National background checks are essential for HR managers to ensure a safe and compliant workplace. They provide a detailed overview of an individual's history, including criminal records, employment history, education credentials, etc. This article aims to guide HR managers through the importance, process, and best practices of conducting national background checks.
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive Candidate Evaluation: National background checks provide a thorough review of an individual's history, including criminal records, employment verification, education credentials, and professional licenses, offering a holistic view of the candidate.
- Distinction Between Federal and National Checks: While federal background checks focus on information from federal agencies like the FBI, national background checks encompass federal, state, and local records, ensuring a more extensive assessment.
- Significance of Multi-State Searches: Conducting multi-state background checks uncovers potential issues that single-state checks might miss, providing a complete picture of a candidate's background and enhancing workplace security.
- Advantages of Professional Screening Services: Utilizing reputable background screening services ensures access to comprehensive databases, legal compliance, and efficient processes, reducing risks associated with DIY approaches.
- Legal Compliance and Best Practices: Adhering to laws like the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is crucial during background checks. Consistency, respect for privacy, and contextual evaluation of findings are essential best practices for HR managers.
Understanding National Background Checks
A national background check involves reviewing an individual's criminal, financial, and personal history across all 50 states and territories. For HR managers, the most relevant aspects include:
- Criminal History: Checking for any national-level criminal convictions to identify potential risks.
- Sex Offender Registry: Ensuring the candidate is not listed on the national sex offender registry.
- Employment Verification: Confirming the candidate's employment history to verify their work experience.
- Education Verification: Ensuring the candidate's educational credentials are valid and accurate.
- Professional Licenses: Verifying any required professional licenses or certifications.
- Credit History: Assessing the candidate's financial responsibility, if relevant to the role.
- Drug Testing: Conducting a national drug test to ensure a drug-free workplace.
- Driving Record: Checking the candidate's driving history for roles involving driving.
- Global Watchlist Checks: Screening against global watchlists to identify potential security risks.
National Background Check Concepts
Federal Background Checks vs National Background Checks
Federal background checks focus on information collected by federal agencies, such as the FBI, and are often used for positions requiring security clearance. On the other hand, national background checks encompass a broader scope, including federal, state, and local records, to provide a comprehensive view of an individual's history. Understanding the differences between these two checks is crucial for employers to ensure they conduct the appropriate screening level for their hiring needs.
The Importance of Multi-State Background Checks
Multi-state background checks are crucial for employers who want to make informed hiring decisions by uncovering potential issues that might not be visible in a single-state check. By covering multiple states, these checks help to create a more complete picture of a candidate's background, which is essential for maintaining workplace safety and security.

Choosing the Right Background Screening Services
Regarding national background checks, opting for a professional background screening service offers several advantages over a do-it-yourself (DIY) approach. A reputable service provides access to a wider range of databases, ensuring a more thorough and accurate check. They also have expertise in legal compliance, reducing the risk of violating privacy laws. Additionally, professional services can streamline the process, saving time and resources for employers. Overall, using a background check company enhances the reliability and efficiency of national background screenings.
EXPERT INSIGHT: The foundation of every healthy workplace is trust and national background checks help in building a safe and inclusive work ecosystem where everyone can thrive. As HR professionals, our role is to balance the importance of maintaining due diligence and empathy. We must understand that every file is not just paperwork but behind that, someone is seeking an opportunity to contribute, grow, and belong. What I have learned from working in this field? At the heart of HR is not just compliance, it’s compassion. - Charm Paz, CHRP
Delving into Criminal Background Screening
Criminal background screening is a crucial element of national background checks. It involves searching national databases to uncover criminal records, including convictions, arrests, and outstanding warrants. This comprehensive approach ensures that employers understand a candidate's criminal history entirely, essential for making informed hiring decisions and maintaining a safe work environment. By delving into criminal records at a national level, employers can better assess the suitability of candidates for specific roles.
Ensuring Accuracy with Employment Verification Checks
For HR professionals, employment verification checks are vital for confirming the accuracy of a candidate's work history on a national level. This ensures that the information provided is truthful and reliable, which is crucial for making informed hiring decisions. By verifying employment history across different states, HR can identify any discrepancies or potential red flags, thus enhancing the overall integrity of the hiring process and ensuring that the best candidates are selected for the organization.
Navigating FCRA Compliance in Background Checks
Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is essential when conducting national background checks. Employers must ensure they follow proper procedures, including obtaining consent from candidates and providing them with any adverse action notices if the background check influences hiring decisions.
Adhering to EEOC Guidelines for Background Checks
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) provides guidelines to prevent discrimination through background checks. Employers must ensure that their screening practices are consistent, non-discriminatory, and relevant to the job requirements to comply with these guidelines.
Integrating Background Checks into the Hiring Process
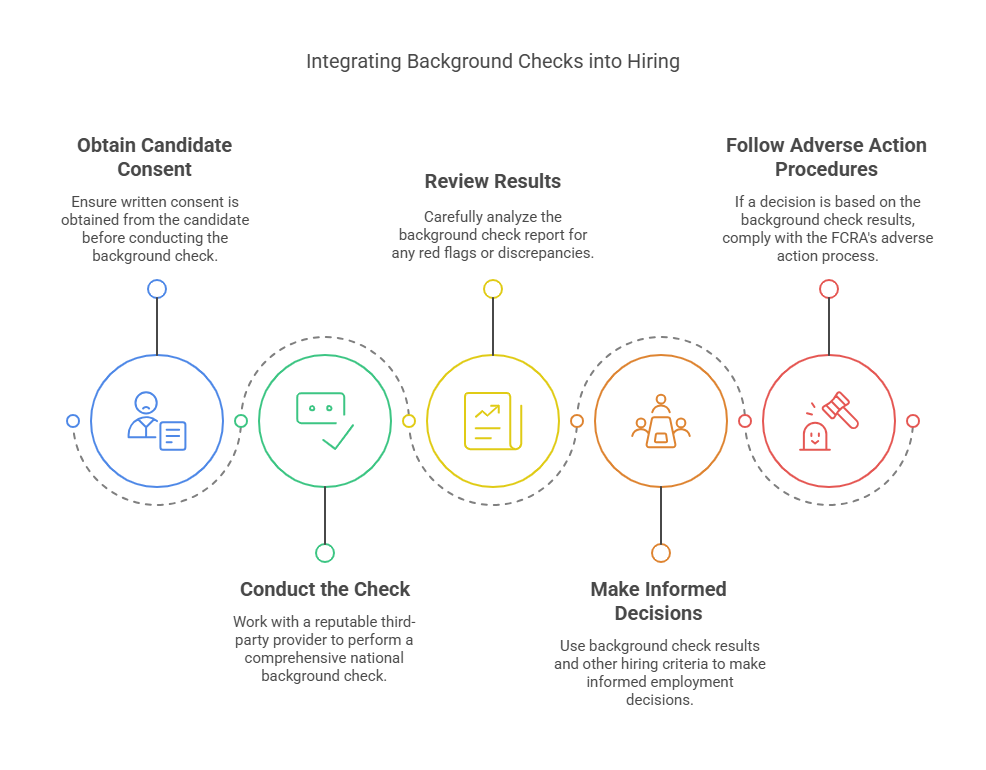
To effectively integrate national background checks into the hiring process, HR managers should:
- Obtain Candidate Consent: Ensure written consent is obtained from the candidate before conducting the background check.
- Conduct the Check: Work with a reputable third-party provider to perform a comprehensive national background check.
- Review Results: Carefully analyze the background check report for any red flags or discrepancies.
- Make Informed Decisions: Use background check results and other hiring criteria to make informed employment decisions.
- Follow Adverse Action Procedures: If a decision is based on the background check results, comply with the FCRA's adverse action process.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
HR managers must navigate various legal and compliance requirements when conducting national background checks:
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): Ensure compliance with FCRA regulations, including obtaining consent and providing adverse action notices.
- Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Guidelines: Follow EEOC guidelines to prevent discrimination in hiring practices.
- Ban the Box Laws: Be aware of state and local laws restricting inquiries about criminal history during the initial hiring stages.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Comply with regulations specific to your industry, such as healthcare or finance.

Best Practices for HR Managers
To ensure a fair and effective background check process, HR managers should:
- Be Consistent: Apply the same criteria and process to all candidates to avoid discrimination claims.
- Respect Privacy: Handle background check results with care to protect the candidate's privacy.
- Consider the Context: Evaluate the relevance of any findings to the job role and the candidate's overall qualifications.
- Promote Transparency: Communicate the background check process and criteria to candidates.
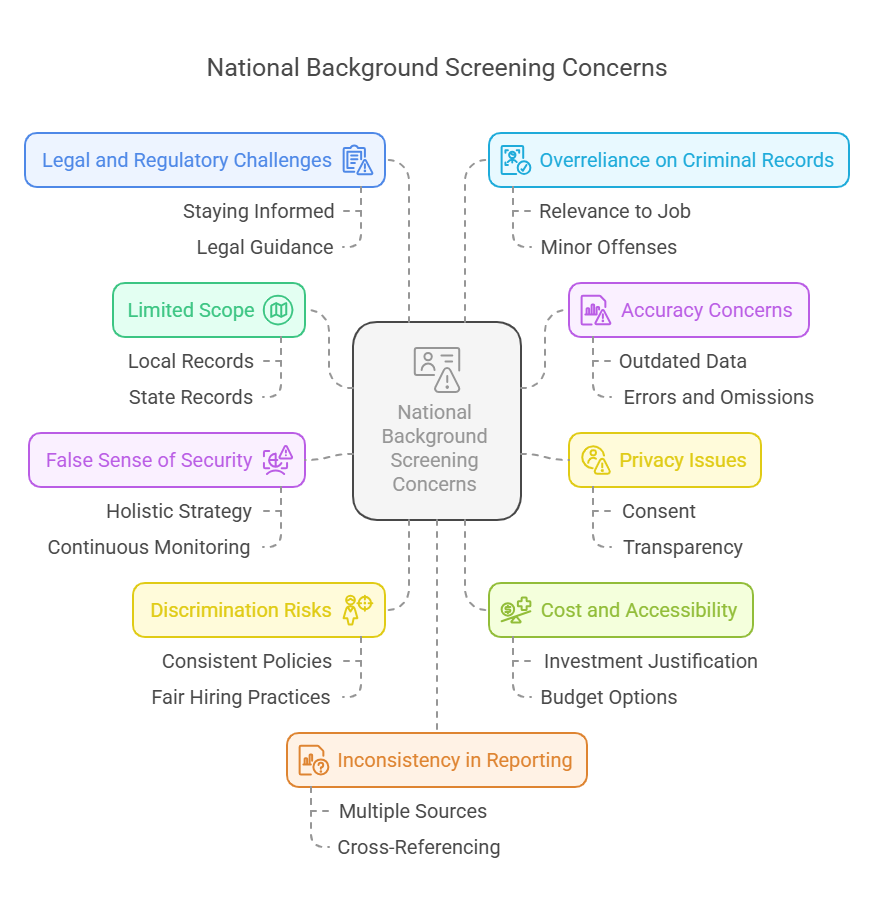
Top 10 National Background Screening Concerns
Limited Scope
While national background checks provide a broad overview, they may not capture all relevant local or state-level records. Critics argue that relying solely on national checks could lead to oversight of crucial information.
While it's true that national background checks may not capture all local or state-level records, they are a crucial first step in a comprehensive screening process. Employers are encouraged to supplement national checks with more localized searches to ensure thorough vetting.
Accuracy Concerns
National databases are vast and may not always be up-to-date. Errors, omissions, or outdated information could lead to unfair decisions based on inaccurate data.
To mitigate the risk of errors, it's recommended that employers use reputable background check providers that regularly update their databases and have mechanisms in place to correct inaccuracies.
Privacy Issues
Some may argue that national background checks infringe on personal privacy. The comprehensive nature of these checks could lead to unnecessary exposure to sensitive information.
National background checks are conducted with the individual's consent and in compliance with privacy laws. To address privacy concerns, employers should be transparent about the purpose and scope of the checks.
False Sense of Security
Relying heavily on national background checks might give employers a false sense of security. They might overlook the importance of additional checks or continuous monitoring.
Employers should view national background checks as a component of a holistic security strategy. Regular monitoring and additional vetting methods are essential to maintaining a safe and secure environment.
Discrimination Risks
Critics worry that national background checks could disproportionately impact specific groups, leading to discrimination in hiring practices. Ensuring fairness and equality remains a concern.
To prevent discrimination, employers should apply background check policies consistently and use the information only for relevant job-related decisions. Training on fair hiring practices can also help mitigate this risk.
Cost and Accessibility
The potential cost of hiring unsuitable candidates justifies the investment in national background checks. Various options are available to accommodate different budgetary needs.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Navigating the legal landscape of national background checks can be complex. Organizations must ensure compliance with various laws and regulations, which can be burdensome.
Employers can navigate the legal landscape by staying informed about current laws and seeking guidance from legal experts. Compliance is essential to avoid potential legal repercussions.
Overreliance on Criminal Records
There is a debate about overemphasizing criminal records in national background checks. Critics argue that this focus could exclude qualified candidates who have had minor or irrelevant offenses in the past.
Employers should consider the nature and relevance of criminal records to the job position. Not all offenses should automatically disqualify a candidate.
Inconsistency in Reporting
The information reported in national background checks can vary widely. This inconsistency can make it difficult for employers to make informed decisions.
Employers can address inconsistencies using multiple sources for background checks and cross-referencing information for accuracy.
Impact on Rehabilitation and Second Chances
There is a concern that national background checks could hinder the rehabilitation and reintegration of individuals with criminal records, limiting opportunities for those seeking a second chance.
Employers can support rehabilitation and second chances by adopting fair chance hiring practices and evaluating candidates on a case-by-case basis.
Conclusion
National background checks are a vital component of the hiring process for HR managers. By understanding the scope, legal requirements, and best practices, HR managers can effectively use these checks to make informed decisions, ensuring a safe and compliant workplace. HR managers may achieve a balance between workplace security and giving every applicant equal opportunity by putting in place a rigorous yet equitable screening procedure. Transparency, consistency, and a dedication to moral hiring processes are crucial when it comes to background checks. In the end, a properly designed background check procedure not only safeguards the company but also promotes an inclusive, trustworthy, and accountable work environment.

