Government jobs often come with a host of screenings designed to ensure that candidates are not only qualified but also trustworthy and fit for public service. Whether you're an HR professional, a recruiter aiming to refine your processes, or a job seeker navigating the complexities of public sector applications, this guide will shed light on everything you need to know about government job screening.
Key Takeaways
- Government job screening is essential to ensure that candidates are qualified, reliable, and do not pose security risks.
- The screening process involves multiple checks, including background checks, security clearances, drug testing, financial background checks, qualification verifications, and medical examinations.
- Both job seekers and HR professionals must be prepared; job seekers should have their documents in order and be transparent about their past, while HR professionals should develop clear policies and select reputable vendors.
- Legal considerations, including adherence to EEOC guidelines and ADA compliance, are crucial to ensure ethical practices and protect candidates' rights.
- Common challenges such as screening delays, handling discrepancies, and ensuring compliance can be managed through proactive strategies and transparent communication.
Introduction
Thorough screening in government employment isn't just a formality—it's a crucial barrier that separates the truly qualified and trustworthy from those who might compromise public trust. Imagine the intricacies of government work being handled by someone without the requisite checks; the ramifications could range from mild inefficiencies to serious breaches of national security.
Government job screenings are designed to assess multiple facets of a candidate’s background, from their criminal history to their financial stability. These screenings affect everyone in the public sector pipeline, from aspiring fresh graduates looking for their first gig to seasoned professionals transitioning between roles at different levels of government—federal, state, or local.
This article dives deep into these multifaceted screening procedures, providing HR professionals, recruiters, and job seekers alike with a comprehensive guide to navigating and understanding this essential process.

What is Government Job Screening?
Government job screening is the vetting process used to ensure that candidates for public service roles are qualified and reliable. Its primary objectives include verifying credentials, assessing reliability and trustworthiness, and ensuring that candidates do not pose any security risks.
These screenings are rigorous for several reasons. Public trust hinges on the caliber and integrity of government employees. Whether it's handling sensitive information, enforcing laws, or making decisions that impact communities, government roles carry significant responsibility. Thus, the screening processes are designed to mitigate risks associated with deceitful, unqualified, or potentially dangerous hires. Furthermore, in positions that involve national security, the stakes are even higher. Any lapse in the vetting process could have severe repercussions.
Government job screening is widespread across all levels of government. At the federal level, positions in agencies like the FBI, CIA, and Department of Defense necessitate meticulous background checks and security clearances. State governments also implement stringent screening for roles within law enforcement, public health, and education sectors. Local governments, responsible for community-centric services like policing, firefighting, and public works, similarly enforce thorough vetting to ensure community safety and efficiency.
In essence, government job screening is a multifaceted, essential process aimed at upholding public service's efficacy, security, and trustworthiness.
EXPERT INSIGHT: As an HR professional, I have always believed that trust is the essential currency of any model recruitment process; in government, this trust is exponentially greater. While I have no direct experience with the governmental recruitment process, I have a deep appreciation for the gravity of the responsibility of hiring someone into a role that impacts whole communities. The review process for government roles is more than procedural adherence—it is about protecting the integrity of public service and ensuring every applicant is duly qualified to maintain its standards. In conducting the screening process with compassion, rigor, and objectivity, we are not only hiring but also contributing to a fairer and safer society. - Charm Paz, CHRP
Types of Government Job Screenings
Background Checks
- Overview: Background checks are a non-negotiable part of the government hiring process, scrutinizing personal history to ensure integrity and suitability. This encompasses various facets, such as criminal records, employment verification, and even social media profiles. For a deeper dive, including frequently asked questions, check out these valuable insights.
- Criminal History: Criminal background checks are conducted to identify any past legal issues that could pose a risk to government operations or public trust. These checks can range from local and state databases to national and international criminal records, ensuring a comprehensive review.
- Employment Verification: This confirms that a candidate's work history is accurate and aligns with their resume. It involves contacting previous employers to verify job titles, dates of employment, and reasons for leaving.
Security Clearances
- Levels of Clearance: Security clearances come in multiple levels: confidential, secret, and top secret. Each level requires a different depth of investigation and is tied to the sensitivity of the information the employee will handle.
- Detailed Process: Obtaining a security clearance is a rigorous journey, beginning with an extensive background investigation. This includes interviews with acquaintances, financial history checks, and sometimes even polygraph tests. The process can take from a few months to over a year, depending on the clearance level and complexity.
Drug Testing
- Prevalence: Drug tests are standard in government employment due to the potential impact of substance abuse on job performance and public safety. Random drug testing may also continue throughout employment.
- Legal Aspects: Federal regulations govern drug testing policies, mandating procedures that respect privacy while ensuring a drug-free workplace. These regulations are designed to uphold fairness and accuracy in testing.
Financial Background Checks
- Rationale: For certain government roles, a clear financial history is essential. This is particularly crucial for positions involving financial decision-making or access to classified information, where financial instability could render individuals vulnerable to coercion.
- Key Areas: Financial background checks examine several aspects, such as credit scores, outstanding debts, and any history of bankruptcies. This assessment helps in understanding the candidate's financial responsibility and potential risks.
Qualification Verifications
- Education: Verification of academic credentials is crucial to confirm that candidates have the necessary educational background for the job. This involves checking the authenticity of degrees and certifications provided by the applicant.
- Professional Licenses: Certain government positions require specific professional licenses or certifications. Verifying these credentials ensures that candidates are legally permitted and properly qualified to perform their job functions.
Medical Examinations
- Purpose: Medical exams are part of ensuring that candidates meet the physical and mental demands of the job. This is especially important for roles that involve strenuous activity or critical decision-making.
- Scope: Common assessments may include physical fitness tests, vision and hearing exams, and psychological evaluations. These examinations verify that the candidate can perform their duties without health-related limitations compromising their effectiveness.
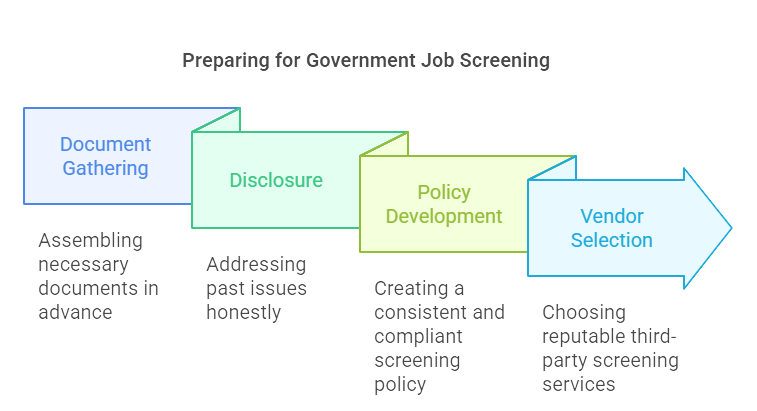
Preparing for Government Job Screening
For Job Seekers:
Document Gathering: Start by assembling all necessary documents well in advance. These typically include valid identification, academic transcripts, certifications, past employment records, and references. It's crucial to have these orderly and easily accessible to avoid last-minute scrambles and ensure a smooth screening process.
Disclosure: Facing your past issues head-on is key. If there are elements in your history that might raise red flags—such as criminal records or financial difficulties—prepare to discuss them honestly during the application process. Transparency is essential; employers appreciate candidates who are upfront and can explain past challenges and how they have overcome them. Consider seeking legal advice if you're unsure how to disclose sensitive information.
For HR Professionals and Recruiters:
Policy Development: A well-defined, consistent, and legally compliant screening policy is a cornerstone of efficient government hiring. This entails understanding and adhering to federal regulations, including EEOC guidelines, to ensure fair and unbiased screenings. Document these procedures clearly and train your team to apply them uniformly.
Vendor Selection: Engage only reputable third-party screening services. Vet potential vendors to ensure they follow legal standards, deliver accurate results, and provide detailed reporting. Reliability in vendor selection not only affects the quality of your screening process but also impacts your organization's integrity and compliance. Prioritize those with positive reviews, transparent pricing, and proven track records in government employment screenings.
Legal Considerations
When it comes to screening for government employment, adhering to legal guidelines is crucial to ensure ethical practices and protect candidate rights. This section covers key legal aspects that HR professionals and recruiters must navigate.
Fair Hiring Practices
EEOC Guidelines: Compliance with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines is non-negotiable. The EEOC enforces laws that make it illegal to discriminate against a job applicant or an employee due to race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or genetic information. When designing screening policies, it’s essential to develop criteria that do not inadvertently exclude these protected groups. For instance, blanket bans on hiring individuals with criminal records could disproportionately affect certain demographics and lead to claims of indirect discrimination.
ADA Compliance: The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) adds another layer of complexity to the screening process. The ADA prohibits discrimination based on disability and requires that employers make reasonable accommodations for qualified individuals. Pre-employment screenings must be navigated carefully to stay compliant. This means medical examinations and disability-related questions should only be conducted after a conditional offer of employment has been made. Moreover, any medical information obtained must be kept confidential and separate from general personnel files.
Candidate Rights and Privacy
Informed Consent: Before conducting any screening, you must obtain written consent from the candidate. This is typically standard but cannot be overlooked. Informed consent involves disclosing what types of checks will be conducted, how the information will be used, and the potential consequences of the findings. Transparent communication builds trust and ensures that candidates are fully aware of what to expect.
Data Protection: Handling sensitive information responsibly is not just good practice; it's a legal requirement. The information gathered during screenings often includes personal identification details, financial records, and medical history. Best practices for data protection involve secure storage solutions, limited access to sensitive information, and clear policies for data retention and disposal. Compliance with laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) guidelines for consumer information could be necessary, depending on the jurisdiction and the data involved.
By meticulously adhering to these legal considerations, HR professionals and recruiters can ensure fair, non-discriminatory, and transparent screening processes, thereby safeguarding both the organization and the candidates.
Common Challenges and Solutions
When it comes to screening for government employment, obstacles are inevitable. It's not just about identifying them but tackling them head-on without sacrificing the integrity of the hiring process. Here’s how you can manage some of the most common challenges.
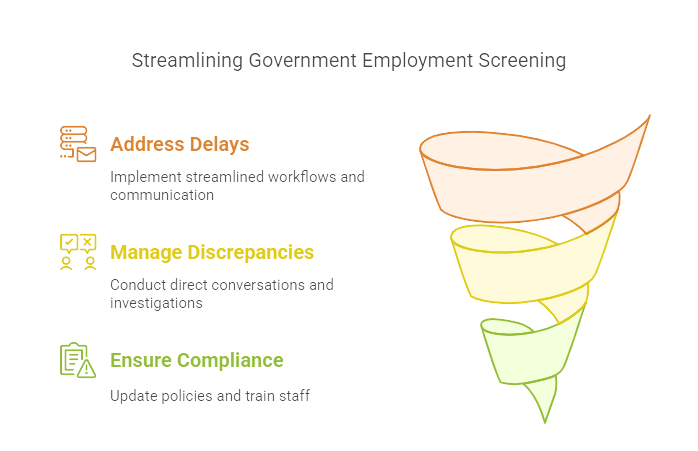
Addressing Screening Delays
Screening delays can throw a wrench in the hiring process, leading to extended vacancies and frustrated candidates. To mitigate these delays, consider implementing a more streamlined workflow. Automate wherever possible—integrate software that can handle initial background checks and flag discrepancies early. Additionally, keep an open line of communication with all parties involved. Transparency about expected timelines can soften the frustration of delays.
Handling Discrepancies
Discrepancies between candidate-provided information and screening results can be a thorny issue. The key is to approach this methodically. Start with a direct conversation with the candidate—sometimes, some simple explanations or errors can be easily clarified. For more serious conflicts, establish a set protocol for further investigation. Maintaining detailed records and documentation throughout this process can be invaluable for both resolving the issue and protecting your organization legally.
Ensuring Compliance
Staying compliant with the myriad of legal requirements is a continuous challenge. Regularly review and update your screening policies in alignment with current regulations. It’s prudent to consult with legal advisors to ensure your practices comply with the latest federal and state laws, including EEOC and ADA guidelines. Training your staff on these policies and protocols can also go a long way in maintaining a consistent and fair screening process.
In essence, while screening for government employment is fraught with challenges, proactive strategies can significantly smoothen the process. By addressing delays, managing discrepancies wisely, and rigorously ensuring compliance, you can uphold both the efficiency and integrity of your screening procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What happens if discrepancies are found during a background check?
If discrepancies are discovered during a background check, the hiring agency will typically follow a set protocol. This might include further investigation or requesting additional documentation from the candidate to clarify the discrepancy. The outcome can vary: it might delay the hiring process, lead to disqualification, or, if satisfactorily resolved, have no further impact. Transparency and prompt communication with the hiring body can often mitigate potential issues.
Can candidates be denied employment based on their financial history?
Yes, candidates can be denied employment based on their financial history, especially for positions that require a high level of trust or involve financial responsibilities. Factors such as unresolved debt, bankruptcies, or poor credit scores can raise red flags about a candidate's reliability and risk management abilities. It's essential, however, that the evaluation is fair and considers the context of the financial issues.
How long does it typically take to obtain a security clearance?
The time required to obtain a security clearance can vary widely depending on the level of clearance sought and the thoroughness of the background investigation. On average, confidential and secret clearances may take a few weeks to several months, while top-secret clearances could take up to a year or longer. Factors affecting this include the complexity of the applicant's background, foreign contacts, and the thoroughness of the vetting process.
Are there resources available for job seekers to check their background in advance?
Yes, several resources are available for job seekers to preemptively check their background. Websites like AnnualCreditReport.com allow individuals to obtain a free credit report annually. Additionally, various online services offer criminal background checks for a fee. It's wise to review these reports for accuracy and address any discrepancies or issues before applying for government positions. This proactive approach can expedite the overall screening process and reduce potential obstacles.
Conclusion
Government job screening is a multilayered process, crucial for maintaining national security and public trust. From thorough background checks and security clearances to detailed financial and medical evaluations, each step serves a purpose in ensuring that only the most suitable candidates enter public service.
Looking ahead, we can anticipate more advanced technologies and AI in the screening process, potentially reducing delays and increasing accuracy. Additionally, evolving legal frameworks will likely shape new guidelines and best practices, requiring HR professionals and recruiters to stay informed and adaptive.
Ultimately, the importance of diligence and transparency in government job screenings cannot be overstated. By adhering to rigorous standards and being mindful of legal considerations, we can foster a more secure and trustworthy public sector.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






