Navigating the layers of employment laws can be daunting for any employer, especially when it comes to regulations like Illinois' Ban-the-Box law. Designed to promote fair hiring practices by delaying questions about a candidate’s criminal background, this law has significant implications for your hiring process. This guide provides a roadmap for Illinois Ban-the-Box compliance, helping you understand how to align your hiring practices with state requirements. We'll explore what the law entails, the specific requirements for employers, and tips for maintaining compliance while still making informed hiring decisions.
Key Takeaways
- The Illinois Ban-the-Box law changes hiring by delaying criminal history inquiries until after the initial interview, promoting fairness for candidates.
- Employers must notify candidates about background checks and provide opportunities to explain any findings.
- Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act requires a clear consent process and specific steps if a report affects hiring decisions.
- Developing clear hiring policies and conducting regular training sessions ensure adherence to Illinois Ban-the-Box requirements.
- Effective hiring requires structured interviews, consideration of criminal record context, and documentation of decision-making to create a fair workplace.
Introduction
Imagine you’re a job seeker with a past, sitting in a waiting room, hoping for another shot. This is the reality for many in Illinois. The Ban-the-Box law steps in, reshaping how employers approach hiring.
Illinois’ Ban-the-Box law holds a crucial place in promoting fair hiring. It shifts the power balance, allowing applicants to showcase their skills before discussing their past. The law targets discrimination against those with criminal records, offering them a chance to be evaluated on merit first.
This guide dives into the Illinois Ban-the-Box compliance process. By reading on, you'll get practical insights into aligning your hiring practices with this law. The aim? To enable you to make informed decisions while remaining compliant.
What is the Illinois Ban-the-Box Law?
The Illinois Ban-the-Box law is a regulation that aims to promote fair hiring practices by restricting when employers can ask about a candidate's criminal background. Instead of this inquiry happening early in the application process, the law delays it to later stages. This delay helps ensure that candidates are considered based on their qualifications first, without the automatic disqualification that a criminal history might bring.
The legislation originated as part of a broader movement to reduce employment discrimination against individuals with criminal records. The term "Ban-the-Box" refers to the removal of the checkbox that asks about criminal history on job applications. Illinois implemented this law to help individuals with criminal backgrounds reintegrate into the workforce and reduce recidivism by offering more equitable job opportunities.
Since its enactment, the law has evolved to cover both public and private employers in Illinois, impacting how businesses conduct their hiring processes. Its primary objective is to create a fairer, more inclusive hiring environment where candidates are judged on their skills and experiences first.
If you're an employer, you might consider if the timing of your criminal background checks aligns with these regulations. By ensuring you're in compliance, you not only adhere to legal requirements but also contribute to a more just and equitable job market. Have you reviewed your current hiring procedures to ensure they meet these standards?
Key Requirements of Illinois Ban-the-Box Law
The Illinois Ban-the-Box law applies to private employers with 15 or more employees, as well as public employers. If your business meets this criterion, this law's requirements are crucial for your hiring processes.
Application Process Changes
Under the law, you can't ask about a candidate's criminal history on the job application. Instead, you must wait until after the initial interview. This shift aims to ensure candidates are assessed based on their qualifications first. For example, if you shortlist candidates based on experience, you can only check their criminal history after you meet them face-to-face.
Notification Obligations
Once you decide to conduct a criminal background check, you must notify the candidate clearly. If the check reveals a criminal record, you're required to inform the candidate of this finding. It's important to provide them with a chance to explain or dispute the information. Transparency at this stage is crucial to maintain a fair hiring environment.
Being up to date with these requirements helps protect you from legal missteps. Are your current hiring practices in line with these stipulations? If not, it might be time to review and adjust your procedures to avoid potential penalties for non-compliance.
Understanding the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) in Illinois
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a critical piece of legislation that affects how you conduct background checks in Illinois. At its core, the FCRA ensures transparency and fairness in the process of gathering and using consumer information. When you're handling criminal history checks as part of your hiring, the FCRA sets the ground rules.
Before diving into any background check, you must obtain the applicant's consent. The FCRA mandates a specific process: you need to provide a clear and conspicuous disclosure in writing, informing the applicant that a report may be used for employment purposes. This needs to be a standalone document, not buried in the application form. Only after you have the applicant's written authorization can you proceed.
The process doesn't stop there. If you decide that the results of a background check could impact your hiring decision, you must follow an adverse action process. This involves two main steps. First, before taking any adverse action, provide the candidate with a pre-adverse action notice. Include a copy of the background report and a summary of rights under the FCRA. Give the candidate a chance to review and dispute any inaccuracies.
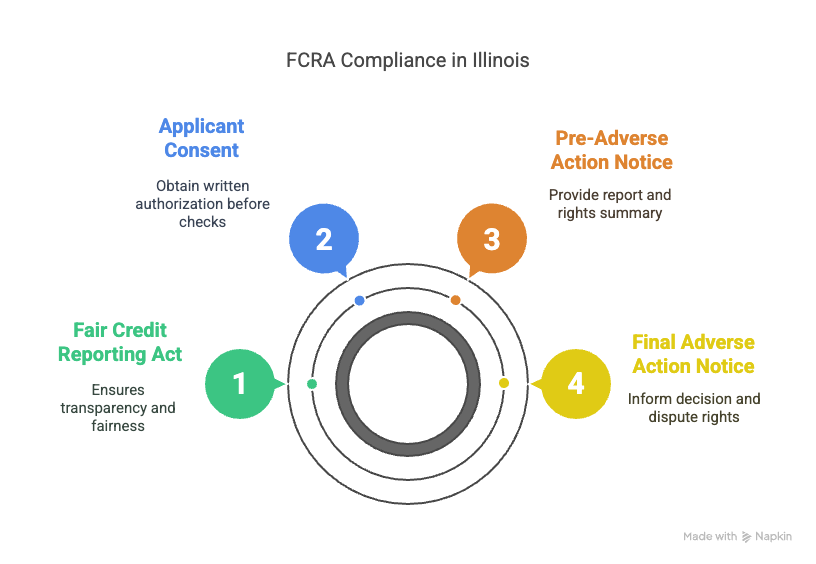
If you still choose to take adverse action after giving the candidate an opportunity to respond, you must provide a final adverse action notice. This notice informs the candidate of the decision, their right to receive another copy of the report, and their right to dispute its accuracy.
Staying compliant with FCRA in Illinois isn't just about ticking boxes. It's about maintaining a fair and transparent hiring process. Are your background check practices respecting the rights of applicants? Complying with the FCRA not only protects candidates but also safeguards your company from potential legal issues.
Balancing Compliance with Effective Hiring
Creating a fair hiring process while adhering to the Illinois Ban-the-Box law requires a strategic approach. Start by integrating the requirements of the Illinois Human Rights Act with other employment laws. Design your hiring protocols to assess candidates objectively and reduce the risk of bias. Consider structured interviews that focus on job-relevant skills and experiences. A consistent interview process mitigates the potential for discrimination.
When evaluating criminal records, context matters. Distinguish between offenses that impact job performance and those that do not. Consider factors like the nature of the crime, the time elapsed, and any evidence of rehabilitation. Align these evaluations with Illinois employment discrimination laws to ensure your decisions are both fair and legal.
It's essential to document your decision-making process. Maintaining records of the criteria used in each hiring decision can protect your organization if questioned about compliance with state laws. Foster an organizational culture that prioritizes both compliance and fairness in hiring, thereby building a diverse and inclusive workforce.
Practical Steps for Compliance
Establishing and maintaining compliance with the Illinois Ban-the-Box Law requires a methodical approach. Here’s how you can keep your hiring practices above board.
Policy Development: Start by crafting hiring policies that align with the Ban-the-Box Law. Your policies should clearly outline when criminal history information can be requested and how it will be considered. This includes making adjustments to your job application forms and interview processes. For instance, ensure your initial job applications exclude questions about criminal history. Instead, introduce these inquiries after the initial interview. Your internal policies should also specify how background check results will impact hiring decisions, keeping fairness and the law in mind.
Training and Education: Equip your HR team and managers with the right knowledge. Conduct regular training sessions that cover the Illinois Ban-the-Box Law, the Fair Credit Reporting Act, and associated state laws. This education is critical not just for compliance, but for fostering an understanding of fair hiring practices. Use real-life scenarios to illustrate points and encourage discussions on best practices.
Monitoring and Auditing: Compliance isn’t a one-and-done task. Regularly audit your hiring practices to ensure they meet legal standards. Set up a schedule for reviewing job applications and interviewing procedures. Use checklists to verify that your processes are consistently followed and that exceptions are documented with valid reasons. Catching issues early allows you to address them before they lead to compliance breaches.
Building a compliant hiring framework takes effort, but these steps can make the process manageable. By prioritizing policy clarity, thorough training, and consistent audits, you can not only abide by Illinois laws but also build a fairer hiring environment.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Compliance with Illinois' Ban-the-Box law can be tricky if you're not fully aware of its implications. Many employers stumble by failing to shift the timing of background checks to the post-interview stage. This simple mistake can lead to non-compliance and accusations of unfair hiring practices. Implementing a checklist for your hiring team can address this, ensuring that criminal history inquiries only occur after initial interviews.
Another pitfall is not properly notifying candidates about the background check procedures. It’s crucial to have a clear communication strategy. Ensure your application and onboarding materials are updated and transparent about the process.
What if you find a criminal record that raises concerns? Avoid making impulsive decisions. Establish a consistent review process for such instances. This might involve weighing the relevance of the offense to the job role. Consider consulting with legal professionals to guide these evaluations, ensuring they align with both the Ban-the-Box law and broader anti-discrimination statutes.
Complacency in monitoring and auditing your hiring practices can also lead to problems. Regularly reviewing your processes can catch issues before they become legal problems. Consider scheduling semi-annual audits to ensure your team is following all necessary steps and procedures.
Finally, if non-compliance is an issue, corrective action is vital. Conduct training workshops for HR staff and hiring managers to educate them on the legal requirements and best practices related to fair hiring. In situations that seem daunting, don't hesitate to seek legal counsel. They can provide guidance tailored to the complexities of your specific hiring landscape.
Resources for Employers
Understanding employment laws can be complex, but leveraging available resources can streamline compliance. Start by exploring internal resources. Your company's existing materials, like training documents and policy manuals, might hold valuable insights into aligning with Illinois Ban-the-Box regulations. For instance, reference relevant content such as the GCheck Blog. These posts can offer updates or best practices related to fair hiring.
The Professional Background Screening Association provides a wealth of information, including industry standards and legislative updates. Joining associations like these allows you to access a network of professionals who share insights and experiences in navigating employment background checks.
To aid practical implementation, consider using templates and checklists. They can help ensure no steps are missed in the compliance process. Compliance checklists, for example, can guide you through necessary actions like adjusting interview protocols or modifying application forms in line with Ban-the-Box requirements.
Taking the time to educate yourself and your team can significantly impact how smoothly your company adheres to legal obligations. Exploring these resources is a proactive step towards effective and compliant hiring practices.
Conclusion
Compliance with the Illinois Ban-the-Box law is not just about meeting legal obligations; it's about crafting an equitable hiring strategy. Reflect on the adjustments you can make to align with these legal requirements and promote fair hiring. Every step, from revising application processes to educating staff, strengthens your commitment to fairness and compliance.
Integrating the law into your daily operations requires vigilance. Regularly refine your policies, maintain open communication about your practices, and provide ongoing training. These actions build a foundation of fairness in your hiring procedures.
As you implement these changes, focus on cultivating an inclusive workplace. Each equitable hiring decision enhances your company culture, benefiting both your workforce and community. Keep fairness at the forefront, ensuring your hiring practices reflect both compliance and integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Ban-the-Box law in Illinois?
The Ban-the-Box law in Illinois limits when employers can ask about an applicant's criminal history. Employers cannot inquire about this until after the applicant has been deemed qualified for the job or selected for an interview.
Can employers ask about criminal history in Illinois?
Yes, but only at specific stages in the hiring process. Employers can ask about criminal history after an applicant is found qualified for the job or after an interview.
How does Ban-the-Box affect Illinois job applications?
It removes the checkbox asking about criminal history from job applications. This ensures that an applicant’s qualifications are considered first before any criminal history.
What are penalties for violating Ban-the-Box in Illinois?
Employers violating this law may face civil penalties and fines. The Illinois Department of Human Rights oversees enforcement and can impose penalties if violations occur.
Does Illinois Ban-the-Box apply to all employers?
No, it applies to private employers with 15 or more employees, employment agencies, and any person with employees in Illinois.
How to dispute a background check in Illinois?
If you find errors in your background check, contact the company that conducted it. Provide documentation to prove inaccuracies. You can also file a complaint with the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau if needed.
Are misdemeanors included in Illinois background checks?
Yes, background checks in Illinois can include misdemeanors unless specific laws or regulations restrict their disclosure.
How far back do Illinois background checks go?
Generally, background checks cover up to seven years of criminal history. Some exceptions exist, such as jobs in education or law enforcement, which may require more extensive checks.
Do Illinois schools follow Ban-the-Box?
No, schools in Illinois are exempt. They can inquire about criminal history earlier in the hiring process due to the sensitive nature of working with children.
Can a felony prevent employment in Illinois?
It can, depending on the job and the nature of the felony. Employers must consider how the offense relates to the responsibilities of the position.
Does the Ban-the-Box law apply to federal jobs in Illinois?
No, the Ban-the-Box law is state-level legislation and does not automatically apply to federal jobs, which follow federal guidelines.
Is it legal to conduct a background check before an interview in Illinois?
No, employers should only conduct background checks after determining an applicant is qualified for the job or after an interview has taken place.
Can Ban-the-Box laws affect my chances of being hired?
Yes, they allow you to be assessed based on your qualifications first, giving you a fair chance before any criminal history is considered.
Can I be denied employment based solely on a background check in Illinois?
If an employer decides not to hire you based on your background check, they must provide a copy and allow you to dispute any inaccuracies.
Definitions
Ban-the-Box Law
The Ban-the-Box Law in Illinois restricts when employers can ask about a candidate’s criminal history during the hiring process. Employers must wait until after the initial interview before making criminal background inquiries. This allows applicants to first be evaluated based on their skills and experience.
Criminal Background Check
A criminal background check is the process of reviewing an individual's criminal history records to inform employment decisions. In Illinois, employers must notify applicants before conducting a background check and give them an opportunity to respond to any findings before taking adverse action.
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
The Fair Credit Reporting Act is a federal law that regulates how employers obtain and use background reports. Under the FCRA, employers must get written consent from job applicants before running a background check and follow a two-step notice process if the report leads to a negative employment decision.
Adverse Action
Adverse action happens when an employer makes a negative decision against a candidate based on information from a background check. This includes denying employment or rescinding a job offer. Employers must send both a pre-adverse action notice and a final adverse action notice under the FCRA.
Illinois Human Rights Act
The Illinois Human Rights Act prohibits discrimination on several grounds, including criminal history in certain cases. Under the Act, employers must evaluate the relevance of a criminal record to the job role rather than automatically excluding candidates based on their past.Section-by-Section Integration of Authoritative Studies and Surveys
References
- Prison Policy Initiative – "Out of Prison & Out of Work: Unemployment among formerly incarcerated people" https://www.prisonpolicy.org/reports/outofwork.html
- Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) – "New Illinois Law Protects Workers with Criminal Records" https://www.shrm.org/topics-tools/news/talent-acquisition/new-illinois-law-protects-workers-criminal-records
- U.S. EEOC – "Enforcement Guidance on the Consideration of Arrest and Conviction Records in Employment Decisions" https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/enforcement-guidance-consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment-decisions

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





