When securing a job in the federal sector, one crucial step often stands between you and your dream role: the federal background check. Whether you're eyeing a position within the Department of Defense, Homeland Security, or any other federal agency, this screening process will play a pivotal role. Understanding the nuances of these checks, how they differ from private sector screenings, and how to navigate potential challenges will put you in a great position to succeed.
Key Takeaways
- Federal background checks are significantly more rigorous than private sector checks and essential for positions affecting national security or public trust.
- These checks comprehensively verify personal, financial, and professional history to ensure integrity and suitability for federal employment.
- Different security clearance levels—Confidential, Secret, and Top Secret—determine the depth of the investigation required.
- The background check process includes pre-employment screening, personal identification verification, criminal and credit history reviews, and additional checks for higher clearance levels.
- Be thoroughly prepared, transparent, and proactive to navigate common challenges and secure favorable outcomes in the federal background check process.
Introduction
Landing a federal job goes beyond nailing interviews and showing a killer resume. Here's a stat to put things into perspective: nearly 96% of federal positions require some background check. These checks are more rigorous than in the private sector, ensuring that the candidates are skilled but also trustworthy and reliable.
So, what exactly does a federal background check entail, and why is it necessary? A federal background check is a deep dive into your personal, financial, and professional history. It’s a means to validate that you are a person of integrity and suitable for positions that could affect national security or public trust. The stakes are high, and so is the scrutiny.
This article will break down everything you need about federal background checks. You'll get a step-by-step guide through the process, learn how they differ from private sector checks, and discover valuable tips to navigate everyday challenges. By the end, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle this crucial phase of your federal job application journey.
The background check is one of the most important—and most often disregarded—steps in the federal employment application process. It is not merely a paperwork obstacle; it is a test of responsibility and trust. Most striking is how the process captures the values of transparency, responsibility, and preparation—values representative of good candidates and excellent employees. While the process is intimidating, approaching it honestly and openly can make a thorny step a chance to show your integrity and commitment to public service.
What is a Federal Background Check?
A federal background check is a comprehensive review and verification process conducted to assess applicants' suitability, trustworthiness, and reliability for federal employment. This check serves several critical purposes, primarily ensuring national security, protecting sensitive information, and maintaining public trust in federal institutions.
Primary Objectives
At its core, a federal background check aims to confirm that candidates are who they claim to be and verify their personal history, including criminal records, financial stability, employment history, and educational credentials. This assessment helps determine if an individual poses any risks or vulnerabilities that could impact their ability to perform their duties effectively and securely.
Key Agencies Involved
Several agencies play significant roles in conducting and overseeing federal background checks. The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) is typically responsible for most civilian background investigations. The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) handles the criminal background portion, thoroughly scrutinizing any legal issues in a candidate's past. Specific departments—such as the Department of Defense for military personnel and sensitive roles within national security—also conduct their specialized checks. Together, these agencies work to maintain high standards of integrity and security within the federal workforce.
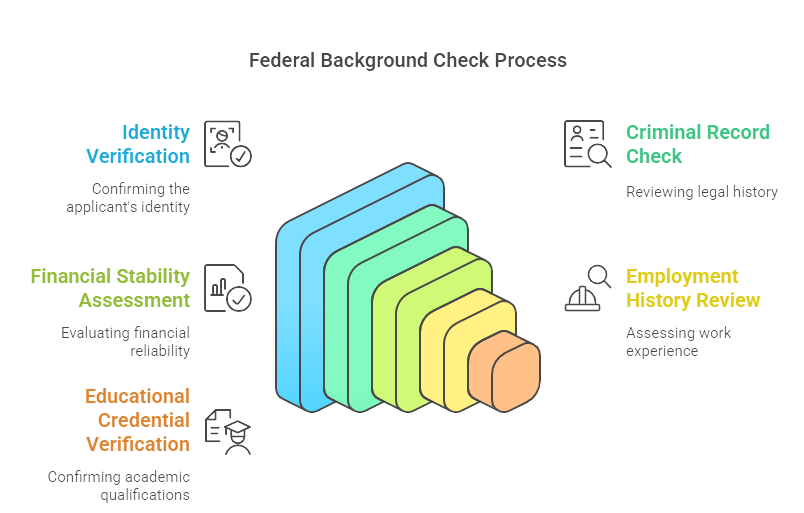
Differences Between Federal and Private Sector Background Checks
The background check undergoes a significant upgrade from the private sector to a federal job. Federal background checks are more extensive and built entirely to a different standard, reflecting the high stakes of government work. Here's how they differ.
Scope and Detail
Federal background checks dig much more profound than their private sector counterparts. While a private company might verify your employment history and criminal record and perhaps run a credit check, federal checks go further. They delve into a broader range of personal history, including your financial standing, criminal background, personal associations, and foreign contacts. They're thorough because the stakes are higher; federal positions often involve access to sensitive information that impacts national security.
Security Levels
Another key difference is the impact of security clearance levels, which do not exist in private sector checks. Federal checks vary based on the clearance required for the position: Confidential, Secret, or Top Secret.
- Confidential: The lowest level involves checks for basic criminal, financial, and employment records.
- Secret: A mid-level clearance involving more detailed background checks, including interviews and possibly a polygraph test.
- Top Secret: The highest level, requiring a deep dive into every detail of your life. This could include investigative fieldwork and interviews with neighbors, colleagues, and other personal contacts to build a comprehensive profile of your character and reliability.
For more detailed information about these security clearances, you might find USAJobs a valuable resource.
Legal Framework
Federal background checks are also governed by a unique set of regulatory bodies and legal frameworks. Executive Orders, federal statutes, and guidelines from the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) and the Federal Investigative Services play a pivotal role. This legal scaffold ensures stringent standards are applied, protecting national security interests while respecting individual rights.
Understanding these subtleties can help you understand what to expect and how to navigate the process efficiently. It’s about knowing the stakes and preparing for an intense but crucial screening.
Step-by-Step Guide to Federal Background Checks
1. Pre-Employment Screening
Pre-employment screening is your first major hurdle in the federal background check journey. While it might seem straightforward, overlooking the small stuff can trip you up.
Initial Application: It all starts here. Double-check that every piece of information on your application is accurate and complete. Typos or missing details can lead to delays or even disqualification. The federal system is designed to cross-check every bit of data, so accuracy isn't just recommended—it's essential.
Resume and Documentation: Prepare a detailed resume including your work history, education, and relevant certifications. Keep a digital file of all your important documents, such as degrees, professional licenses, and letters of recommendation. This isn't just about having them handy; it's about being ready to verify every claim you make.
Getting this stage right sets the tone for the rest of the process. Remember, the federal sector sees thousands of applications, and the details matter. Being thorough now can prevent headaches later.
2. Standard Background Investigation
The federal background check starts to get real when you move past the initial application stage. Here's what you're in for:
Personal Identification Verification
First things first, they’ll confirm you are who you say you are. Think of it as a high-stakes version of showing your ID at a bar. They’ll cross-check your personal information like your Social Security number, date of birth, and any aliases to ensure there's no funny business.
Criminal History
Next is a look into your life on the right—or wrong—side of the law. They'll dig into local, state, and national criminal databases to see if you've got a record. This isn't just about convictions; pending charges and even certain arrests can come under the spotlight. You can find more about what they look for here.
Credit History
Your financial past isn’t just for creditors anymore. Federal jobs often involve public trust, so they like to see how you've handled money. They’ll check for issues like bankruptcy, excessive debt, or a history of late payments. If you’ve struggled financially, you might be susceptible to bribery or fraud.
Employment Verification
Then there's the employment verification. They'll contact past employers to confirm your job titles, responsibilities, and the dates you worked there. But they’ll also be looking at your performance and reliability—were you fired for cause and left on good terms? These details paint a fuller picture of your work ethic.
Educational Verification
Finally, they’ll ensure you graduate from the institutions listed on your resume. This isn’t just a diploma check; they might also examine your academic performance and disciplinary actions.
Understanding these key components will help you better prepare and eliminate surprises. Honesty and accuracy are your best allies in this part of the process.
3. Additional Checks for Higher Clearance Levels
Reaching for a higher clearance level brings a new layer of scrutiny. It’s about your past actions, trustworthiness, and reliability for sensitive roles.
Interviews and Polygraphs: Expect to sit down for in-depth interviews and polygraphs. These aren’t casual chats. You will be asked about your background, associations, and loyalty to the U.S. Polygraphs will measure your physiological responses to specific questions, aiming to root out any potential deception. This might feel invasive for many, but it’s a standard process.
Investigative Fieldwork: This is where it gets even more personal. Background investigators conduct field interviews. They’ll talk to your neighbors, colleagues, and other personal contacts. Their goal? To confirm your character and reliability. Think of it as a deeper dive into your personal and professional life.
Drug Testing: High-security posts often require drug testing. This is non-negotiable. You’ll be tested for illegal substances, and these tests are typically conducted under strict protocols to ensure accuracy.
Navigating these steps can seem daunting, but knowing what to expect can ease some stress and help you prepare effectively.
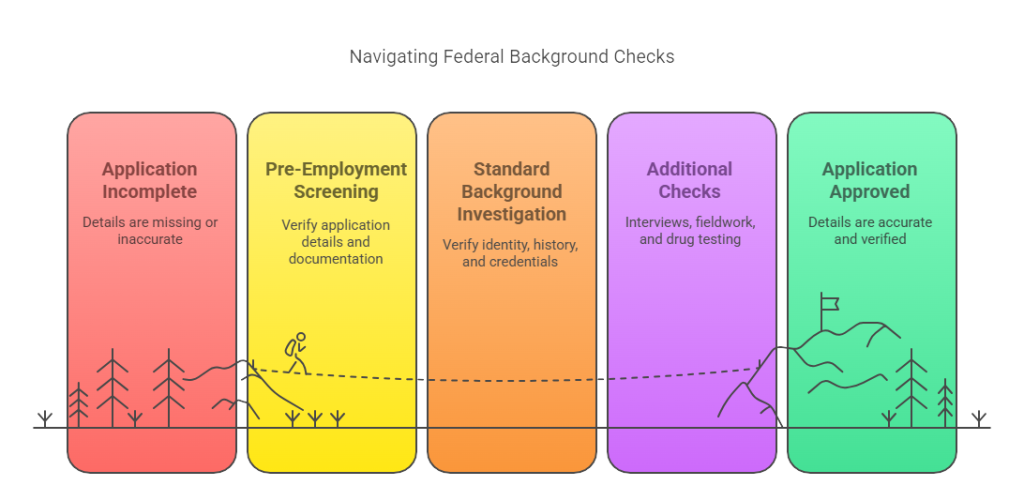
Review and Final Decision
Processing Time
Waiting for federal background check results can test anyone's patience. Depending on the level of clearance you're seeking and the complexity of your background, the process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months. Expect a quicker turnaround for more straightforward, lower-clearance positions, often within a month or two. Higher-level clearances involving more exhaustive investigations can stretch out the timeframe significantly, sometimes taking six months or more. It's essential to be mindful of this timeline and plan accordingly, especially if transitioning from another job.
Adjudication
Once all the data is gathered, your background check enters the adjudication phase. Here, trained personnel from the relevant federal agency will review the compiled information to determine your suitability. Adjudicators will weigh any derogatory information against federal guidelines and your overall profile. They’re assessing whether any findings could compromise national security or the integrity of the agency you're applying to. Key factors under review might include criminal history, financial responsibility, past employment behavior, and personal conduct.
Consistency and honesty in your application and interview responses are critical during adjudication. Any discrepancies can lead to delays or even denial of your clearance. Remember, the goal is to ensure that you are trustworthy and reliable.
As this phase can be nerve-wracking, patience and transparency are your best allies. If additional information is requested, provide it promptly to avoid further delays. Once the review is complete, you will be notified of the decision, which can be a precise pass, a conditional pass with some follow-up checks, or a denial, which you can appeal.
Common Challenges in Federal Background Checks and How to Address Them
Navigating the federal background check process can be a minefield of potential issues, but forewarned is forearmed. Here are some common hiccups candidates face and how to handle them.
Inconsistencies in Records
One misreported date or discrepancy in your resume, and you might hit a snag. Triple-check all the information you submit. Cross-reference your application with your resume, employment records, and educational certificates. Keep a meticulous record of your jobs, addresses, and contacts. Consistency is key.
Financial Issues
Credit history is more than just a number in the federal hiring process; it reflects your reliability and trustworthiness. If your credit report has blemishes, take proactive steps. Reach out to a credit counselor if needed and address unpaid debts. In your application, be upfront about any past financial troubles and detail the measures you've taken to resolve them.
Past Legal Issues
Legal hiccups can be daunting but aren’t necessarily a deal-breaker. Transparency is your best policy. If you have a criminal record or past legal problems, disclose them. Attach a detailed explanation outlining the context and your actions to turn things around. Honesty here can mitigate potential red flags.
Preparing for Interviews and Polygraphs
Higher security roles often come with interviews and polygraphs. It's natural to feel nervous, but preparation can help. For interviews, review potential questions and practice clear, concise answers. For polygraphs, stay calm and truthful. They measure physiological responses, not just answers so that honesty will be your best ally.
In sum, thoroughness, honesty, and proactive problem-solving will help you navigate common challenges in federal background checks.

Legal Rights and Appeals Process
Official Documentation
Are you getting hit with an adverse decision on your federal employment application? Don’t worry; you have the right to request official documentation. This could include everything from the specific reasons for your disqualification to detailed reports on the findings from your background check. Knowing precisely what’s in these documents can give you an edge in understanding where things may have gone sideways.
Right to Appeal
If you think the decision was unjust, exercising your right to appeal is smart. Generally, you'll need to submit a formal appeal within a specific timeframe—usually 30 days from the decision notice. The appeals process often involves reviewing the original findings, submitting additional evidence, and sometimes appearing before an administrative judge. Please don’t leave this to the last minute; getting a head start and gathering all necessary documentation early is better.
Privacy Protections
Are you worried about your info being out there for the world? Stringent privacy protections bind federal background checks. Only authorized personnel directly involved in the hiring process can access your data. This means your private details—financial history, criminal records, whatever it may be—are safeguarded against unnecessary disclosure. These checks comply with the Privacy Act of 1974, ensuring your information remains secure and confidential.
Understanding these legal rights can help demystify the process and offer a sense of control in what can otherwise be a nerve-wracking experience. Whether disputing a decision or knowing your data is well-protected, these legal frameworks are designed to give you a fair shot at securing that coveted federal job.
FAQs About Federal Background Checks for Employment
Federal background checks can seem daunting, especially if you're a new candidate. To help dispel what's involved, below are some of the most common questions candidates ask when applying for federal jobs. Whether it's your first check or you need a refresher, this useful guide lays out the basics.
What is a federal background check for employment?
A federal background check is an in-depth review of a candidate’s history, including criminal records, federal employment, and sometimes credit history, eligibility for federal jobs or jobs with government contractors.
How long does a federal background check take?
The duration of a federal background check can vary but typically takes anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the level of clearance required and the complexity of the candidate’s history.
What is included in a federal background check?
A federal background check may include reviewing criminal records, employment history, education verification, credit reports, and previous federal employment or military service.
Who needs a federal background check?
Federal background checks are required for individuals seeking employment with federal agencies, government contractors, or positions that need access to sensitive government information.
Can I fail a federal background check?
Yes, failing a federal background check can occur if there are issues such as undisclosed criminal records, falsified information, or adverse findings in your credit history or employment verification.
How can I prepare for a federal background check?
To prepare for a federal background check, ensure all your personal, employment, and educational information is accurate and up-to-date. Be ready to provide necessary documentation and be transparent about any past issues that might arise.
Conclusion
To wrap up, federal background checks are a pivotal part of the hiring process, designed to ensure candidates are suitable for the sensitive and essential roles they aspire to attain. Understanding and navigating these checks with diligence and transparency is critical. Yes, the process can be exhaustive and sometimes stressful, but remember that it's a pathway to rewarding opportunities in federal employment. Stay honest, be meticulous with your records, and maintain patience. With these approaches, you'll enhance your chances of stepping into a fulfilling career within the federal sector. Good luck!

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






