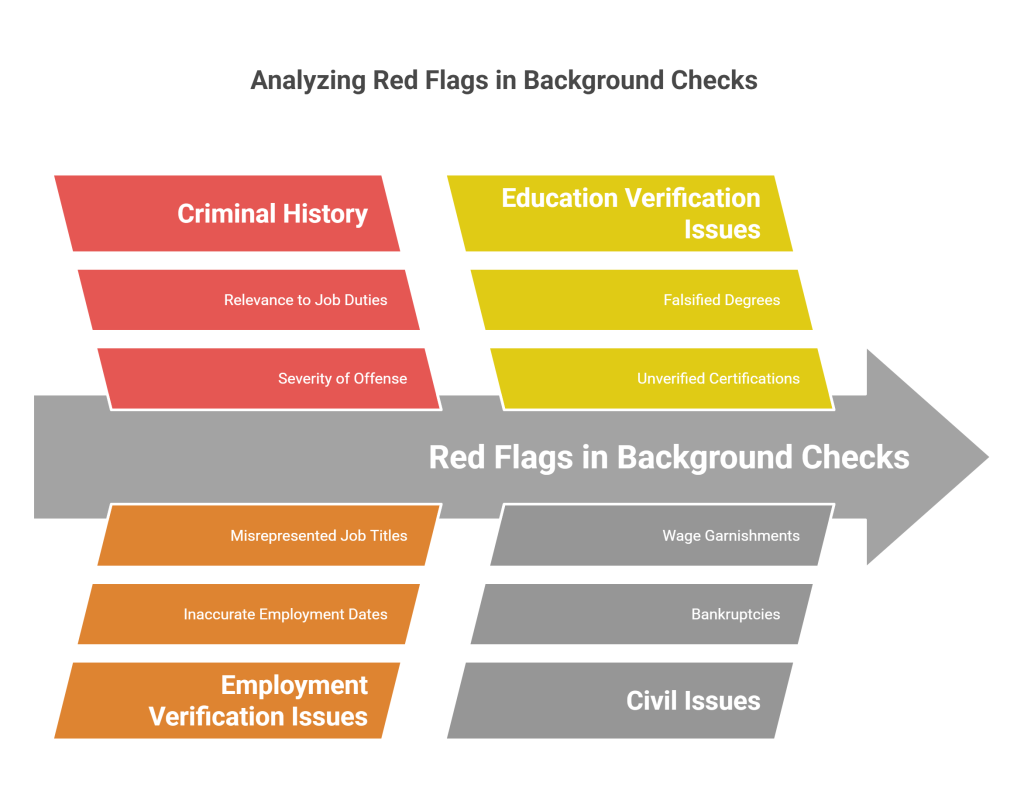
Criminal History
Criminal records are among the most significant red flags employers may encounter on background checks. When analyzing a criminal record, consider the severity of the offense, its relevance to the job duties, and the time elapsed since the incident. It's essential to evaluate criminal history on a case-by-case basis and in the context of the specific job requirements rather than applying a blanket exclusion policy.
Employment Verification Issues
Discrepancies in employment history can raise concerns about a candidate's honesty and suitability. These can include:
- Inaccurate dates of employment
- Misrepresented job titles or responsibilities
- Fabricated employment at a company
- Unexplained gaps in employment history
- Frequent job changes without clear reasons
- Inconsistent career progression
- Overstating job responsibilities
- Lack of verifiable references
- Failure to provide required documentation
- Frequent job changes in a short period
When faced with these red flags, HR professionals should verify information directly with previous employers and explore reasons for discrepancies or gaps with the candidate.
Education Verification Issues
Falsified educational credentials present significant red flags during the hiring process. Employers must take proactive measures to verify the authenticity of degrees and certifications claimed by candidates, utilizing reputable verification services and cross-referencing with educational institutions.
Civil Issues
Civil judgments, bankruptcies, or wage garnishments may also appear on a background check and can reveal aspects of a candidate's financial stability or history of legal issues. While these may not always be directly job-related, employers must carefully consider the context to ensure compliance with legal regulations when hiring.
Strategies for Addressing Red Flags
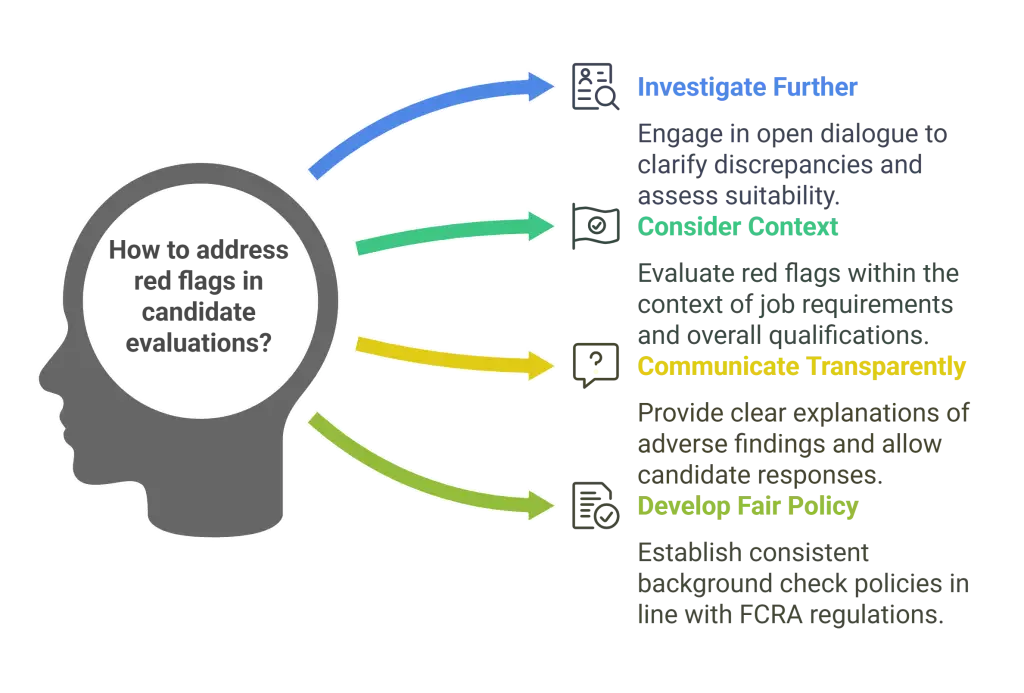
Investigate Further
Upon encountering red flags, HR professionals should conduct additional inquiries to obtain clarification from candidates and gather relevant context. This may involve engaging in open dialogue with applicants to address discrepancies and assess their suitability for the role.
Consider Context and Relevancy
It's essential to evaluate red flags within the context of the job requirements and the candidate's overall qualifications. Not all red flags carry the same weight, and discerning their relevancy is crucial in making informed hiring decisions.
Communication with Candidates
Transparency and adherence to FCRA guidelines are paramount when communicating potential red flags with candidates. HR professionals should provide candidates with clear and concise explanations of adverse findings and allow them to respond or dispute inaccuracies.
Developing a Fair Hiring Policy
Establishing a fair and consistent background check policy is foundational to promoting equity and compliance in the hiring process. HR professionals should collaborate with legal counsel to devise policies that align with FCRA regulations and organizational values.
Conclusion
As HR professionals navigate the complexities of background checks, vigilance and adherence to best practices are essential. By proactively managing red flags and maintaining compliance with FCRA regulations, organizations can mitigate risks, safeguard their reputation, and cultivate a talented workforce. Staying informed about evolving regulations and investing in robust screening processes is paramount in today's dynamic employment landscape.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






