Background checks are a crucial part of the hiring process. They help employers make informed decisions and ensure a safe workplace. In Texas, specific laws and regulations govern these checks, making it essential for employers to understand the requirements and best practices.
Key Takeaways
- Compliance with Federal and State Laws: Employers must adhere to the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and Texas-specific regulations, including obtaining written consent from candidates before conducting background checks.
- Ban the Box Law: Texas prohibits employers from inquiring about criminal history on initial job applications, allowing candidates to be evaluated based on qualifications first.
- Types of Background Checks: Employers can conduct various checks, such as criminal background checks (state, national, and county-level), employment and education verification, and professional license verification, tailored to the job requirements.
- Data Protection: Employers are required to protect personal information obtained during background checks, ensuring confidentiality and compliance with data protection laws.
- Risk Mitigation: Thorough background checks help mitigate risks associated with negligent hiring, contributing to a safe and secure workplace.
This guide covers everything you need to know about Texas background checks for employers. We'll explore why background checks matter, understand Texas laws, discuss the types of checks available, and provide a step-by-step process for conducting them. Additionally, we'll share best practices and answer common FAQs.
By the end of this guide, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of background checks in Texas, ensuring compliance and making sound hiring decisions.
Different states have unique laws and generally accepted practices. This reading is essential for those operating out of TexasâÂÂboth HR professionals and business leaders. It also serves as a valuable resource for job seekers. While the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and ""Ban the Box"" policies are widely recognized and implemented, there are specific laws in Texas that demand attention. Companies and HR leaders cannot afford the risks associated with non-compliance. Investing a few minutes to become knowledgeable about these regulations is crucial for maintaining legal and ethical standards."
Why Background Checks Matter for Texas Employers
Risk Mitigation
Background checks play a vital role in mitigating risks associated with negligent hiring. Employers are responsible for ensuring their workplace is safe and secure. Hiring someone with a history of violent behavior, theft, or other criminal activities without proper screening can lead to significant legal and financial consequences.
Safe and Secure Workplace
Maintaining a safe and secure workplace is paramount. Background checks help employers identify potential red flags that could jeopardize workplace safety. By thoroughly vetting candidates, employers can prevent incidents that could harm employees and damage the company's reputation.
Legal Implications
Failing to conduct thorough background checks can result in legal implications. If an employee causes harm and itâÂÂs found that proper background checks were not conducted, employers can face negligent hiring lawsuits. Employers can avoid such legal issues by performing due diligence and complying with relevant laws and regulations.
Understanding Texas Laws and Regulations
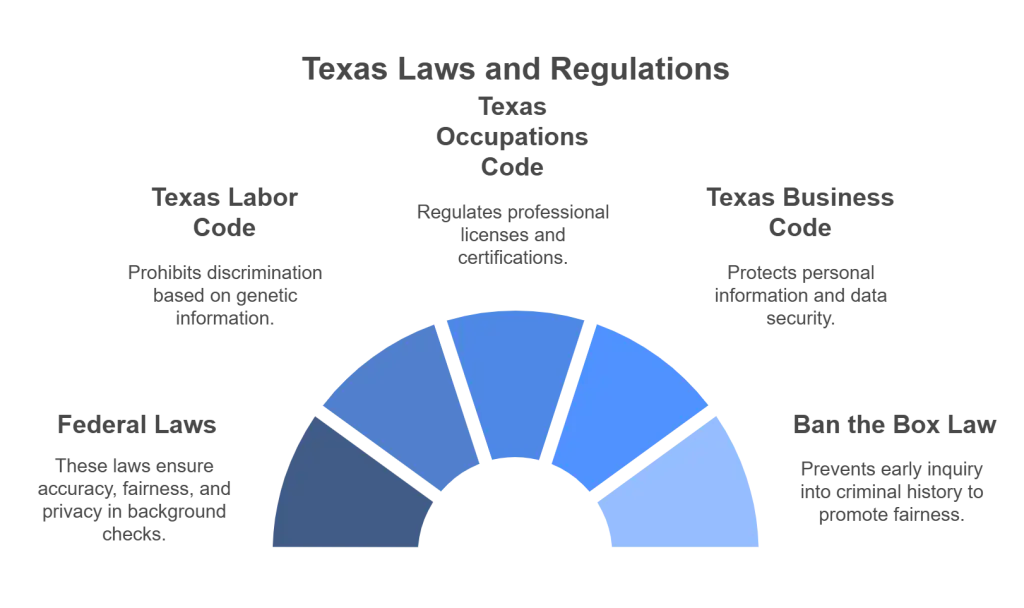
Federal Laws
Several federal laws, including the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), impact background checks. The FCRA ensures the accuracy, fairness, and privacy of information used in consumer reports. Employers must comply with FCRA requirements when conducting background checks, including obtaining written consent and providing specific disclosures and notices.
Texas-Specific Laws
Texas Labor Code Section 21.402
The Texas Labor Code Section 21.402 prohibits employers from refusing to hire or discriminate against individuals with respect to compensation or the terms, conditions or privileges of employment on the basis of genetic information concerning the individual or because of the refusal of the individual to submit to a genetic test.
Texas Occupations Code
The Texas Occupations Code regulates various professional licenses and certifications. Employers must verify the licenses of applicants for specific occupations, ensuring they meet the necessary qualifications and have no disciplinary actions against them.
Texas Business & Commerce Code
The Texas Business & Commerce Code includes provisions related to protecting personal information. Employers must ensure that the data they collect and store during background checks is secure and confidential, complying with state data protection laws.
Ban the Box Law
Texas has a "Ban the Box" law prohibits employers from asking about criminal history on initial job applications. This law aims to provide fairer opportunities for individuals with criminal records by allowing them to be judged based on their qualifications first. Employers can inquire about criminal history later in the hiring process, ensuring compliance with this regulation.
Types of Background Checks Available in Texas
Criminal Background Checks
- State and National Criminal Searches: Criminal background checks are essential for identifying past criminal behavior. Employers can conduct state and national criminal searches to view an applicant's criminal history comprehensively. State searches provide records within Texas, while national searches cover a broader scope, including federal and out-of-state records.
- Fingerprint-Based Checks: Fingerprint-based checks are more accurate and reliable than name-based checks. They involve cross-referencing an applicant's fingerprints with state and federal databases. This method helps eliminate false positives and correctly identifies any criminal records.
- County-Level Records: Checking county-level records is crucial for thorough background screening. These records often contain the most up-to-date and detailed information about an individual's criminal history within specific counties in Texas. Employers should not overlook this critical step.
Credit Reports
Credit reports can provide insight into an applicant's financial responsibility. In Texas, employers can request credit reports for positions that involve financial responsibilities. However, they must comply with the FCRA and ensure the information is relevant to the job.
Employment Verification
Verifying an applicant's employment history helps confirm their qualifications and experience. Employers should contact previous employers to verify job titles, dates of employment, and job performance. This step ensures the accuracy of the information provided by the applicant.
Education Verification
Education verification is essential for positions that require specific degrees or certifications. Employers should contact educational institutions to confirm the applicant's academic credentials. This verification helps prevent fraudulent claims and ensures the applicant is qualified for the position.
Reference Checks
Reference checks provide additional insight into an applicant's work ethic and character. Employers should contact professional references to gather information about the applicant's job performance, strengths, and areas for improvement. Handling reference checks carefully and ensuring they are conducted legally and respectfully.
Other Checks
- Driving Records: Checking an applicant's driving record is crucial for positions involving driving. This check provides information about traffic violations, accidents, or license suspensions. Employers can ensure the applicant is a safe and reliable driver.
- Professional License Verification: For certain professions, verifying professional licenses is mandatory. Employers should check with the relevant licensing boards to confirm the applicant's credentials and ensure there are no disciplinary actions against them. This verification helps maintain professional standards and compliance with regulatory requirements.
The Process of Conducting Background Checks
Obtaining Written Consent
Before conducting a background check, employers must obtain written consent from the applicant. This consent should clearly explain the background check process and what information will be collected. Ensuring transparency with the applicant is crucial for compliance and trust.
Choosing a Reputable Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA)
Selecting a reputable Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA) is vital for accurate and reliable background checks. Employers should research and choose a CRA that complies with FCRA requirements and has a track record of providing comprehensive and precise reports.
Providing Pre-Adverse and Adverse Action Notices
If an employer decides to take adverse action based on the background check results, they must provide the applicant with pre-adverse and adverse action notices. The pre-adverse action notice should include a copy of the background check report and a summary of rights under the FCRA. This allows the applicant to review the information and dispute any inaccuracies. After considering any disputes, the employer can provide the final adverse action notice if they still decide not to hire the applicant.
Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
Throughout the background check process, employers must comply with the FCRA. This includes providing proper disclosures, obtaining written consent, using the information for permissible purposes, and handling disputes appropriately. Failing to comply with the FCRA can result in legal penalties and damages.
Best Practices for Texas Employers
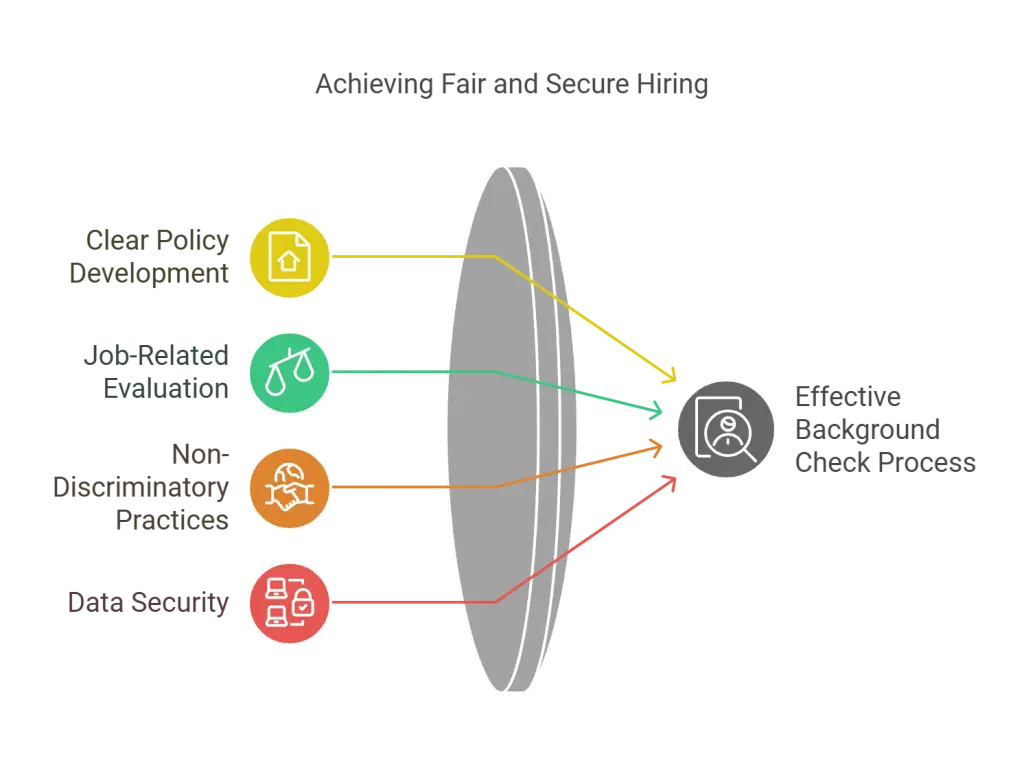
Develop a Clear and Consistent Background Check Policy
Employers should develop a clear and consistent background check policy that outlines the types of checks conducted, the information collected, and how the information will be used. This policy should be communicated to all applicants and employees to ensure transparency and compliance.
Focus on Job-Relatedness
When evaluating background information, employers should focus on the job-relatedness of any findings. This means considering whether the information is relevant to the position and whether it impacts the applicant's ability to perform the job. This approach helps avoid discrimination and ensures fair hiring practices.
Avoid Discriminatory Practices
Employers must treat all applicants fairly and avoid discriminatory practices during the background check process. This includes ensuring all applicants' background checks are conducted consistently and making decisions based on relevant and job-related information.
Ensure Data Security and Confidentiality
Protecting the data collected during background checks is crucial. Employers must ensure that personal information is stored securely and accessed only by authorized personnel. This helps maintain confidentiality and compliance with data protection laws.
FAQs About Texas Background Checks
What are the legal requirements for conducting background checks in Texas?
Employers in Texas must comply with both federal laws, such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), and state-specific regulations, including the "Ban the Box" law, which restricts when employers can inquire about an applicant's criminal history during the hiring process.
How far back do background checks go in Texas?
While the FCRA limits the reporting of certain information to seven years, there are exceptions, especially for positions with higher salaries or specific responsibilities. Additionally, Texas does not have a strict limitation, and the look-back period can vary based on the employer's discretion and the nature of the job.
What types of background checks are commonly conducted by Texas employers?
Common background checks include criminal history searches, employment verification, education verification, professional license verification, motor vehicle records checks, and pre-employment drug tests.
Are there any restrictions on using criminal records in hiring decisions in Texas?
Yes, employers must ensure that the use of criminal records in hiring decisions is job-related and consistent with business necessity. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) provides guidelines to prevent discrimination based on criminal history.
Do Texas employers need consent to perform background checks?
Yes, under the FCRA, employers must obtain written consent from the applicant before conducting a background check. Additionally, if adverse action is taken based on the report, the employer must provide the applicant with a copy of the report and a summary of their rights.
What is the 'Ban the Box' law in Texas?
The 'Ban the Box' law in Texas restricts employers from asking about an applicant's criminal history on initial job applications, allowing candidates to be evaluated based on their qualifications first.
How can employers ensure compliance with background check laws in Texas?
Employers should familiarize themselves with both federal and state regulations, obtain proper consent, use reputable background check services, and apply consistent screening policies to all applicants to ensure compliance.
What should an employer do if a background check reveals negative information?
If a background check reveals negative information, employers should assess the relevance of the information to the job position, provide the applicant with a copy of the report, and allow them an opportunity to dispute any inaccuracies before making a final decision.
Are there specific industries in Texas with additional background check requirements?
Yes, certain industries, such as education, healthcare, and finance, may have additional background check requirements to ensure the safety and security of vulnerable populations and sensitive information.
Can an applicant's credit history be considered in Texas employment background checks?
Employers may consider an applicant's credit history, especially for positions involving financial responsibilities. However, they must comply with the FCRA and ensure that the information is relevant to the job role.
Conclusion
Conducting thorough background checks is essential for Texas employers to make informed hiring decisions and maintain a safe workplace. By understanding and complying with relevant laws and regulations, developing clear policies, and following best practices, employers can navigate the complexities of background checks effectively.
Staying informed about legal updates and best practices is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding legal pitfalls. Employers should consider consulting with legal professionals to ensure their background check processes are robust and compliant.
For more information or assistance with background checks, consider using GCheck, a leading provider of employment background check services. GCheck can help you streamline the process, ensure compliance with Texas laws, and provide accurate and comprehensive reports.
Additional Reads
- Texas Labor Code Section 21.402 (2023) - Discriminatory Use of Genetic Information Prohibited :: 2023 Texas Statutes :: US Codes and Statutes :: US Law :: Justia
- Texas Labor Code Section 21.402 â Discriminatory Use of Genetic Information Prohibited

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.







