The employment background check process is a crucial step in the hiring process for many employers. It involves verifying the information candidates provide to ensure they are suitable for the position. In this guide, we'll take you through each step of the background check process, providing insights and debunking common misconceptions.
Employment background checks have become an integral part of modern hiring practices, with studies showing that over 90% of employers now conduct some form of pre-employment screening. These systematic investigations into a candidate's history, qualifications, and character serve as a critical risk management tool for organizations of all sizes.
At its core, an employment background check is a comprehensive review of publicly available records and verified information about a job candidate's past employment history. This process helps employers make informed hiring decisions by providing crucial insights into a candidate's reliability, integrity, and suitability for specific roles.
The increasing prevalence of background checks reflects growing awareness among employers about the importance of due diligence in hiring. With workplace violence, fraud, and litigation risks on the rise, background checks have evolved from a nice-to-have to an essential component of responsible hiring practices. They serve multiple critical functions: mitigating risk, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, maintaining workplace safety, building trust with stakeholders, and ultimately improving the quality of hire.
According to SHRM research, about 40% of employers conduct drug testing for both regulated and nonregulated roles, with an additional 14% performing tests only for regulated positions.Though the subject of drug testing can be sensitive, it remains a crucial topic for discussion. Understanding its importance is vital for both legal compliance and workplace safety. Employers and employees alike benefit from being well-informed about the intricacies of labor laws and company policies.
Why Do Employment Background Checks
Verification of Candidate Qualifications and Credentials
One of the primary reasons employers conduct background checks is to verify the accuracy of information provided by candidates. Studies indicate that up to 40% of resumes contain some form of inaccuracy or embellishment. Background checks help employers confirm educational achievements, employment history, professional licenses, and other credentials that are essential for job performance.
Ensuring Workplace Safety and Minimizing Risk
Background checks play a crucial role in maintaining a safe work environment. By screening for criminal history, particularly for violent offenses, employers can identify potential risks before an individual enters the workplace. This is especially important for positions involving access to sensitive areas, working with vulnerable populations, or handling valuable assets.
Reducing Risk of Negligent Hiring and Associated Litigation
Negligent hiring occurs when an employer fails to exercise reasonable care in the hiring process, potentially putting employees, customers, or the public at risk. The legal and financial consequences can be severe, with negligent hiring lawsuits resulting in average settlements exceeding $1 million. Comprehensive background checks demonstrate due diligence and help protect organizations from these costly claims.
Compliance with Federal, State, and Local Regulations
Many industries are subject to specific regulatory requirements regarding employee screening. For example, healthcare organizations must comply with Office of Inspector General (OIG) exclusion list checks, while financial institutions must adhere to banking regulations. Background checks ensure compliance with these mandatory requirements and help avoid regulatory penalties.
Building Trust with Customers, Clients, and the Public
A thoroughly vetted workforce enhances an organization's reputation and builds trust with stakeholders. Customers are more likely to feel confident doing business with companies that demonstrate a commitment to safety and security through comprehensive screening practices.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Specific industries have heightened screening requirements due to the nature of their work:
- Healthcare: Requires checks for sanctions, license verification, and OIG exclusion lists
- Education: Mandates criminal background checks for those working with minors
- Transportation: Requires Department of Transportation (DOT) drug testing and driving record checks
- Financial Services: Often requires credit checks and regulatory database searches
Types of Background Checks and What They Reveal
| Type of Background Check | What It Verifies | Details Revealed |
|---|---|---|
| Criminal Record Checks | Criminal history at the federal, state, and county levels | Felony/misdemeanor convictions, pending charges, sex offender registry |
| Employment Verification | Work history credentials | License status, disciplinary actions, expiration dates, and scope of practice |
| Education Verification | Academic background | Degrees/certifications, graduation dates, institutions, academic honors/distinctions |
| Professional License Checks | Credential validity for licensed professions | Public profiles, online behavior, privacy concerns, and FCRA compliance |
| Driving Records (MVR Checks) | Driving history and eligibility | License status, traffic violations, DUI/DWI, suspensions/restrictions |
| Civil Court Records | Non-criminal legal history | Bankruptcies, lawsuits, restraining orders, judgments/liens |
| Credit History | Financial responsibility (where legally allowed) | Debt handling, security clearance readiness, fiduciary trustworthiness |
| Drug Testing | Substance use compliance | Pre-employment, random, post-incident, return-to-duty testing |
| Immigration & Work Authorization | Legal right to work in the U.S. | Form I-9 compliance, E-Verify results, visa status |
| Social Media Screening | Digital reputation and behavior | Criminal activity alerts, MVR monitoring, license renewals, and re-screening protocols |
| Healthcare Sanctions Checks | Healthcare-related compliance | OIG exclusion lists, Medicaid exclusions, disciplinary board actions |
| Ongoing Monitoring | Continuous compliance tracking | Form I-9 compliance, E-Verify results, and visa status |
How Long Does It Take for a Pre-Employment Background Check?
The timeline for completing a pre-employment background check can vary based on several factors; however, the process typically takes 3 to 7 business days. However, certain situations may extend or shorten this timeframe. Here’s what influences the duration of a background check:
Factors That Affect the Timeline
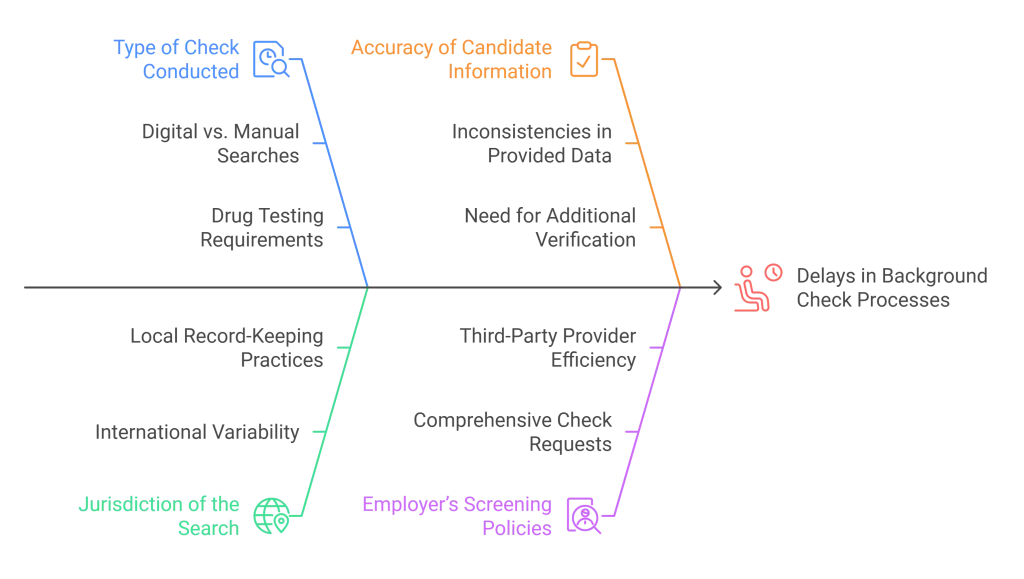
Type of Check Conducted: Different types of background checks—such as criminal record searches, employment verification, education verification, and drug testing—require varying amounts of time. For instance:
- Criminal background checks can be completed in as little as one day if the records are digital, but manual searches may take longer.
- Employment and education verifications can take 3-5 days or more if previous employers or schools are unresponsive.
Jurisdiction of the Search: Background checks that require searches in multiple jurisdictions, especially internationally, may take longer due to varying record-keeping practices and processing speeds.
Accuracy of Candidate Information: Errors or inconsistencies in the candidate’s provided information (e.g., incorrect dates of employment or misspelled names) can delay the process as additional verification steps may be required.
Employer’s Screening Policies: Some employers request comprehensive checks that include multiple screening components, which can extend the timeline.
Third-Party Background Check Providers: The efficiency and technology used by the screening company can significantly impact turnaround times.
Why It May Take Longer
- Manual Record Retrieval: Certain jurisdictions or institutions still rely on manual processes, which can add several days.
- Holidays and Weekends: Requests made around holidays or weekends often experience delays.
- Global Searches: If the candidate has lived or worked abroad, international verifications may take additional time due to varying country-specific regulations.
How to Speed Up the Process
- Provide Accurate Information: Ensure that all personal details, such as name, date of birth, and past employment details, are accurate and up to date.
- Respond Promptly to Requests: Candidates may be asked to provide additional documents or clarification during the process. Timely responses can prevent delays.
- Choose a Reliable Background Check Provider: Employers can mitigate delays by working with providers that leverage advanced technology for faster results.
While most background checks are completed within a week, employers and candidates should always plan for potential delays. Effective communication between all parties is crucial to ensuring a smooth and efficient process.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Pre-Employment Background Check Process
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to the employment background check process! Follow along as we outline each step, debunk common misconceptions, and provide valuable insights. Understanding this process is crucial whether you're an employer or a candidate.
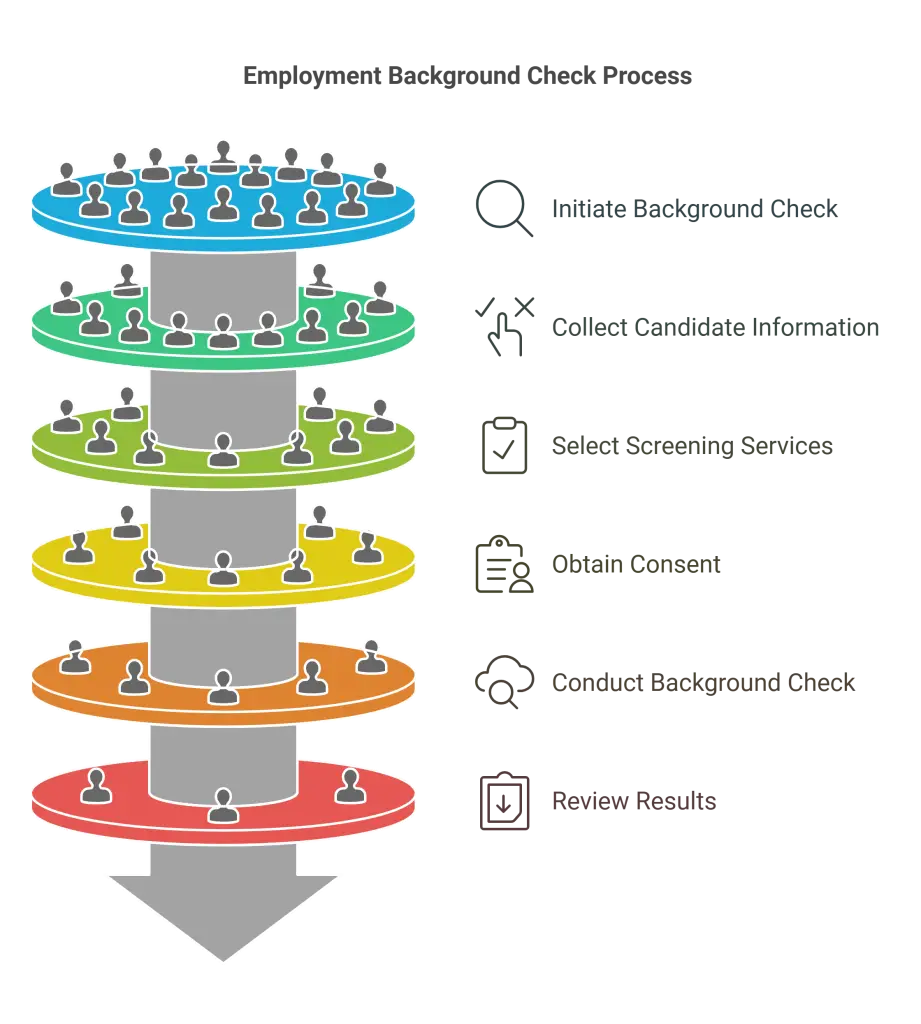
Step 1: Initiation of Background Check Order
Employers typically initiate background checks after a job offer is accepted.
- Fact: 95% of employers conduct background checks on potential hires.
- Common Misconception: Background checks are only for high-level positions (they're standard for most job roles).
Step 2: Collection of Candidate Information
Candidates provide personal details such as full name and SSN.
- Fact: According to a 2020 survey by Checkster Research, approximately 78% of job applicants admit to fibbing on their resumes regarding skills, job titles, degrees, or achievements.
- Common Misconception: Providing personal information poses identity theft risks (reputable companies use secure methods).
Step 3: Screening Services Selection
Employers select the types of background checks to perform.
- Fact: Criminal history checks are the most common type of background check.
- Common Misconception: Background checks are one-size-fits-all (employers can customize them based on job requirements).
Step 4: Background Check Authorization and Disclosure
Candidates provide written consent for the background check.
- Fact: Background checks are regulated by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
- Common Misconception: Employers can conduct checks without consent (consent is legally required).
Step 5: Background Check Process
Screening companies gather information from various sources.
- Fact: Background checks can take several days to complete.
- Common Misconception: Background checks provide instant results (complexity can delay them).
Step 6: Review of Background Check Results
Employers review results for accuracy and completeness.
- Fact: Errors can occur in background checks, so reviewing them is crucial.
- Common Misconception: Background checks are always accurate (errors can still happen).
Step 7: Decision Making
Employers consider background check results, among other factors.
- Fact: Background checks help employers make informed hiring decisions.
- Common Misconception: A negative result always leads to disqualification (legal requirements must still be followed).
Step 8: Communication of Results
Employers inform candidates of the results.
- Fact: Candidates have the right to dispute inaccuracies.
- Common Misconception: Candidates have no rights regarding background check information (candidates can dispute inaccuracies).
Step 9: Dispute Resolution
Candidates can dispute any inaccuracies.
- Fact: Screening companies are required to investigate and resolve disputes.
- Common Misconception: Disputes are rarely successful (screening companies work to correct errors).
Step 10: Final Hiring Decision
Employers make the final decision based on all factors.
- Fact: Background checks are just one piece of the hiring puzzle.
- Misconception: Background checks are the sole determinant of hiring decisions (they are only a part of the process).
Conclusion
Employment background checks have evolved into a sophisticated risk management tool that serves multiple critical functions in modern hiring practices. When conducted properly, they help organizations build safer workplaces, make informed hiring decisions, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect against various forms of liability.
The key to successful background screening lies in balancing thorough due diligence with respect for candidate rights and legal compliance. This requires understanding the complex web of federal, state, and local laws that govern employment screening, staying current on evolving regulations, and implementing comprehensive policies and procedures.
Organizations that invest in proper background check processes benefit from:
- Reduced risk of negligent hiring claims
- Enhanced workplace safety and security
- Improved quality of hire and employee retention
- Stronger compliance with regulatory requirements
- Enhanced reputation and stakeholder trust
- More informed decision-making throughout the hiring process
As the employment landscape continues to evolve, background check practices must adapt to address new challenges while maintaining focus on fairness, accuracy, and legal compliance. The integration of new technologies, changing workforce dynamics, and evolving legal requirements will continue to shape the future of employment screening.
Ultimately, effective background check programs represent an investment in organizational success and sustainability. By implementing comprehensive, compliant, and fair screening practices, employers can build stronger teams, reduce risk, and create safer, more productive work environments for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a background check take?
The time it takes to complete a background check can vary depending on several factors, including the type of check being conducted, the complexity of the individual's background, and the responsiveness of the sources contacted. Generally, background checks can take a few days to several weeks to complete.
Can a candidate dispute the results of a background check?
Yes, candidates have the right to dispute the results of a background check under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). If a candidate believes the information in their background check is inaccurate or incomplete, they can dispute it with the provider. The provider must then investigate the disputed information and correct any inaccuracies.
Are background checks mandatory for all positions?
Background checks are not mandatory for all positions. The employer typically decides to conduct a background check based on the nature of the job and the responsibilities involved. Certain positions, such as those that require access to sensitive information or working with vulnerable populations, may require a background check as part of the hiring process.
What is an employment background check?
An employment background check is a review of a person's past, typically conducted by an employer, to assess their suitability for a job. This check often includes verifying a candidate's employment history, education, criminal record, and sometimes credit history.
Why do employers conduct background checks?
Employers conduct background checks to verify the accuracy of a candidate's information, ensure workplace safety, and assess potential risks. This process helps in making informed hiring decisions and maintaining a trustworthy work environment.
What information is typically included in a background check?
A standard background check may include verification of employment history, education credentials, criminal records, credit history, driving records, and reference checks. The specific components can vary based on the employer's requirements and the nature of the job.
How long does the background check process take?
The duration of a background check can vary depending on the complexity of the individual's history and the types of checks being performed. Generally, it can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks to complete.
Can a candidate dispute the results of a background check?
Yes, candidates have the right to dispute the results of a background check if they believe the information is inaccurate or incomplete. Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), candidates can request a re-investigation of any disputed information.
Do background checks include social media screening?
Some employers may include social media screening as part of the background check process to gain insights into a candidate's character and professionalism. However, this practice must be conducted in compliance with privacy laws and regulations.
Are background checks mandatory for all job positions?
Background checks are not mandatory for all positions; the necessity depends on the employer's policies and the job's responsibilities. Positions involving sensitive information, financial responsibilities, or interaction with vulnerable populations are more likely to require thorough background checks.
How can candidates prepare for a background check?
Candidates can prepare by ensuring all information provided to potential employers is accurate and up-to-date, informing references about potential contact, and reviewing their own records for any discrepancies that might arise during the background check process.
What are the legal considerations for employers when conducting background checks?
Employers must comply with laws such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines, which regulate the collection and use of background information to prevent discrimination and ensure privacy.
Can a job offer be withdrawn based on background check results?
Yes, an employer can rescind a job offer if the background check reveals information that disqualifies the candidate from the position. However, the employer must follow legal protocols, including providing the candidate with a pre-adverse action notice and a copy of the report, allowing them to dispute any inaccuracies.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






