Illinois rideshare background checks operate under a dual-jurisdiction framework where Chicago's municipal requirements significantly exceed state-level Transportation Network Provider (TNP) regulations. This creates compliance challenges for fleet operators managing drivers across multiple jurisdictions. This comprehensive guide decodes the complex screening requirements, disqualifying offenses, and jurisdictional differences that distinguish Illinois—particularly Chicago—from both state standards and competing rideshare markets nationwide.
Key Takeaways
- Illinois state law requires 7-year criminal background checks for all rideshare drivers, while Chicago mandates lifetime felony reviews and additional fingerprint-based FBI checks for public chauffeur licenses.
- Chicago rideshare drivers must obtain a Public Chauffeur License before applying for TNP permits, adding 4-6 weeks to the credentialing timeline compared to downstate Illinois markets.
- DUI convictions within 3 years create automatic disqualification under Illinois state law, but Chicago extends this lookback period to 5 years for certain violent offenses.
- Fleet operators managing 10+ vehicles in Chicago face enhanced compliance burdens including quarterly driver eligibility audits and municipal business licensing separate from state TNP permits.
- Illinois rideshare background checks must include both SSN trace verification and county-level criminal searches across all jurisdictions where the applicant has lived during the lookback period.
- Chicago's Traffic Regulation Vehicle-for-Hire ordinance requires annual background check renewals, compared to Illinois' state requirement for checks every three years.
- Major disqualifying factors include violent felonies (lifetime ban in Chicago), sexual offenses, human trafficking convictions, and patterns of reckless driving within specified timeframes.
- Transportation staffing agencies operating across Illinois-Indiana borders must navigate three separate regulatory frameworks (Illinois state, Chicago municipal, and Indiana TNP laws) for optimal driver deployment.
Understanding Illinois' Dual-Jurisdiction Rideshare Compliance Framework
Illinois presents a uniquely complex regulatory landscape for rideshare operations. State Transportation Network Provider laws establish baseline requirements. However, Chicago—as a home rule municipality—enforces substantially stricter screening standards. The Illinois Transportation Network Providers Act (625 ILCS 57) governs rideshare operations statewide. Chicago Municipal Code Chapter 9-115 supersedes state law within city boundaries. This jurisdictional overlap creates what industry professionals call a "compliance layer cake."
The practical implications affect hiring timelines, operational costs, and driver pool availability. A rideshare driver operating exclusively in Springfield or Peoria faces significantly different requirements than someone working Chicago's O'Hare airport queue. Chicago requires both a Public Chauffeur License and a separate TNP Vehicle Permit. Drivers in collar counties need only satisfy state-level TNP requirements. Understanding these distinctions separates compliant operations from those risking enforcement actions.
For multi-market fleet operators, this regulatory split creates strategic considerations around driver allocation. Companies must maintain separate compliance tracking systems for Chicago versus non-Chicago drivers. Chicago-credentialed drivers can work statewide while non-Chicago drivers cannot legally accept rides originating within city limits. This asymmetry influences recruitment targeting and determines which background check packages to order for different driver segments.
State-Level Illinois TNP Background Check Requirements
The Illinois Transportation Network Providers Act mandates that all TNP companies conduct local and national criminal background checks covering a minimum 7-year lookback period. These state-level checks must include multi-state criminal database searches, national sex offender registry verification, and driving record reviews through the Illinois Secretary of State. The law specifically prohibits platforms from activating drivers with disqualifying convictions including violent crimes, sexual offenses, acts of terror, or patterns of serious traffic violations.
Illinois state requirements establish these core screening components:
- Criminal History Search: County-level criminal court records in all jurisdictions where the applicant resided during the past 7 years
- Sex Offender Registry Check: Verification against the National Sex Offender Public Website and Illinois State Police database
- Driving Record Review: Complete Illinois driving abstract showing all violations, suspensions, and license status changes
State law requires TNP companies to perform updated background checks every three years for active drivers. This creates an ongoing compliance obligation beyond initial onboarding. However, the statute delegates specific disqualification criteria to individual platforms. Fleet operators must understand both state minimums and platform-specific requirements, which often exceed statutory baselines.
Chicago Municipal Rideshare Background Check Requirements
Chicago's vehicle-for-hire regulations impose significantly more stringent background screening requirements. These include fingerprint-based FBI checks and lifetime criminal history reviews for specific offense categories. The city requires all rideshare drivers to first obtain a Public Chauffeur License. This necessitates FBI fingerprint background checks processed through the Illinois State Police. This fingerprint requirement—absent from state law—adds both cost (approximately $75-90 per applicant) and processing time (typically 4-6 weeks) to the credentialing workflow.
Chicago's enhanced screening requirements include these components. The criminal lookback period extends to lifetime for felonies versus the state's 7 years. Fingerprint-based FBI checks are mandatory but not required at the state level. The DUI lookback period matches the state at 3 years. Background check renewals occur annually compared to every 3 years statewide. County court searches must cover all lifetime residences versus only 7-year residences. These differences create substantially higher compliance costs and longer timelines.
The Chicago Business Affairs and Consumer Protection (BACP) department maintains ultimate authority over chauffeur license approvals. The department can deny applications based on factors beyond criminal history. These include patterns of traffic violations or previous vehicle-for-hire license revocations. Fleet operators should build 6-8 weeks into Chicago onboarding timelines versus 2-3 weeks for downstate Illinois markets.
Disqualifying Offenses Under Illinois Rideshare Background Checks
Illinois rideshare driver disqualifications fall into two categories: permanent lifetime bans for specific serious offenses and time-based restrictions where conviction age determines eligibility. State law establishes minimum disqualification standards. However, Chicago and individual rideshare platforms often impose stricter criteria. Understanding these distinctions helps fleet operators pre-screen applicants efficiently and avoid wasting resources on applications likely to face denial.
Permanent Disqualifying Convictions
Certain criminal convictions create lifetime disqualification from rideshare driving in Illinois regardless of how much time has passed since conviction or sentence completion. These permanent bars reflect safety priorities around protecting passengers from drivers with histories of violent, sexual, or exploitation-related crimes. Both state TNP regulations and Chicago municipal code identify similar categories for lifetime prohibition, though Chicago's list extends slightly broader.
Lifetime disqualifying offenses include:
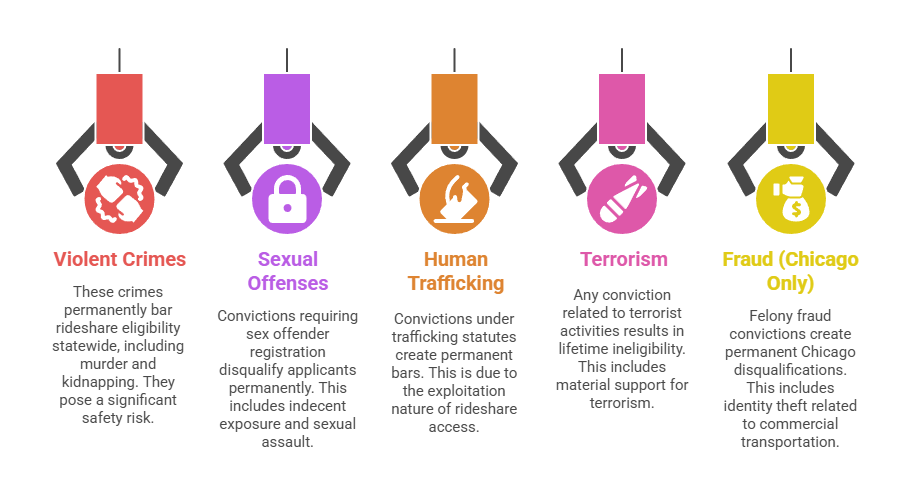
- Violent Crimes: Murder, manslaughter, armed robbery, aggravated assault, kidnapping, and felony battery permanently bar rideshare eligibility statewide
- Sexual Offenses: Any conviction requiring sex offender registration, including indecent exposure, sexual assault, child pornography, and exploitation crimes disqualify applicants permanently
- Human Trafficking: Convictions under Illinois' trafficking statutes (720 ILCS 5/10-9) or federal trafficking laws create permanent bars due to the exploitation nature of rideshare access
- Terrorism: Any conviction related to terrorist activities, material support for terrorism, or acts intended to intimidate civilian populations results in lifetime ineligibility
- Fraud (Chicago Only): Felony fraud convictions and identity theft related to commercial transportation or vehicle-for-hire services create permanent Chicago disqualifications
Fleet operators should implement preliminary screening questionnaires asking about these conviction categories before investing in formal background checks. Third-party screening providers can structure packages with tiered pricing—initial database searches to identify obvious disqualifiers before proceeding to comprehensive county-level searches.
Time-Based Disqualifying Offenses
Most disqualifying convictions operate on lookback periods where crimes beyond a specific timeframe no longer affect rideshare eligibility. Illinois state law primarily uses a 7-year lookback for time-limited disqualifications. Chicago extends certain periods to better align with public safety research on recidivism patterns. These time-based restrictions create a "waiting period" concept where applicants with past convictions may become eligible as years pass from conviction or release dates.
The following offense categories follow specific lookback periods. DUI and impaired driving convictions disqualify drivers for 3 years from conviction date under both state and Chicago standards. Drug-related felonies have a 7-year lookback from release from custody at both levels. Theft crimes (non-felony) follow 7-year periods from conviction date statewide. Burglary offenses extend to 10 years in Chicago versus 7 years statewide, calculated from release from custody. Domestic violence convictions disqualify for 7 years from conviction date. Reckless driving patterns (3+ incidents) create 3-year lookbacks from the most recent violation.
The "release from custody" calculation significantly extends practical waiting periods for applicants who served prison sentences. A felony drug conviction from 2016 with a 4-year prison sentence (release in 2020) wouldn't satisfy the 7-year lookback until 2027. The same conviction with probation only would clear by 2023.
Chicago Public Chauffeur License Requirements for Rideshare Drivers
The Chicago Public Chauffeur License represents the most substantial difference between Chicago and downstate Illinois rideshare compliance. This municipal license is mandatory before TNP permit applications. It requires fingerprint-based FBI background checks, in-person application submission, and ongoing annual renewals. The chauffeur license system predates rideshare platforms by decades. Originally designed for taxi operators, it now extends to all commercial passenger transport within Chicago city limits.
Chicago Business Affairs and Consumer Protection (BACP) issues approximately 65,000 active chauffeur licenses as of 2025. Rideshare drivers represent roughly 75% of this population. The licensing process involves multiple steps spanning 4-8 weeks under normal processing conditions. Expedited services exist for fleet operators submitting batch applications. Understanding this timeline matters critically for workforce planning, as drivers cannot generate revenue until holding both the chauffeur license and platform activation.
FBI Fingerprint Background Check Process
Chicago's fingerprint-based FBI background check requirement distinguishes it from virtually all other Illinois jurisdictions and most major rideshare markets nationwide. This enhanced screening provides access to the FBI's Criminal Justice Information Services (CJIS) database, which maintains the most comprehensive criminal record repository in the United States. The fingerprint-based approach offers significant advantages over name-based searches alone, eliminating alias-related gaps and providing definitive identity verification.
The FBI fingerprint process follows these key stages:
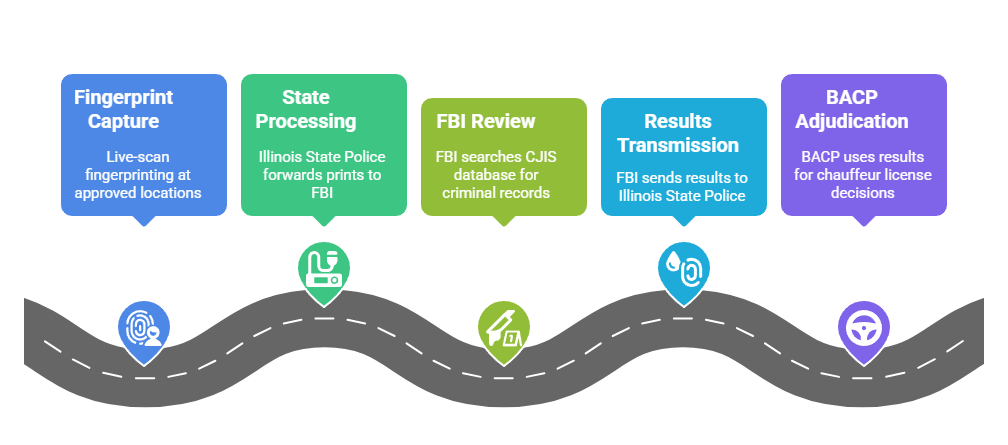
- Fingerprint Capture: Live-scan fingerprinting at approved Illinois State Police vendors or Chicago BACP offices for FBI criminal history submission
- State Processing: Illinois State Police serves as intermediary, forwarding prints to FBI while checking state-level criminal databases
- FBI Review: CJIS database search covering nationwide criminal records with special focus on out-of-state convictions
- Results Transmission: FBI transmits results to Illinois State Police, which forwards to BACP for chauffeur license adjudication
- Timeline Variability: Processing typically requires 4-6 weeks but extends to 8+ weeks during high-volume periods (January-March)
Fleet operators should plan for 8-week worst-case scenarios when projecting driver availability. Illinois State Police serves as the intermediary for Chicago chauffeur license fingerprint submissions, forwarding prints to the FBI while simultaneously checking state-level criminal databases. The FBI component specifically identifies out-of-state convictions that might not appear in Illinois court searches, making this screening significantly more comprehensive than state-only background checks.
Annual Chauffeur License Renewal Requirements
Chicago chauffeur licenses expire annually, requiring renewal background checks and creating ongoing compliance obligations that exceed state TNP requirements. This annual renewal cycle means Chicago rideshare drivers undergo background screening three times more frequently than drivers in other Illinois markets. State law mandates checks every three years. The renewal process involves abbreviated background checks focusing on new criminal activity and driving violations since the previous review.
Annual renewals require several key components. Updated driving records from the Illinois Secretary of State show any violations or license actions from the past 12 months. Criminal history updates identify any new arrests, charges, or convictions since the previous background check. Sex offender registry verification confirms continued absence from registries. License status verification confirms that no other jurisdictions have suspended or revoked driver licenses or commercial driving privileges. Renewal background checks cost substantially less than initial screenings since they exclude fingerprint processing and focus on incremental changes.
Illinois Rideshare Driving Record Requirements

Driving history evaluation represents a critical component of Illinois rideshare background checks separate from criminal record review. The Illinois Secretary of State maintains comprehensive driving records for all licensed drivers. These document traffic violations, accidents, license suspensions, and administrative actions. Both state TNP regulations and Chicago municipal code establish specific driving-related disqualifications that can prevent rideshare eligibility even when criminal backgrounds are clear.
Illinois uses a point system for traffic violations, where specific infractions carry point values that remain on driving records for 4-5 years. Accumulating excessive points triggers license suspensions regardless of rideshare status. However, TNP regulations and platform policies establish lower thresholds for disqualification than general license suspension criteria. A driver might maintain a valid Illinois license while being ineligible for rideshare work due to violation patterns that fall below suspension thresholds but exceed platform safety standards.
Disqualifying Moving Violations and Patterns
Rideshare platforms and Illinois regulations focus on both specific serious violations and patterns of lesser infractions that suggest risky driving behavior. Three or more moving violations within a 3-year period typically trigger disqualification under platform policies, even when individual violations seem minor. This pattern-based approach recognizes that frequency of violations indicates driving habits posing elevated passenger risk.
Serious moving violations creating immediate disqualification include:
- Reckless Driving: Any conviction under 625 ILCS 5/11-503 for willful/wanton disregard for safety disqualifies drivers for 3 years from conviction date
- Street Racing: Drag racing or speed contest violations result in automatic platform deactivation and 7-year lookback periods
- Driving on Suspended/Revoked License: Operating vehicles while license privileges are suspended creates 7-year disqualification periods
- Leaving Accident Scenes: Hit-and-run convictions or failing to report accidents disqualify drivers for 7 years
- School Zone Violations: Chicago specifically scrutinizes speeding violations in school zones and automated traffic enforcement violations around parks and schools
While parking tickets don't affect rideshare eligibility, Chicago's automated speed cameras generate moving violations that count toward the 3-violation threshold. Drivers accumulating multiple automated violations may face disqualification even without traditional traffic stops.
License Suspension and Revocation Impacts
Any current license suspension or revocation creates automatic rideshare ineligibility in Illinois. However, the treatment of past suspensions varies by cause and resolution status. Administrative suspensions for insurance lapses, child support non-payment, or parking ticket accumulation affect rideshare eligibility differently than safety-based suspensions. Safety-based suspensions include DUI or excessive violations. Platforms evaluate suspension history context when making eligibility determinations.
Past suspensions impact eligibility based on specific factors. DUI statutory summary suspensions are disqualifying for 3 years from restoration and require full license reinstatement with SR-22. Points-based suspensions also disqualify for 3 years from restoration and require completion of remedial programs. Administrative suspensions for non-safety issues may not disqualify after 1 year from restoration with proof of issue resolution. Revocations disqualify for 7 years from restoration and require the full license reinstatement process. Fleet operators should request certified Illinois driving abstracts directly from the Secretary of State rather than relying on third-party database reports.
Required Background Check Components for Illinois Rideshare Compliance
Compliant Illinois rideshare background checks must include multiple verification components addressing criminal history, identity confirmation, driving records, and specialized registry searches. State TNP law establishes minimum requirements. However, Chicago's enhanced standards and platform-specific policies typically necessitate more comprehensive screening packages. Understanding these components helps fleet operators structure background check orders that satisfy all applicable requirements without purchasing redundant or unnecessary searches.
The multi-component nature of rideshare screening requires coordination among several data sources and jurisdictions. A comprehensive Illinois rideshare background check typically involves 8-12 separate searches or verifications. Each addresses specific regulatory requirements or risk factors. Background screening providers offer pre-packaged "rideshare screening bundles" that combine these components. Fleet operators benefit from understanding individual elements to evaluate package completeness and identify potential gaps.
Criminal Background Search Requirements
Criminal history verification forms the foundation of Illinois rideshare background checks. It encompasses both database searches for broad coverage and county-level court record searches for detailed accuracy. Illinois does not provide statewide criminal record access to private employers or screening companies. Criminal searches require contacting individual county courts where applicants have lived or worked. This county-by-county approach creates complexity for applicants with frequent relocations or multi-state residency histories.
Required criminal search components include these elements. Multi-state criminal databases provide aggregated records from state repositories, corrections departments, and administrative sources. These offer nationwide coverage with 95-98% hit rates for felony convictions. County criminal court searches involve direct courthouse searches in all counties where the applicant resided during the lookback period. This means 7 years for state law and lifetime for Chicago felonies. Federal district court searches cover U.S. District Court records for federal criminal convictions. National sex offender registry verification checks the National Sex Offender Public Website aggregating all state registries.
Social Security Verification and Address History
Social Security number verification serves dual purposes in rideshare background checks—confirming identity authenticity and developing the address history needed to determine which jurisdictions require criminal searches. SSN traces reveal all names associated with the Social Security number, addresses reported to credit bureaus and data furnishers, and potential indicators of identity theft or fraud. This foundational verification step must occur before criminal searches to ensure searches target correct name variations and appropriate geographic jurisdictions.
The SSN trace typically reveals several key data points:
- Name Variations: All name formats associated with the SSN including maiden names, nicknames, and aliases used in credit applications or employment
- Address History: Comprehensive list of addresses associated with the SSN typically spanning 7-10 years of reporting history
- Death Index Check: Verification that the SSN doesn't appear in the Social Security Death Master File
- Validity Indicators: Confirmation that the SSN was issued, issue date aligns with applicant age, and issue state matches biographical information
Background screening professionals use address history to identify which county criminal courts require searching. An applicant who lived in Chicago (Cook County) for three years, then Naperville (DuPage County) for two years, then Rockford (Winnebago County) for two years requires criminal searches in all three counties to cover a 7-year lookback. Without accurate address history, screening gaps emerge where criminal records exist but aren't checked.
Background Check Processing Timelines for Illinois Rideshare Operators
Understanding background check processing timelines directly impacts workforce planning, driver onboarding schedules, and revenue projections for rideshare fleet operations. Illinois rideshare screening timelines vary dramatically between Chicago and downstate markets. This stems from the chauffeur license fingerprinting requirement and Chicago's enhanced review processes. Fleet operators must build realistic timelines into recruiting workflows to avoid driver attrition during extended waiting periods.
Standard background check components process within 3-7 business days under normal circumstances. However, specific elements can extend overall timelines significantly. County criminal searches in rural Illinois counties using manual courthouse research may require 7-10 business days. Jurisdictions with online access return same-day results. The slowest component determines overall completion time.
Chicago Rideshare Background Check Timeline
Chicago rideshare background checks typically require 5-8 weeks from application initiation to final platform activation. The FBI fingerprint processing represents the primary bottleneck. This extended timeline reflects the sequential nature of Chicago's requirements. Chauffeur license approval must be completed before TNP permit application. Background check results must return before license issuance. Fleet operators should segment the Chicago onboarding timeline into distinct phases with separate duration estimates.
The fingerprinting appointment phase takes 3-7 days for scheduling and completing fingerprint capture. Vendor availability and appointment capacity affect this timeline. FBI background processing requires 3-5 weeks for FBI CJIS database checks and results transmission. Volume-dependent FBI processing queues determine actual processing times. BACP application review takes 1-2 weeks for Chicago staff review and license determination. Platform background checks need 3-7 days for criminal, driving, and registry searches. Platform approval and activation adds 1-3 days for document review and account activation. The FBI fingerprint processing component experiences the least predictability, ranging from as fast as 2 weeks during low-volume periods to 6+ weeks during peak times.
Downstate Illinois Rideshare Background Check Timeline
Illinois rideshare markets outside Chicago experience significantly compressed timelines since they avoid the chauffeur license requirement and FBI fingerprinting process. Drivers in markets like Springfield, Peoria, Rockford, Champaign-Urbana, and Naperville can typically complete background checks and achieve platform activation within 2-3 weeks. This timeline advantage makes downstate markets more attractive for drivers seeking faster income generation and reduces fleet operator recruiting friction.
Standard downstate Illinois processing follows this sequence:
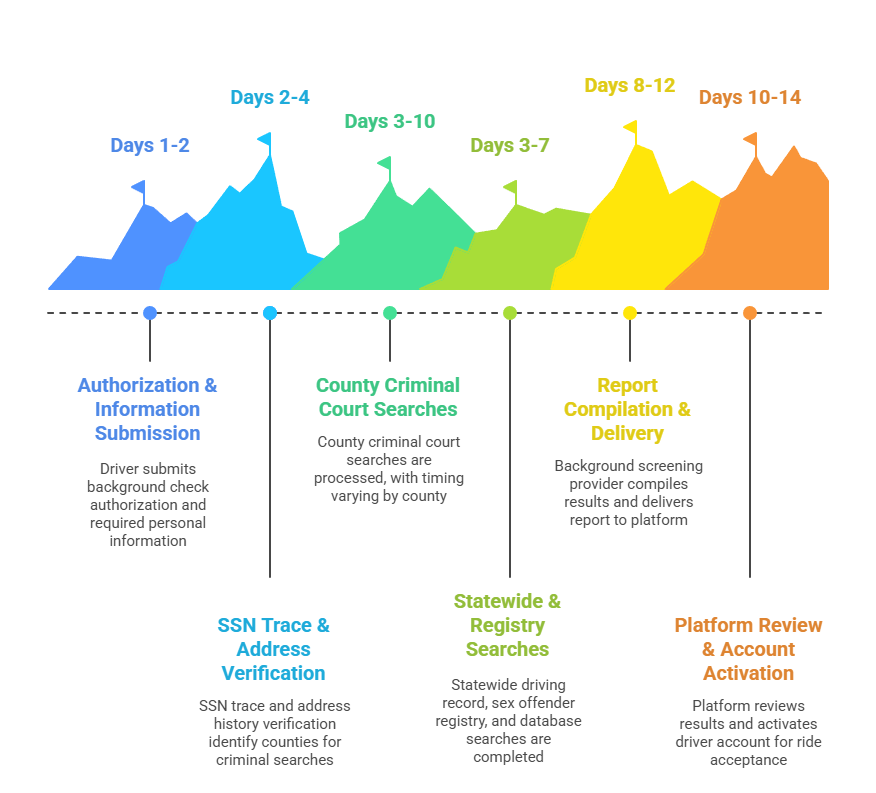
- Days 1-2: Driver submits background check authorization and required information (SSN, address history, driver's license)
- Days 2-4: SSN trace and address history verification complete, identifying counties requiring criminal searches
- Days 3-10: County criminal court searches process (timing varies by specific counties in driver's history)
- Days 3-7: Statewide driving record, sex offender registry, and database searches complete
- Days 8-12: Background screening provider compiles results and delivers report to platform
- Days 10-14: Platform reviews results and activates driver account for ride acceptance
The fastest downstate timelines occur for drivers with simple residential histories in counties offering online court record access. A driver who has lived only in DuPage County (which offers comprehensive online records) for the past seven years might complete background screening in 5-7 days total.
Compliance Considerations for Multi-Jurisdiction Fleet Operators
Fleet operators managing rideshare drivers across multiple Illinois markets face unique compliance challenges stemming from the state-municipal regulatory split. Companies with operations spanning Chicago and collar counties must maintain dual compliance programs. They need separate credentialing workflows and jurisdiction-specific driver eligibility tracking. These operational complexities create both challenges and competitive advantages for organizations that develop sophisticated compliance infrastructure.
The Chicago-downstate regulatory divide creates strategic implications for driver recruitment and deployment. Chicago-credentialed drivers holding Public Chauffeur Licenses can legally accept rides anywhere in Illinois. This makes them more valuable assets for fleet operators. Conversely, drivers credentialed only under state TNP requirements cannot accept rides originating in Chicago. This limits their deployment flexibility. This asymmetry influences whether fleet operators should credential all drivers to Chicago standards regardless of primary operating location.
Managing Chicago and State-Level Requirements Simultaneously
Organizations operating in both Chicago and downstate markets benefit from establishing parallel compliance tracks rather than attempting to force-fit all drivers into Chicago's enhanced requirements. While Chicago credentialing provides maximum flexibility, the additional cost ($75-90 for fingerprinting, extended timelines) may not justify benefits for drivers who will never work Chicago routes. Fleet operators should segment driver populations by intended operating geography and apply appropriate screening requirements to each segment.
Dual-track compliance management requires several key components:
- Geographic Assignment Protocols: Clear systems determining whether new driver recruits will operate in Chicago, downstate only, or flexible across markets
- Credential Tracking Systems: Databases identifying which drivers hold Chicago chauffeur licenses versus state-only TNP compliance, preventing unauthorized Chicago deployment
- Renewal Management: Separate tracking for annual Chicago chauffeur license renewals versus 3-year state background check renewals
- Cost Allocation: Budget planning accounting for substantially higher per-driver costs ($150-200) for Chicago credentialing versus downstate ($75-100)
Some fleet operators adopt "Chicago-first" credentialing strategies where all drivers undergo Chicago-standard background checks regardless of initial deployment plans. This approach maximizes operational flexibility and simplifies compliance systems by maintaining a single standard.
Quarterly Audit Requirements for Large Fleet Operators
Illinois TNP law requires transportation network providers to conduct periodic audits of driver eligibility. However, specific frequency and methodology requirements remain ambiguous in state statute. Chicago Business Affairs and Consumer Protection has interpreted this to require quarterly driver eligibility audits for fleet operators managing 10 or more vehicles. This creates formalized compliance obligations beyond individual platform requirements. These audits verify that active drivers maintain valid credentials. They confirm drivers haven't acquired disqualifying convictions or violations. They ensure drivers meet ongoing eligibility standards.
Quarterly audit programs should include several verification steps. License status verification confirms all active drivers maintain valid Illinois driver's licenses without suspensions or revocations. Chauffeur license renewal verification ensures Chicago drivers have renewed expiring chauffeur licenses and received updated licenses. Criminal record monitoring runs database searches identifying any new arrests or convictions for active drivers since previous background checks. Driving record updates pull recent driving abstracts for drivers approaching violation thresholds or with recent traffic incidents. Technology solutions including continuous monitoring services partially automate quarterly audits by flagging new criminal records, license suspensions, or driving violations as they occur.
Working with Background Screening Providers for Illinois Rideshare Compliance
Selecting appropriate background screening vendors significantly impacts compliance quality, processing speed, and cost efficiency for rideshare fleet operators. The background screening industry includes both generalist providers serving multiple industries and specialized companies focusing exclusively on transportation and mobility markets. Illinois-specific expertise matters substantially given the state's unique dual-jurisdiction framework and Chicago's specialized chauffeur license requirements.
When evaluating background screening providers for Illinois rideshare operations, fleet operators should assess both technical capabilities and regulatory expertise. Providers must access all required data sources including county courts, state driving records, and FBI fingerprinting channels. They must understand Illinois-specific lookback periods and disqualification criteria. They must offer responsive customer service for exception handling and complex scenarios. Not all national background screening companies maintain strong Illinois county court coverage or understand Chicago chauffeur license nuances.
Key vendor evaluation criteria include several important factors. Illinois county coverage means direct access to online court records in Cook, DuPage, Lake, Kane, Will, and other major counties rather than relying on third-party database resellers. Chicago chauffeur license services involve the ability to manage fingerprinting coordination, BACP application submission, and license status tracking as end-to-end service. Turnaround time commitments provide service level agreements specifying maximum processing times for each background check component. Platform integration offers direct API connections with Uber, Lyft, and other rideshare platforms for automated report delivery. Continuous monitoring options provide ongoing database monitoring services that alert fleet operators to new criminal or driving violations for active drivers. Compliance expertise means access to knowledgeable account managers who understand Illinois TNP regulations and can advise on complex disqualification scenarios.
Conclusion
Illinois rideshare background check requirements represent some of the most complex in the nation due to the dual-jurisdiction framework where Chicago's municipal standards substantially exceed state-level TNP regulations. Fleet operators managing drivers across Illinois markets must navigate fingerprint-based FBI checks, annual Chicago chauffeur license renewals, and jurisdiction-specific disqualification criteria that vary between Chicago and downstate markets. Success requires understanding the distinction between 7-year state lookback periods and Chicago's lifetime felony reviews, planning for 5-8 week Chicago credentialing timelines, and establishing compliance systems that appropriately credential drivers for their intended operating geography. Organizations that master these complexities gain competitive advantages through superior driver deployment flexibility, reduced compliance risk, and streamlined onboarding workflows that minimize time-to-activation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does an Illinois rideshare background check take?
Illinois rideshare background checks take 2-3 weeks for downstate markets and 5-8 weeks for Chicago operations. The extended Chicago timeline reflects the mandatory FBI fingerprint-based background check required for Public Chauffeur Licenses, which typically processes in 3-5 weeks. Downstate Illinois drivers avoid fingerprinting requirements and complete standard criminal and driving record checks within 2-3 weeks. Fleet operators should plan Chicago onboarding timelines around the FBI fingerprint bottleneck and consider batching driver applications to improve processing efficiency.
What disqualifies you from driving for Uber or Lyft in Illinois?
Illinois rideshare disqualifications include violent felonies (permanent ban), sexual offenses requiring registry (permanent ban), DUI convictions within 3 years, and drug-related felonies within 7 years. Patterns of three or more moving violations within 3 years also trigger disqualification. Chicago extends some lookback periods beyond state minimums, including lifetime felony reviews and 5-year windows for certain violent crimes. Major platforms typically apply stricter standards than state law minimums, so drivers should review platform-specific requirements beyond statutory baselines.
Does Chicago require different background checks than the rest of Illinois for rideshare drivers?
Yes, Chicago requires substantially more comprehensive background checks including FBI fingerprint-based criminal history searches, lifetime felony record reviews, and annual background check renewals through the Public Chauffeur License system. Downstate Illinois drivers undergo name-based criminal searches with 7-year lookback periods and background check renewals every three years. Chicago's enhanced requirements add $75-90 in fingerprinting costs per driver and extend credentialing timelines by 3-5 weeks compared to other Illinois markets.
Can I drive for rideshare companies in Illinois with a felony conviction?
Felony eligibility depends on conviction type, age, and operating location. Violent felonies, sexual offenses, human trafficking, and terrorism convictions create permanent disqualification statewide. Other felonies follow a 7-year lookback period under Illinois state law—convictions older than 7 years from release date generally don't disqualify applicants in downstate markets. However, Chicago reviews all felonies regardless of age and maintains discretion to deny chauffeur licenses based on lifetime criminal history.
How much do Illinois rideshare background checks cost?
Illinois rideshare background checks cost $75-100 for downstate markets and $150-200 for Chicago credentialing. Chicago's higher costs reflect FBI fingerprinting fees ($60-75), enhanced county criminal searches covering lifetime residency, and Public Chauffeur License application fees ($150 currently). Background screening provider charges typically range $35-50 for standard packages covering criminal history, driving records, and registry checks. Fleet operators processing high volumes can negotiate discounted bulk rates, often reducing per-driver costs by 20-30%.
What is the lookback period for Illinois rideshare background checks?
Illinois state law mandates a 7-year lookback period for criminal and driving record reviews, calculated from conviction date for most offenses or release from custody date for felonies involving imprisonment. Chicago extends lookback periods for specific offense categories, including lifetime reviews for all felony convictions and 10-year lookback periods for violent property crimes. DUI convictions disqualify drivers for 3 years from conviction date statewide. Sex offender registry searches and violent crime convictions carry lifetime review periods regardless of jurisdiction.
Do rideshare drivers need a chauffeur license in Illinois?
Only Chicago rideshare drivers require Public Chauffeur Licenses—drivers operating exclusively in other Illinois markets need only satisfy state TNP requirements and individual platform standards. The Chicago chauffeur license involves FBI fingerprint background checks, annual renewals, and application submission to Business Affairs and Consumer Protection. Drivers working routes that might originate in Chicago should obtain chauffeur licenses even if primarily operating in suburbs, as rides beginning within city limits require Chicago credentials.
Can Illinois rideshare background checks be expedited?
Background check components other than FBI fingerprinting can be expedited through rush processing services offered by most screening providers, reducing standard 5-7 day timelines to 1-3 days for additional fees ($25-50 per driver). However, FBI fingerprint processing for Chicago chauffeur licenses cannot be meaningfully expedited—it represents a fixed external dependency operating on government timelines. Fleet operators can optimize overall timelines by ensuring complete and accurate driver information at application initiation, establishing vendor relationships for priority fingerprinting appointments, and using background screening providers with direct county court access.
Additional Resources
- Illinois Transportation Network Providers Act - Full Text
https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=3654&ChapterID=49 - Chicago Business Affairs and Consumer Protection - Public Chauffeur License Information
https://www.chicago.gov/city/en/depts/bacp/sbc/public_chauffeurlicense.html - Illinois Secretary of State - Driver's License Services and Abstracts
https://www.ilsos.gov/departments/drivers/drivers_license/drlicid.html - Professional Background Screening Association - Transportation Screening Standards
https://www.psbainc.org/ - FBI Criminal Justice Information Services - Background Check Information
https://www.fbi.gov/services/cjis
