Navigating the landscape of employment laws can be daunting, especially when you're trying to offer equal opportunities while staying on the right side of legislation. Washington's Fair Chance Act is a pivotal piece of legislation that employers and HR professionals need to understand thoroughly. Whether you’re an employer trying to comply with "Ban-the-Box" regulations or a job seeker interested in your rights, this guide breaks down the essentials for you.
Key Takeaways
- The Washington Fair Chance Act prevents employers from asking about criminal history early in the hiring process, promoting fair evaluation based on skills and experience.
- Implementing "Ban-the-Box" policies helps employers tap into diverse talent pools by focusing on candidates' abilities rather than past mistakes.
- To comply with the act, remove questions about criminal history from applications and train your hiring team on the new process.
- Non-compliance can result in significant fines and harm your company's reputation; documented hiring processes can help avoid this.
- For job seekers, this act reduces biases and promotes consideration of merit, making knowledge of your rights crucial during the job search.
Introduction
In 2018, Washington passed the Fair Chance Act, a significant step towards ensuring that those with a criminal record have a fair shot in the job market. This legislation curtails the ability of employers to ask about an applicant's criminal history until later in the hiring process, providing applicants a fair chance to be evaluated on their skills and experience first. The act mirrors broader fair hiring practices gaining traction across the United States, such as "Ban-the-Box" initiatives, aiming to whittle down the biased barriers against individuals with criminal backgrounds. These measures are not just about compliance; they echo a shift towards evaluating candidates based on merit. As an employer, understanding and implementing these changes is about aligning with this larger movement for equality in the workplace. Wouldn't you prefer a system that genuinely values potential over past mistakes?
Understanding "Ban-the-Box" Legislation
"Ban-the-Box" is an initiative that aims to remove the checkbox asking about criminal records from job applications. It helps level the playing field by allowing applicants to be evaluated on their qualifications first. The idea is simple: let someone's skills and experience speak before any past mistakes do.
This movement started gaining traction in the early 2000s, with grassroots activism pushing for change. It began with local governments, then moved to state legislatures, each working toward more equitable hiring practices. Today, many jurisdictions across the U.S. have adopted "Ban-the-Box" laws, making it a significant element of the hiring process landscape.
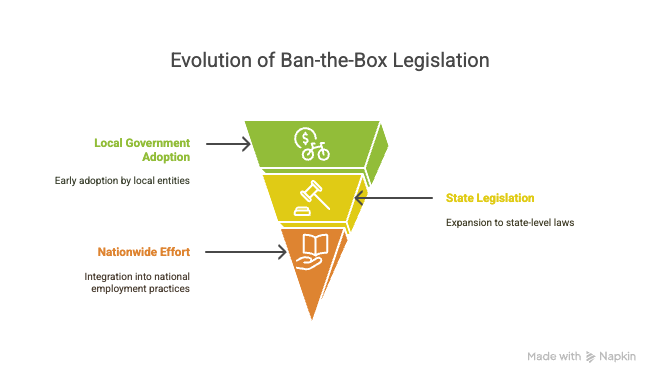
The "Ban-the-Box" initiative fits into a broader nationwide effort to promote fair employment. Industries and organizations like the Professional Background Screening Association provide insights and advocate for balanced background check procedures. By aligning with these principles, you can help eliminate early hiring biases and foster a more inclusive job market.
Consider how removing that dreaded box might change your company's hiring. Would it open doors to untapped talent? Would it change the dynamics of your team for the better? Ensuring your processes reflect this initiative might just be the step you need to build a more diverse workforce.
Key Provisions of the Washington Fair Chance Act
This section clarifies what Washington's Fair Chance Act demands from employers when it comes to criminal history inquiries. First off, the law restricts employers from asking about criminal history during the initial stages of the hiring process. This means that when you're crafting job applications, you can't include that checkbox about criminal convictions. The aim is to give applicants a fair chance to present their qualifications without being immediately dismissed due to their past.
Once you're ready to conduct interviews, remember that inquiries about criminal history are still off-limits during initial screenings. It's only after determining a candidate's qualifications for the position that you can consider their criminal record. Compliance with this provision changes the traditional hiring approach by focusing first on the applicant's skills and experience.
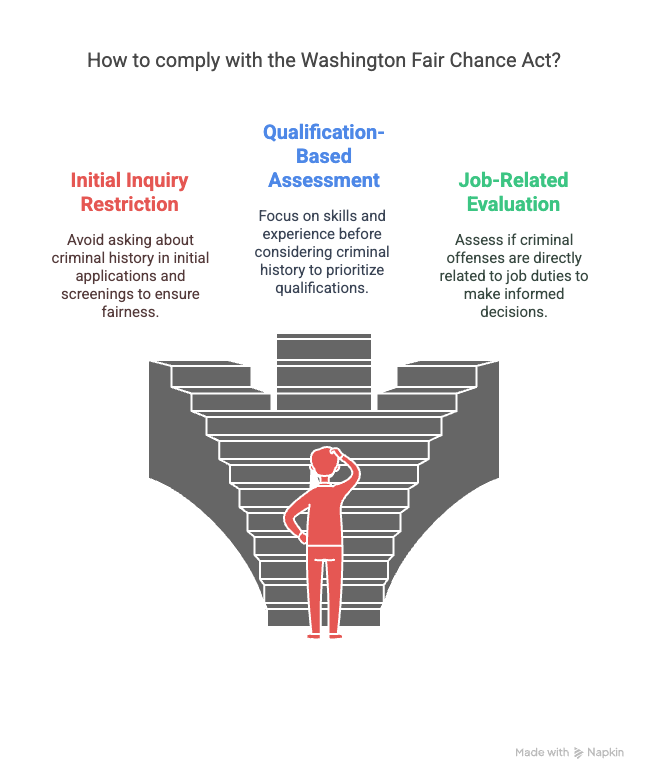
When it finally becomes permissible to consider a candidate's criminal history, the act requires a careful approach. You must evaluate whether the nature of any criminal offense is directly related to the job in question. This means you'll need to assess if the details of a criminal conviction have any direct impact on the duties or responsibilities the job entails.
Are you prepared to handle this nuanced decision-making? It's not enough to just be aware of these provisions; you need to integrate them into your existing hiring framework. This demands a shift in perspective where the focus remains on fair evaluation, enhancing both your hiring practices and the opportunities available to qualified applicants.
Compliance Tips for Employers
To stay compliant with Washington's Fair Chance Act, take a hard look at your hiring procedures. Start with your job applications. Remove any boxes or questions asking about criminal history. During interviews, avoid discussing an applicant's criminal record until the law allows it.
Train your HR staff. Everyone involved in hiring needs to know the rules. Hold workshops or online training sessions to go over the steps and timelines related to the Fair Chance Act. Make sure they understand how to handle sensitive information and when it’s appropriate to ask about an applicant’s criminal record.
Keep thorough records. Document your hiring processes and maintain records that show your compliance. This isn’t just about covering your bases—it's a useful practice that can protect you legally if questions arise later.
By handling these elements well, you not only comply with the law but also foster a fairer hiring environment. Are you confident your practices align with legal expectations? Consider these steps carefully to ensure smooth and lawful operations.
Legal Implications and Consequences
Failing to comply with the Washington Fair Chance Act can lead straight to legal trouble. Employers who ignore the rules risk penalties that aren't just financial but reputational. Fines for non-compliance can reach steep amounts, putting a dent in any company's budget. It's not just about the money, though. Legal battles drain time and resources, not to mention the damage they cause to your brand image.
Take a look at real-life cases where companies didn't follow the rules. A well-known retailer faced hefty fines after bypassing the fair hiring rules. Their HR department continued to ask about criminal history too early in the process, leading to a lawsuit. It wasn't just the fines that hurt; the PR fallout was severe, impacting customer trust.
Another company, a regional delivery service, was caught out when a rejected applicant proved they'd been unfairly questioned about past convictions. Their hiring managers were untrained, and the oversight landed them in hot water. The penalties served as a wake-up call for other businesses.
These examples are more than stories; they are cautionary tales encouraging you to take compliance seriously. Are your hiring practices in line with the law? Have you educated your staff? The ripple effects of non-compliance can be significant, so don’t wait until you're the example others learn from. Make sure your practices hold up under scrutiny, saving you from costly penalties and preserving your company's integrity.
The Impact on Job Seekers
The Washington Fair Chance Act has been a significant step forward in creating equal job opportunities. By delaying criminal history inquiries, it helps level the playing field for job seekers. Early barriers often deter qualified individuals from pursuing jobs, even when they have the skills needed. The act removes this initial hurdle, allowing candidates to be evaluated first on their experience and merits.
You, as a job seeker, have the right to be considered based on your capabilities and not be judged prematurely for past mistakes. If you sense a company is not adhering to these practices, it's crucial to know you have avenues for addressing suspected violations. Knowing your rights not only empowers you but can also guide you in seeking remedies if necessary.
The act also raises awareness among employers to focus on skills and fit before considering criminal records. This shift can open doors for many skilled workers who might otherwise be overlooked. It encourages businesses to make more conscious decisions about who they hire, often leading to a more diverse and qualified workforce.
Are you aware of your rights under this act? Knowing them can steer your job search towards environments that respect fair hiring principles, which can make a crucial difference in your career path.
Conclusion
The Washington Fair Chance Act reshapes hiring landscapes by restricting early inquiries into applicants' criminal histories, promoting equitable opportunities. Employers play a crucial role in integrating these changes, improving both legal compliance and workplace diversity.
Job seekers benefit significantly from this shift. Immediate biases from criminal record disclosures are reduced, increasing chances for interviews based on merit. Understanding your rights is essential. If you suspect a breach by a potential employer, utilize the available legal means to address it.
For businesses, grasping the act's nuances is pivotal in avoiding penalties. Review your hiring practices meticulously; ensure your team is trained. Implement well-documented procedures to reflect compliance. Real-life cases reveal common pitfalls leading to fines, serving as warnings.
Instilling fair hiring practices isn't just about adhering to laws; it's aligning with a broader commitment to equality and inclusivity. Stay vigilant and adaptable to an evolving legal landscape. It’s essential for maintaining a responsible, fair, and diverse workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When can WA employers ask about criminal history?
Employers in Washington State can inquire about criminal history after making a conditional offer of employment.
What jobs are exempt from WA’s Fair Chance Act?
Certain positions, such as those in law enforcement, education, and care for vulnerable populations, are exempt from the Fair Chance Act.
How to update job applications for compliance?
Remove any questions about criminal history from your initial job application forms to comply with the Fair Chance Act.
Can employers rescind offers based on records in WA?
Yes, employers can rescind a job offer based on criminal history, but they must provide the candidate an opportunity to explain or correct the information first.
Are gig workers covered under WA’s law?
Gig workers are not specifically covered under the Fair Chance Act, as it primarily applies to traditional employment situations.
What penalties apply for violations?
Violations of the Fair Chance Act can result in fines, with the amount depending on the frequency and severity of the violation.
Do WA schools follow Ban-the-Box?
Yes, public schools in Washington must follow Ban-the-Box regulations, delaying inquiries into criminal history until after a conditional job offer.
How to handle disclosures after a conditional offer?
Review the candidate's explanation and any additional information they provide. Make an informed decision based on job-relatedness, time passed, and evidence of rehabilitation.
Are misdemeanors included in WA background checks?
Yes, misdemeanors can be included in background checks, but the decision should consider relevance to the job and other factors.
Does WA’s law apply to out-of-state remote workers?
If the employer is based in Washington, the law applies to all employees, including remote workers residing out of state.
Are arrests without convictions included in background checks?
No, Washington law generally prohibits considering arrests that did not lead to a conviction in employment decisions.
What should you do if a candidate appeals a decision based on their criminal record?
Review the appeal carefully, considering any new information or context provided by the candidate.
Can an employer in WA ask about juvenile records?
Employers typically cannot inquire about sealed juvenile records when making employment decisions.
How can an applicant address their criminal record during interviews?
Applicants should be honest, provide context, and discuss any steps they have taken towards rehabilitation or personal growth.
Definitions
Fair Chance Act
A statewide employment law passed in Washington in 2018. It limits when employers can ask about a candidate’s criminal history. You can only bring up a criminal background after deciding a person is qualified for the role. This law aims to reduce unfair screening during early job application steps and shift focus to work experience and skills.
"Ban-the-Box"
A hiring reform initiative that removes the checkbox on applications asking about criminal convictions. This gives applicants an opportunity to showcase their qualifications before criminal history is reviewed. Many cities and states follow this approach to support fairer hiring. Does your current job application still include the box?
Criminal History Inquiry
Any question or investigation into an applicant’s past criminal convictions. Under laws like the Fair Chance Act, these questions must be delayed until later in the hiring process. Asking too early can lead to legal trouble and limit access to qualified candidates.
Hiring Process
The steps an employer follows to recruit and select new employees. It typically starts with a job posting, then applications and interviews, and finishes with background checks and job offers. Laws like the Fair Chance Act require you to change when and how certain questions are asked during this process. Are your current steps clearly documented and legally compliant?
Compliance
Following the rules laid out by employment laws and regulations. In the context of the Fair Chance Act, this means adjusting your hiring practices, training your team, and keeping records. If you skip these steps, you risk fines, legal action, and damage to your company’s credibility. Are your policies and procedures up to date?

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





