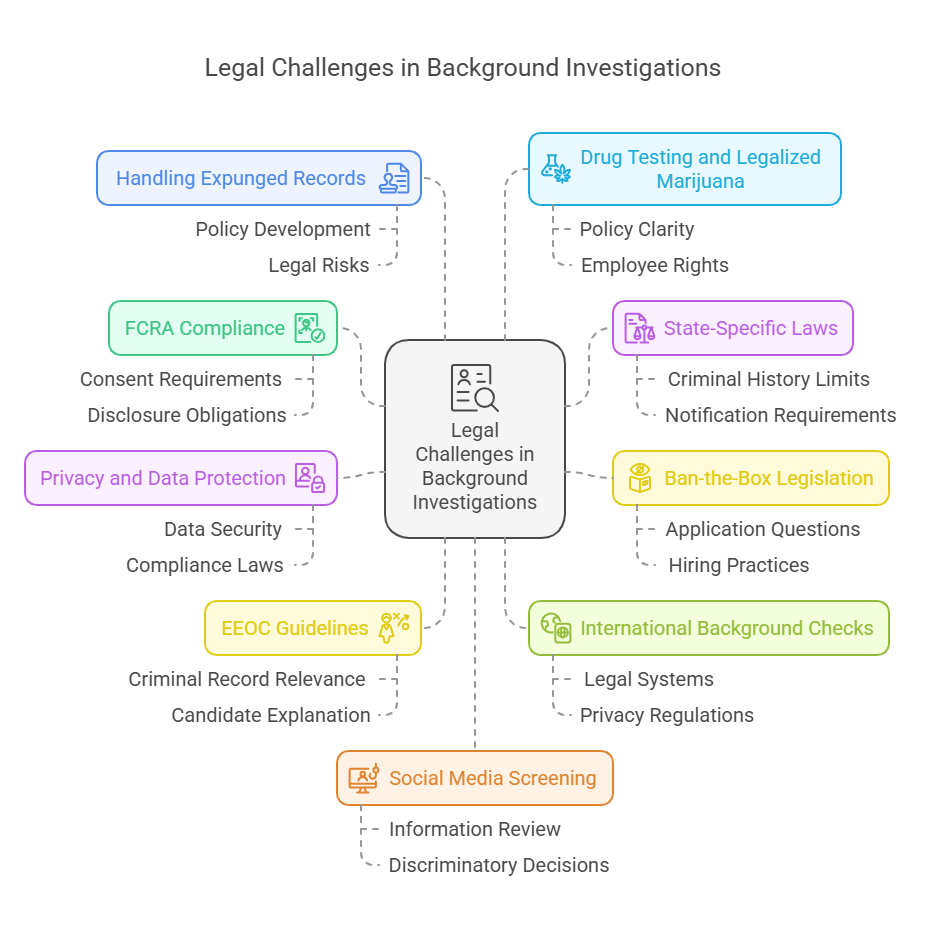
Background investigations are crucial to the hiring process, ensuring that candidates are qualified and trustworthy. However, these checks come with legal challenges employers must navigate to avoid costly mistakes and legal issues. Here are the top ten legal challenges in background investigations:
1. Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
The FCRA governs how employers obtain and use consumer reports, including credit reports and criminal background checks. Employers must obtain written consent from the candidate, provide a clear disclosure that a background check will be conducted, and follow specific procedures if they decide not to hire based on the report. This includes providing a pre-adverse action notice, a copy of the report, and an opportunity for the candidate to dispute any inaccuracies.
As an HR professional, I truly believe that background investigations are essential in ensuring we hire individuals who are not only qualified based on technical skills but also trustworthy. However, we must keep in mind that one misstep can lead to costly mistakes, not only for the company but for the candidate’s future as well. Therefore, everyone involved in the process (employer, job seeker, and HR) should work hand-in-hand to attain success in this process. Being well-informed can help everyone navigate the challenges that may arise and can lead us to a sound background screening process.
2. Navigating State-Specific Laws
In addition to federal regulations, each state has laws governing background checks. Employers face restrictions when checking a candidate's background, such as limits on criminal history checks, notification requirements, and credit report usage restrictions. Employers must be familiar with the laws in each state where they operate to ensure compliance.
3. Ban-the-Box Legislation
"Ban-the-Box" laws aim to provide individuals with criminal records a fair chance at employment by prohibiting employers from asking about criminal history on job applications. Employers must adapt hiring practices to comply with location-specific laws regarding criminal history inquiries.
4. Privacy Concerns and Data Protection
Protecting the privacy of candidates during the background check process is crucial. Employers must ensure that they collect, store, and dispose of personal information securely and comply with data protection laws. This includes safeguarding against unauthorized access and ensuring that sensitive information is only used for its intended purpose.
5. Discrimination and Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Guidelines
Employers must be careful not to discriminate against candidates based on information obtained in a background check. The EEOC provides guidelines to help employers avoid discriminatory practices, such as considering the nature and relevance of a criminal record to the job and providing an opportunity for the candidate to explain any negative information.
6. International Background Checks
Conducting background checks on candidates who have lived or worked abroad presents additional challenges. Employers must navigate different legal systems, privacy regulations, and cultural norms. They must also consider the accuracy and reliability of international records.
7. Handling Expunged or Sealed Records
Employers must be cautious when using criminal records in hiring decisions, especially if those records have been expunged or sealed. They need policies to avoid mishandling these records, which can result in legal issues.
8. Drug Testing and Legalized Marijuana
As more states legalize marijuana for medical or recreational use, employers face challenges in enforcing drug testing policies. They must balance safety and productivity concerns with respecting employees' rights to privacy and legal marijuana use. Clear policies and communication are essential to navigate this evolving legal landscape.
9. Social Media Screening
Using social media for background checks can raise legal privacy, discrimination, and accuracy issues. Employers should have clear policies outlining what information they will review and how it will be used in the hiring process. They must also ensure that their social media screening practices comply with privacy laws and do not lead to discriminatory decisions.
10. Adverse Action Procedures
If an employer decides not to hire a candidate based on information in a background check, they must follow specific adverse action procedures. This includes providing a pre-adverse action notice, a copy of the report, and an opportunity for the candidate to dispute any inaccuracies. Employers must also provide a final notice of adverse action once the decision is finalized.
Conclusion
Navigating the legal challenges of background investigations requires a careful and informed approach. Employers must stay current with federal and state laws, develop clear policies, and seek legal counsel to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues. By doing so, they can conduct thorough and fair background checks that protect both their organization and the rights of candidates.
Additionally, it is crucial to establish a work environment where applicants can trust their sensitive personal information. It is essential to establishing trust as a strong basis that will bind employers and employees together. Ultimately, we are establishing a relationship and a culture in addition to a legal compliance procedure.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






