Massage therapist background checks typically reveal criminal history records, professional licensing verification, sex offender registry status, employment history, and education credentials—with screening depth varying by state regulations and employer requirements. Understanding what appears on these screenings helps hiring managers maintain compliant, safe practices while enabling massage therapy candidates to prepare for the employment verification process.
Key Takeaways
- Criminal background checks for massage therapists typically screen for felonies, misdemeanors, and sex offenses going back 7-10 years depending on state law.
- Licensing verification confirms active massage therapy credentials, disciplinary actions, and compliance with continuing education requirements in regulated states.
- Most spa and wellness employers conduct multi-component screenings including identity verification, sex offender registry checks, and employment history validation.
- FCRA compliance requires employers to obtain written consent before screening and provide adverse action notices if background check results affect hiring decisions.
- Certain convictions including sexual offenses, violent crimes, and theft-related charges typically disqualify candidates from massage therapy positions due to client safety concerns.
- State-specific regulations determine record accessibility, with some jurisdictions limiting background check scope to 7 years while others allow lifetime criminal history searches.
What Background Screening Reveals for Massage Therapy Positions
Background checks for massage therapists serve as essential risk management tools that protect clients receiving intimate, hands-on care. The massage therapy employment screening process examines multiple data sources to verify candidate suitability and regulatory compliance. Understanding these components helps hiring managers implement thorough vetting procedures while respecting candidate privacy rights.
The typical massage therapy criminal history check extends beyond simple database searches to include professional credential verification and specialized registries. Employers must balance thorough screening with legal limitations on what information they can access and how they use it. State regulations significantly influence what shows up on massage therapist background checks, with some jurisdictions imposing strict limitations on report content and lookback periods.
Criminal History Records and Conviction Searches
Criminal background screening forms the foundation of massage therapist vetting procedures, revealing court records that indicate potential risk factors. These searches examine county, state, and federal databases to identify felony convictions, misdemeanor charges, and pending criminal cases. The massage therapy industry prioritizes criminal screening due to the vulnerable position clients occupy during treatment sessions.
Most employers conduct multi-jurisdictional searches covering all locations where candidates have lived, worked, or attended school during the past seven years. National criminal databases provide broad coverage but may contain incomplete or outdated information requiring county-level verification. Criminal lookback periods vary significantly by jurisdiction, with seven-year limitations common in states like California, New York, and Texas for most positions.
Background check providers typically search these criminal record categories:
- Felony convictions: Serious crimes including assault, sexual offenses, fraud, and drug trafficking that appear in state repositories and federal databases.
- Misdemeanor records: Lesser offenses such as theft, simple assault, drug possession, and disorderly conduct that may indicate character concerns.
- Pending charges: Active criminal cases not yet resolved that employers may consider during hiring decisions depending on state ban-the-box laws.
- Arrest records: Documented detainments that some states prohibit employers from considering unless resulting in conviction.
Healthcare-related roles including massage therapy often qualify for exemptions allowing lifetime criminal history searches in many states. This means serious offenses can appear indefinitely rather than falling off after seven years.
Federal and Multi-State Offense Searches
Federal criminal databases capture offenses prosecuted in U.S. district courts including interstate crimes, federal drug charges, and immigration violations. Multi-state searches through national repositories provide broader coverage than single-state checks but require county-level confirmation for accuracy. These comprehensive searches reveal patterns of criminal behavior across jurisdictions that might otherwise remain hidden.
Professional Licensing and Credential Verification
Massage therapy licensing verification confirms candidates hold active, valid credentials required by state regulatory boards. Currently, 46 states plus the District of Columbia regulate massage therapy practice through licensing, certification, or registration requirements. Employers must verify these credentials to ensure legal compliance and protect against liability from employing unlicensed practitioners.
License verification reveals more than simple active/inactive status—it exposes disciplinary actions, restrictions, and compliance with continuing education mandates. State massage therapy boards maintain public databases showing licensing history and regulatory compliance. Professional credential verification extends beyond state licenses to include nationally recognized certifications from organizations like the National Certification Board for Therapeutic Massage & Bodywork (NCBTMB).
| Verification Component | Information Revealed | Typical Timeframe |
| License Status | Active, expired, suspended, revoked credentials | Current status |
| Disciplinary Actions | Board complaints, sanctions, probation terms | Lifetime history |
| Continuing Education | Compliance with required training hours | Current renewal cycle |
| Practice Restrictions | Limited scopes, supervision requirements | Active restrictions |
These certifications demonstrate advanced competency and commitment to professional standards. Employers should verify educational credentials by confirming graduation from accredited massage therapy programs approved by agencies like the Commission on Massage Therapy Accreditation (COMTA).
Multi-State License Verification Requirements
Massage therapists practicing in multiple states must maintain separate licenses for each jurisdiction since no interstate massage therapy compact currently exists. Background screening for multi-state practitioners requires verification across all jurisdictions where candidates claim credentials. This process becomes particularly important for traveling massage therapists and those seeking positions with multi-location spa chains operating across state lines.
Sex Offender Registry and Predator Database Checks
Sex offender registry searches represent non-negotiable screening components for massage therapy positions given the intimate nature of client interactions. These specialized databases identify individuals convicted of sexual offenses who must register with state and federal authorities. The National Sex Offender Public Website (NSOPW) aggregates data from all 50 states, territories, and tribal jurisdictions into a searchable platform.
Registry checks reveal conviction details, risk assessment levels, and registration compliance status for individuals with qualifying sexual offenses. Most spa employers conduct sex offender screenings as standalone checks rather than relying solely on general criminal searches. States maintain varying registration requirements, but serious sexual offenses typically mandate lifetime registration regardless of sentence completion.
Employers must understand that sex offender registry inclusion constitutes public information not subject to FCRA restrictions applicable to traditional background reports. However, hiring managers should still document legitimate business reasons for using this information in employment decisions. The massage therapy screening process should include registry checks at both state and national levels to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Employment History and Reference Verification

Employment verification confirms work history accuracy and reveals performance patterns relevant to massage therapy positions. Background screening providers contact previous employers to validate dates of employment, job titles, rehire eligibility, and reasons for separation. This process helps identify candidates who misrepresent experience levels or omit problematic employment situations.
Reference checks provide qualitative insights beyond factual employment confirmation, though many employers now limit references to basic information due to defamation liability concerns. Employment gaps warrant attention during massage therapy employment screening, particularly if candidates provide vague explanations or avoid discussing specific periods. Verifying employment with state licensing boards can reveal if practitioners held active licenses during claimed employment periods.
When conducting background checks for spa employees, hiring managers should specifically inquire about these areas:
- Client interaction skills: Professionalism during treatment sessions and appropriate boundary maintenance with clients.
- Technical competency: Skill levels with various massage modalities and techniques relevant to position requirements.
- Reliability factors: Punctuality, schedule commitment, and consistent attendance patterns during previous employment.
- Supervision response: Willingness to follow protocols, accept feedback, and adhere to workplace policies.
- Ethical standards: History of maintaining professional boundaries and following industry best practices.
These insights help employers assess candidate suitability beyond what appears in criminal records or license verification. Comprehensive reference checks complement other screening components to provide a complete candidate profile.
Verification Challenges in Wellness Industry
The wellness and spa industry presents unique employment verification challenges due to high independent contractor prevalence and frequent business closures. Many massage therapists work as contractors rather than employees, complicating traditional employment verification processes. Background screening may require alternative documentation such as 1099 forms, client testimonials, or business licenses for self-employed practitioners.
Education and Training Credential Confirmation
Educational background verification ensures massage therapist candidates completed required training from legitimate institutions. Most states mandate 500-1,000 hours of education from approved massage therapy schools before licensing eligibility. Employers verify education credentials by contacting schools directly or using third-party verification services like the National Student Clearinghouse.
Credential verification reveals graduation dates, programs completed, and accreditation status of attended institutions. This screening component protects against diploma mill fraud and candidates who misrepresent educational achievements. Specialized massage therapy modalities often require additional certification beyond basic licensure, such as prenatal massage, sports massage, or lymphatic drainage techniques.
| Education Component | Verification Method | Red Flags |
| Diploma/Certificate | Direct school contact | Unaccredited programs, online-only training |
| Program Hours | Transcript review | Insufficient hours for state licensing |
| Specialized Training | Certification body verification | Expired certifications, unrecognized credentials |
Employers should verify specialty credentials through issuing organizations to confirm current certification status. Continuing education verification ensures practitioners maintain required training hours for license renewal, typically ranging from 12-24 hours per two-year cycle depending on state requirements.
Identity Verification and Social Security Number Validation
Identity verification confirms candidates are who they claim to be and possess legal work authorization. This foundational screening component uses Social Security Number (SSN) validation, address history verification, and identity document authentication. SSN traces reveal names, addresses, and potential aliases associated with provided identification numbers.
Address history verification through SSN traces helps employers identify all jurisdictions requiring criminal record searches during the background check process. Comprehensive identity verification detects identity theft, fraud, and attempts to conceal criminal histories under different names. Employment eligibility verification through Form I-9 documentation remains separate from background checks but equally important for legal compliance.
Standard identity checks include these components:
- SSN validation: Confirms number issuance, valid format, and matches candidate-provided information for accuracy verification.
- Address history: Reveals residential locations for past 7-10 years to guide jurisdiction-specific criminal searches.
- Alias identification: Uncovers maiden names, nicknames, and other identities used in official records or court documents.
- Death Master File check: Ensures SSN doesn't belong to deceased individual which serves as fraud indicator.
Employers must examine original documents establishing identity and work authorization within three days of hire. While E-Verify provides electronic confirmation of employment eligibility, it doesn't replace comprehensive background screening for massage therapy positions.
Motor Vehicle Records and Driving History
Driving record checks apply primarily to massage therapists providing mobile services, making house calls, or operating as independent contractors traveling between clients. Motor vehicle record (MVR) searches reveal license status, traffic violations, DUI convictions, and at-fault accidents. Employers with company vehicles or those whose massage therapists drive as job duties should include MVR checks in screening protocols.
Even for spa-based positions without driving requirements, DUI convictions appearing on criminal background checks may influence hiring decisions due to judgment and impulse control concerns. States maintain varying MVR access rules, with some limiting employer access to driving records unless driving constitutes an essential job function. Insurance carriers often mandate MVR screening for employees operating company vehicles regardless of massage therapy role.
Civil Court Records and Litigation History
Civil record searches reveal lawsuits, judgments, liens, and bankruptcies that may indicate character concerns or financial desperation. While less common than criminal checks, civil searches help employers identify patterns of unprofessional behavior, client disputes, or legal issues suggesting risk factors. Massage therapy-specific concerns appearing in civil records include malpractice lawsuits, sexual harassment claims, and contract disputes with previous employers.
Professional liability concerns warrant particular attention, as civil judgments related to massage therapy malpractice indicate potential competency or ethical issues. Employers should investigate any civil cases involving former clients, particularly those alleging inappropriate conduct, injury from improper technique, or boundary violations. However, numerous civil filings might simply indicate litigious personality rather than actual wrongdoing requiring careful evaluation.
Drug Screening and Substance Abuse Testing
Drug testing complements background checks in comprehensive massage therapy employment screening programs, though it constitutes a separate process from traditional background reports. Many spas, wellness centers, and healthcare facilities require pre-employment drug screening to ensure practitioners can safely deliver client care. Substance abuse poses particular risks in massage therapy due to impaired judgment during intimate client interactions.
Standard 5-panel drug tests screen for marijuana, cocaine, opiates, amphetamines, and PCP, while more comprehensive 10-panel tests add benzodiazepines, barbiturates, methadone, propoxyphene, and methaqualone. State marijuana legalization complicates employment drug testing, with some jurisdictions prohibiting adverse employment actions based solely on lawful cannabis use. However, federal illegality and safety concerns allow most employers to maintain marijuana-free workplace policies for massage therapy positions.
State-Specific Massage Therapy Background Check Requirements
Background check requirements vary significantly across states due to differing massage therapy regulations and privacy laws. States with comprehensive massage therapy licensing statutes typically mandate specific screening components for initial licensure and may require periodic rechecking during renewal cycles. Understanding state-specific requirements ensures compliance while avoiding unnecessary screening expenses.
Some states prescribe exact background check procedures, while others grant employers discretion within general legal parameters. Employers operating multi-state spa chains must develop background check policies accommodating the most restrictive state requirements while maintaining consistent screening standards. Jurisdictional complexity increases for mobile massage therapists working across state lines who may need licensure and background clearance in multiple states.
Key state variations include these regulatory differences:
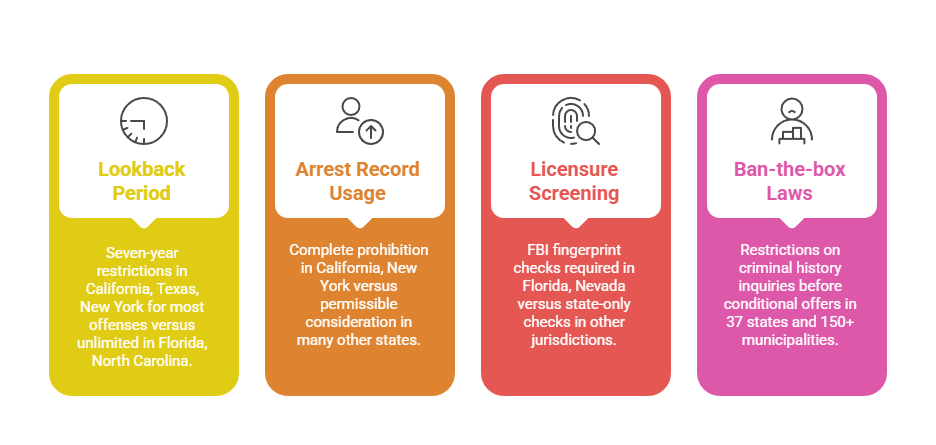
- Lookback period limitations: Seven-year restrictions in California, Texas, New York for most offenses versus unlimited in Florida, North Carolina.
- Arrest record usage: Complete prohibition in California, New York versus permissible consideration in many other states.
- Licensure screening mandates: FBI fingerprint checks required in Florida, Nevada versus state-only checks in other jurisdictions.
- Ban-the-box laws: Restrictions on criminal history inquiries before conditional offers in 37 states and 150+ municipalities.
These variations create compliance challenges requiring careful navigation. Employers must follow the most restrictive standard when operating across multiple jurisdictions.
High-Regulation State Examples
States like Florida, New York, and Washington maintain particularly comprehensive massage therapy regulations requiring enhanced background screening. Florida mandates Level 2 background screening including FBI fingerprint checks for all licensed massage therapists. New York requires criminal background checks through the Division of Criminal Justice Services for licensure, while Washington state demands national background checks with fingerprint submission for initial licenses.
Disqualifying Offenses and Red Flag Convictions
Certain criminal convictions create automatic or presumptive disqualification from massage therapy positions due to direct client safety risks. While individualized assessments are legally required in most jurisdictions, specific offense categories raise substantial concerns warranting careful evaluation. Employers must balance public safety obligations with fair chance employment principles when reviewing criminal histories.
Sexual offenses represent the most serious disqualifying category given the vulnerable client position during massage therapy sessions. Any conviction involving sexual assault, sexual battery, indecent exposure, prostitution, or child pornography typically results in permanent licensure denial and employment ineligibility. Theft and fraud convictions concern employers due to client valuables present during massage sessions and payment processing responsibilities.
Violence-related convictions also raise significant red flags:
- Assault and battery: Charges involving physical harm, particularly against vulnerable populations or in domestic settings.
- Stalking and harassment: Offenses suggesting boundary issues and inability to respect personal autonomy.
- Kidnapping and false imprisonment: Crimes indicating dangerous control impulses during private interactions.
Drug-related offenses require contextual evaluation considering timing, severity, and evidence of rehabilitation. Simple possession charges from years past may not disqualify candidates, while recent drug trafficking convictions suggest ongoing risk.
EEOC Guidance on Criminal History Consideration
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) requires employers to conduct individualized assessments considering offense nature, time elapsed, and job duties relevance before rejecting candidates with criminal histories. Blanket policies automatically excluding all individuals with criminal records may violate Title VII of the Civil Rights Act by creating disparate impact. Employers should evaluate three factors: the nature and gravity of the offense, the time elapsed since conviction, and the nature of the job sought.
FCRA Compliance Requirements for Massage Therapy Screening
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs background checks conducted through third-party screening companies, imposing strict procedural requirements on employers. FCRA compliance protects candidate privacy rights while establishing standardized processes for obtaining and using background information. Violations carry significant penalties including actual damages, punitive damages up to $1,000 per violation, and attorney fees.
State Fair Credit Reporting Acts (FCRAs) often impose additional requirements beyond federal law, with California, Minnesota, Oklahoma, and Washington maintaining particularly strict provisions. California's Investigative Consumer Reporting Agencies Act (ICRAA) requires specific disclosure language and extended waiting periods before adverse actions. Employers must comply with both federal FCRA and applicable state FCRAs, following the more restrictive standard when conflicts exist.
Essential FCRA obligations for massage therapy employment screening include:
| FCRA Requirement | Timing | Key Components |
| Written disclosure and authorization | Before screening | Standalone documents disclosing intent and obtaining consent |
| Pre-adverse action notice | Before rejection | Report copies, rights summary, dispute timeframe |
| Adverse action notice | After final decision | Screening company identification, dispute rights explanation |
| Proper disposal | After retention period | Secure destruction preventing identity theft |
These requirements protect candidates while ensuring employers follow consistent, transparent procedures. Documentation of FCRA compliance provides essential legal protection during discrimination claims.
Ban-the-Box and Fair Chance Hiring Laws
Approximately 37 states and 150+ municipalities have enacted ban-the-box laws restricting when employers can inquire about criminal histories. These laws typically prohibit criminal history questions on initial applications, requiring employers to wait until after conditional job offers before conducting background checks. Some jurisdictions mandate individualized assessments, while others create presumptive disqualifications only for directly related convictions.
Background Check Timelines and Processing Periods
Massage therapy criminal history checks typically complete within 2-5 business days for standard searches, though complex cases requiring court record retrieval may extend to 2-3 weeks. Processing timelines depend on search comprehensiveness, jurisdiction efficiency, and court record accessibility. Instant database checks provide preliminary results within minutes but require county-level confirmation for FCRA compliance.
Expedited background screening services offer faster turnaround for urgent hiring needs at premium costs. However, rushed screenings may sacrifice thoroughness, potentially missing criminal records requiring manual courthouse searches. Employers should balance speed with screening comprehensiveness to ensure client safety and liability protection.
Factors affecting background check turnaround times include:
- Multi-state searches: Additional 3-7 days per state requiring separate court system navigation and record retrieval processes.
- Court record retrieval: Extra 5-10 days for manual courthouse research when electronic access remains unavailable.
- Name discrepancies: Additional 2-5 days for identity confirmation when candidate names don't match official records exactly.
- International checks: Extended 2-4 weeks for foreign records requiring overseas documentation and translation services.
Planning screening during candidate notice periods helps accommodate extended timelines. Employers should initiate background checks immediately after receiving signed authorization forms.
Continuous Monitoring and Ongoing Screening
Some employers implement continuous background monitoring programs that alert them to new criminal activity among current massage therapy employees. These services monitor court records, sex offender registries, and professional licensing databases for changes affecting employed practitioners. Continuous monitoring helps identify misconduct between periodic re-screening cycles, though FCRA compliance requires employee consent and proper adverse action procedures.
Candidate Rights and Dispute Resolution Procedures
Massage therapy candidates possess specific rights under FCRA when employers conduct background checks through third-party screening companies. Understanding these protections helps candidates address inaccurate information that might otherwise prevent employment. Background reports frequently contain errors, with Federal Trade Commission studies indicating roughly 20% of consumers identify mistakes on credit reports that may extend to background checks.
Dispute procedures require candidates to notify screening companies in writing identifying specific inaccuracies and supporting documentation. Screening companies must investigate disputes within 30 days, verify information with original sources, and remove unverifiable items. If investigations support candidate claims, corrected reports must be provided free of charge.
Candidates have the right to these protections:
- Pre-screening disclosure: Receive notification before employers conduct background checks and provide written authorization.
- Report access: Obtain background report copies before adverse employment actions occur based on findings.
- Dispute process: Challenge inaccurate or incomplete information with screening companies through formal procedures.
- Investigation timeline: Have disputed items investigated within 30 days of notification submission.
- Statement addition: Add explanatory statements to background reports regarding disputed information.
- Adverse action notice: Receive notifications identifying reasons for employment denial based on background findings.
These rights ensure fair treatment and accuracy in employment screening. Candidates should exercise them whenever background reports contain errors.
Correcting Criminal Record Errors
Criminal record errors often stem from identity confusion, incomplete court updates, or database entry mistakes. Common background check mistakes include reporting expunged records, attributing someone else's criminal history due to similar names, showing dismissed charges as convictions, or listing outdated information beyond legal reporting limits. Candidates should obtain personal background reports before job searches to identify and correct errors proactively.
Cost Considerations for Massage Therapy Background Screening
Background check costs for massage therapists range from $25-$150 per candidate depending on screening comprehensiveness and provider selection. Basic criminal searches start around $25-40, while comprehensive packages including multi-jurisdiction searches, employment verification, and license checks reach $100-150. Employers must balance thoroughness with budget constraints when designing screening protocols.
Many background screening providers offer bundled massage therapy packages combining commonly required components at discounted rates compared to à la carte selection. Employers should request customized packages matching their specific risk tolerance and regulatory obligations. While cost considerations matter, inadequate screening creates liability exposure far exceeding savings from budget background checks.
Cost factors affecting massage therapy employment screening include:
- Geographic scope: National searches cost more than single-state checks with $15-30 additional per state searched.
- Verification components: Each added element like employment, education, or license checks increases costs $10-25.
- Search depth: Seven-year lookbacks cost less than comprehensive lifetime criminal history searches.
- Volume discounts: High-volume employers negotiate per-check rates 20-40% below standard pricing.
- Turnaround speed: Expedited processing carries premium charges of 25-50% above standard rates.
These variables allow customization based on specific hiring needs. Strategic component selection balances cost control with adequate risk management.
Best Practices for Massage Therapy Hiring Managers
Implementing effective background screening programs requires standardized procedures balancing thoroughness with legal compliance. Hiring managers should develop written policies documenting screening components, evaluation criteria, and decision-making processes for massage therapy positions. Consistent application of background check policies protects against discrimination claims while ensuring all candidates receive fair evaluation.
Training hiring managers on proper background check procedures prevents legal violations and promotes consistent candidate evaluation. Many discrimination claims stem from improper use of background information rather than conducting checks themselves. Clear documentation demonstrating legitimate business reasons for employment decisions based on background findings provides essential legal protection.
Recommended best practices for background screening of spa employees include:
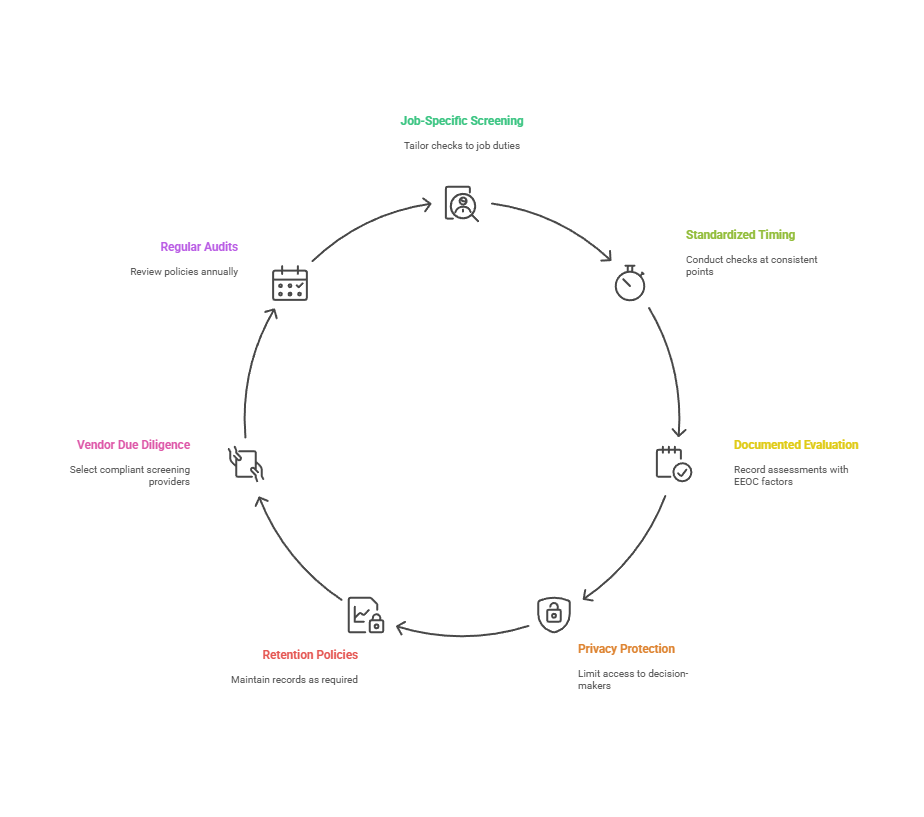
- Job-specific screening: Match background check components to actual position duties and client interaction levels for relevance.
- Standardized timing: Conduct background checks at consistent hiring process points, typically after conditional offers are extended.
- Documented evaluation: Record individualized assessments of criminal histories considering EEOC three-factor analysis requirements.
- Privacy protection: Limit background report access to decision-makers with legitimate need-to-know for information security.
- Retention policies: Maintain background records according to EEOC requirements (typically one year minimum) then securely destroy.
- Vendor due diligence: Select FCRA-compliant screening providers with accurate databases and proper court research procedures.
- Regular audits: Review background check policies annually for legal updates and effectiveness in protecting client safety.
These practices create legally defensible screening programs. Consistent implementation reduces liability while improving hiring quality.
Creating Legally Compliant Criminal History Assessment Policies
Criminal history assessment policies should specify which offense categories relate to massage therapy duties, timeframes for consideration, and individualized evaluation factors. For example, policies might establish that sexual offenses permanently disqualify candidates due to direct client safety risks, while non-violent misdemeanors older than five years receive case-by-case review. Written policies demonstrate good faith efforts to comply with fair chance hiring requirements.
Background Screening for Independent Contractors vs. Employees
The employment classification debate affects background check practices for massage therapists working as independent contractors versus employees. While both arrangements warrant screening due to client safety concerns, independent contractors typically undergo less comprehensive background checks than direct employees. However, spa and wellness facility owners maintain duty-of-care obligations to clients regardless of therapist employment status.
The independent contractor relationship limits employer control over screening specifics but doesn't eliminate liability exposure from negligent contractor selection. Courts may hold businesses responsible for client injuries from contractors with discoverable criminal histories suggesting foreseeable risks. Documentation of reasonable screening efforts provides essential protection against negligent hiring claims.
Businesses engaging independent contractor massage therapists should implement these screening protocols:
- License verification: Confirm active professional licenses and current credential status with state regulatory boards.
- Insurance confirmation: Validate professional liability insurance coverage meeting minimum policy limits for practice protection.
- Criminal background checks: Conduct searches focusing on sex offenses, violent crimes, and client safety-related convictions.
- Registry searches: Check sex offender registries at both state and national levels for comprehensive coverage.
- Identity validation: Verify identity and right-to-work authorization through standard authentication procedures.
These components create reasonable screening baselines. Additional verification may be warranted based on specific business circumstances.
Liability Considerations in Contractor Arrangements
Massage therapy franchises, spa chains, and wellness facilities allowing independent practitioners to use their premises face particular liability exposure requiring robust contractor screening. These businesses may be vicariously liable for contractor misconduct if they failed to implement reasonable background check procedures. Written contractor agreements should specify screening requirements, credential maintenance obligations, and immediate removal provisions for criminal conduct or licensing violations.
Conclusion
Comprehensive background screening for massage therapist positions reveals criminal histories, professional licensing status, identity verification, and employment credentials essential for protecting client safety. Employers must navigate complex state regulations, FCRA compliance requirements, and fair chance hiring principles while implementing thorough vetting procedures. The massage therapy screening process balances risk management with candidate privacy rights, requiring standardized policies and documented evaluation criteria. As regulations continue evolving in 2025, hiring managers should regularly review background check procedures to maintain legal compliance while ensuring only qualified, trustworthy practitioners provide client care.
Frequently Asked Questions
How far back do massage therapist background checks go?
Massage therapy background checks typically review 7-10 years of criminal history for most positions, though many states allow unlimited lookback periods for healthcare-related roles. Seven-year limitations apply in California, New York, Texas, and other jurisdictions for non-conviction records, while felony convictions may appear indefinitely. State licensing boards often conduct lifetime criminal history checks for initial massage therapy licenses, particularly for offenses involving violence, sexual misconduct, or fraud. Employers should consult state-specific laws determining applicable lookback periods for their jurisdiction.
What disqualifies you from becoming a licensed massage therapist?
Sexual offenses, violent felonies, and crimes involving abuse of vulnerable populations typically disqualify candidates from massage therapy licensure and employment. Convictions for sexual assault, sexual battery, child abuse, prostitution, human trafficking, and indecent exposure create presumptive or automatic disqualification in most states. Recent drug trafficking convictions, fraud charges, and assault convictions also raise serious concerns during licensing applications. However, state boards conduct individualized assessments considering offense age, rehabilitation evidence, and crime relevance to massage therapy practice before final determinations.
Do massage therapy employers check employment history?
Yes, most spa and wellness employers verify employment history for massage therapist candidates by contacting previous employers to confirm dates worked, positions held, and rehire eligibility. Employment verification helps identify candidates who misrepresent experience levels or omit problematic work situations from applications. Many employers now limit reference information to basic factual confirmation due to defamation concerns, though some still provide performance details when proper releases are signed. Gaps in employment history warrant explanation during background screening, particularly if candidates provide vague reasons for extended absences from the field.
Can you work as a massage therapist with a misdemeanor?
Many massage therapists work successfully with misdemeanor convictions on their records, though specific offense types and timing significantly affect employability. Non-violent misdemeanors like traffic violations or minor drug possession from several years ago typically don't disqualify candidates after individualized assessment. However, misdemeanors involving theft, assault, domestic violence, or sexual misconduct raise serious concerns about client safety and professional trustworthiness. State licensing boards and employers evaluate misdemeanors based on crime nature, time elapsed since conviction, and evidence of rehabilitation before making licensing or hiring decisions.
How long does a massage therapist background check take?
Standard massage therapy background checks typically complete within 2-5 business days for basic criminal searches, though comprehensive screenings including multi-state searches and employment verification may require 1-2 weeks. Processing timelines depend on court record accessibility, the number of jurisdictions searched, and whether manual courthouse research becomes necessary. Instant database checks provide preliminary results within minutes but require verification at county courthouses for FCRA compliance. International background checks for foreign-born candidates may extend timelines to 3-4 weeks due to documentation requirements and overseas record retrieval processes.
Are massage therapists required to pass drug tests?
Drug testing requirements for massage therapists vary by employer rather than universal state mandates, though many spas, wellness centers, and healthcare facilities require pre-employment screening. Substance abuse poses safety risks during client care, leading most professional employers to implement drug-free workplace policies. Standard 5-panel or 10-panel drug tests screen for marijuana, cocaine, opiates, amphetamines, and other controlled substances. State marijuana legalization complicates employment drug testing, with some jurisdictions restricting adverse actions based solely on lawful cannabis use, though most employers can still maintain marijuana-free policies for safety-sensitive massage therapy positions.
Do massage therapy licenses show disciplinary actions?
Yes, state massage therapy licensing boards maintain public records showing disciplinary actions, sanctions, complaints, and license restrictions for all licensed practitioners. These records appear during license verification searches conducted by potential employers and include details about violations, investigation findings, and imposed penalties. Disciplinary actions may result from client complaints, criminal convictions, continuing education non-compliance, or practice standard violations. License verification reveals not only current active/inactive status but complete disciplinary history that employers consider when evaluating candidate suitability for massage therapy positions requiring client trust and professional integrity.
Can expunged records appear on massage therapist background checks?
Legally expunged or sealed criminal records should not appear on background checks for massage therapists, though database errors sometimes include removed records. Expungement orders direct courts and law enforcement agencies to delete or seal criminal records, making them unavailable for employment screening purposes. However, commercial background check databases may contain outdated information not yet updated to reflect expungement orders. Candidates with expunged records who find them appearing on background reports should dispute the information with screening companies and provide court documentation confirming expungement to force record removal.
Additional Resources
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) Compliance Guide
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/using-consumer-reports-what-employers-need-know - EEOC Guidance on Criminal Records in Employment Decisions
https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/enforcement-guidance-consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment - National Certification Board for Therapeutic Massage & Bodywork
https://www.ncbtmb.org - Federation of State Massage Therapy Boards
https://www.fsmtb.org - State-by-State Massage Therapy Licensing Requirements
https://www.amtamassage.org/about/state-regulation - Ban-the-Box Laws by State and Locality
https://www.nelp.org/publication/ban-the-box-fair-chance-hiring-state-and-local-guide - Professional Background Screening Association Best Practices
https://www.psbassociation.org - National Sex Offender Public Website Search Tool
https://www.nsopw.gov
Still have questions?
Get in touch with our team today for a personalized demo and discover how our tailored volume pricing and packages can drive results for your business!
How useful was this page?*
Note: your comments are anonymous. We use them to improve the website. Do not include any personal details.
Visit our FCRA Compliance Tool or leave a message here if you need a response.
From the blog Explore the GCheck Content Hub

How Long Does a Background Check Take? A Complete 2025 Guide
13 Dec, 2023 • 14 min read
The Ultimate Background Check Guide
13 Dec, 2023 • 4 min read
The Ultimate Guide to Employment Background Checks
13 Dec, 2023 • 10 min readThe information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as legal advice or a substitute for consultation with qualified legal counsel. While we strive to ensure accuracy, employment screening laws and regulations—including but not limited to the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines, state and local ban-the-box laws, industry-specific requirements, and other applicable federal, state, and local statutes—are subject to frequent changes, varying interpretations, and jurisdiction-specific applications that may affect their implementation in your organization. Employers and screening decision-makers are solely responsible for ensuring their background check policies, procedures, and practices comply with all applicable laws and regulations relevant to their specific industry, location, and circumstances. We strongly recommend consulting with qualified employment law attorneys and compliance professionals before making hiring, tenant screening, or other decisions based on background check information.

