When conducting background checks, HR professionals and recruiters often encounter disputes from candidates concerning the information revealed. Handling these disputes effectively is essential for maintaining the integrity of the hiring process and ensuring compliance with legal standards. This guide aims to demystify the background check dispute process, providing practical steps and insights to handle candidate disputes professionally and efficiently.
Key Takeaways
- Prompt Acknowledgment of Disputes: When a candidate disputes information in their background check, acknowledge the dispute promptly to demonstrate professionalism and commitment to resolving the issue.
- Thorough Investigation: Conduct a comprehensive investigation into the disputed information, collaborating with the background check provider to verify accuracy and rectify any errors.
- Transparent Communication: Maintain open communication with the candidate throughout the dispute resolution process, informing them of findings and any corrective actions taken to ensure transparency and trust.
- Legal Compliance: Adhere to the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and other relevant laws, ensuring candidates are aware of their rights and the procedures for disputing inaccuracies in their background reports.
- Pre-Dispute Measures: Implement clear communication strategies, obtain informed consent, and verify information accuracy before conducting background checks to minimize the likelihood of disputes arising.
Introduction
Picture this: you're all set to hire a promising candidate when their background check reveals a discrepancy. The candidate, confident in their history, raises an immediate dispute. It's a scenario more common than you might think, with a notable percentage of background checks leading to some form of contention. In fact, data from recent surveys suggests an upward trend in disputes, largely driven by increased access to personal information and heightened awareness of one’s rights.
So, why is it crucial to resolve these disputes efficiently? Simply put, mishandling them can cost you a great hire and expose your organization to legal risks. Moreover, a proactive and fair dispute resolution process reinforces your company's commitment to transparency and respect for candidate rights.
In this article, you'll find a step-by-step roadmap to help HR professionals and recruiters deftly navigate background check disputes. From understanding the legal landscape to implementing best practices, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to handle disputes effectively and stay compliant in a rapidly evolving regulatory environment.
EXPERT INSIGHT: No matter how careful we are in following the process, no one is safe in facing disputes. As HR professionals, how we handle them reflects how we embody fairness and transparency. It is vital that we address each dispute with care and respect, ensuring that both the candidate's concerns and the organization's integrity are given the utmost consideration. Not only that, clear communication throughout the process reassures candidates that their concerns are taken seriously. Overall, an effective dispute resolution process fosters a more inclusive environment for all the people involved. - Charm Paz, CHRP
Understanding the Background Check Dispute Process
What is a Background Check Dispute?
When a candidate raises an issue with the information uncovered during a background check, that's a background check dispute. Disputes can stem from various issues, such as inaccuracies in the report, identity theft, or outdated information. Essentially, it’s any challenge by the candidate to contest the findings in their background report.
Legal Framework
Navigating the legal landscape of background check disputes is crucial. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is the cornerstone for these regulations in the United States. Under the FCRA, candidates can dispute any information they believe is incorrect. Employers must then conduct an investigation, typically in collaboration with the consumer reporting agency, to verify the accuracy of the contested information.
Why Disputes Occur
Disputes commonly arise for several reasons:
- Clerical Errors: Simple mistakes in data entry can lead to incorrect information being reported.
- Identity Confusion: Sharing a name or similar personal details with another individual can lead to mismatched data.
- Outdated Records: Not all databases update in real-time; sometimes, old information slips through.
- Identity Theft: Fraudulent activities where someone else's information is used can significantly skew a background report.
Understanding these factors can help HR professionals prepare and respond more effectively when disputes occur.

Pre-Dispute Measures
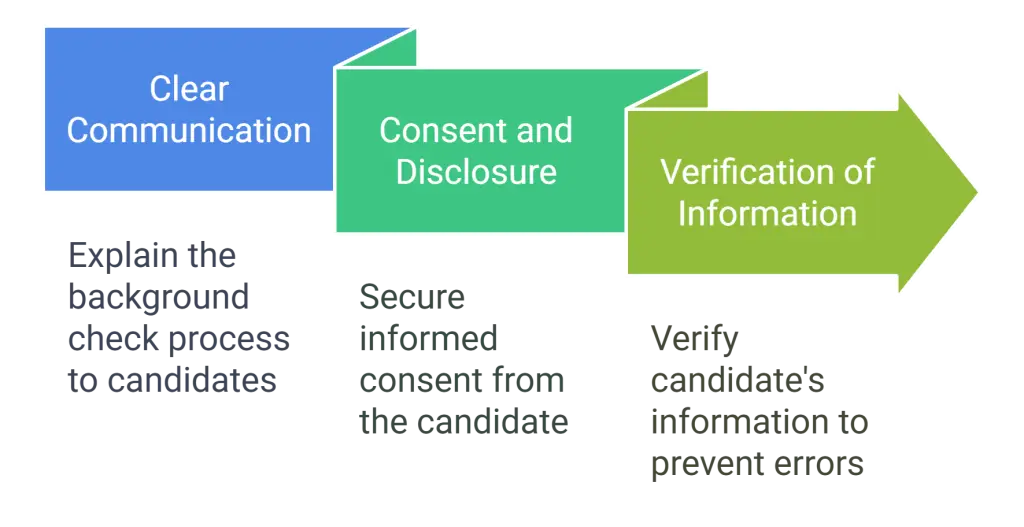
Clear Communication
First things first, your communication with the candidate needs to be top-notch. When you're clear and upfront about the background check process, you reduce the ambiguities that often lead to disputes. Lay the groundwork for transparency right from the get-go. Explain to candidates what the background check entails, what information will be reviewed, and why it's necessary. A well-informed candidate is less likely to be surprised or upset by the findings, making disputes less frequent.
Consent and Disclosure
A fundamental step in the process is securing informed consent from the candidate. This is a legal requirement under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and sets a tone of mutual respect and professionalism. Make sure the consent form is easy to understand and openly accessible. When candidates are fully aware of their rights and the scope of the background check, they're better prepared, and this clarity can help preempt some common disputes.
Verification of Information
Before you hit "send" on that background check report, take a moment to double-check. Verification of information is your safety net against avoidable errors. Cross-reference the candidate's details with the information gathered to ensure everything aligns accurately. This check involves confirming employment dates and educational qualifications and ensuring no clerical errors like spelling mistakes in names. It's an extra step but can save you and the candidate a significant headache.
Steps for Handling Candidate Disputes
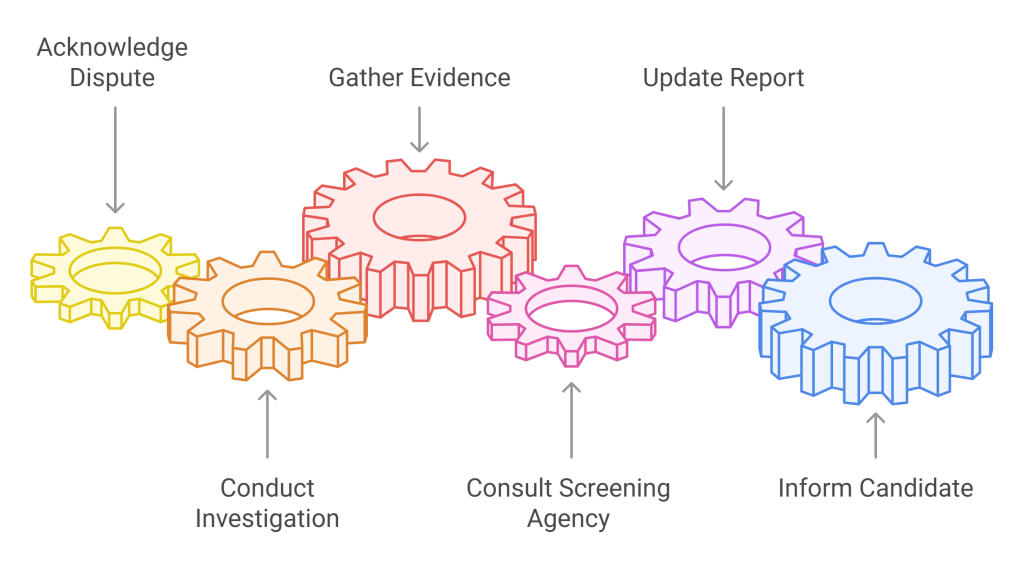
1. Acknowledge the Dispute
First, you need to acknowledge the dispute as soon as it arises promptly. Ignoring or delaying this can lead to many problems, from disgruntled candidates to potential legal issues. Quick acknowledgment demonstrates professionalism and sets the tone for a transparent resolution process.
Start with a clear, direct communication. You don’t need to reinvent the wheel; a concise template can work wonders. Here’s a straightforward example:
Subject: Acknowledgment of Your Background Check Dispute
Dear [Candidate’s Name],
We have received your dispute regarding the background check and are currently reviewing the information in question. Your concerns are important to us, and we are committed to resolving this matter as quickly and fairly as possible.
We will keep you informed of our progress and any necessary steps we may need to take.
I appreciate your patience.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
[Your Position]
[Company Name]
[Contact Information]
This type of communication serves two main purposes: it reassures the candidate that their dispute is being taken seriously, and it buys you a bit of time to gather your ducks in a row for the next steps. Balancing promptness with thoroughness is key—act swiftly, but don’t rush the process.
2. Investigation
Once a dispute is acknowledged, the next crucial step is to conduct a thorough investigation. This isn't the time for half-measures. Thoroughness is key to ensuring the credibility of your hiring process remains intact.
Gathering Evidence
Start by collecting all pertinent documents related to the disputed information. This includes the candidate’s initial application, any records obtained from the background check, and any additional documentation the candidate provides to support their dispute. Every piece of information should be scrutinized meticulously.
Create a checklist:
- Candidate’s original application/resume
- Background check report
- Supporting documents from the candidate (e.g., letters of explanation, identity documents)
- Correspondence between the candidate and your team regarding the dispute
Consulting the Screening Agency
Communication with your background check provider is essential. Inform them about the dispute and request a re-verification of the specific information. Screening agencies are legally required to reinvestigate the item disputed by the candidate and update the information if necessary.
Steps to consult the screening agency:
- Notify: Inform the screening agency about the dispute in detail.
- Details: Provide specific details and documents concerning the dispute.
- Follow-up: Maintain a channel of communication for updates on the re-verification process.
Keep notes of every interaction:
- Dates of communication
- Representatives spoken to
- Information exchanged
Throughout the investigation, maintain an impartial stance. Your goal is not to prove the candidate right or wrong but to ensure that all information is accurate and fair. This approach helps maintain the integrity of your hiring process and your organization's reputation.
3. Resolution
Handling the resolution phase of a background check dispute involves updating the report to reflect accurate information and informing the candidate of the outcome. Here’s a straightforward approach to tackle both tasks effectively.
Updating the Report
Once an investigation confirms an error in the background check, the first step is to update the report. This process includes the following actions:
- Correcting Inaccuracies: Amend any incorrect information documented in the initial background check report. Ensure that all erroneous entries are accurately rectified.
- Documenting Changes: Keep a detailed log of all modifications made to the report. This is crucial for maintaining an audit trail and for potentially providing evidence in case of future disputes.
- Verifying Updates: After making necessary amendments, verify that the corrections align with credible sources. Double-check with databases or entities that provided the initial data to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Informing the Candidate
Once the report is updated, the next crucial step is to notify the candidate of the resolution. Here's how to do that properly:
- Clear Communication: Explain the outcome of the dispute to the candidate using straightforward, concise language. Avoid jargon and ensure your explanation is easy to understand.
- Provide Documentation: Supply the candidate with a copy of the revised background check report and a summary of the changes made.
- Outcome Notification: Clearly state whether the disputed item was found to be incorrect and was subsequently updated or if the original information was verified as accurate and remains unchanged.
- Next Steps Guidance: If the candidate's dispute was not resolved satisfactorily, offer guidance on potential next steps. This could include providing contacts for further appeals or letting them request additional information related to the dispute.
By promptly updating the report and efficiently communicating with the candidate, you demonstrate a commitment to fairness and transparency, which is crucial in maintaining trust and compliance in the hiring process.
Best Practices for Resolving Background Check Disputes
Adopting a structured approach can make a significant difference when navigating background check disputes. Incorporating best practices ensures efficiency and transparency, so let's focus on the essentials:
Documentation
It is crucial to keep meticulous records at every step of the dispute process. This includes logging the initial dispute submission, outlining all subsequent communications with the candidate and any third parties involved, and documenting the investigation process. Detailed records serve as a reference point for future disputes and are indispensable in demonstrating compliance with legal requirements.
Timeliness
Addressing disputes promptly is vital. Delays can stall the hiring process, causing frustration for both the candidate and the hiring team. Establish a clear timeline for each step of the dispute process, from acknowledgment to resolution, and strive to adhere to these deadlines. Quick resolutions reflect positively on your organization and mitigate the risk of legal complications.
Transparency
Maintaining transparency with the candidate is key to building trust and ensuring a fair process. Clearly communicate each stage of the dispute process, provide regular updates, and explain any findings or decisions comprehensively. An open approach not only eases candidate anxiety but also underscores your commitment to fairness and accuracy.
By diligently documenting the dispute process, acting swiftly, and maintaining transparency, HR professionals and recruiters can handle disputes effectively, ensuring a seamless hiring experience while upholding the integrity of their background check procedures.
Post-Dispute Actions
After the dust has settled, it's crucial to step back and evaluate the entire dispute resolution process to ensure continual improvement in handling future disputes. Here's a structured approach to post-dispute actions that deserves your attention.
Review and Reflect
Once a dispute has been resolved, take the time to review the steps taken and the outcomes achieved thoroughly. This process should involve:
- Team Debrief: Hold a meeting with your HR team and any involved parties to discuss what worked well and what didn’t. This collaborative reflection can uncover valuable insights.
- Identify Root Causes: Determine the core issues that led to the dispute. Was it a clerical error, outdated information, or perhaps a gap in your communication process? Understanding these underlying causes will help prevent similar disputes in the future.
Policy Updates
Based on your review and reflection, you may identify areas where your internal policies and procedures need adjustment. This might include:
- Updating Templates and Scripts: Revise your communication templates and scripts to address any deficiencies identified during the dispute.
- Enhancing Verification Processes: Ensure your verification processes are robust enough to catch errors before they escalate into disputes.
- Training Programs: Implement or refresh existing training programs to update your team on best practices and current legal standards.
Continuous Improvement
The goal is to turn each dispute into an opportunity for improvement. Establishing a culture of continuous improvement involves:
- Feedback Loop: Create a feedback mechanism where candidates and employees can report issues and suggestions for handling disputes better.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your background check processes to ensure compliance with legal standards and to maintain high accuracy.
- Benchmarking: Compare your procedures with industry best practices and adjust accordingly. Keeping an eye on trends and new regulations will keep your processes current and effective.
By taking these post-dispute actions seriously, you will strengthen your background check procedures and enhance your overall hiring process, making it fairer and more efficient for all parties involved.
Legal Considerations and Compliance
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is the cornerstone of handling background check disputes. Enacted in 1970, the FCRA regulates how consumer credit information is collected, accessed, and used. For HR professionals, this means strict adherence to procedures when disputes arise. The FCRA mandates that candidates have the right to know if information in their background check has been used against them, and they must be provided with a notice outlining their rights, including the ability to dispute inaccurate or incomplete information with the reporting agency.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with the FCRA can lead to severe repercussions for both the organization and the individual employees responsible. Potential penalties include fines, litigation costs, and reputational damage. Organizations can be fined up to $1,000 per violation in addition to any actual damages incurred by the candidate. Furthermore, non-compliance can erode trust and lead to costly and time-consuming legal battles.
Resources for Staying Informed
Staying current with legal requirements is imperative for minimizing risks. Resources like the Professional Background Screening Association (PBSA) offer a wealth of information, including legal updates, best practices, and training opportunities. It's crucial for HR professionals to regularly consult legal counsel and subscribe to industry updates to stay ahead of changes in the regulatory landscape.
By understanding and adhering to these legal frameworks, HR professionals can navigate the complexities of background check disputes while safeguarding their organization against legal pitfalls.

Common Challenges and Solutions
Dealing with background check disputes can be tricky. Here are some common challenges and ways to handle them effectively.
Uncooperative Candidates
Finding yourself dealing with an uncooperative candidate? It can be frustrating, but it's important to remain professional. Start by ensuring all communication is clear and respectful. Document every interaction meticulously. You might need to set response deadlines, clarifying that the hiring process depends on their cooperation. If a candidate continues unresponsive, consider escalating the matter to higher management or legal advisors while complying with all relevant legal guidelines.
Complex Cases
Supporting candidates in resolving complex disputes, such as those involving cross-border information or identity theft, requires a nuanced approach. For cross-border disputes, be aware of the different privacy laws and regulations in play. It might be necessary to consult with legal experts who specialize in international law. In identity theft cases, the candidate may need to gather substantial evidence, such as police reports or affidavits. Work closely with your screening agency to ensure thorough re-verification and involve third-party experts if necessary.
Balancing Fairness and Company Interests
Striking a balance between fairness to the candidate and protecting your company's interests is crucial. One approach is establishing a consistent policy for handling disputes, ensuring that every case is treated fairly. Apply the same scrutiny and process for all candidates to avoid any bias. When in doubt, consult with legal counsel to ensure your approach aligns with fairness and compliance standards. Remember, a transparent process protects the candidate and enhances your company's reputation and trustworthiness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What should I do if a candidate disputes their background check information?
If a candidate disputes their background check information, the first step is promptly acknowledging their concern. Use a standard template to communicate that their dispute has been received and that you take their claim seriously. Here's a simple script:
"Dear [Candidate's Name],
Thank you for bringing this to our attention. We have received your dispute regarding the background check information and are investigating the matter. We will update you with the findings as soon as possible. If we need additional information from you, we will reach out promptly."
Then, follow the necessary steps to validate the dispute, including gathering evidence and consulting with the screening agency.
How long does the dispute process typically take?
The length of the dispute process can vary depending on the complexity of the dispute and the responsiveness of all parties involved. Generally, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) mandates that disputes should be resolved within 30 days. However, it's best to aim for a quicker resolution to maintain the flow of your hiring process and show candidates that you value their time and concerns.
Can a candidate be hired if there is an unresolved dispute in their background check?
It depends on your company’s policy and the nature of the position being filled. In some cases, candidates may be hired provisionally or conditionally, with the understanding that their employment is contingent upon resolving the dispute. It’s crucial to communicate clearly with the candidate about their employment status during the dispute resolution process to manage expectations and maintain transparency.
What are the most common reasons for background check disputes?
Common reasons for background check disputes include:
- Clerical Errors: Mistakes made in data entry that result in incorrect information being reported.
- Identity Confusion: Instances where an applicant’s information is confused with another individual with a similar name or details.
- Outdated Information: Records that have not been updated to reflect more recent, accurate information.
- Misleading Information: Data misrepresented or taken out of context leads to incorrect conclusions about the candidate’s background.
- Identity Theft: Cases where the candidate is a victim of identity theft and fraudulent activities are incorrectly attributed to them.
Addressing these issues accurately and promptly helps maintain trust in the hiring process and ensures compliance with legal standards.
What is a candidate dispute in a background check?
A candidate dispute occurs when a job applicant challenges the accuracy of information in their background check report, such as incorrect criminal records or employment history.
How can candidates dispute background check errors?
Candidates can dispute errors by contacting the background check company directly, providing evidence of inaccuracies, and requesting an investigation under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
What is the employer’s role during a background check dispute?
Employers must pause adverse hiring decisions during a dispute and allow the candidate time to resolve the issue with the background check provider.
How long does it take to resolve a background check dispute?
Disputes typically take 30 days to resolve, as required by the FCRA. However, the timeline may vary depending on the complexity of the issue.
What are common reasons for background check disputes?
Common reasons include outdated information, identity mix-ups, incomplete criminal records, or inaccuracies in employment or education history.
Can a job offer be rescinded during a background check dispute?
Employers cannot rescind a job offer solely based on disputed information until the issue is resolved, as required by FCRA guidelines.
What are FCRA requirements for candidate disputes?
The FCRA requires background check companies to investigate disputes within 30 days, correct inaccuracies, and provide the candidate with updated results.
What should candidates do if a background check dispute is unresolved?
If a dispute remains unresolved, candidates can file a complaint with the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) or take legal action for non-compliance under the FCRA.
Do employers have to notify candidates of background check results?
Yes, if adverse action is being considered, employers must notify candidates with a pre-adverse action notice, a copy of the background check report, and a summary of their rights under the FCRA.
How can employers minimize disputes in background checks?
Employers can minimize disputes by partnering with reputable, FCRA-compliant background check providers and ensuring clear communication with candidates about the process.
Conclusion
Navigating candidate disputes during background checks can be challenging, but it's imperative for a fair and compliant hiring process. You can handle these situations professionally and efficiently by following key steps—acknowledging disputes promptly, conducting thorough investigations, and ensuring transparent communication.
Recap the essentials: communicate clearly with candidates from the outset, verify information meticulously, and keep detailed records throughout the dispute process. Timeliness and transparency are not just best practices but vital to maintaining trust and avoiding legal repercussions.
Remember, every dispute is an opportunity to refine your background check procedures and strengthen your company's reputation for fairness. As you implement these recommendations, stay vigilant about legal updates and industry best practices.
Dive into our comprehensive guide, adjust your processes as needed, and ensure your hiring practices are as robust and fair as possible. Explore our resources and stay informed for more insights and updates. Your commitment to fair hiring practices will serve your organization and your candidates well.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.






