The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) is a federal agency responsible for enforcing laws that prohibit discrimination in the workplace. For HR decision-makers, understanding the EEOC complaint process is crucial, as mishandling them can lead to severe consequences for businesses. Employers need to comprehend the intricacies of EEOC complaints to protect their employees and maintain a positive workplace environment.
For HR professionals, maintaining a record free of EEOC complaints (or any local equivalent) is a significant achievement and a true point of pride. Addressing employee concerns and complaints with compassion, coupled with a robust understanding of legal requirements, is essential for building a portfolio of trust and a strong track record in HR. This article offers valuable insights on effectively handling such cases, helping you to establish a trustworthy HR brand for yourself.
What Is an EEOC Complaint?
An EEOC complaint is a formal allegation of discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex (including pregnancy, gender identity, and sexual orientation), national origin, age, disability, or genetic information. It serves as a means for individuals to seek redress for discriminatory practices in employment. The EEOC investigates these complaints to determine if there is reasonable cause to believe that discrimination occurred. If the EEOC finds evidence of discrimination, it may attempt to resolve the complaint through mediation or pursue legal action against the employer.
How Does an EEOC Complaint Hurt an Employer?
EEOC complaints can have serious consequences for employers. They can tarnish the company's reputation, leading to negative publicity and affecting its brand image. Additionally, EEOC complaints can lower employee morale and productivity, creating a toxic work environment. Employers may also face financial implications, including legal fees and settlement costs, if the EEOC finds evidence of discrimination. It is essential for employers to take EEOC complaints seriously and address them promptly to mitigate these risks.
How Serious Is an EEOC Complaint?
An EEOC complaint is a serious matter that can have long-lasting effects on a business. When the EEOC receives a complaint, it conducts an investigation to determine its merit. If the EEOC finds evidence of discrimination, it may pursue legal action against the employer. This can result in significant financial losses, damage to the company's reputation, and ongoing monitoring by the EEOC. Employers should understand the potential consequences of an EEOC complaint and take proactive steps to prevent discrimination in the workplace.
EEOC Complaints and Litigation Costs
Defending against an EEOC complaint can be costly for employers. Legal fees, settlement costs, and potential damages can add up quickly, impacting the company's bottom line. Employers may also incur costs related to hiring legal counsel, gathering evidence, and preparing for litigation. To minimize these costs, employers should strive to create a workplace that is free from discrimination and harassment and implement policies and procedures that promote equal opportunity for all employees.
Indemnifications and Penalties from EEOC Complaints
In cases where the EEOC finds evidence of discrimination, employers may be required to pay indemnifications to affected individuals. Indemnifications are monetary awards intended to compensate victims of discrimination for any harm they have suffered. Additionally, the EEOC can impose penalties on employers found guilty of discriminatory practices. These penalties can include fines, back pay, and injunctive relief. Employers should be aware of the potential indemnifications and penalties associated with EEOC complaints and take steps to prevent discrimination in the workplace.
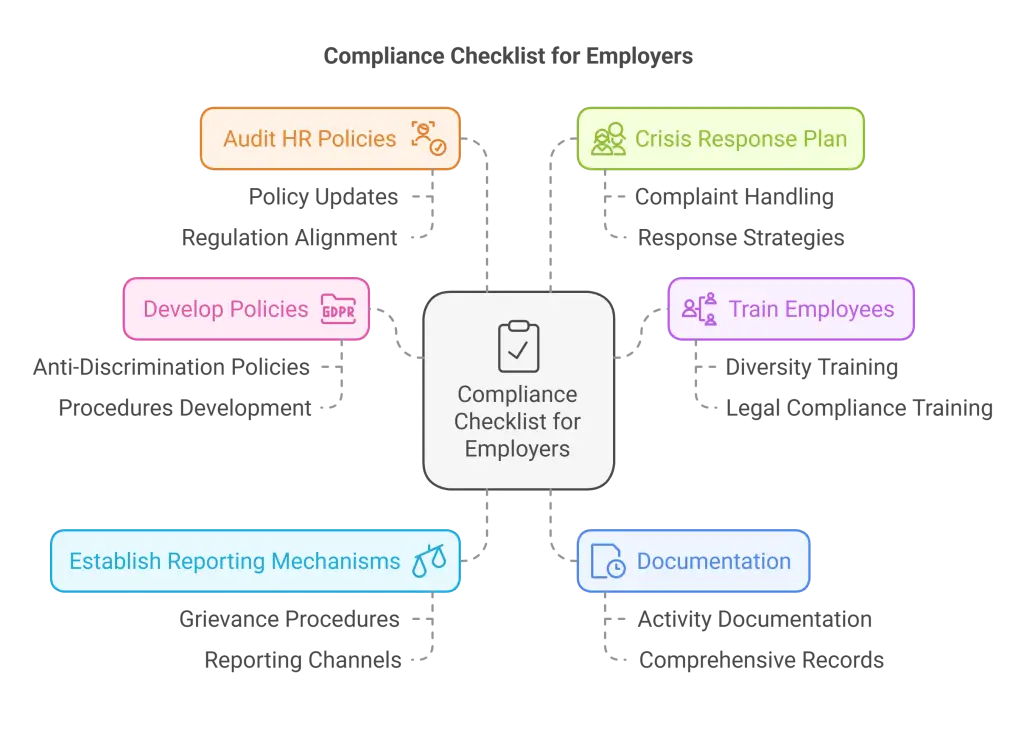
EEOC Complaint Prevention Strategies
Preventing Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) complaints begins with proactive measures that create an inclusive, respectful, and legally compliant workplace. Here are specific strategies businesses can implement to reduce the risk of complaints:
- Establish Clear Anti-Discrimination Policies: Develop and communicate comprehensive anti-discrimination and anti-harassment policies. Ensure these policies outline unacceptable behaviors, reporting procedures, and the consequences of violations.
- Implement Regular Training Programs: Provide mandatory training for employees and managers on diversity, inclusion, and recognizing discriminatory practices. Emphasize the importance of workplace respect and compliance with employment laws.
- Conduct Regular Policy Audits: Periodically review company policies, employee handbooks, and procedures to ensure alignment with the latest legal standards and EEOC guidelines.
- Promote Open Communication: Encourage employees to voice concerns through anonymous feedback channels or open-door policies. Early detection of issues can prevent formal complaints.
- Maintain Thorough Documentation: Document all workplace incidents, performance reviews, disciplinary actions, and investigations. Detailed records can demonstrate compliance efforts and provide critical evidence in case of an EEOC investigation.
- Foster a Culture of Inclusion: Build a workplace culture where diversity is celebrated, and employees feel valued. Promote equal opportunities for all, regardless of race, gender, age, or other protected characteristics.
EEOC Complaint Action Items
When faced with an EEOC complaint, businesses must act swiftly and methodically. Here are actionable steps to manage the situation effectively:
- Immediate Acknowledgment: Acknowledge receipt of the complaint promptly. Demonstrating professionalism and cooperation from the outset can set the tone for the investigation.
- Assemble a Response Team: Designate a team comprising HR representatives, legal counsel, and relevant managers to address the complaint. Clear role assignments ensure an organized response.
- Review the Complaint Thoroughly: Analyze the details of the complaint to understand the allegations fully. Focus on identifying key dates, individuals involved, and specific incidents mentioned.
- Conduct an Internal Investigation: Initiate a fair and unbiased internal investigation. Interview involved parties, review relevant documents, and gather evidence to assess the validity of the claims.
- Communicate Transparently: Keep all parties informed about the investigation's progress while respecting confidentiality. Transparency builds trust and demonstrates a commitment to resolving the issue.
- Take Corrective Action, If Necessary: If the investigation confirms discriminatory practices, implement corrective actions promptly. This may include disciplinary measures, policy updates, or additional training programs.
- Maintain Ongoing Compliance: Use lessons learned from the incident to improve workplace practices. Regularly revisit prevention strategies and update procedures to ensure continued compliance with EEOC standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an EEOC complaint?
An EEOC complaint is a formal grievance filed with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) alleging workplace discrimination. This discrimination can be based on factors such as race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or genetic information, all of which are protected under federal law.
Who can file an EEOC complaint?
Any current or former employee, job applicant, or individual who believes they have experienced workplace discrimination can file an EEOC complaint. The complaint must allege a violation of federal anti-discrimination laws within the EEOC's jurisdiction.
What is the process for filing an EEOC complaint?
The process typically starts by contacting the EEOC, either online, in person, or by mail, and filing a charge of discrimination. Once filed, the EEOC may offer mediation, conduct an investigation, or issue a "right to sue" letter if further legal action is warranted.
How long do employees have to file an EEOC complaint?
Employees generally have 180 days from the date of the alleged discriminatory act to file a complaint. In cases where a state or local anti-discrimination law applies, the filing deadline may extend to 300 days.
What happens after an EEOC complaint is filed?
Once a complaint is filed, the EEOC notifies the employer and reviews the allegations. The agency may conduct an investigation, offer mediation, or determine if there is reasonable cause to believe discrimination occurred.
What is the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)?
The FCRA is a federal law that governs how employers obtain and use consumer reports, such as background checks, for employment purposes. It ensures that information is accurate and used fairly while protecting the privacy of individuals.
How do the FCRA and EEOC intersect?
The FCRA outlines the process for obtaining and using background checks, while the EEOC ensures that the results of these checks are used equitably without discriminatory practices. Employers must comply with both sets of regulations when using consumer reports in hiring decisions.
Can an EEOC complaint lead to a lawsuit?
Yes, an EEOC complaint can lead to a lawsuit if the agency finds reasonable cause or issues a "right to sue" letter to the employee. Employees can then pursue legal action in court to address the alleged discrimination.
What is the purpose of the EEOC mediation program?
The EEOC mediation program offers an opportunity to resolve disputes between the employer and employee through informal negotiation. It is a confidential process aimed at saving time, resources, and avoiding litigation.
What are common EEOC complaint examples?
Common complaints include allegations of sexual harassment, racial discrimination, age discrimination, retaliation for reporting misconduct, and failure to provide reasonable accommodations for disabilities. Each complaint is evaluated based on its specific circumstances and applicable laws.
How can employers prevent EEOC complaints?
Employers can prevent complaints by implementing clear anti-discrimination policies, providing regular training for staff, and fostering an inclusive workplace culture. Creating a system for employees to report issues confidentially can also help address concerns early.
What penalties can employers face from EEOC complaints?
Penalties may include financial damages, back pay, or compensatory and punitive damages. Employers may also be required to reinstate employees, implement workplace policy changes, or provide mandatory anti-discrimination training.
What is a formal complaint with the EEOC?
A formal complaint is filed after initial contact with the EEOC if mediation does not resolve the issue. It triggers a more detailed investigation into the allegations of workplace discrimination.
Are employers notified of EEOC complaints?
Yes, employers are notified when a charge of discrimination is filed against them. They are given an opportunity to respond, submit documentation, and participate in the mediation or investigation process.
What should employers do when notified of an EEOC complaint?
Employers should take the complaint seriously, respond promptly, and consult legal counsel to prepare a detailed response. It’s also essential to cooperate fully with the EEOC’s investigation and provide all requested documentation.
How does the EEOC define discrimination?
Discrimination includes treating someone unfavorably because of their race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age (40 or older), disability, or genetic information. The EEOC also protects against retaliation for asserting rights under federal anti-discrimination laws.
Can employers use background checks without violating the FCRA and EEOC?
Yes, employers can use background checks legally by providing clear disclosures, obtaining written consent, and using the results equitably. Adhering to adverse action procedures when denying employment based on a background check is also critical.
What is adverse action under the FCRA?
Adverse action refers to any negative employment decision made based on a background check, such as rescinding a job offer or termination. Employers must notify the individual, provide a copy of the report, and allow them time to dispute inaccuracies before finalizing the decision.
What is the EEOC’s role in workplace investigations?
The EEOC investigates allegations of workplace discrimination to determine whether federal anti-discrimination laws were violated. Investigations may include interviewing witnesses, reviewing documents, and issuing findings.
What resources are available to employers to ensure compliance?
Employers can access resources from the EEOC website, legal counsel, and compliance tools like employee handbooks or HR software. Regular training and updates on employment laws also help ensure policies align with federal regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding the EEOC complaint process is essential for employers and businesses to avoid costly legal battles and maintain a positive workplace culture. By proactively addressing discrimination and fostering an inclusive environment, businesses can mitigate the risk of facing EEOC complaints and build a stronger, more resilient workforce. Employers should educate themselves and their employees about their rights and responsibilities under the law and take prompt action to address any complaints of discrimination or harassment. By doing so, employers can create a workplace that is fair, respectful, and free from discrimination for all employees.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






