Navigating the landscape of background checks can be daunting, especially in a bustling place like New York. Whether you're a volunteer coordinator ensuring your organization remains compliant, or a professional stepping into volunteering roles looking to understand what's involved, this guide covers all bases. Focused on the intricacies of the New York Volunteer Background Check process, weâll also briefly touch on how these differ from employment background checks.
Key Takeaways
- Volunteer background checks are crucial for protecting organizations and those they serve, focusing on safety and integrity.
- They typically include criminal record searches and identity verification, tailored to the role's specific needs.
- Background checks help build trust and community support by demonstrating a commitment to safety.
- Legal compliance requires adherence to guidelines like obtaining consent and avoiding discrimination.
- Consider how thorough your checks are and ensure they respect volunteer privacy while maintaining organizational security.
Understanding Volunteer Background Checks
Volunteer background checks are essential to ensuring that individuals participating in nonprofit activities are suitable for the roles they take on. They differ from other types of checks in their scope and focus on maintaining the safety and integrity of the organization.

What is a Volunteer Background Check?
Volunteer background checks dig into a person's past to ensure they are fit to join non-profit activities. While the specifics depend on what the organization needs, these checks usually involve looking at criminal records and sometimes checking education or references.
- Primary Goal: Keep the organization's activities and stakeholders safe.
- Common Elements: Criminal history, identity checks, and occasionally driving records.
Consider a community center that operates a children's program. They might focus heavily on criminal background checks to prevent risks. On the other hand, a volunteer driver service might prioritize driving record checks.
Why do these checks? To avoid letting someone with a violent history work closely with kids or entrusting someone with numerous driving violations to transport people.
Ask yourself: What specific risks does your organization need to guard against? Tailor the background checks accordingly to address those concerns.
Why Are They Important?
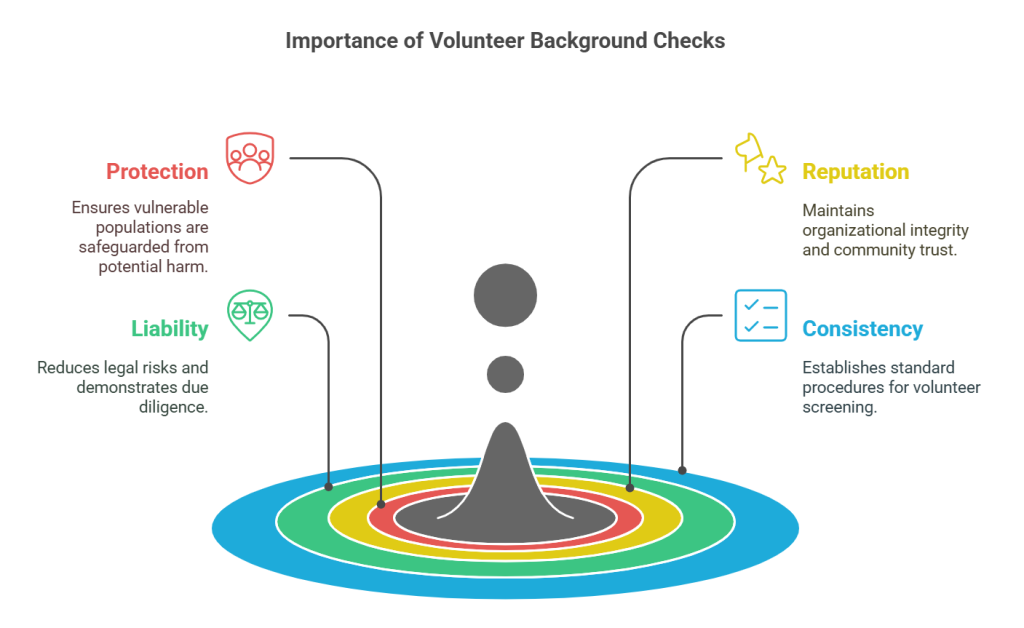
Volunteer background checks play a critical role in ensuring the safety and trustworthiness of community services. Here's why they matter:
- Protection: Vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly, rely on volunteers for support. Background checks help prevent individuals with concerning histories from gaining access to these groups.
- Reputation: Organizations maintain their reputation through responsible volunteer management. By screening volunteers, they can demonstrate a commitment to safety and integrity, which is crucial for community trust and ongoing support.
- Liability: Conducting these checks can reduce potential legal liabilities for organizations. This proactive step shows due diligence, should any issues arise in the future.
- Consistency: Regular background checks establish a standard procedure, ensuring all volunteers meet certain criteria for participation. This consistency helps in creating a reliable volunteer workforce.
Have you considered the impact of not performing background checks on your organization? What measures are in place to ensure volunteer reliability and safety?
Legal Framework of Volunteer Background Checks in New York
Regulatory Requirements
Navigating the legal landscape is essential when conducting volunteer background checks in New York. Here's what you need to know:
- State Laws: You must adhere to the New York Human Rights Law, which prohibits discrimination based on criminal records unless there's a direct connection to the volunteer role. This ensures that decisions are made fairly and justly, balancing safety with opportunity.
- Federal Guidelines: The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) outlines crucial steps for conducting background checks, including obtaining consent and providing proper disclosures. These guidelines are foundational in maintaining transparency and integrity.
Compliance and Best Practices
Adhering to best practices ensures that your organization remains compliant and respects the rights of volunteers.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate with volunteers about the background check process. Provide details on what checks will be conducted and how the information will be used.
- Consent: Always obtain written consent from volunteers before initiating any background checks. This is not just a legal requirement but also a best practice for maintaining trust.
- Relevance: Use the background check results responsibly. Focus on how the information relates to the specific duties of the volunteer position. This approach helps to evaluate candidates fairly and effectively.
By understanding these legal requirements and practices, you can run compliant background checks confidently, ensuring a safe and equitable environment for your organization and its volunteers.
Regulatory Requirements
Background checks in New York must align with specific state and federal guidelines.
- New York Human Rights Law: This law ensures criminal records are not used in discriminatory ways. Organizations must demonstrate that any disqualification based on criminal history directly impacts the volunteer role's requirements.
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): Before conducting a background check, organizations must provide clear disclosures and get consent from the volunteer. This fosters transparency and gives volunteers control over their personal information.
- Child Safety: For roles involving vulnerable groups, such as children, adherence to additional screening standards, including fingerprinting or more extensive checks mandated by state law, may be required.
Compliance is about more than just ticking boxes. It's about aligning with ethical standards and upholding trust. How does your organization handle these expectations? Do your current policies reflect both legal requirements and your mission?
Organizations that manage these requirements effectively don't just protect themselves legally; they also ensure a safer environment for everyone involved.
Conducting Volunteer Background Checks: Steps and Processes
Preparation
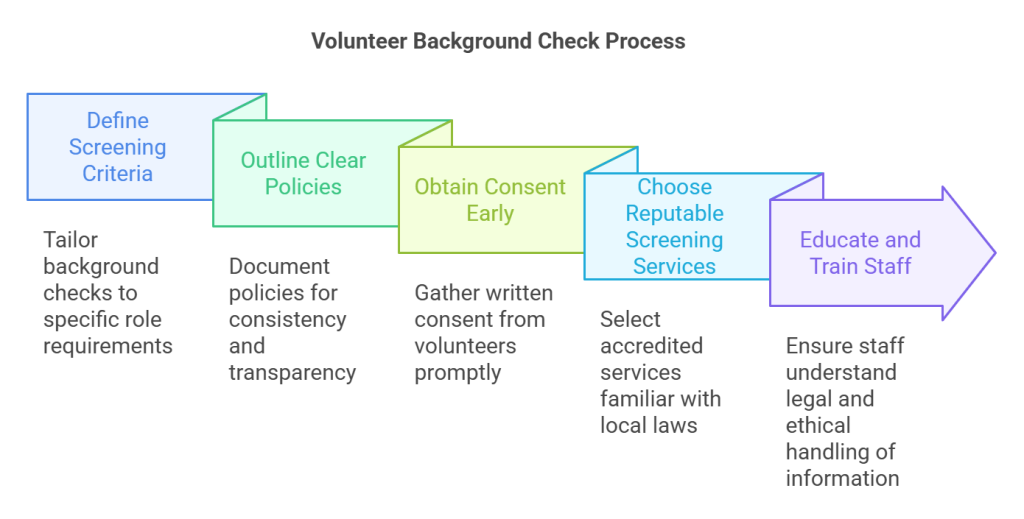
Before beginning a background check, there are essential steps to streamline the process.
- Define Screening Criteria: Tailor the background check to the specific volunteer role requirements. Determine if the role requires checking criminal history, driver records, or other specific details.
- Outline Clear Policies: Have a well-documented policy that explains what checks are required for different roles. This will help maintain consistency and transparency.
- Obtain Consent Early: Make sure to gather written consent from volunteers well ahead of starting the screening process. Clearly explain what the check entails and how the information will be used.
- Choose Reputable Screening Services: Find an accredited background check service that understands New York laws. Consider using resources like the PBSA to identify certified services that offer reliable results.
Educate and Train Staff: Ensure staff involved in the screening process understand the legal requirements and how to handle sensitive information ethically.
Execution
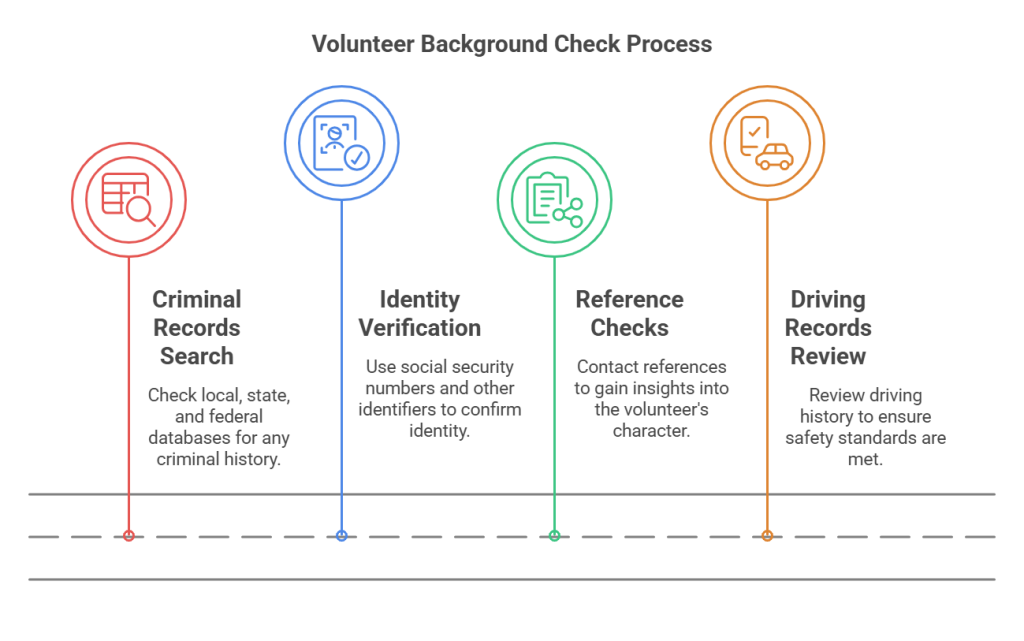
Conducting a comprehensive background check requires a few straightforward steps:
- Criminal Records Search: Check local, state, and federal databases for any criminal history. This ensures you're aware of any past offenses that could impact the volunteer role.
- Identity Verification: Use social security numbers and other identifiers. This confirms that the information provided by the volunteer matches official records.
- Reference Checks: Although optional, contacting references can provide insights into the volunteer's character and reliability. This can be particularly useful for roles involving sensitive duties.
- Driving Records: If the volunteer role involves driving, review their driving history to ensure they meet safety standards.
Are there other components you should consider? Think about the specific requirements of the volunteer role and the potential risks involved. Tailoring the background check to these needs can improve safety and suitability assessments.
Taking these steps allows you to conduct thorough checks efficiently, ensuring both the safety of your organization and the welfare of those you serve.
Differences Between Volunteer and Employment Background Checks
Key Distinctions
Volunteer and employment background checks share the goal of ensuring a safe environment, but their differences are worth noting.
- Scope and Depth: Employment checks often dig deeper. Employers might look at credit history, work history, and more. Volunteer checks usually stick to criminal history and identity verification unless the role has specific demands.
- Frequency: Employment checks are part of regular hiring processes. Volunteer checks might be less frequent unless roles involve sensitive responsibilities or vulnerable populations.
Contextual Application
Understanding these distinctions helps in managing each process effectively.
- Tailored Approach: Organizations should design their screening processes to match the level of responsibility. For example, a volunteer role working directly with children might need standards similar to employment checks.
- Role-Specific Needs: Volunteer positions requiring trust, like handling finances or confidential information, may need a more thorough background review.
Organizations can benefit from distinguishing between these processes, ensuring they meet both legal requirements and safety standards without unnecessary procedures. This knowledge empowers organizations and individuals to streamline their processes, ensuring each check is relevant and necessary. Understanding the specific context allows them to maintain high standards of safety without unnecessary invasions of privacy.
For those curious about the employment check process, the GCheck Blog offers an in-depth look.
Addressing Common Concerns
Privacy Issues
Privacy concerns often surface when discussing background checks. You might wonder about the impact on your personal information. It's critical for organizations to respect this aspect.
- Confidentiality Assurance: Organizations should explain how they will use and store your data. This clarity can build trust.
- Data Protection: Look for organizations that prioritize data security. They should use encryption and secure databases to prevent data breaches.
- Consent is Key: Always give permission before a background check starts. Without your consent, the process should not proceed.
- Disclosure of Findings: Find out if you'll receive a copy of the background check report. Knowing what information is shared ensures transparency.
Are you worried about privacy when volunteering? Asking questions about data usage can help relieve those concerns. Do you know how your data will be managed? It's important to feel secure about your information.
Impact of Results
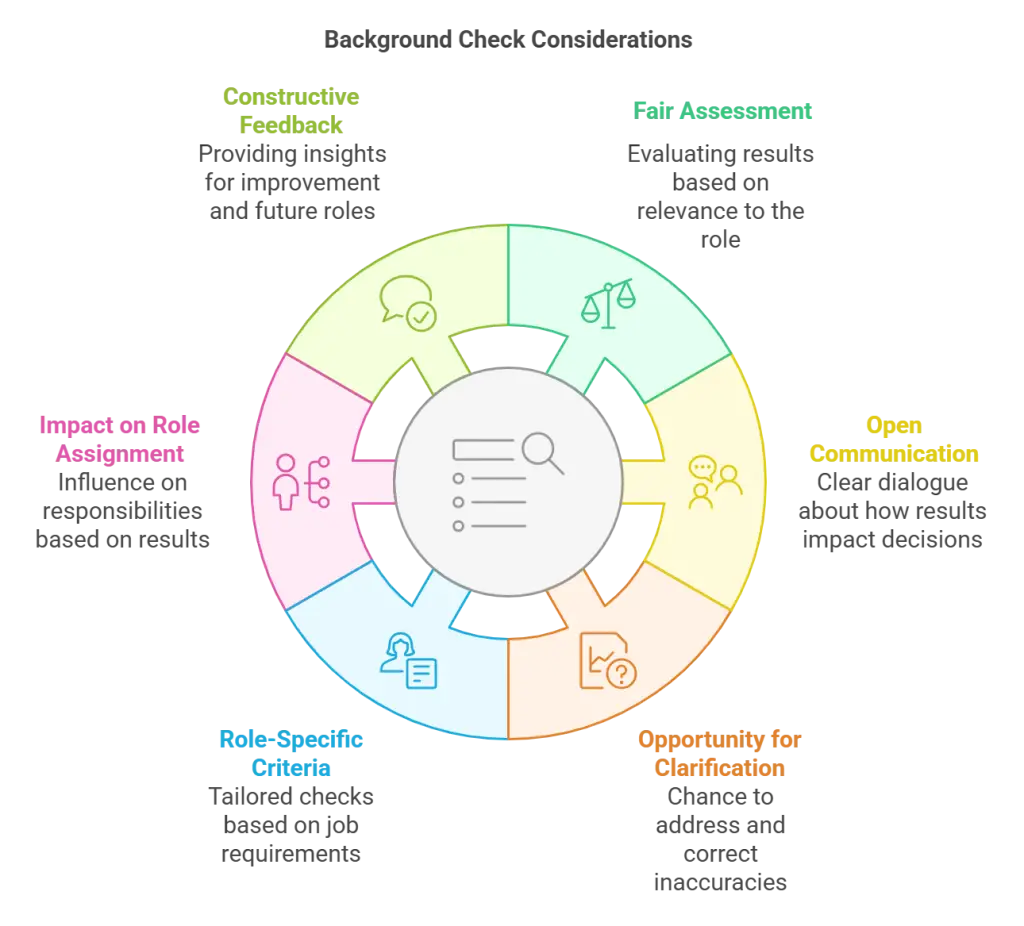
How do the results of a background check affect your chances as a volunteer? Here are key points to consider:
- Fair Assessment: An organization should evaluate results fairly, focusing only on information relevant to the role. For example, a past non-violent offense may not impact your eligibility for many positions.
- Open Communication: Clear communication is essential. Organizations need to inform you how results will be used in decision-making. This helps you understand their criteria and expectations.
- Opportunity for Clarification: Mistakes can happen in background reports. You should be allowed to address any inaccuracies. Be prepared to provide context or explain circumstances if needed.
- Role-Specific Criteria: Different roles require different checks. If working with children, a check will likely focus on any history that could affect their safety. Understanding what the organization looks for can guide you in discussing results.
- Impact on Role Assignment: Even if some results raise red flags, it might not mean total disqualification. Instead, it could influence the type or level of responsibility you're assigned.
Constructive Feedback: A transparent process should provide constructive feedback. This offers you a chance to improve your suitability for future opportunities or different roles.
Being aware of these factors can better prepare you for any outcomes and foster a positive and open discussion with potential volunteer organizations.
Resources and Services
Navigating the world of volunteer background checks can be simplified using the right tools and resources. Here's a compact list to consider:
- PBSA Certification: When choosing a screening service, ensure it's accredited by the Professional Background Screening Association (PBSA). Their standards ensure compliance and reliability.
- Local Nonprofits: Organizations like Volunteer New York offer insight into local best practices and guidance specific to the New York area.
- Legal Assistance: To ensure compliance with New York State laws, consulting with a legal professional experienced in employment and volunteer regulations can be invaluable.
Online Platforms: Services like Verified Volunteers offer online platforms for streamlining background checks tailored specifically for volunteer organizations.
- Government Resources: The New York State Division of Criminal Justice Services (DCJS) provides information and support for organizations conducting background checks.
Empower your organization and streamline the volunteering process by leveraging these resources effectively. They bring clarity and reliability, ultimately supporting your goal of maintaining a safe, trustworthy volunteer environment.
Conclusion
The New York Volunteer Background Check process is a crucial component for both organizations and volunteers committed to community safety. Staying informed about legal responsibilities, procedural steps, and the key differences from employment checks enhances the experience for everyone involved.
Additional Readings
iMentor. (n.d.). NYC Background Check Procedures. Retrieved from https://partners.imentor.org/help/nyc-background-check-procedures
New York State Justice Center. (n.d.). Criminal Background Check (CBC). Retrieved from https://www.justicecenter.ny.gov/criminal-background-check-cbc
Definitions
- Volunteer Background Check - A volunteer background check is a screening process used by nonprofits to evaluate the suitability of individuals for specific roles. It typically focuses on criminal records, identity verification, and other relevant information to ensure the safety and trustworthiness of the volunteers in relation to the organizationâs mission.
- Criminal Record Search - A criminal record search examines databases at the local, state, and federal levels for any prior convictions or pending charges against an individual. This step helps organizations identify potential risks, especially for roles involving interaction with vulnerable populations.
Identity Verification - Identity verification confirms that a volunteerâs personal information matches official records. This is often done using documents like social security numbers or government-issued IDs to ensure the person is exactly who they claim to be.
- Consent - Consent is the volunteerâs written agreement permitting an organization to conduct a background check. Itâs a required legal step that ensures transparency and allows the individual to understand how their information will be collected and used.
- New York Human Rights Law - This law restricts organizations from disqualifying volunteers based on criminal records unless the offenses are directly related to the volunteerâs role. It promotes fairness in decision-making while protecting individuals from discrimination.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





