Navigating the complex landscape of employment screening is crucial for any business, especially in Georgia, where specific legal requirements demand attention. Whether you're a small business owner or manage a large HR department, understanding Georgia background check laws is essential for maintaining compliance and protecting your business from potential legal issues. This guide delves into the intricacies of these laws, providing you with the necessary knowledge to conduct background checks effectively while aligning with both state and federal regulations.
Key Takeaways
- Background checks in Georgia are essential for mitigating hiring risks, influenced by both state laws and federal regulations, particularly the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
- Georgia's unique legal framework requires businesses to navigate specific state laws regarding criminal records and credit checks without a statewide Ban the Box law for private employers.
- Compliance with the FCRA is crucial in Georgia, as it mandates explicit candidate consent for background checks, aligning with state regulations to maintain transparency and fairness.
- Businesses must develop clear policies, select compliant screening services, and ensure precise decision-making processes to adhere to both Georgia's and federal laws.
- Non-compliance with background check laws in Georgia can lead to legal repercussions, financial penalties, and reputational damage, emphasizing the need for meticulous adherence to state and federal guidelines.
Introduction
Background checks have become a standard part of the hiring landscape, serving as a vital tool to vet potential employees and mitigate risks. In Georgia, these checks play a crucial role in the employment process due to specific state laws that add layers of complexity to federal regulations. Understanding the nuances of Georgia’s background check requirements can help businesses avoid legal pitfalls and maintain a robust hiring process.
This guide aims to equip businesses with the essential knowledge needed to navigate Georgia's background check laws successfully. By breaking down the legal landscape and highlighting key compliance areas, we provide a valuable resource to ensure your company's hiring practices align with both state and federal standards. Whether you're running a small local shop or managing the HR operations of a large corporation, this guide will arm you with the insights necessary for conducting thorough, compliant background checks in Georgia.
Understanding Georgia Background Check Laws
Legal Framework
Georgia's background check laws operate within a specific legal framework that integrates both state mandates and federal guidelines. At the state level, employers are required to navigate laws that govern the extent and method of background investigations, particularly concerning criminal records and credit checks. The laws ensure that businesses do not overstep privacy boundaries while maintaining necessary scrutiny for employment decisions.
Federal oversight also plays a significant role through the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), which provides a baseline for how background checks, including credit reports, should be handled nationwide. The FCRA aims to protect the privacy of individuals and ensure the accuracy of information used in employment decisions. The interaction of FCRA with Georgia's laws creates a dual compliance challenge for employers, requiring them to adhere to both sets of regulations. For more detailed insights on FCRA compliance, consider reviewing resources such as FCRA Compliance.
Key Differences in Georgia Laws
Georgia distinguishes itself with specific legal provisions that aren't necessarily mirrored in other states. Unlike some states, Georgia does not have a statewide Ban the Box law for private employers, which means there's more flexibility in asking about criminal history on job applications. However, understanding local ordinances that may implement similar measures in specific municipalities remains critical.
When it comes to financial checks and credit reports, Georgia law requires explicit consent from candidates, and this practice dovetails with FCRA's national standards. Employers must ensure that the purpose of collecting this information is clearly related to the job in question. This focus on clear communication and relevancy helps prevent potential overreach and maintains candidate trust.
Government and Legal Resources
For businesses operating in Georgia, staying informed requires access to reliable resources. The EEOC's guide on background checks offers essential guidelines on preventing discrimination and ensuring the lawful use of background information. Additionally, the FTC guidelines can provide further clarity on the rights of candidates and the responsibilities of employers during the screening process. Leveraging these resources can help businesses remain compliant and uphold fair hiring practices in Georgia.
I've had the opportunity to work in human resources for multinational and global companies, and I have seen crystal clear the need to keep up with national and international laws, particularly those about background checks. In Georgia for example, every HR professional and business owner must pay careful attention to the complexity of compliance; there is no space for oversight. Navigating the state's specific regulations, such as credit check limitations and the nuances of criminal record screening, can be challenging, but doing so is necessary to prevent future legal problems. Undoubtedly, protecting our organizations and ensuring that hiring practices are transparent and equitable enables us to create teams we can trust.
The Role of FCRA in Georgia Employment Screening
What is FCRA?
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is federal legislation that governs how consumer information is collected and used, particularly in areas like employment screening. Essentially, it sets the bar for transparency and fairness when employers request background checks from third-party reporting agencies. In practice, FCRA ensures that job applicants are treated fairly by requiring that they give explicit consent before such checks are conducted and that they are notified when adverse action is taken based on information derived from these reports.
FCRA Compliance in Georgia
In Georgia, the interplay between FCRA and state-specific background check laws necessitates a careful approach to compliance. While FCRA provides the overarching framework, Georgia doesn't have a state law that significantly deviates from FCRA's requirements, making federal compliance pivotal. To align with FCRA, businesses need to ensure that they follow a clear protocol: obtain written consent from applicants, utilize reliable consumer reporting agencies, and deliver pre-adverse action notices if hiring decisions might be negatively influenced by the results.
Employers should stay updated with FCRA regulations and leverage internal resources like Ensuring Compliance in Employment Background Checks for best practices. By maintaining rigorous adherence to FCRA guidelines while being aware of Georgia’s specific context, businesses can mitigate legal risks, facilitate fair hiring practices, and build trust with prospective employees.
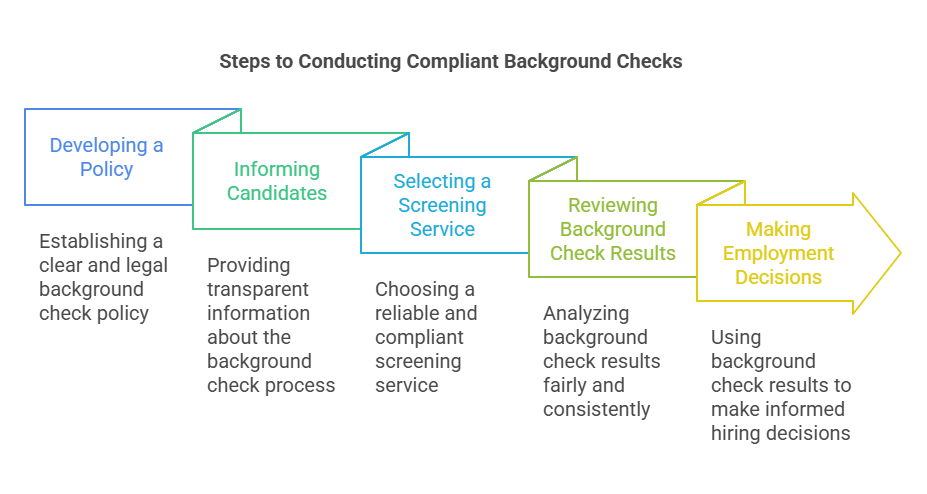
Steps to Conducting Compliant Background Checks
Step 1: Developing a Policy
Creating a solid background check policy is the cornerstone of compliant employment screening. Tailored to Georgia’s legal landscape, your policy should address the types of checks you’ll perform, the positions they apply to, and the rationale behind them. It’s vital to document procedures clearly and include steps for updating the policy as laws evolve. Lean towards simplicity and clarity—over-complexity can lead to confusion and compliance hiccups. Engage legal counsel familiar with Georgia employment law to review your policy.
Step 2: Informing Candidates
Transparency builds trust, and nowhere is this more important than in background checks. Inform candidates up front about the process. Written disclosure is more than courteous—it's legally required before conducting a check. This includes clarifying the checks’ nature and scope. Consent must be unequivocally obtained; a wavering nod is not enough. Use straightforward forms and avoid burying consent requests in application paperwork.
Step 3: Selecting a Screening Service
Choosing the right screening service can set the tone for the accuracy and compliance of your checks. Look for providers well-versed in both state and federal regulations, drawing on resources like SHRM to compare your options. Evaluate their track record in delivering precise, timely reports. Additionally, ensure they provide comprehensive support in the case of discrepancies or disputes, and hold themselves accountable for following the FCRA and Georgia-specific guidelines.
Step 4: Reviewing Background Check Results
Once you’ve got the results, your next move requires a delicate balance of thoroughness and fairness. Look beyond the data—context can narrate different stories. Establish review procedures that align with compliance, including a consistent method for analyzing varying checks. Use the results to assess qualifications pertinent to the role, not to delve into superfluous details. Training your team in this process is essential; their decisions can carry significant weight.
Step 5: Making Employment Decisions
Incorporating background check results into hiring decisions is where legal lines often blur. Align each decision with the job’s requirements, documenting the process meticulously. Georgia law, alongside federal statutes like the FCRA, sets clear protocols on how findings can influence hiring. If adverse actions are necessary, provide candidates with a copy of the report and explain their rights. Not adhering to these norms can lead to costly litigations, so precision and care are crucial.
Navigating these steps with diligence and transparency not only fortifies compliance but also enhances your business’s reputation and candidate relations.
Useful Georgia Background Check Resources
Having the appropriate resources is crucial in Georgia to guarantee compliance and make wise choices when negotiating the background check system. Thankfully, there are a number of important governmental offices and agencies that provide useful information and tools. These materials can make it easier for employers to adhere to Georgia's regulatory framework, especially when combined with publicly available data and legislative changes. For further information, please see the table below.
| Website Name | URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Labor (Georgia) | https://dol.georgia.gov | Offers resources on labor laws, employment regulations, and licensing impacting background checks. |
| Department of Public Safety (Georgia) | https://dps.georgia.gov | Provides access to criminal history records, fingerprinting services, and background check information. |
| Judicial Branch (Georgia) | https://www.georgiacourts.gov | Access to court records, legal information, and public records relevant to background checks. |
| Department of Corrections (Georgia) | https://www.dcor.state.ga.us | Information on criminal records, parolees, and public safety concerns. |
| Office of the Attorney General (Georgia) | https://law.georgia.gov | Offers guidance on legal matters, including consumer protection and employment law. |
| Department of Economic Development (Georgia) | https://www.georgia.org | Provides resources for business development and compliance with state regulations. |
| Georgia Technology Authority | https://gta.georgia.gov | Information on state IT policies, data privacy, and security for handling sensitive background check data. |
| Georgia State Archives | https://georgiaarchives.org | Access to public records, historical documents, and archives useful for in-depth background research. |
| Georgia General Assembly | https://www.legis.ga.gov | Stay updated on laws and regulations passed by the state legislature that may affect background checks. |
| Department of Public Health (Georgia) | https://dph.georgia.gov | Information on health regulations, requirements for employee screenings, and background checks in healthcare settings. |
Common Challenges and Solutions
Conducting background checks in Georgia comes with its own set of hurdles. For businesses aiming to stay compliant, knowing these challenges and how to handle them is essential.
Handling Incomplete or Inaccurate Information:
Occasionally, background checks yield incomplete or incorrect data. To manage this, first verify the information with your screening service. It's crucial to provide candidates the opportunity to clarify or correct inaccuracies, as mandated by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). This step not only ensures fairness but also helps avoid potential disputes.
Navigating Georgia's Ban the Box Law:
Georgia's Ban the Box law, applicable to public employers, restricts when employers can ask about criminal records during the hiring process. Even if your business is private, adopting similar practices can reduce bias and widen your pool of candidates. Implementing a compliant hiring policy involves evaluating candidates on their qualifications before considering their criminal history.
Dealing with Negative Findings:
When background checks reveal unfavorable information, proceed judiciously. Balance the nature and relevance of such findings against the job's requirements. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) encourages businesses to consider the severity, time elapsed, and relevance of any criminal history. Consulting a legal advisor or HR compliance expert can ensure that your employment decisions are both fair and lawful. Emphasizing transparency with candidates during this phase not only reinforces your commitment to equitable hiring practices but also shields your business from potential legal fallout.
By tackling these common challenges with consideration and adherence to legal guidelines, your business can maintain a compliant and effective background check process in Georgia.
Legal Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with Georgia's background check laws can put your business at risk, exposing you to significant legal and financial penalties. Failing to adhere to these regulations could result in hefty fines and legal fees—a costly consequence for any company, but especially for small businesses operating on tight budgets. Beyond financial repercussions, businesses might also face lawsuits from affected individuals, which can harm reputations and erode trust among current and prospective employees.
The law demands meticulous adherence to state and federal regulations, such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). If legal actions lead to restrictions or sanctions, non-compliance might also impair one's ability to operate effectively within one's industry.
Real-world cases highlight these risks clearly. For instance, a Georgia-based retail company recently settled a costly lawsuit after plaintiffs accused it of bypassing critical steps in candidate consent and data verification processes—key elements of FCRA compliance. Another notable incident involved a staffing agency that suffered reputational damage after it was revealed they were using outdated criminal history data, leading to a prolonged legal battle and settlements.
These examples underscore the importance of staying informed and proactive in following background check laws. Neglecting this crucial aspect of hiring can lead to serious, often avoidable, consequences that are detrimental to business operations and success.
Conclusion
Conducting background checks in Georgia requires a keen understanding of state and federal laws. By aligning your hiring practices with these guidelines, you protect your business from legal pitfalls while ensuring fairness in the recruitment process. Remember, knowledge is your first line of defense. Staying updated on compliance laws shields your company and reinforces your commitment to transparency and equity. For ongoing education, tap into resources like PBSA and SHRM, which offer invaluable insights into maintaining compliant and ethical hiring frameworks. Your due diligence today fortifies your operations for the future, fostering a responsible and informed workplace.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






