Navigating the maze of background check regulations can be daunting for businesses, especially when state-specific laws come into play. For companies operating in Iowa, understanding and adhering to Iowa background check laws is crucial in ensuring smooth hiring processes and maintaining compliance. Whether you're in staffing, healthcare, transportation, or any other industry where employee screening is a critical component, this guide will arm you with the knowledge needed to stay compliant.
Key Takeaways
- Iowa's background check laws require a nuanced understanding due to the state's permissive legal framework, which permits employers to inquire about criminal history without a "ban the box" mandate, though discretion is advised.
- Compliance with federal regulations, particularly the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines, is crucial for Iowa employers to ensure non-discriminatory and legally sound hiring practices.
- The employment screening process in Iowa demands industry-specific best practices, thorough candidate consent and disclosure, and careful handling of adverse actions to align with state and federal laws.
- Common challenges in Iowa background checks include misunderstanding consent and disclosure requirements and navigating industry-specific regulations. A deep understanding of state laws is essential for legal compliance.
- To maintain continuous compliance, Iowa businesses must engage in ongoing education, conduct regular internal audits, leverage technology to adapt to legal changes and ensure a thorough background check process.
Introduction
In the intricate world of hiring, Iowa background check laws are vital for anyone seeking employment or those employed in the state. For business owners, HR professionals, and recruiters across sectors such as staffing, healthcare, and transportation, grasping these laws isn't just a good ideaâÂÂit's essential. It helps ensure that hiring practices align with legal standards, thus protecting the organization and its potential employees.
This guide aims to clarify the often complex labyrinth of Iowa's employment screening requirements. We'll explore the distinct legal framework specific to Iowa, outline the intersection with federal rules like those from the FCRA, and clarify industry best practices. We'll explore compliance, consent, disclosure, and handling adverse actions. This knowledge will empower stakeholders to navigate the hiring process effectively while remaining firmly on the right side of the law.
I remember when a top-notch candidate almost slipped through our radar because we were doing background check compliance so loosely. In Iowa, where we have no âÂÂban the boxâ law, gray areas of legality can be temptingâÂÂbut a trap if we approach without caution and heart. As HR professionals, we are not gatekeepers; we are bridge-builders between people and policy. True compliance isn't check-the-boxesâÂÂit's about preserving dignity in making smart, informed hires. When we approach from head and heart, we design a hiring process that isn't merely compliant, but human.
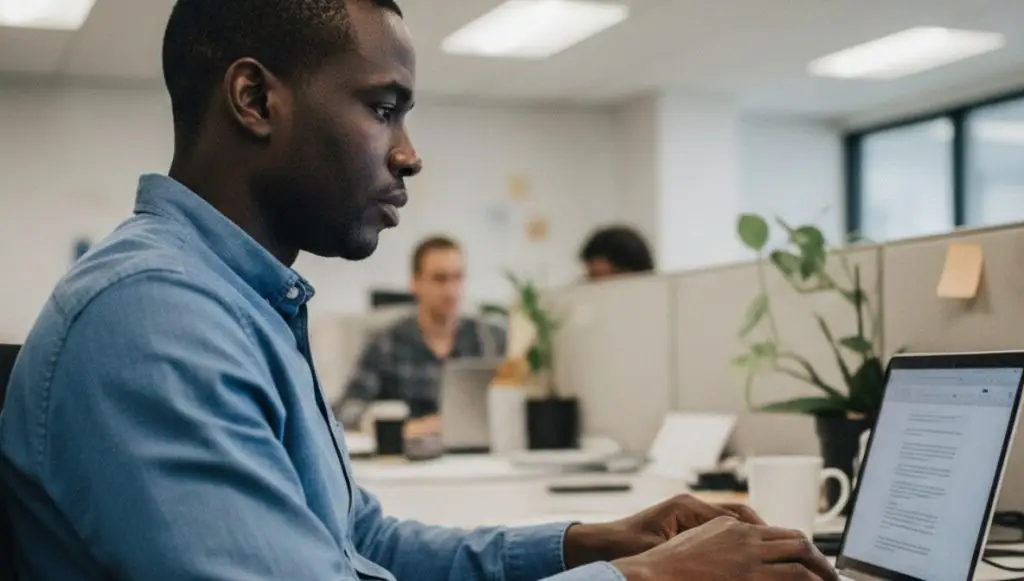
Understanding Iowa Background Check Laws
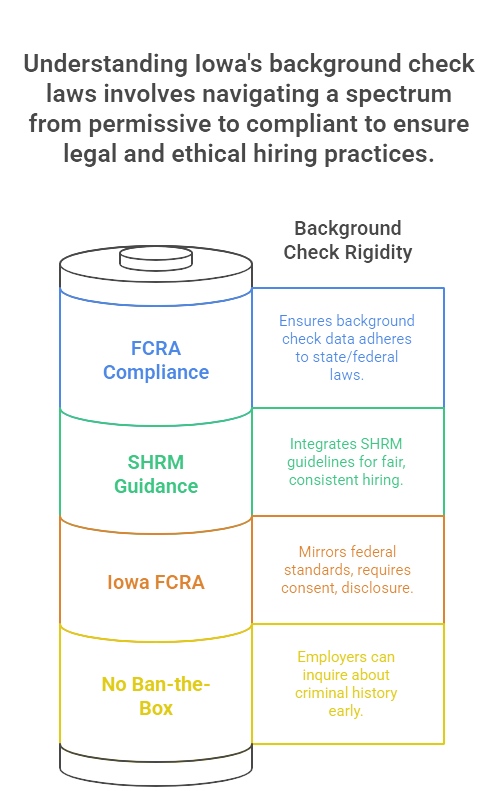
When it comes to Iowa background check laws, specific nuances distinguish them from those of other states. Unlike some regions with rigid mandates, Iowa leans towards a more permissive framework, yet there are crucial elements businesses must understand. For starters, Iowa does not have a "ban the box" law at the state level, although certain localities might. This absence means employers can inquire about criminal history at any stage, but discretion and relevance should guide these inquiries to avoid discrimination claims.
Additionally, the Iowa Fair Credit Reporting Act (Iowa Code ç 692.2) aligns with federal standards, requiring employers to obtain written consent before conducting background checks and to disclose findings before taking adverse actions. These regulations are crucial for businesses to ensure compliance and fairness during hiring, minimizing risks of discrimination claims and maintaining transparency with job applicants. Understanding the specific local and state requirements helps employers avoid legal pitfalls while building a compliant and equitable hiring process.
The legal landscape also integrates guidelines from the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), which advises on fair and consistent hiring practices. Businesses in Iowa must align such guidance with state specifics to minimize legal exposure. For instance, adopting SHRM's stance on balancing the relevance and timing of background checks can be beneficial without contravening Iowa's business-friendly legal environment.
Consumer reporting agencies can lawfully provide confusing information in gray areas. In Iowa, it's crucial to ensure that background check data complies with state and federal laws as set by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). Understanding these distinctions allows employers to tread cautiously through the nebulous space of employment screening, ensuring thorough compliance while respecting individual privacy rights. Iowa businesses can maintain an edge in lawful hiring practices by navigating these specific differences and potential ambiguities.
The Role of Federal Regulations
Understanding Iowa background check laws requires a grasp of federal guidelines, namely the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). This act is pivotal for Iowa employers as it outlines the standards for obtaining and using consumer reports. To comply with the FCRA, you need to lawfully request background checks, provide clear disclosures to job applicants, and obtain their explicit permission before proceeding. Ignoring these steps can lead to hefty penalties and legal challenges.
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) also casts a long shadow over state-specific practices. It mandates that any background check used in employment decisions must be consistently applied to all candidates to ensure checks do not unintentionally result in discrimination. An Iowa employer must balance these federal mandates with state laws, creating a seamless adherence strategy. With guidance from the EEOC, Iowa businesses should base their hiring decisions on equal opportunity principles.
The Employment Screening Process in Iowa
When conducting employment screenings in Iowa, there's no one-size-fits-all approach. If you're an employer, understanding the nuances of the process can save you a lot of headaches. Whether hiring for healthcare, technology, or hospitality, adopting industry-specific best practices is key. For instance, healthcare employers should emphasize thorough checks regarding credentials and past infractions, whereas tech firms might prioritize assessing digital footprints and cybersecurity expertise.
Consent and disclosure are vital. DonâÂÂt shortcut these steps. Before proceeding with any background check, you need explicit, written permission from the candidate. This is not only a fair practice but also aligns with both state and federal laws. Disclose what the screening will entailâÂÂit's part of maintaining transparency and trust within the hiring process.
But what happens when a candidate's check raises red flags? Handling adverse actions requires a delicate touch. If you decide not to hire someone based on what you find, you're legally obliged to follow specific steps. Iowa law requires you to inform the candidate, provide them with the report for review, and allow time for disputing inaccuracies by federal guidelines. Familiarize yourself with guidance from the FTC to ensure you're navigating this responsibly.
By integrating these practices, employers in Iowa can streamline their hiring processes, minimize legal risks, and foster a recruitment environment that's as fair as it is effective.
Iowa Background Check Resources
| Website Name | URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Labor (Iowa) | iowadivisionoflabor.gov | Provides information on employment laws, safety regulations, and workplace rights. |
| Iowa State Patrol | iowastatepatrol.org | Offers services for criminal history checks and background screening. |
| Department of Transportation (Iowa) | iowadot.gov | Manages driver records and regulations important for background checks related to transportation jobs. |
| Iowa Workforce Development | iowaworkforcedevelopment.gov | Offers resources on employment regulations and hiring practices for businesses. |
| Iowa Secretary of State | sos.iowa.gov | Provides business registration, compliance information, and resources for employers. |
Challenges in Iowa Background Checks
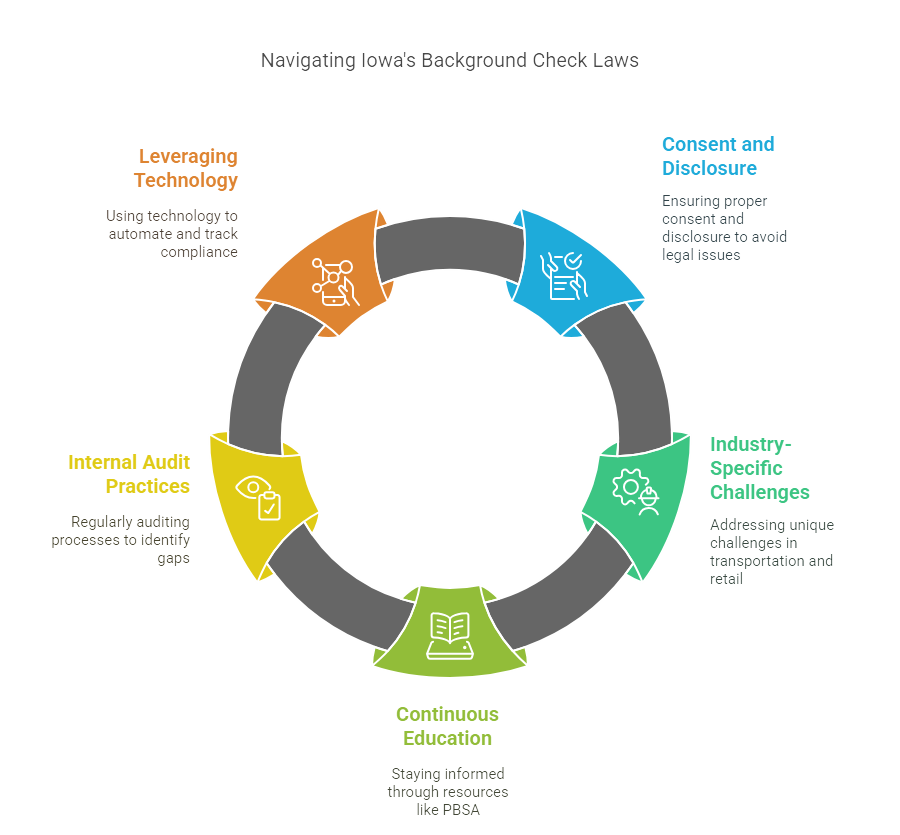
Navigating Iowa's background check laws can be a minefield for businesses, with common pitfalls appearing all too often. One frequent mistake is neglecting the specific consent and disclosure requirements mandated by the state. Employers sometimes assume federal guidelines cover all bases, only to find Iowa's regulations demand more nuanced compliance. For example, failing to obtain proper written consent from applicants or providing insufficient disclosure can lead to legal repercussions and damaged reputations.
Industry-specific challenges further complicate the landscape. The transportation sector requires thorough checks due to federal Department of Transportation regulations, leading to confusion about state and federal obligations. The retail industry struggles to balance quick hiring during peak seasons with the need for comprehensive checks, risking non-compliance when rushing to onboard staff.
To avoid these traps, businesses must stay laser-focused on the specifics of Iowa law, ensuring transparency and fairness in their screening processes. By dedicating time and resources to understanding these nuances, companies can avoid legal complications and foster a compliant, efficient hiring environment.
Ensuring Continuous Compliance
Staying compliant with Iowa's background check laws isn't a one-and-done deal. It's more of an ongoing practice, akin to maintenance on a well-oiled machine. For businesses, this means keeping up with law updates, auditing internal processes, and embracing technology.
Continuous Education
First and foremost, keep learning. The landscape of employment law, including background checks, can shift like Midwestern weather. Use resources like the Professional Background Screening Association (PBSA) to stay informed. They provide updates and educational materials that help you anticipate and adapt to legal changes.
Internal Audit Practices
Routine checkups of your hiring processes are vital. Conducting regular audits can help identify gaps and inefficiencies in your current system. Auditing ensures forms are up-to-date, disclosures are clear, and consent procedures are airtight. It'sn't just a bureaucratic box to tick; it's your safety net against potential legal complications.
Leveraging Technology
Incorporating technology into your compliance strategy can provide a significant edge. Tools that automate background check processes and track compliance metrics can reduce human error and save time. Review GCheck's blog for past strategies that have worked to maintain compliance. Integrating these tech solutions can help Iowa businesses navigate regulations more effectively.
In sum, continuous compliance demands vigilance and adaptability. It's about creating a robust framework that meets today's standards and is flexible enough to meet tomorrow's challenges.
The Impact on Job Seekers
Understanding background check laws in Iowa isn't just for employers. Job seekers need to be aware of their rights and the implications these laws have on their job search. First, knowing that you have legal protections during the hiring process is essential. Under Iowa law and the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), you must be informed if a background check is being conducted and consent to this process. Transparency is your ally.
Preparing for a background check involves a bit of self-assessment. Before applying, ensure your resume and application accurately reflect your history, as inaccuracies can raise red flags. If you have a problematic history, be prepared to discuss it honestly with potential employers. Iowa has restrictions on considering arrests that didn't result in a conviction for employment decisions.
Finally, it's crucial to approach the background check process with a mindset of readiness. Obtain a copy of your own records through various services to understand what employers will see. Address any discrepancies with the proper channels, and ensure that your digital profiles reflect you as a trustworthy candidate. By understanding your rights and taking these preparatory steps, you confidently and clearly navigate the background check process, aligning your presentation with what Iowa employers expect.
Frequently Asked Questions
When employers and job candidates in Iowa consider Iowa background checks, everyone has a lot of similar important questions about what is legal, what is required, and what is fair. This FAQ page distills the most common questions from laws like the FCRA and EEOC and concentrates on Iowa practice specifically. It is important to be knowledgeable about these laws in your capacity as a business owner or HR manager in order to maintain a compliant and fair hiring process.
What are the key requirements for background checks in Iowa?
In Iowa, employers must comply with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) when conducting background checks. This means obtaining written consent from job applicants before running a background check. Employers should also ensure that they use background check reports fairly and notify applicants if adverse action is taken based on the report.
How do Iowa background check laws impact employers?
Iowa background check laws require employers to balance the need for information with respecting applicant rights. This includes providing applicants with a copy of their rights under the FCRA, handling criminal history information carefully, and avoiding practices that could be considered discriminatory under the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines.
Can employers in Iowa use criminal records for hiring decisions?
Yes, employers in Iowa can use criminal records for hiring decisions, but they must follow FCRA guidelines. They should consider the nature of the job, the severity of the offense, and the time elapsed since the conviction to avoid discrimination claims. Adverse action based on criminal records requires notifying the candidate and providing an opportunity to dispute the findings.
What is the process for conducting a background check in Iowa?
To conduct a background check in Iowa, employers must first obtain written consent from the applicant. They should then choose a reputable background check service that complies with FCRA requirements. After receiving the report, employers must review it thoroughly and, if necessary, provide a pre-adverse action notice before making a final decision.
Are there any restrictions on background checks for employment in Iowa?
While Iowa does not have state-specific restrictions beyond FCRA compliance, employers must ensure they do not engage in discriminatory practices. ItâÂÂs important to avoid blanket policies that disqualify applicants based on criminal history without considering individual circumstances and the relevance to the job role.
How long does it take to complete a background check in Iowa?
Completing a background check in Iowa typically takes 1 to 5 business days, depending on the depth of the search and the services used. Factors like verifying education, employment history, and conducting thorough criminal background checks can extend the timeline.
What information can be included in an Iowa background check report?
An Iowa background check report can include criminal history, employment verification, education history, credit checks (if job-relevant), driving records, and references. It must be used in accordance with FCRA guidelines, ensuring the accuracy and relevance of the information to the job position.
Do Iowa laws require employee consent for background checks?
Yes, Iowa laws, in line with the FCRA, require employers to obtain written consent from job applicants before conducting a background check. Consent forms must be clear, stand-alone documents, separate from the job application, to ensure transparency with the applicant.
How can businesses ensure compliance with Iowa background check regulations?
Businesses can ensure compliance by following FCRA guidelines, using reputable background check services, providing applicants with pre-adverse action notices, and keeping thorough records of consent. ItâÂÂs also advisable to consult with legal counsel to ensure adherence to state and federal laws.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with Iowa background check laws?
Penalties for non-compliance with background check laws in Iowa can include lawsuits from applicants, potential fines, and damage to the companyâÂÂs reputation. Violations of the FCRA can result in statutory damages ranging from $100 to $1,000 per violation, plus potential punitive damages.
How have Iowa background check laws changed in recent years?
In recent years, Iowa has seen a focus on aligning with federal FCRA standards while considering fair hiring practices. While no state-specific "ban the box" law exists, employers are encouraged to consider the relevance of criminal history to job roles to avoid discrimination claims.
Can an employee dispute the results of a background check in Iowa?
Yes, employees have the right to dispute the results of a background check in Iowa if they believe the information is inaccurate or incomplete. The FCRA mandates that the employer provide a copy of the report and inform the candidate of their right to dispute the information with the reporting agency.
What role does the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) play in Iowa background checks?
The FCRA sets the standard for conducting background checks in Iowa, requiring employers to get written consent, provide a copy of the report if adverse action is considered, and ensure the accuracy of information. It serves as the primary federal regulation guiding background checks in Iowa.
Are there any industries in Iowa with stricter background check requirements?
Certain industries in Iowa, such as healthcare, childcare, and positions involving vulnerable populations, may have stricter background check requirements. These industries often require additional checks, like fingerprinting and child abuse registry searches, to ensure the safety of individuals served by the organization.
What should employers do if a background check reveals a criminal history in Iowa?
If a background check reveals a criminal history in Iowa, employers should assess the nature of the offense, its relevance to the job role, and the time elapsed since the conviction. They must provide a pre-adverse action notice to the applicant, along with a copy of the report and a summary of rights, before taking any adverse action.
Conclusion
Iowa's background check laws are essential for responsible employment practices. Adhering to Iowa's hiring regulations fosters transparency and trust. For business owners and HR professionals, prioritizing knowledge of these laws translates to smoother, more efficient hiring processes. Investing in compliance-friendly practices isn't just about avoiding penalties; it's about cultivating a workforce that enhances the company's reputation and operational health. Similarly, job seekers should be proactive, understand their rights, and prepare accordingly to confidently navigate the employment landscape.
Mastering Iowa's background check regulations creates a win-win scenario for all parties involved. Employers thrive with reduced legal risks and a robust vetting system, while job seekers enjoy a fair and informed examination in their career pursuits.
Resources
- Iowa Legislature. (n.d.). Iowa Code - Chapter 692: Criminal History Checks. Retrieved from https://www.legis.iowa.gov/docs/code/692.pdf
- Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. (2012). EEOC Enforcement Guidance on the Consideration of Arrest and Conviction Records in Employment Decisions. Retrieved from https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/enforcement-guidance-consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment-decisions
- U.S. Department of Labor. (n.d.). Background Checks: What Employers Need to Know. Retrieved from https://www.dol.gov/agencies/ofccp/resources/background-checks-what-employers-need-know
- Iowa Workforce Development. (n.d.). Employment Law Guide. Retrieved from https://www.iowaworkforcedevelopment.gov/employment-law-guide
- National Conference of State Legislatures. (2020). State Laws on Employment-Related Background Checks. Retrieved from https://www.ncsl.org/research/labor-and-employment/state-laws-on-employment-related-background-checks.aspx

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.







