Navigating the world of employment background checks can be a minefield for both job seekers and employers. With so much information (and misinformation) out there, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. But don't worry, we've got you covered! This comprehensive guide will tackle the top 10 questions people have about background checks, providing clear, concise, and accurate answers to put your mind at ease.

Understanding Employment Background Checks
1. What is an employment background check?
An employment background check is a review of a person's past, typically by an employer, to assess their suitability for a job. This check often includes verifying a candidate’s employment history, education, criminal record, and sometimes credit history. Employers use these checks to ensure that they make informed hiring decisions, minimize risks to their organization, and maintain a safe workplace. Various background checks exist, each serving a specific purpose, such as criminal background checks, employment verification, and education verification.
Within Human Resources, I've learned that background checks are more than paperwork; they're a bridge of integrity between organizations and candidates. I've seen how the process might look imposing to prospective hires; but it is also a moment where organizations can showcase fairness, transparency, and respect. When approached with care, background checks don't just reduce risk but also fortify a culture of integrity where people feel respected for their skills as much as their integrity. At its core, the goal is never to look to the past but to build a platform for a safer and stronger future together.
2. Is it legal for employers to conduct background checks?
Yes, it is legal for employers to conduct background checks, but they must comply with various laws and regulations. In the United States, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) sets the standards for conducting background checks. Employers must obtain written consent from the candidate before conducting the check and follow specific procedures if they decide not to hire someone based on the results. Additionally, state laws may have additional requirements or restrictions. Privacy concerns are also important; employers must handle the information obtained through background checks confidentially and responsibly.
3. What types of information are included in an employment background check?
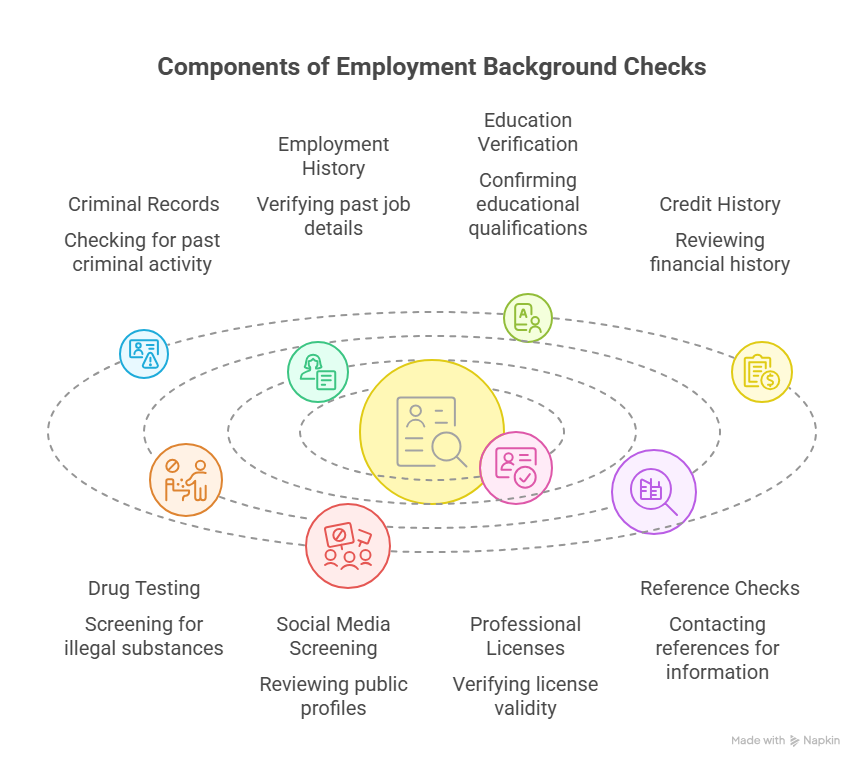
Employment background checks can include a wide range of information. Common checks performed include:
- Criminal Records: Checking for any past criminal activity to assess potential risks.
- Employment History: Verifying past job titles, employment dates, and responsibilities.
- Education Verification: Confirming degrees, certifications, and attendance dates.
- Credit History: Reviewing financial history, especially for positions involving financial responsibilities.
- Drug Testing: Screening for illegal substances.
- Social Media Screening: Reviewing public profiles for inappropriate behavior or information.
- Professional Licenses: Verifying the validity of necessary professional licenses.
- Reference Checks: Contact previous employers or other references to gather more information about the candidate.
Additional checks may be required for certain industries, like healthcare and finance, to comply with industry-specific regulations.
The Background Check Process
4. How long does an employment background check take?
The duration of an employment background check can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of check being performed, the location of the candidate, and the responsiveness of institutions being contacted for information. Generally, a standard background check can take several days to a few weeks. Criminal checks might take longer if multiple jurisdictions are involved. Education and employment verifications can also vary based on how quickly schools and previous employers respond. On average, most background checks are completed within 3 to 10 business days.
5. Can I run a background check on myself?
Yes, running a background check on yourself is a proactive step that can help you ensure your records are accurate and up-to-date. Self-checks allow you to see what potential employers will see and allow you to correct any inaccuracies beforehand. To run a self-check, you can use services provided by background check companies, access your criminal records through local or state agencies, and request copies of your credit report. By verifying your information, you can address any discrepancies and be better prepared for the job application process.
6. How accurate are employment background checks?
Employment background checks are generally accurate, but errors can occur. Mistakes can happen due to clerical errors, outdated information, or incorrect data entry. To minimize inaccuracies, it is crucial to use reputable screening companies that follow best practices and comply with the FCRA. Under the FCRA, you have the right to dispute incorrect information found in your background check. The screening company must investigate and correct any errors. Ensuring the accuracy of your records and promptly addressing discrepancies can help improve the reliability of background checks.
Your Rights and Legal Considerations
7. What are my rights during an employment background check?
As a job seeker, you have specific rights under the FCRA during an employment background check. These rights include:
- Consent: Employers must obtain your written consent before conducting a background check.
- Notification: If an employer intends to take adverse action (e.g., not hiring you) based on the background check, they must notify you and provide a copy of the report.
- Dispute: You can dispute inaccurate or incomplete information in your background check report. The screening company must investigate and correct any errors.
- Access to Information: You can request a copy of your background check report from the employer or the screening company.
Understanding these rights helps you confidently navigate the background check process and ensures your privacy is respected.
8. What are the consequences of a negative finding on a background check?
A negative finding on a background check can impact your job prospects, but it doesn’t necessarily mean the end of your job search. Employers typically consider the nature and relevance of the negative information about the job role. For instance, a minor offense from years ago may be viewed differently than a recent, serious crime. It's important to be honest with potential employers about your background. If you believe a negative finding is inaccurate, you can dispute it. If the finding is accurate, demonstrating how you’ve addressed the issue and taken steps to improve can help mitigate its impact.
9. How can I correct errors on my background check report?
If you find errors in your background check report, follow these steps to correct them:
- Request a Copy: Obtain a copy of the report from the employer or screening company.
- Identify Errors: Review the report carefully and note any inaccuracies.
- File a Dispute: Contact the screening company to dispute the errors. Provide documentation to support your claims.
- Investigation: The screening company will investigate your dispute and must correct any inaccuracies within 30 days.
- Follow-up: Verify that the corrections have been made and request a new copy of the corrected report.
Employers must also be notified of the corrections. Maintaining accurate records helps prevent future discrepancies and ensures a smoother job application process.
Best Practices for Employers
10. What are the best practices for employers conducting background checks?
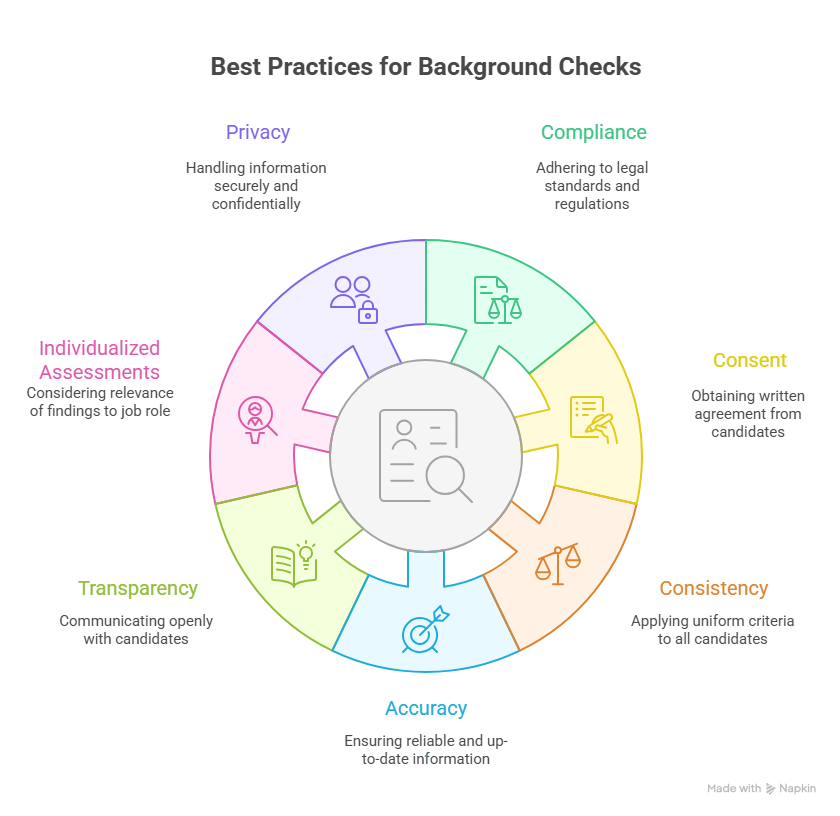
Employers conducting background checks should follow these best practices:
- Compliance: Adhere to federal, state, and local laws, including the FCRA and industry-specific regulations.
- Consent: Obtain written consent from candidates before conducting background checks.
- Consistency: Apply the same screening criteria consistently across all candidates to avoid discrimination claims.
- Accuracy: Use reputable screening companies to ensure accurate and up-to-date information.
- Transparency: Communicate openly with candidates about the background check process and any findings.
- Individualized Assessments: Consider the nature and relevance of any adverse findings about the job role.
- Privacy: Handle background check information confidentially and securely to protect candidates’ privacy.
By following these best practices, employers can conduct fair and effective background checks, ensuring they make informed hiring decisions while respecting candidates' rights.
Conclusion
Understanding employment background checks is crucial for both job seekers and employers. By being informed and knowing your rights, you can confidently navigate the process. Remember, knowledge is power! Whether you're a job seeker preparing for a background check or an employer conducting one, this guide provides the essential information you need to ensure a smooth and fair process.
FAQ Section
What is included in an employment background check?
An employment background check typically includes verifying a candidate's criminal records, employment history, education, credit history, and sometimes drug testing and social media screening.
How long does an employment background check take?
The duration of a background check can vary, but most checks are completed within 3 to 10 business days, depending on the type and scope of the check.
Can I dispute errors in my background check?
Yes, under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), you can dispute any inaccurate or incomplete information in your background check report.
What should I do if I have a negative finding on my background check?
If you have a negative finding, be honest with potential employers about your background. You can also dispute any inaccuracies and demonstrate steps you’ve taken to address past issues.
Do employers need my permission to run a background check?
Yes, employers must obtain your written consent before conducting a background check.
How can I run a background check on myself?
You can run a self-check using background check services, access your criminal records through local or state agencies, and request credit report copies.
Are background checks different for specific industries?
Certain industries like healthcare and finance may require additional checks to comply with industry-specific regulations.
What laws govern employment background checks?
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) sets the standards for background checks in the United States. State and local laws may also apply.
How can employers ensure the accuracy of background checks?
Employers should use reputable screening companies and follow best practices to ensure the accuracy of background checks.
What are the benefits of running a self-check?
Running a self-check can help you verify your records, address discrepancies, and better prepare for the job application process.

GCheck Editorial Team
Meet the GCheck Editorial Team, your trusted source for insightful and up-to-date information in the world of employment background checks. Committed to delivering the latest trends, best practices, and industry insights, our team is dedicated to keeping you informed.
With a passion for ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in background screening, we are your go-to experts in the field. Stay tuned for our comprehensive articles, guides, and analysis, designed to empower businesses and individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
At GCheck, we're here to guide you through the complexities of background checks, every step of the way.





