Ensuring that your workforce is both highly qualified and trustworthy is crucial in the IT industry. The significance of thorough screening processes cannot be overstated, from technical proficiency to cybersecurity awareness. This guide aims to offer in-depth insights into the various facets of IT industry screening, including legal considerations, recommended practices, and the types of checks involved.
Key Takeaways
- IT industry screening is essential for mitigating risks like cyber threats and data breaches while ensuring a reliable, proficient workforce.
- The screening process incorporates multiple layers, including technical assessments, background checks, and soft skills evaluations to ensure comprehensive evaluations of potential hires.
- Legal compliance with U.S. regulations, such as the EEOC, FCRA, and data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA, is crucial for maintaining a trustworthy and reputable screening process.
- Employing a combination of automated tools and manual checks, along with continuous improvement and adaptation to new trends, enhances the screening process's efficiency and effectiveness.
- Challenges like skill mismatches, false information, and maintaining a positive candidate experience can be mitigated through structured interview processes, third-party services, and continuous refinement of screening strategies.
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of information technology, where innovation moves at lightning speed, the stakes are higher than ever. The IT industry is booming, but with great opportunities come significant risks. Cyber threats are evolving, data breaches are costly, and the importance of having a reliable, proficient workforce has never been more critical.
IT industry screening is the process of thoroughly evaluating potential and current employees to ensure they possess the required skills and integrity. It's a multi-layered approach that includes technical assessments, background checks, and soft skills evaluations. Without robust screening processes, businesses leave themselves vulnerable to both internal and external threats.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the dimensions of IT industry screening. We’ll explore everything from the types of checks needed to legal considerations and best practices, equipping you with the knowledge to strengthen your workforce and safeguard your company’s future.

Why IT Industry Screening Is Crucial
In the realm of IT, the stakes are sky-high. You're dealing not just with lines of code but with vast amounts of sensitive data. A security breach can cost a company millions, and that’s just the beginning. It could also mean a severe hit to your credibility and customer trust, things that can be tougher to regain than money.
Regulatory compliance is another key player here. Laws like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific standards such as HIPAA demand rigorous screening processes. Slip up, and you’re not just facing fines—you could be in for long-drawn legal battles and a tarnished reputation.
Reputation management in itself is a beast. One bad hire can impact your brand's image, leading to lost contracts and skeptical clients. In the IT industry, where trust and reliability are paramount, screening isn't just a formality—it’s the foundation of your company's integrity.
In tech recruiting, I've found that a resume scan isn’t enough—it’s what lies beneath that truly counts in the end. A missed single red flag during the screening process can be more expensive to remediate—the loss of client trust, data security, and team morale can’t be budgeted for. That's why we don’t simply look for skills—we look for integrity, flexibility, and a shared mission. Militant IT screening isn’t blocking—the preservation of access isn’t the game. When you hire a team you can trust, you’re not simply protecting systems—you’re building the foundation for innovation.
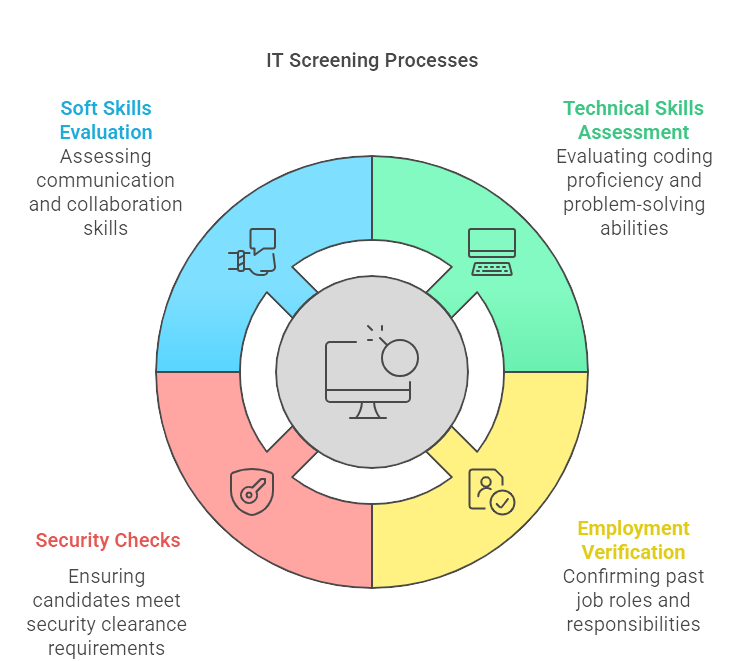
Types of Screening Processes
Screening in the IT industry requires a multi-faceted approach to ensure the right fit for both technical and cultural roles. Here is a breakdown of the key processes involved:
Technical Skills Assessment
Coding Tests
Coding tests are tailored to evaluate a candidate’s technical proficiency in specific programming languages and problem-solving skills. These tests usually take the form of timed exercises or competitions, where candidates have to solve coding problems of varying difficulty. Practical examples include algorithmic challenges on platforms like HackerRank or LeetCode.
Problem-Solving Scenarios
Beyond coding, problem-solving scenarios are used to gauge a candidate’s ability to tackle real-world issues. These assessments typically involve presenting a candidate with a complex problem that simulates day-to-day tasks, requiring them to outline their thought process and eventual solutions. This helps reveal their critical thinking and decision-making capabilities under pressure.
Certifications Verification
Verifying certifications ensures that candidates genuinely possess the knowledge they claim to have. This involves checking the validity of certifications from recognized institutions or platforms such as CompTIA, Cisco, or AWS. This step confirms that candidates have undergone standardized training and are qualified in specific technical areas.
IT Verification
Previous Employment Verification
It's crucial to verify past employment to ensure that candidates have the experience they list on their resumes. This can be achieved through formal employment verification processes, which often involve contacting previous employers to confirm job titles, responsibilities, and duration of employment. Accurate verification helps in painting a true picture of a candidate’s professional background.
Reference Checks
References play a vital role in the IT sector. Professional references are usually former managers or colleagues who can provide insights into the candidate's work ethic, technical skills, and behavior in a professional setting. Conducting thorough reference checks assists in acquiring a comprehensive view of a candidate’s past performance and cultural fit.
Project Verification
Verifying claimed projects or contributions ensures that candidates have genuinely worked on significant projects. This might involve reviewing the work they've done, checking code repositories, or contacting project stakeholders. Project verification validates the candidate’s hands-on experience and their ability to deliver results in practical scenarios.
Cybersecurity Checks
Security Clearance
Different IT roles may require varying levels of security clearances, especially in sensitive environments like government or defense. Security checks can range from basic identity verification to more comprehensive investigations involving criminal records, financial history, and personal associations. Clearances guarantee that the candidate can be trusted with sensitive information.
Background Checks
IT-specific background checks focus on areas particularly relevant to the tech industry. This can include verifying educational qualifications, checking for criminal records, and assessing any history of cybersecurity breaches or unethical behavior. Comprehensive background checks minimize the risk of internal threats.
Risk Assessments
Assessing potential internal threats involves not just background checks but also risk assessments designed to evaluate a candidate’s behavior and likelihood of posing a security risk. This might involve psychological testing or scenario-based assessments that gauge integrity and reliability.
Soft Skills Evaluation
Communication Skills
Effective communication is critical in team-driven environments. Evaluating communication skills can involve written tests, presentations, or practical exercises where candidates must articulate complex technical concepts in an easy-to-understand manner. This ensures candidates can share ideas clearly and collaborate effectively.
Adaptability and Problem-Solving
Socio-dynamic environments require personnel who can adapt and solve problems efficiently. Evaluating these skills often involves scenario-based questions where candidates must showcase flexibility and innovative thinking. This helps assess their ability to thrive amidst challenges and changes.
Collaboration
Collaboration skills are crucial in a sector that thrives on teamwork. Verifying experience in collaborative projects includes scrutinizing past projects where teamwork was essential. This can involve discussions during interviews or obtaining direct feedback from team members or project leads, ensuring candidates can work well within a team structure.
Covering these various screening dimensions ensures a balanced approach to hiring, ultimately leading to a competent and trustworthy IT workforce.
Technical Skills Assessment
Before getting someone onboard in an IT role, you need to make sure they know what they're doing. This means testing their technical skills rigorously. Here's how to approach it:
Coding Tests: It's standard practice to put candidates through coding tests. These tests usually come in various formats like live coding sessions, take-home assignments, or timed online tests. They help evaluate a candidate’s grasp of programming languages, problem-solving abilities, and how they approach algorithms and data structures. The aim is to assess not just if they can code, but how they think while coding.
Problem-Solving Scenarios: Another crucial evaluation tool is problem-solving scenarios. These scenarios simulate real-world problems and are designed to assess how candidates tackle challenges. Do they break down problems logically? Are they creative in finding solutions? This method goes beyond coding and checks how candidates approach and resolve unexpected issues, much like they would on the job.
Certifications Verification: Finally, it’s essential to verify any certifications and educational qualifications listed on a candidate's resume. Certifications can add a layer of validation to their skill set – think CompTIA, Cisco, Microsoft, or AWS certifications. Verifying these credentials ensures that the candidate has the claimed formal education and training.
The combination of these assessments helps ensure that the person you’re bringing into your IT team is not only capable but also proficient in the skills required for the job.
Legal Considerations and Best Practices
In the bustling realm of IT, ensuring your screening processes toe the legal line is non-negotiable. Regulatory compliance isn’t just about dodging fines; it's about safeguarding your company’s reputation and trustworthiness.
U.S. Regulations and Guidelines
Let’s break down some cornerstone legal frameworks that govern the terrain:
- Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC): The EEOC emphasizes non-discriminatory screening practices. Ensure your checks don’t inadvertently sideline candidates based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. Discover more
- Department of Labor (DOL): The DOL provides comprehensive guidelines on lawful hiring practices. Staying compliant not only keeps you out of hot water but boosts your hiring credibility. Get detailed information
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): If you’re running background checks, the FCRA is your bible. It mandates clear procedures for obtaining and using candidate information. Tripping up here could mean legal repercussions and a battered reputation. FCRA compliance is a must.
- Data Protection Laws: In the globalized IT world, GDPR and CCPA loom large. Peace of mind for your candidates means adhering to these regulations, ensuring their personal data is treated with the utmost confidentiality.
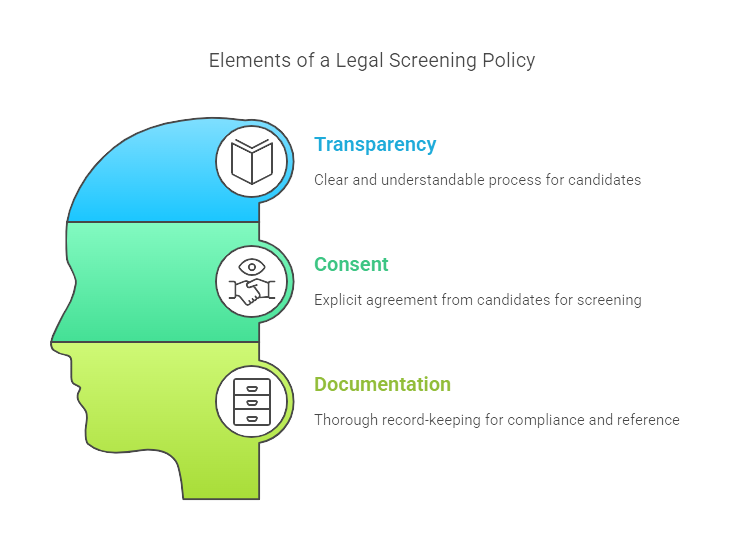
Crafting a Legal Screening Policy
Creating a bulletproof screening policy blends transparency, consent, and meticulous documentation.
- Transparency: Lay it all out—candidates should be crystal clear about what the screening process entails. From the get-go, let them know what checks they can expect and why they matter.
- Consent: This isn’t just a formality; it's a legal prerequisite. Obtaining explicit consent prior to conducting checks builds trust and shields your organization from potential disputes.
- Documentation: Keeping thorough records is your safety net. It’s not only key for accountability but also essential if you need to defend your processes down the line. Document every step, from consent forms to compliance checks.
Adhering to these legal considerations while implementing best practices not only streamlines your hiring process but also fortifies your organization’s standing in the competitive IT sector.
U.S. Regulations and Guidelines
Navigating the labyrinth of U.S. regulations and guidelines is a crucial aspect of conducting IT industry screening. First, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) plays a pivotal role in ensuring that background checks are conducted fairly and without discrimination. Employers must walk a fine line, ensuring compliance with EEOC guidelines to avoid any potential legal repercussions. For a deeper dive into this, refer to the EEOC's guidance.
Next, the Department of Labor (DOL) offers additional layers of regulation that employers should be aware of. These guidelines cover a broad spectrum—from minimum wage standards to occupational safety. Staying compliant with DOL regulations is not just about adhering to the law, but also about fostering a fair and safe workplace. More details can be found on the DOL’s official site.
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is another piece of the puzzle, setting the rules for obtaining and using consumer reports, including background checks. The FCRA mandates that employers must get written consent from candidates before conducting a background check and provide them with a copy of the report if any adverse action is taken based on its findings. This ensures transparency and fairness throughout the hiring process.
Finally, Data Protection Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have added another layer of complexity. While GDPR is EU-specific, it impacts U.S. companies dealing with EU citizens. Similarly, the CCPA affects how companies collect, store, and protect the personal data of California residents. Both regulations advocate for the protection and privacy of personal data, requiring employers to handle information responsibly.
In summary, understanding and adhering to these regulations not only helps in staying legally compliant but also builds a foundation of trust and transparency. This is indispensable in constructing a reliable and responsible IT workforce.
Crafting a Legal Screening Policy
Transparency
Open communication is key. Your screening process should be clear and understandable to all candidates. A well-documented policy that outlines each step of the screening process helps eliminate confusion. Make it accessible during the recruiting phase, perhaps through a detailed section on your careers webpage. Candidates should know what to expect—what types of checks will be conducted, why they're necessary, and how their data will be used. Transparency builds trust and sets the tone for a positive candidate experience right from the start.
Consent
This isn't just a formality; it’s a legal necessity. Before conducting any screening, obtain explicit, informed consent from candidates. This includes background checks, reference checks, and any other forms of verification. Clearly explain what they are consenting to and give them an opportunity to ask questions. A digital signature on a consent form not only ensures compliance but also protects your company from potential legal issues down the line.
Documentation
Maintaining thorough records is vital for multiple reasons. First, it ensures legal compliance, particularly with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Second, it serves as a reference point should any disputes arise. Keep records of the consent forms, the results of all screening processes, and communication with candidates. Good documentation practices enable you to demonstrate that your processes are fair, consistent, and legally sound.
Conducting Effective IT Industry Screening
Steps to Implement a Screening Process
Setting up an effective IT screening protocol starts with a solid plan. First, you need a clear strategy that outlines your screening objectives—whether they focus on technical skills, cultural fit, or cybersecurity awareness. Identifying what you want to achieve will drive the rest of your process.
Once you have a strategy, allocate resources. No screening process works without proper tools, trained personnel, and, yes, a budget. Invest in key software and services, and ensure your HR team is well-trained in using these tools. Additionally, look into budget allocations for third-party services and certifications.
Training is crucial. Your HR professionals and recruiters should be trained not just in the operational aspects but also in the ethical considerations of screening. This ensures your process is both effective and compliant with legal standards.
Technological Tools for Screening
Embrace automated tools to streamline your screening process. Systems like applicant tracking software (ATS) can filter candidates based on predefined criteria, saving time and reducing human error. However, automation has its limits; some nuances can only be caught through manual checks. For roles that demand high-level security clearances, manual evaluations may be indispensable. Combining both methods ensures a balanced, thorough screening process, leveraging the strengths of each approach.
Special Considerations for Remote Roles
With remote work on the rise, remote verification tools have become essential. Platforms like Zoom or specialized verification software can be used for virtual interviews and document verification. Always stay on the right side of the law, especially where remote roles cross state or national boundaries. Be aware of the legal nuances that come with international hiring, from data protection laws to employment regulations.
By carefully planning and implementing these steps, you can establish a robust and efficient screening process that meets the unique needs of your IT organization.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Common Hurdles
When it comes to screening in the IT industry, there are several common hurdles that organizations face. Identifying these challenges early on can help mitigate long-term issues.
- Skill Mismatches: One of the most frequent headaches is the gap between a candidate's claimed skills and their actual abilities. Many candidates inflate their technical prowess on resumes, leading to skill mismatches when they're put to the test in a real-world setting. Tackling this requires well-designed technical assessments and practical coding tests that can effectively gauge a candidate's true potential.
- False Information: Instances of candidates providing false information about their educational background, certifications, or previous employment are not uncommon. This can pose a major risk, especially in an industry where trust and competency are essential. Comprehensive background checks, including verification of academic credentials and past employment through multiple reliable sources, can weed out such discrepancies.
- Candidate Experience: Another tricky balance to strike is ensuring a thorough screening process without alienating potential hires with excessive rigor or delays. A cumbersome process can frustrate candidates and harm your employer's brand. Streamlining the screening steps while maintaining their effectiveness is key to keeping top talent engaged.
By understanding these common hurdles, companies can better prepare to address them, ensuring a smoother and more effective screening process.
Solutions
Structured Interview Processes
One of the most effective ways to mitigate challenges in IT screening is by formalizing your interview approach. A structured interview process ensures consistency and fairness. Begin with well-defined stages: initial screenings, technical assessments, and behavioral interviews. Use standardized questions and criteria to evaluate candidates uniformly, thus minimizing bias and increasing reliability. This not only streamlines the process but also provides clear benchmarks for decision-making.
Third-Party Services
For those seeking extra rigor or lacking internal resources, third-party screening services offer an attractive solution. These services specialize in comprehensive background checks, technical assessments, and employment verification. While outsourcing can free up internal resources, it comes with its own set of pros and cons. Third-party services provide expertise and scalability but may entail higher costs and less control over the process. Careful vetting of these services is crucial to ensure they align with your organization's standards and compliance requirements.
Continuous Improvement
Screening processes should not be static. Regularly updating and refining these procedures based on feedback and technological advancements can drastically improve effectiveness. Collect data on screening outcomes, identify bottlenecks, and be open to adopting new methodologies or tools. Incorporate feedback from both successful and unsuccessful candidates to enhance the candidate experience. Staying agile and proactive in refining the screening process ensures your methods remain cutting-edge and efficient, keeping you a step ahead in the competitive IT landscape.
Conclusion
Conducting effective IT industry screening is not just a procedural necessity; it's a strategic imperative. This guide has dissected the critical aspects of screening, from assessing technical skills to ensuring cybersecurity readiness and adherence to legal stipulations. In summary, a well-rounded approach—combining technical assessments, verification of past experiences, and thorough background checks—fortifies the hiring process, ensuring that only the best and most trustworthy candidates join your organization.
As we look toward the future, trends like AI-driven screening tools and increasingly stringent data protection laws will shape how screenings are conducted. However, the essence will remain unchanged: a robust screening process is foundational to building a secure and proficient IT workforce. Always prioritize thorough vetting, stay informed about emerging practices, and continuously refine your strategies to meet evolving challenges. By doing so, you’re not just filling positions; you're fortifying the pillars of your company's success.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






